Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/jiang111/awesome-android-tips
some code tips for android 💯
https://github.com/jiang111/awesome-android-tips
List: awesome-android-tips
android awesome tips
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
some code tips for android 💯
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/jiang111/awesome-android-tips
- Owner: jiang111
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2015-10-09T03:18:07.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-03-02T01:24:41.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-02-06T23:47:13.994Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: android, awesome, tips
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.4 MB
- Stars: 2,532
- Watchers: 170
- Forks: 481
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README-en.md
- License: LICENSE.txt
Lists
- lists - awesome-android-tips
- collection - awesome-android-tips
- awesomelist - awesome-android-tips
- fucking-lists - awesome-android-tips
- awesome-from-stars - jiang111/awesome-android-tips
- awesome - awesome-android-tips - some code tips for android 💯 (Others)
- awesome-lists-Definative-Lists - awesome-android-tips
- awesome-stars - awesome-android-tips - some code tips in android (Others)
- awesome-stars - jiang111/awesome-android-tips - some code tips for android 💯 (Others)
- my-awesome-stars - jiang111/awesome-android-tips - some code tips for android 💯 (Others)
README

[](https://github.com/jiang111/awesome-android-tips)
中文版 ->_->:https://github.com/jiang111/awesome-android-tips
Worthy collection of AS plugin ->_->:https://github.com/jiang111/awesome-androidstudio-plugins
Here we collect some of the commonly used Android code, continuous updates, the content from their usual accumulation and see the article on the network, part of the original address at the bottom. If there is an error welcome correction, if there is infringement, please contact me to delete. There may be duplicate content, please ignore or remind me to delete. the content is translated by https://translate.google.com
# 
* SetBackgroundResource(0) can remove View background color
* Resources.getSystem().GetDisplayMetrics(). Density can not use the Context can also get the screen density
* You can implement a simple mask effect by overloading ViewGroup's dispatchDraw. For example, when you drop down, you can add a layer of mask to the contentView. Canvas.drawRect (0, mContentView.getTranslationY (), getWidth (), getHeight (), mMaskPaint);
* New out of the View can be used View.generateViewId()(API 17 above available) to generate id, the system guarantees only
* Use GridView android: padding android: clipToPadding = "false" with the use of better
* In the layout file, if only for the occupancy, you can use Space to replace View. The best thing is that Space can skip this process.
* TypedValue.applyDimension (int unit, float value, DisplayMetrics metrics) to facilitate the conversion between dp, px, and sp.
* Activity.startActivities() This method is the most direct understanding of the use of intent to open multiple Activity
* TextUtils.isEmpty() Returns true if the passed String is NULL or Length is 0.
* Html.fromHtml() If you are familiar with Html, you can quickly through this method to deal with some rich text operation. Such as hyperlinks and graphic layout and other processing.
* TextView.setError() Sets the text box error reminder
* Build.VERSION_CODES Sometimes our app needs to perform different actions according to different SDK versions
* PhoneNumberUtils.convertKeypadLettersToDigits This method is simple and crude, will enter the letters according to the mapping on the keyboard into a number.
* ArgbEvaluator ArgbEvaluator.evaluate (float fraction, Object startValue, Object endValue); According to a starting color value and an end color value and an offset to generate a new color, the minutes are similar to the bottom of the WeChat.
* ValueAnimator.reverse() smooth cancellation of the animation effect
* DateUtils.formatDateTime() This method can output the corresponding formatted time or date
* Pair This class can be used to store a "group" of data. But not the relationship between key and value.
* SparseArray There are many places from the performance optimization side to use SparseArray to replace the hashMap, to save memory and improve performance.
* Linkify.addLinks () This class makes it easier to add hyperlinks to text.
