Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/cdoersch/vae_tutorial
Caffe code to accompany my Tutorial on Variational Autoencoders
https://github.com/cdoersch/vae_tutorial
Last synced: 18 days ago
JSON representation
Caffe code to accompany my Tutorial on Variational Autoencoders
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/cdoersch/vae_tutorial
- Owner: cdoersch
- License: mit
- Created: 2016-06-19T20:37:00.000Z (about 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2016-12-22T15:58:28.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-02-26T23:34:15.474Z (4 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Size: 1010 KB
- Stars: 484
- Watchers: 26
- Forks: 136
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Lists
- Awesome-Caffe - VAE
README
# Tutorial on Variational Autoencoders
### Introduction
This code is a supplement to the [Tutorial on Variational Autoencoders](http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.05908). It allows you to reproduce the example experiments in the tutorial's later sections.
This code contains two demos. The first is a standard Variational Autoencoder (VAE) for MNIST. The second is a Conditional Variational Autoencoder (CVAE) for reconstructing a digit given only a noisy, binarized column of pixels from the digit's center. For details on the experimental setup, see the paper.
No additional Caffe layers are needed to make a VAE/CVAE work in Caffe. The only requirements are a working Caffe/pycaffe installation. A GPU will make the experiments run faster, but is not necessary (comment out set_mode_gpu() in the python files if you don't have one). On my system (a Titan X), these experiments all complete in about 10 minutes.
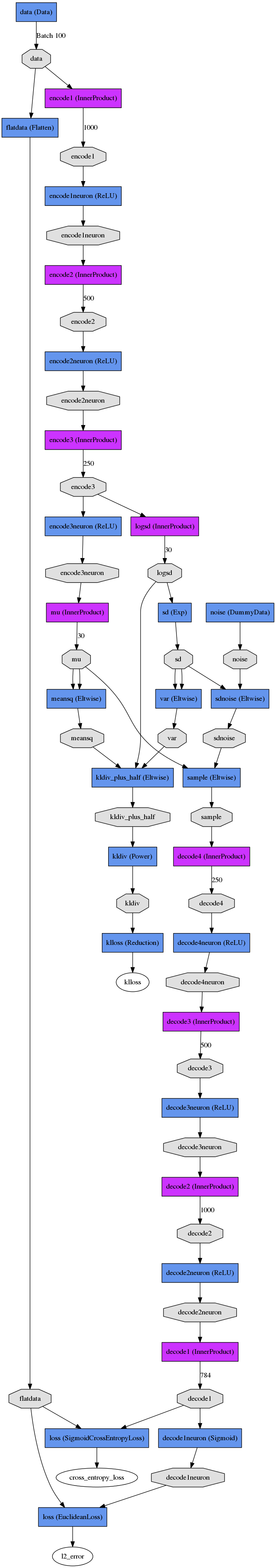
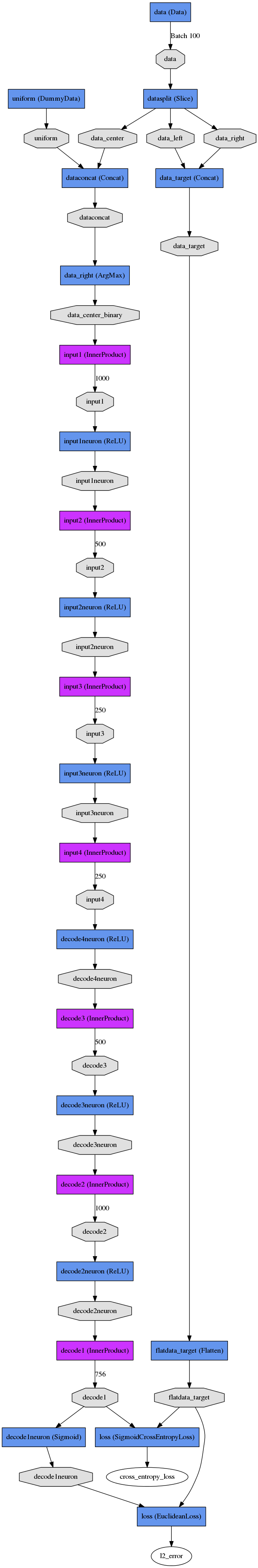
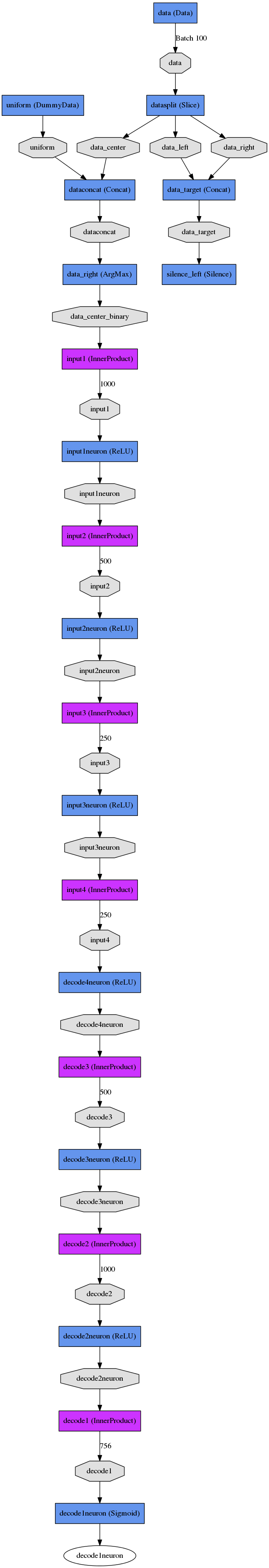
### VAE and CVAE Network Structure
The code will generate a network drawing, but for convenience I've included the result of that drawing here. This is for the VAE:
VAE
Train Net
Test Net
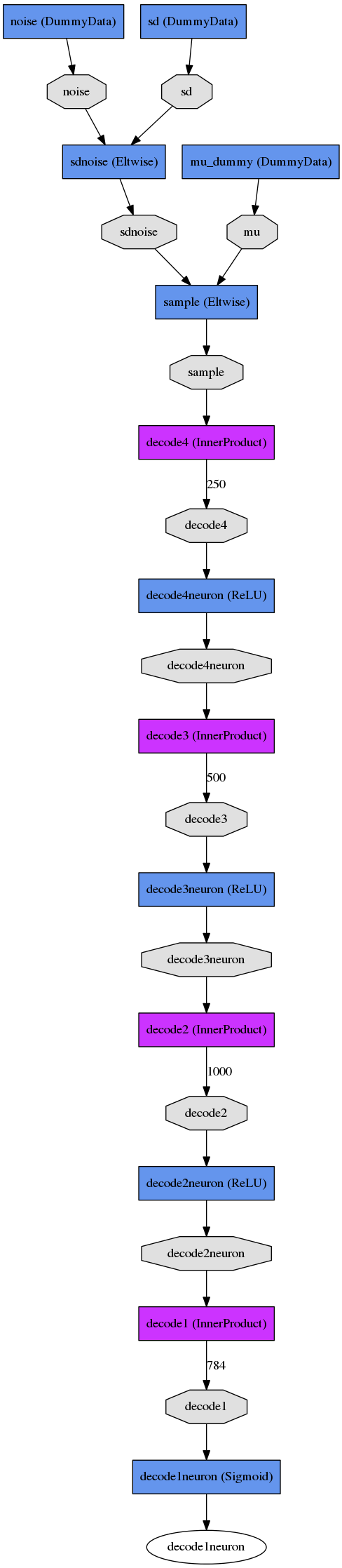
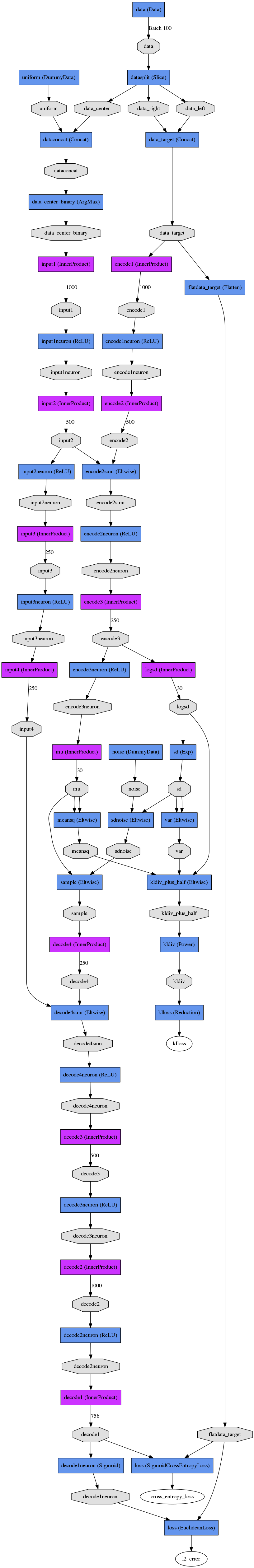
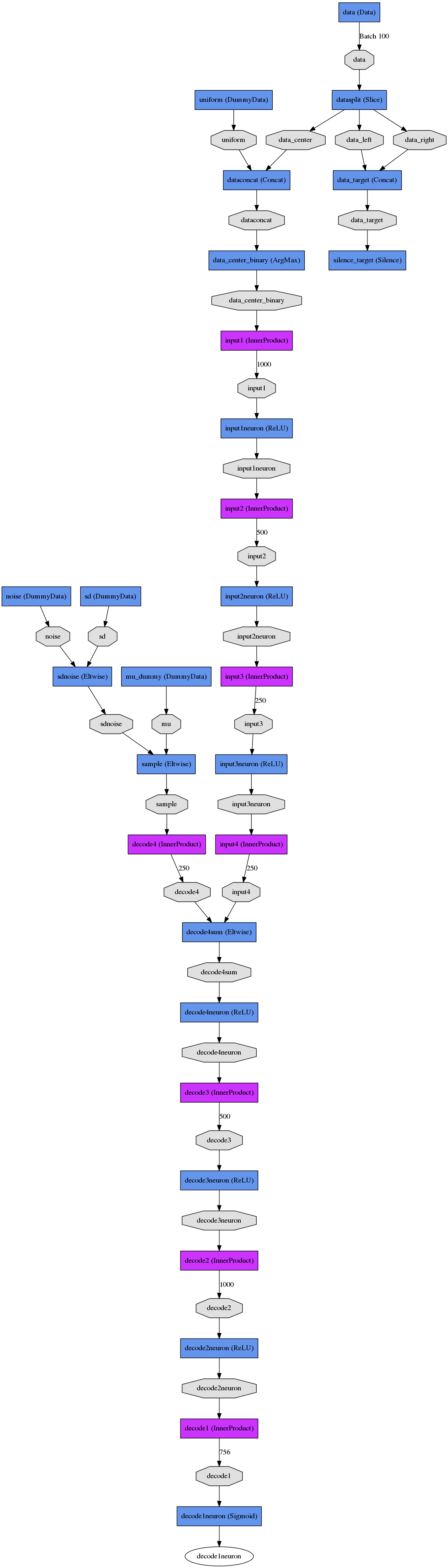
Here is a side-by-side comparison between the CVAE and regressor which solve the same problem. Note that both networks have several initial layers for constructing the input and output data that's used to train the network.
CVAE and Regressor
CVAE Train Net
CVAE Test Net
Regressor Train Net
Regressor Test Net
### Setup
1. Install Caffe (see: [Caffe installation instructions](http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/installation.html)). Build `Caffe` and `pycaffe`. For this readme, we'll call the installation path $CAFFE_PATH.
2. Clone this repo. For this readme, we'll call the installation path $TUTORIAL_PATH
```Shell
git clone https://github.com/cdoersch/vae_tutorial.git
