Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/GAP-LAB-CUHK-SZ/gaustudio
A Modular Framework for 3D Gaussian Splatting and Beyond
https://github.com/GAP-LAB-CUHK-SZ/gaustudio
3d-reconstruction 3dgs gaussian-splatting multi-view-reconstruction nerf pytorch surface-reconstruction
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
A Modular Framework for 3D Gaussian Splatting and Beyond
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/GAP-LAB-CUHK-SZ/gaustudio
- Owner: GAP-LAB-CUHK-SZ
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-12-16T16:28:54.000Z (7 months ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-03-28T03:18:28.000Z (3 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-03-28T13:42:02.322Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: 3d-reconstruction, 3dgs, gaussian-splatting, multi-view-reconstruction, nerf, pytorch, surface-reconstruction
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 4.29 MB
- Stars: 376
- Watchers: 18
- Forks: 21
- Open Issues: 4
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Lists
- awesome-3D-gaussian-splatting - GauStudio - Unified framework with different paper implementations (Open Source Implementations / Framework)
README

GauStudio is a modular framework that supports the rapidly advancing field of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) and its applications. This framework targets to offer a comprehensive codebase, streamlined pipelines, and a wide range of tools and resources to facilitate the exploration, implementation, and deployment of 3DGS-based solutions, making it easier for users to leverage the potential of this cutting-edge technology.
### [Paper](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1mizzZSXn-YToww7kW3OV0lUbfME9Mobg/view?usp=sharing) | [Colab(Comming Soon)]() | [Document(Comming Soon)]()
# Installation
Before installing the software, please note that the following steps have been tested on Ubuntu 20.04. If you encounter any issues during the installation on Windows, we are open to addressing and resolving such issues.
## Prerequisites
* NVIDIA graphics card with at least 6GB VRAM
* CUDA installed
* Python >= 3.8
## Optional Step: Create a Conda Environment
It is recommended to create a conda environment before proceeding with the installation. You can create a conda environment using the following commands:
```sh
# Create a new conda environment
conda create -n gaustudio python=3.8
# Activate the conda environment
conda activate gaustudio
```
## Step 1: Install PyTorch
You will need to install PyTorch. The software has been tested with torch1.12.1+cu113 and torch2.0.1+cu118, but other versions should also work fine. You can install PyTorch using conda as follows:
```
# Example command to install PyTorch version 1.12.1+cu113
conda install pytorch=1.12.1 torchvision=0.13.1 cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch
# Example command to install PyTorch version 2.0.1+cu118
pip install torch torchvision --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
```
## Step 2: Install Dependencies
Install the necessary dependencies by running the following command:
```sh
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Step 3: Install Customed Rasterizer and Gaustudio
```
cd submodules/gaustudio-diff-gaussian-rasterization
python setup.py install
cd ../../
python setup.py develop
```
## Optional Step: Install PyTorch3D
If you require mesh rendering and further mesh refinement, you can install PyTorch3D follow the [link](https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d/blob/main/INSTALL.md):
# QuickStart
## Mesh Extraction for 3DGS
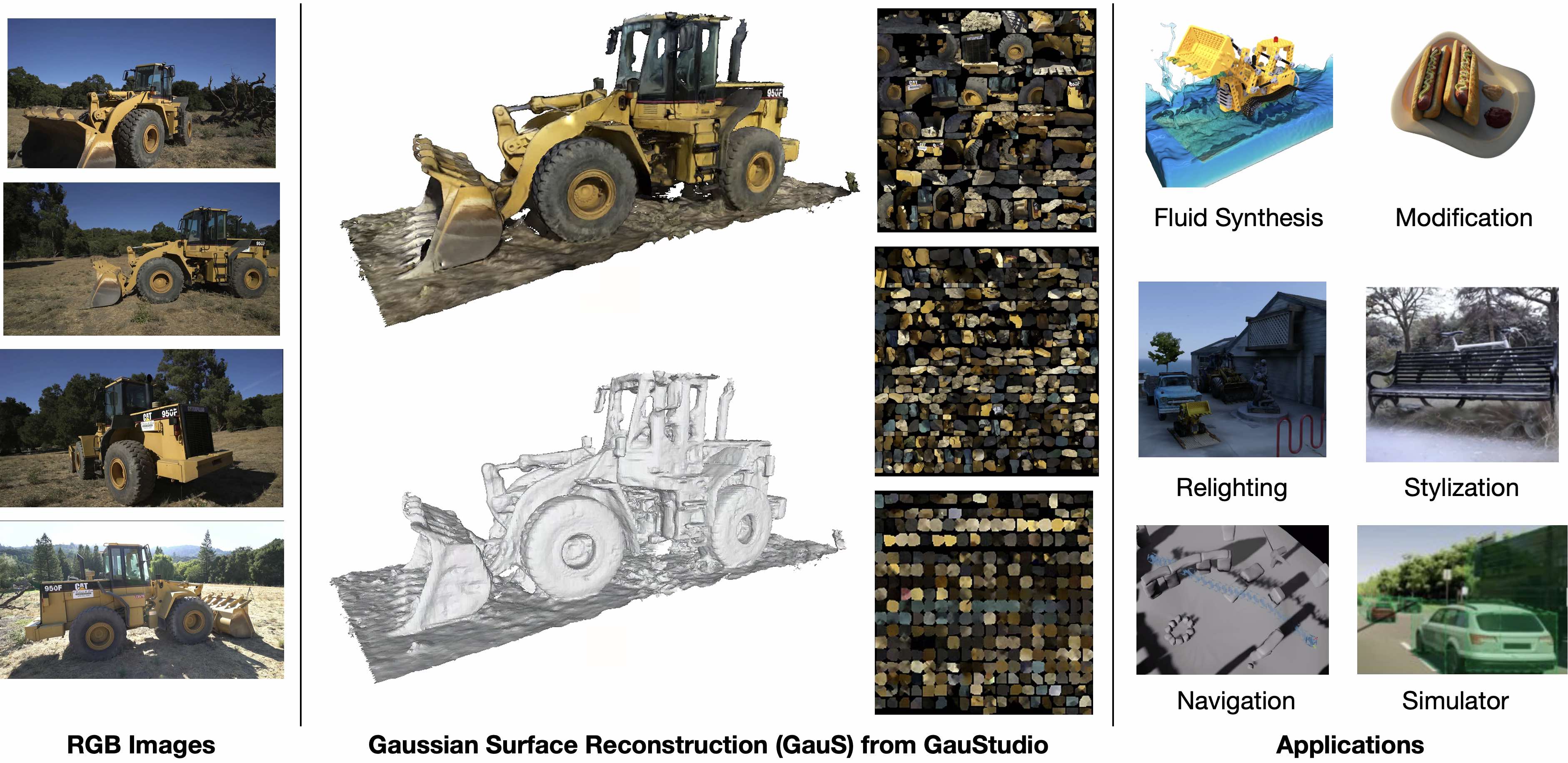
### Prepare the input data
We currently support the output directory generated by most gaussian splatting methods such as [3DGS](https://github.com/graphdeco-inria/gaussian-splatting), [mip-splatting](https://github.com/autonomousvision/mip-splatting), [GaussianPro](https://github.com/kcheng1021/GaussianPro) with the following minimal structure:
```
- output_dir
- cameras.json (necessary)
- point_cloud
- iteration_xxxx
- point_cloud.ply (necessary)
```
We are preparing some [demo data(comming soon)]() for quick-start testing.
### Running the Mesh Extraction
To extract a mesh from the input data, run the following command:
```
gs-extract-mesh -m ./data/1750250955326095360_data/result -o ./output/1750250955326095360_data
```
Replace `./data/1750250955326095360_data/result` with the path to your input output_dir.
Replace `./output/1750250955326095360_data` with the desired path for the output mesh.
### Binding Texture to the Mesh
The output data is organized in the same format as [mvs-texturing](https://github.com/nmoehrle/mvs-texturing/tree/master). Follow these steps to add texture to the mesh:
* Compile the mvs-texturing repository on your system.
* Add the build/bin directory to your PATH environment variable
* Navigate to the output directory containing the mesh.
* Run the following command:
```
texrecon ./images ./fused_mesh.ply ./textured_mesh --outlier_removal=gauss_clamping --data_term=area --no_intermediate_results
```
# Plan of Release
GauStudio will supoort more 3DGS-based methods in the near future, if you are also interested in GauStudio and want to improve it, welcome to submit PR!
- [x] Release mesh extraction and rendering toolkit
- [ ] Release BlendedMVS, Nerf-Synthetic, and Blender datasets in the COLMAP format, along with the corresponding processing code.
- [ ] Release Semi-Dense, MVSplat-based, and DepthAnything-based Gaussians Initialization
- [ ] Release of full pipelines for training
- [ ] Release Gaussian Sky Modeling and Sky Mask Generation Scripts
- [ ] Release VastGaussian Reimplementation
- [ ] Release Mip-Splatting, Scaffold-GS, and Triplane-GS training
- [ ] Release 'gs-viewer' for online visualization and 'gs-compress' for 3DGS postprocessing
- [ ] Release SparseGS and FSGS training
- [ ] Release Sugar and GaussianPro training
# License
The code is released under the MIT License except the rasterizer. We also welcome commercial cooperation to advance the applications of 3DGS and address unresolved issues. If you are interested, welcome to contact Chongjie at [email protected]