* Android.media.ThumbnailUtils This class is mainly used to deal with thumbnail-related work, such as: used to get the media (pictures, video) thumbnails
```
CreateVideoThumbnail (String filePath, int kind)
ExtractThumbnail (Bitmap source, int width, int height)
```
* Bitmap.extractAlpha(); returns a new Bitmap, capture the alpha value of the original image. Sometimes we need to dynamically modify the background image of an element and do not want to use multiple pictures of the time, through this method, combined with Canvas and Paint can dynamically modify a solid color Bitmap color.
* When there is a message between modules, use the LocalBroadcastManager instead of the Listener for module decoupling. In addition to decoupling, this sends a message and executes a message that is worse than a thread loop that can reduce the method of calling the chain, and I have encountered a method call chain that is too long to cause StackOverflow.
* Static variables do not directly or indirectly refer to Activity, Service and so on. This will use the Activity and all the objects it references can not be freed, and then the user will run for a long time and the memory will go up.
* Handler mechanism has a feature is not with the Activity, Service's life cycle ends. In other words, if you post a Delay Runnable, and then Runnable before the implementation of the exit from the Activity, Runnable to the time or to be executed. If Runnable contains an updated view operation, it may cause a memory leak, so you can call removeCallbacksAndMessages() to remove the message waiting for execution of this Handler.
* Many people in the sub-thread update View like to use Context.runOnUiThread, this method has a drawback, that is, but the End of the life cycle, such as Activity has been destroyed, a call will collapse.
* SharedPreferences.Editor.commit This method is synchronized, until the data is synchronized to the Flash before the return, by the IO operation is not control, try to use the apply method instead. Apply only in API Level> = 9 will support, need to be compatible. However, the latest `support v4` package has been handled for us, using the` SharedPreferencesCompat.EditorCompat.getInstance().Apply (editor) `.
* PackageManager.getInstalledPackages This method is often used, you may not know, when the number of results obtained more time, in some models above it may take time to call it second, so try to use in the sub-thread. In addition, if the result is too much, more than the upper limit of the maximum amount of Binder data set by the system, a TransactionException occurs. If you use this method to get the list of installed applications on the machine, it is best to do some precautions.
* If you use Context.startActivity to start an external application, it is best to do something exception prevention, because you can not find the corresponding application, it will throw an exception. If you want to open the application of the Activity, not use the explicit Intent, this will improve the efficiency of the system search target Activity.
* Application's lifecycle is the life cycle of the process. Only when the process is killed, Application will be destroyed. Even if there is no Activity, Service is running, Application will exist. So, in order to reduce memory pressure, try not to reference inside the application of large objects, Context and so on.
* There are two ways to set the full-screen method: 1. Through the code settings, 2 through the manifest file settings. When the application is running, you may see a brief status bar, then the full screen, and the second method is not the case, so recommend the second.
```
//method 1:
// no title
RequestWindowFeature (Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
GetWindow (). SetFlags (WindowManager.LayoutParams. FLAG_FULLSCREEN, WindowManager.LayoutParams. FLAG_FULLSCREEN);
// must be called before setContentView ()
SetContentView (R.layout.main);
// Method 2:
```
* ViewCager's setCurrentItem must be in the setAdapter method after the call will be effective.
* Determine whether the phone is not flying mode boolean isEnabled = Settings.System.getInt(context.getContentResolver(), Settings.System.AIRPLANE_MODE_ON,0) == 1;
* TabLayout modifies the font method
The official TabLayout does not provide a way to modify the TextView size, you can create a new style customTabLayoutTextAppearance inheritance TextAppearance.AppCompat.Widget.ActionBar.Title.Inverse, and then add the item,
set up android: textAllCaps is true, and then set up android: textSize you want to set size.

And then in the TabLayout layout file set app: tabTextAppearance="@style/CustomTabLayoutTextAppearance" can be.

The best way to traverse HashMap
```
Public static void printMap (Map mp) {
For (Map.Entry m: mp.entrySet ()) {
System.out.println (m.getKey () + ":" + m.getValue ());
}
}
```
* Use Java to generate random integers in a range
```
Public static int randInt (int min, int max) {
Random rand = new Random ();
Int randomNum = rand.nextInt ((max - min) + 1) + min;
Return randomNum;
}
```
* If the subclass implements the Serializable interface and the parent class is not implemented, the parent class will not be serialized, but the parent must have a no-argument constructor, otherwise the InvalidClassException will be thrown.