```
3. Download MNIST using Caffe's pre-packaged downloader, and run create_mnist.sh to create an lmdb.
```Shell
cd $CAFFE_PATH/data/mnist/
./get_mnist.sh
cd $CAFFE_PATH/
./examples/mnist/create_mnist.sh
```
4. Optional: create a symlink for snapshots.
```Shell
cd $TUTORIAL_PATH
ln -s [...] snapshots
```
### Running the VAE
1. Edit mnist_vae.prototxt and enter the correct "source" path to the training lmdb (line 13)
2. Run the code. Make sure $CAFFE_PATH/python is on your PYTHONPATH.
```Shell
cd $TUTORIAL_PATH
python mnist_vae.py
```
Note that the python is only required for generating the visualizations: the net can also be trained simply by calling
```Shell
$CAFFE_PATH/build/tools/caffe train --solver=mnist_vae_solver_adam.prototxt
```
### Running the CVAE
1. Edit mnist_cvae.prototxt and enter the correct "source" path for BOTH training and testing lmdb's (line 13 AND 29)
2. Run the code. Make sure $CAFFE_PATH/python is on your PYTHONPATH.
```Shell
cd $TUTORIAL_PATH
python mnist_cvae.py
```
Note that the python is only required for generating the visualizations: the net can also be trained simply by calling
```Shell
$CAFFE_PATH/build/tools/caffe train --solver=mnist_cvae_solver_adam.prototxt
```
3. Optional: do the same thing for the regressor to see the baseline results. After altering the "source" paths in mnist_regressor.prototxt, run:
```Shell
cd $TUTORIAL_PATH
python mnist_regressor.py
```