Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/clayrisser/create-react-renderer
learn to build a custom react renderer
https://github.com/clayrisser/create-react-renderer
react react-renderer
Last synced: 4 days ago
JSON representation
learn to build a custom react renderer
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/clayrisser/create-react-renderer
- Owner: clayrisser
- Created: 2019-12-17T21:06:50.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2023-07-07T06:51:56.000Z (12 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-05-18T20:39:36.190Z (about 1 month ago)
- Topics: react, react-renderer
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage: https://nuevesolutions.com
- Size: 2.26 MB
- Stars: 26
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Lists
- awesome-react-renderer - Create React Renderer - open source course to learn how to build a custom react renderer (Learn)
README
# create-react-renderer
> learn to build a custom react renderer

Please ★ this repo if you found it useful ★ ★ ★
### Watch the Video Below
[](https://www.youtube.com/embed/SXx-CymMjDM)
DISCLAIMER: These definitions are not official. They are based on my own understanding of react renderers.
They are not intended for understanding how to use react, but rather are for providing the context of
understanding how a react renderer works.
## Built by Silicon Hills LLC
[](https://nuevesolutions.com)
Silicon Hills offers premium Node and React develpoment and support services. Get in touch at [nuevesolutions.com](https://nuevesolutions.com).
## Setup
```sh
npm install
```
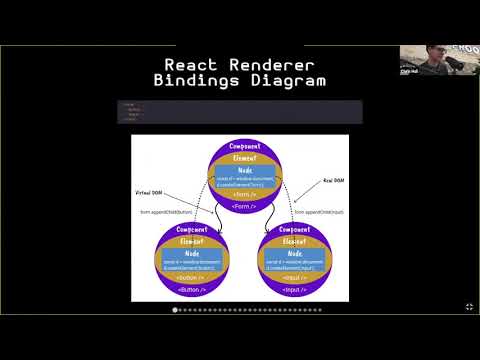
## React Renderer Bindings Diagram
The diagram represents the following code
```jsx
```

## Definitions
### Virtual DOM
A tree structure that represents the current rendered state. Every branch and leaf on the tree is either a
component or element.
### Reconciliation
**Reconciliation** is the process of determining which parts of the virtual dom need to be changed
by diffing the current virtual dom tree with the new virtual dom tree.
### Reconciler
The **reconciler** is the bindings to the react reconciliation lifecycle methods. This is NOT the react
lifecycle hooks even though it is closley related to the react lifecycle hooks.
### Fiber
A **fiber** virtual stack frame of work for the react reconciler. You can think of it as the low level api the
reconciler is built on top of.
### Node
A **node** is the interface of the renderer that the react renderer is binding to. For example
`window.document` would be the **node** used in a react renderer that binds to the dom.
### Root Node
The **root node** is the node used in the top of the react virtual dom tree.
### Element
You can think of an **element** as a react component that is directly bound to the reconciliation lifecycle methods.
This is NOT the same thing as a react component, although it can be used like a react component.
Because it is directly bound to the react reconciliation lifecycle methods it is more powerful, but also more complex.
**Elements** form the foundation that all react components are built on top of.
`
`, `` and `` are all examples of elements in the react dom renderer.
### Base Element
The **base element** is the element all other elements inherit from.
### Component
An encapsulation of components and/or elements.
### Root Element
The **root element** is the element used in the top of the react virtual dom tree. This element is
not created with JSX but is initialized during the initial render.
### Root
This represents the root of the react virutal dom tree.
## Phases
### [Phase A](/phaseA)
setup the reconciler
### [Phase B](/phaseB)
create some custom elements
### [Phase C](/phaseC)
bind some custom elements to reconciler
### [Phase D](/phaseD)
setup node
### [Phase E](/phaseE)
bind base element lifecycle methods
### [Phase F](/phaseF)
bind critical element lifecycle methods to reconciler lifecycle methods
### [Phase G](/phaseG)
create base elements
### [Phase H](/phaseH)
create text bindings
### [Phase I](/phaseI)
finish reconciler bindings
### [Phase J](/phaseJ)
add default props
### [Phase K](/phaseK)
add options
### [Phase L](/phaseL)
create components
## Tips
### Abstraction is your friend
Try to start small. Build your renderer in many layers of abstraction.
This renderer uses the following layers of abstraction.
`reconciler` <- `BaseElement` <- `elements` <- `components` <- `more components`
### Few elements, lots of components
Elements are hard to build and hard to debug. It's best to have a few broad and general elements
and then build lots of specific components on top of the broad elements.
### Start small, increment in small steps
### Use typescript
This can catch lots of unnecessary bugs.
### Test test test (unit test)
### Build a solid foundation
## Debugging
Understanding the react lifecycle can really help with debugging.
### Ref debugging
You can get access to the node data from a ref. For example, the following will log the data
from the node used in the `` element. This is very helpful because the ref runs
before the entire render cycle is finished. This is helpful for debugging bugs that are
preventing rendering from finishing.
```ts
console.log(ref.node)} />
```
This only works on element refs. Since elements are abstractions of your nodes, you can't see the
value of nodes in component refs.
For example, the following would log `undefined`
```ts
console.log(ref.node)} />
```