* The transient keyword modification variable can limit serialization.
* When using JakeWharton's TabPageIndicator, if you need to do some time-consuming operation, and then show TabPageIndicator, you need to set mIndirector.setVisibility (View.GONE); then time-consuming task after the end mIndirector.setVisibility (View.VISIBLE ); Otherwise it will be an error
* Class calls between inheritance parent class static member -> subclass static member -> parent class normal member initialization and initialization block -> parent class constructor -> subclass general member initialization and initialization block -> subclass constructor
* Huawei's mobile phone can not display the log solution. Dial-up interface input (*#*#2846579#*#*) Service menu will appear.Go to "ProjectMenu" -> "Background Setting" -> "Log Setting" Open "Log switch" and set it to ON.Open "Log level setting" and set the log level you wish.
* Background service is often restarted due to the occurrence of onStartCommand() in the Intent passed the parameters of the null, through the onStartCommand() in the return value into return super.onStartCommand(intent, Service.START_REDELIVER_INTENT, startId); can solve the problem The Here are some of the meaning of the flag
* | Flag | explain |
| ------------- |: -------------: |
| START_STICKY | If the service process is killed, keep the status of the service as the start state, but do not keep the delivery of the intent object. The system will then try to re-create the service, because the service state is the starting state, so after creating the service will call onStartCommand (Intent, int, int) method. If no startup commands are passed to the service during this period, the parameter Intent will be null. |
| START_NOT_STICKY | "non-sticky". When using this return value, if the service is killed abnormally after the onStartCommand has been executed, the system does not automatically restart the service. |
| START_REDELIVER_INTENT | Retransmit Intent. When using this return value, if the service is killed abnormally after executing the onStartCommand, the system automatically restarts the service and passes the value of Intent. |
| START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY | The compatible version of START_STICKY, but does not guarantee that the service will be able to restart after being killed. |
* PopupWindow and Dialog can not be displayed if Activity is not fully displayed
* Do not use SharedPreferences between multiple processes to share data, although it can (MODE_MULTI_PROCESS), but very unstable
* Sometimes you can not use the Application of the Context, or will be error (such as start Activity, show Dialog, etc.)
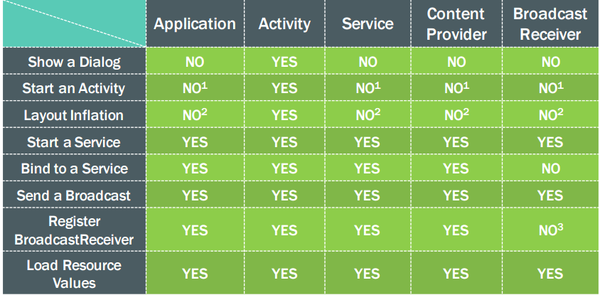
>*Note: we have to see some NO on the addition of some numbers, in fact, these ability is YES from the ability, but why is it NO? One of the following explanations:
1. Number 1: start Activity in these classes is possible, but need to create a new task, the general situation is not recommended;
2. number 2: in these classes to layout inflate is legal, but will use the system default theme style, if you customize some of the style may not be used;
3. Number 3: Allowed when Receiver is null, in 4.2 or above, to get the current value of the sticky broadcast. (Can be ignored);
