Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/flavioaiello/swarm-router
Scalable stateless «zero config» service-name ingress for docker swarm mode with a fresh more secure approach
https://github.com/flavioaiello/swarm-router
automation discovery docker docker-swarm docker-swarm-mode encryption golang haproxy haproxy-docker ingress-controller ingress-haproxy reverse-proxy stack swarm swarm-router tls tls-encryption
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
Scalable stateless «zero config» service-name ingress for docker swarm mode with a fresh more secure approach
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/flavioaiello/swarm-router
- Owner: flavioaiello
- License: mit
- Created: 2016-02-22T07:48:34.000Z (about 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2023-07-14T12:27:05.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-01-23T07:08:30.782Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: automation, discovery, docker, docker-swarm, docker-swarm-mode, encryption, golang, haproxy, haproxy-docker, ingress-controller, ingress-haproxy, reverse-proxy, stack, swarm, swarm-router, tls, tls-encryption
- Language: Go
- Homepage: https://hub.docker.com/r/flavioaiello/swarm-router/
- Size: 1.34 MB
- Stars: 64
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 12
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Funding: FUNDING.yml
- License: LICENSE
Lists
- awesome-stars - flavioaiello/swarm-router - Scalable stateless «zero config» service-name ingress for docker swarm mode with a fresh more secure approach (Go)
- awesome-docker-clone - Swarm Router - A «zero config» service name based router for docker swarm mode with a fresh and more secure approach. By [@flavioaiello](https://twitter.com/flavioaiello) (Container Operations / Reverse Proxy)
- awesome-docker - Swarm Router - A «zero config» service name based router for docker swarm mode with a fresh and more secure approach. By [@flavioaiello](https://twitter.com/flavioaiello) (Container Operations / Reverse Proxy)
- awesome-docker - Swarm Router - A «zero config» service name based router for docker swarm mode with a fresh and more secure approach. By [@flavioaiello](https://twitter.com/flavioaiello) (Container Operations / Reverse Proxy)
- awesome-docker - Swarm Router - A «zero config» service name based router for docker swarm mode with a fresh and more secure approach. By [@flavioaiello](https://github.com/flavioaiello) (Container Operations / Reverse Proxy)
- awesome-docker - Swarm Router - A «zero config» service name based router for docker swarm mode with a fresh and more secure approach. By [@flavioaiello](https://github.com/flavioaiello) (Container Operations / Reverse Proxy)
- awesome-docker - Swarm Router - A «zero config» service name based router for docker swarm mode with a fresh and more secure approach. By [@flavioaiello](https://twitter.com/flavioaiello) (Container Operations / Reverse Proxy)
- awesome-docker-docs - Swarm Router - A «zero config» service name based router for docker swarm mode with a fresh and more secure approach. By [@flavioaiello](https://twitter.com/flavioaiello) (Container Operations / Reverse Proxy)
- awesome-docker - Swarm Router - A «zero config» service name based router for docker swarm mode with a fresh and more secure approach. By [@flavioaiello](https://github.com/flavioaiello) (Container Operations / Reverse Proxy)
README
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/flavioaiello/swarm-router/)
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/flavioaiello/swarm-router/)
[](https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/flavioaiello/swarm-router)
# Swarm-Router
This is the «zero config» ingress router for Docker swarm mode deployments, based on the mature and superior haproxy library and a little of golang offering unique advantages:
- Zero-copy using tcp splice syscall for real gbps throughput at very low cpu
- No root privileges required
- No docker socket mount required for service discovery
- No external dependencies
## Scope
Solves common docker swarm mode requirements:
- Port overlapping due to service name publishing
- Claim based service discovery
- HTTP service forwarding
- TLS service offloading eg. termination and forwarding
- TLS service passthrough
- Stackable as swarm or stack edge
## Docker Swarm
Built for docker swarm mode `docker swarm init` ingress networking: Service discovery is based on claim resolution. Just define your service name urls as network alias names. Due to swarm lacking dns `SRV` support, port discovery is done by automatic port enumeration based on a default port list.
## Mode 1 - Ingress routing
Simply get started having a swarm-router up and running. Now attach and define your app urls. The according inner port will be discoverd automaticly.
```
docker stack deploy -c swarm.yml swarm
docker stack deploy -c app.yml app
```
Now the endpoints below should be reachable:
- http://app.localtest.me
## Mode 2 - Ingress routing with isolated stacks
Deploying the same stack multiple times, eg. for development, testing and production, the service names collission can be avoided only by an additional router per stack. The according inner service name and port will be discoverd automaticly
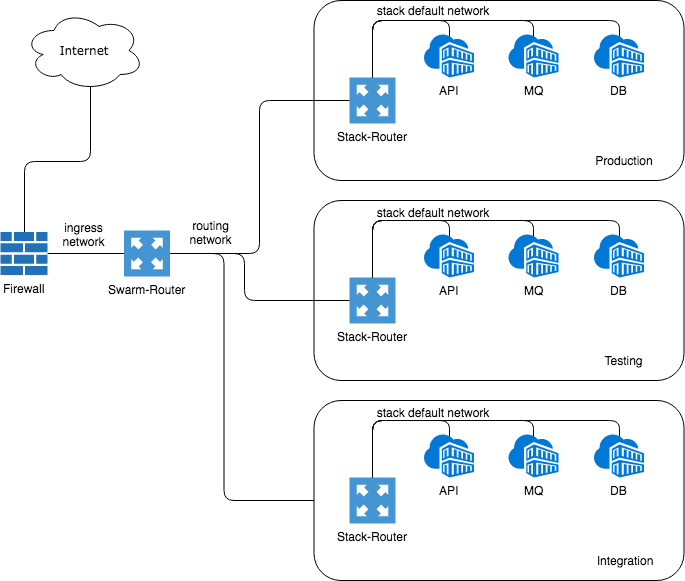
```
docker stack deploy -c swarm.yml swarm
docker stack deploy -c testing.yml testing
docker stack deploy -c production.yml production
```
Now the endpoints below should be reachable:
Testing:
- http://service.testing.localtest.me
- http://api.testing.localtest.me
Production:
- http://service.localtest.me
- http://api.localtest.me
The inner communication of a stack can now be done with service shortnames eg. the service could reach simply a database using db as hostname. This makes portability of stages even simpler.
## Override port discovery
Swarm-router does port discovery based on a default port list:
```
DEFAULT_BACKEND_PORTS=80 443 8000 8080 8443 9000
```
Alternatively port ovveride based on url `startswith` is possible:
```
OVERRIDE_BACKEND_PORTS=myapp:6457 myotherapp:7465
```
## Certificates
When TLS offloading comes into action, according fullchain certificates containing the private key should be provisioned on `/certs` host volume mount as `service.com.pem`. Preferably this one should be mounted using docker secrets.
## TLS Mutual Authentication
TLS mutual authentication can simply be enabled by adding space separated fqdn service names to the `BACKENDS_VERIFY_TLS` environment variable and the CA to the /certs/ directory.
## Performance
This one is built for high throughput and little CPU usage. Haproxy implements zero-copy and tcp-splicing based TCP handling. Even with golang now supporting [splicing](https://github.com/golang/go/issues/10948), haproxy is ways more superior in terms of cpu consumption and latency.