4. ContentProvider, BroadcastReceiver reason in the above table, because in its internal method has a context for use.
* Transparent use of Android's transparent theme, transparent theme will lead to a lot of problems, such as: If the new Activity uses a transparent theme, then the current Activity onStop method will not be called; set to transparent theme of the Activity interface, May lead to brush screen is not clean problem; into the theme of the transparent theme of the interface there will be a clear sense of delay
* Do not initialize ViewStub in non-UI threads, otherwise it will return null
* Try not to cache data through Application, which is not stable
* Huawei mobile phone can not open the USB debugging problem,
1. Insert the data line, dial interface input *#*# 2846579 # * # * into the project mode
2. projectmenu → 3 background settings → 4USB port configuration → Balong debug mode, point to determine
3. Do not pull the line, exit the project mode, directly restart the phone, the computer displays a removable disk (if not yet, repeat steps 1, 2)
4. This is the way to turn off USB debugging in the case of mobile phones using mobile phones on the computer, using the usb option in the drop-down menu is also back.
* Android listview message is blocked by the soft keyboard, and set up in the listview when android:transcriptMode="normal" just fine
* TextUtils is a very useful tool class, the List into a string, comma separated, comma-separated String string, cut into List, respectively, can be used TextUtils join and split method. If you want to repeat the List, you can use the Collection's frequency method.
* Invoke the moveTaskToBack(boolean nonRoot) method in the activity to bring the activity back to the background, noting the finish () exit.
* Activity in the runOnUiThread(Runnable action) method can be directly back to the main thread
* Listview has a footerDividersEnabled and headerDividersEnabled method can set the top of the listview and the bottom divide, but must ensure that you set the headview and footview will have the effect
* Throwable class getStackTrace() method, according to this method can be a function of the layer call address, the return value of StackTraceElement[];
* The StackTraceElement class, where the four methods getClassName(), getFileName(), getLineNumber(), getMethodName() are very useful when the debugger prints Log;
* UncaughtExceptionHandler interface, no matter how bad the code is inevitable, the use of this interface can not catch the exception to the aftermath
* The getIdentifier(name, defType, defPackage) method in the Resources class, which gets its ID based on the resource name, often used as a UI;
* View of the isShown method, only when the view itself and all its ancestors are visible, isShown () only return to TRUE. And usually we call if (view.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE) is only on the view itself without the ancestors of the visibility to judge.
* Arrays class in a series of tools on the array operation methods: binarySearch(), asList(), equals(), sort(), toString(), copyOfRange(), etc .; Collections class on a collection of operations on the tool Method: sort(), reverse();
* Append(CharSequence) method in the TextView class, add text. Some special text directly with the + connection will become String;
* The arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length) method in the System class is used to copy the array;
* The onHiddenChanged(boolean) method in the Fragment class, using hide(), show() in FragmentTransaction only calls the show and hidden states in Fragment, and other lifecycles are not invoked.
* On the object class onWindowFocusChanged(boolean), onNewIntent(intent) and other callback methods;
* The setTransformationMethod(TransformationMethod) method in the TextView class can be used to implement the "Show Password" function
* PageTransformer interface, used to customize the ViewPager page switch animation, setPageTransformer(boolean, PageTransformer) method to set;
* Apache to provide a series of jar package: commons-lang.jar, commons-collections.jar, commons-beanutils.jar, etc., there are many ways you may have used dozens of hundreds of lines of code to achieve, but the implementation of efficiency may Much worse, such as: ArrayUtils, StringUtils ... ...;
* ActivityLifecycleCallbacks interface, used in the Application class to monitor the status of the Activity changes [read address me](http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA3ODkzNzM3NQ==&mid=401277907&idx=1&sn=0b2246f5178292596fc3a8295283359c#rd)
* ActionBar.hide()/.Show() As the name suggests, hide and show ActionBar, you can gracefully switch between full screen and actionbar.
* SystemClock.sleep() This method is very convenient to ensure that a certain time of sleep, usually I used to debug and simulate the network delay.
* UrlQuerySanitizer - Use this tool to easily check the URL.
* ActivityOptions - easy to define the two Activity switch animation. Use ActivityOptionsCompat to solve the old version of the compatibility problem.
* GetParent(). RequestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true); deprives the parent view of the handling of the touch event, who knows who.
* HandlerThread, instead of non-stop new Thread sub-thread repetitive physical writing.
* IntentService, a can be done after the death of their own death and do not need us to manage the sub-thread Service
* Executors. NewSingleThreadExecutor(); This is a java, do not know it before, they spent a lot of effort to study the single-threaded sequential execution of the task queue
* Android: animateLayoutChanges="true", LinearLayout add View animation method, support through setLayoutTransition() custom animation.
* AsyncQueryHandler, if you do the development of system tools, such as contact SMS auxiliary tools, and certainly will not deal with ContentProvider, if the amount of data is not a big case, casually engage, if the amount of data in the case of large, understand the next class Is necessary, it should be noted that this thing to eat abnormal ..
* ViewFlipper, to achieve multiple view of the switch(loop), you can customize the animation, and can be specified for a single switch animation.
* Android util package Pair class, can be easily used to store a "group" of data. Note that the key value is not
* Android: descendantFocusability, ListView item CheckBox and other elements of the focus of the focus of the item click event can not respond, in addition to the corresponding element set focusable, the more simple is the root of the article plus android: descendantFocusability="blocksDescendants"
* IncludeFontPadding = "false", TextView default is a certain padding, and sometimes we may not need this part of the blank, plus it can be.
* Messenger, the interview time will usually be asked to communicate between the process, under normal circumstances we are all endorsement, AIDL Bala Bala. The One day in the gods of the blog to see this, ah, as he said, and can be installed about.
* EditTxt.setImeOptions, use EditText pop-up soft keyboard, modify the Enter key to display the content (has been very annoying to use the Enter key to interact, so do not know this thing before)
* Java8 in the new LocalDate and LocalTime interface, Date is a universal interface, but it really is not easy to use, with these two, and finally can be happy to deal with the date and time.
* WeakHashMap, the direct use of HashMap sometimes bring the risk of memory overflow, using WaekHashMap instantiation Map. When the user no longer has an object reference, WeakHashMap will automatically be removed from the corresponding key value of the object.
* When using SnackBar, do not use view.getRootView () as the view of snackbar, Huawei glory 7 will be a problem.
* Set the TextView single line when the show do not use Lines = 1, and use singleLine = "true", because the Meizu part of the phone in the set Lines = 1, and then the value of TextView all the numbers, you will be muddled The
* TouchDelegate can be used to change the touch area of View. Scene: For example, in the RecyclerView's ItemView contains the CheckBox component, and then want to achieve when you click on the ItemView, you can also trigger the CheckBox, you can use this class
* ArgbEvaluator can be used to calculate the interpolation between different color values, with ValueAnimator.ofObject or ViewPager.PageTransformer use, you can achieve a smooth transition between different colors.
* Palette can be used to extract the color of a picture.
* ViewDragHelper, done custom ViewGroup children's shoes should know this thing, used to deal with touch artifacts, my mother no longer have to worry about my custom control.
* PageTransformer used to define the ViewPager page switch when the animation effect (fade, zoom in and out of the ...) There are examples of official, see it directly.
* Formatter.formatFileSize() This method will format the data size, according to the input byte size, return B KB MB GB and so on (maximum support to PB). Of course, note that the maximum value entered is Long.MAX_VALUE.
* Activity.recreate re-create the Activity. what's the function? You can change the theme after the program, immediately refresh the current Activity, and there will be no obvious restart the animation animation.
* View.getContext As the name suggests, do not have to explain it ... In the previous RecyclerView adapter, in order to use LayoutInflater, often silly in the constructor passed in an external context ... is not only I do not know it (laugh cry face)
* View.post easy to modify the interface in non-UI threads, similar to the role of Handler. And because the post Runnable will ensure that the view is completed under the premise of the call, it can also be used to obtain the View width and height.
* Activity.runOnUiThread and View.post similar to the convenience of non-UI threads in the interface to modify.
* Fragment When working with PagerAdapter, you can override the setUserVisibleHintFragment() method and then execute some logic based on the boolean value of the argument (true that the current Fragment is visible to the user).
* Android: animateLayoutChanges This is a very cool property. In the parent layout plus android: animateLayoutChanges="true", if triggered the layout method (such as its sub-view set to GONE), the system will automatically help you add the layout changes when the animation effects! The
* Android: clipToPadding Set whether the parent view allows its child view to be drawn in its padding(in this case, the parent view padding). Is it a bit around? Give a real scene: If there is a ListView, we want in the initial position, the first item from the top of the distance of 10dp, you can add in the ListView layout android: clipToPadding="false" android: paddingTop ="10dp" can be. Is not it convenient?
* Rv's Layoutmanager can be directly stated in xml, the specific code can be viewed RecyclerView.createLayoutManager method.


* RecyclerView in 23.2. + Version of the new automatic measurement function, due to the addition of automatic measurement, then the root of its item in the direction of the need to measure the direction can not write match_parent, and need to be changed into wrap_content
* GetParent (). RequestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent (true); deprives the parent view of the handling of the touch event, who knows who.
* Canvas in the clipRect, clipPath and clipRegion cut area API.
* GradientDrawable has a shadow effect is also good, that is cut the picture, a look at the code, what ghost ==!
* Some friends mentioned in the custom View when some methods in the open hardware acceleration when there is no problem in the API16 after there are many ways do not support hardware acceleration, usually we close the hardware acceleration is in the list file through the , in fact, android also provides a specific View closed hardware acceleration method, call View.setLayerType (View.LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE, null);
* PointF, graphics package in a class, we often see in dealing with the Touch event, respectively, when the definition of a downX, a downY used to store a coordinate, if the coordinates of less good, if you want to record the coordinates of too much that code is not Look good. Using PointF (float x, float y); to describe a coordinate point will be a lot of clear.
* StateListDrawable, Define Selector The usual way is xml file, but sometimes our picture resources may be dynamically obtained from the server, such as a lot of app so-called skin, this time only through StateListDrawable to complete, AddState.
* Android: duplicateParentState="true", let sub-view follow its Parent state, such as pressed and so on. Common use of the scene is sometimes a button is very small, we want to expand its click area when it is usually given a layer of its layout, the click event will be written to the Parent, this time if you want to be wrapped button click effect The corresponding Selector to continue to take effect, then this time on the use of duplicateParentState.
* ViewConfiguration.getScaledTouchSlop(); trigger the minimum distance of mobile events, custom View processing touch events, sometimes need to determine whether the user really exists movie, the system provides such a method.
* ViewStub, sometimes a region needs to show different layouts according to the situation, usually we will setVisibility method to show and hide the different layout, but this is all loaded by default, with ViewStub can better improve performance.
* OnTrimMemory, rewrite this method in the Activity, the memory will be tight when the callback (to support multiple levels), so that we take the initiative to release the resources to avoid OOM.
* TextView.setCompoundDrawablePadding, the code sets the drawable padding of the TextView.
* ImageSwitcher, which can be used to make a picture toggle a class, similar to a slideshow.
* In the custom control, can draw draw to draw round, or other styles, try to use drawable, because the effect of drawable far better than canvas.drawXXX().
* If you want to customize View support SwipeRefreshLayout, you only need to declare and implement the ScrollingView interface. RecyclerView and NestedScrollView have already implemented this interface.
* AtomicFile - the use of backup files for the atomization of the file. I have written this knowledge before, but it is better to have an official version is better.
* DatabaseUtils - a tool that contains a variety of database operations.
* Activity.isChangingConfigurations() - If the Activity in the Activity will often change, then use this method can not manually save the state of the work.
* SearchRecentSuggestionsProvider - can be created recently prompted the effect of the provider, is a simple and quick way.
* Android: clipChildren(ViewGroup) - If this property is set to not available, then ViewGroup's subview will draw beyond its scope and need to be animated.
* Android: fillViewport(ScrollView) - in this article has a detailed description of the article link, you can solve the ScrollView when the content is insufficient to fill the screen when the problem.
* Android:tileMode (BitmapDrawable) - You can specify the image to use the overlay mode.
* Android: enterFadeDuration/ android: exitFadeDuration (Drawables) - This property has a variety of states when Drawable can define the fade effect before it is displayed.
* Log.wtf() means what a Terrible Failure, not what The Fuck!
* Use RenderScript to blur the image effect. If your app has a minSDK of 16 or less, you need to use the support pattern, because many of the methods are added after the API 17. RenderscriptTargetApi up to 23, but you should set it up to keep the script with the full functionality of the minimum API. If you want the target API 21+ in the support mode you have to use gradle-plugin 2.1.0 and buildToolsVersion "23.0.3" or more. Need to add graderscripttargetApi in gradle 18, renderscriptSupportModeEnabled true these two sentences
```
Public static Bitmap blurBitmap (Context context, Bitmap src, int radius) {
Bitmap dest = src.copy (src.getConfig (), true);
RenderScript rs = RenderScript.create (context);
Allocation allocation = Allocation.createFromBitmap (rs, src);
Type t = allocation.getType ();
Allocation blurredAllocation = Allocation.createTyped (rs, t);
ScriptIntrinsicBlur blurScript = ScriptIntrinsicBlur.create (rs, Element.U8_4 (rs));
BlurScript.setRadius (radius);
BlurScript.setInput (allocation);
BlurScript.forEach (blurredAllocation);
BlurredAllocation.copyTo (dest);
Allocation.destroy ();
BlurredAllocation.destroy ();
BlurScript.destroy ();
T.destroy ();
Rs.destroy ();
Return dest;
}
```
* If you want to save a view as Bitmap, under normal circumstances with the first method can be, but if it is ScrollView, you must use the second method.


* When Activity LauncherMode is singleTask singleInstance, use startActivityForResult to return immediately, can not be called normally. Please see http://www.360doc.com/content/15/0123/14/12928831_443085580.shtml
* When PopupWindow in the EditText control, because Popupwindow acquiescence did not get to the focus, you need to manually set the focus, so look like the view to the event of the monitor. So you need to create the popwindow after setting his focus, popupWindow.setFocusable(true); you can let EditText get the focus.
* PopupWindow default to the external time does not disappear, you need to set a background popupWindow popWindow.setBackgroundDrawable (new BitmapDrawable()); To create an empty object, set to null is not enough, or create a transparent background map.
* Android in the serialization of the official recommendation Parceble, in fact, Parceble is best used for data exchange between memory, if you want to write data to the hard disk, it is recommended to achieve Serializable
* Tools can be very helpful to help developers real-time preview xml effect, through the tools: background can preview the control of the controls, tools: visibility can be a control of the time in the preview show, and run after the tools label The content will not be displayed. For example:
```
```
* Android studio 2.1 has been supporting jdk8, and when used in the gradle added, the need to buildToolsVersion updated to more than 24 versions
```
Android {
DefaultConfig {
...
Jackoptions {
Enabled true
}
}
...
CompileOptions {
TargetCompatibility 1.8
SourceCompatibility 1.8
}
}
```
* 6.0 after the getResources (). GetColor () method is abandoned, we can use ContextCompat.getColor (context, R.color.color_name) replacement, ContextCompat is v4 package, please rest assured that there are also getDrawable () and so on method
* Image resource file official recommendation only put launcher under the mipmap folder, and app the resource file used to put it under the drawable.
* SharedPreference.Editor apply is asynchronous operation, will not return to the successful state, and commit is synchronous operation, therefore, in a number of concurrent commit commit, they will wait for the commit is being processed to save the disk and then operate the next Data, thereby reducing efficiency.
* If you set an activity in the manifest to android: windowSoftInputMode = "adjustResize", then ScrollView (or other scalable ViewGroups) will shrink to make room for the soft keyboard. However, if you set the android: windowFullscreen = "true" in the theme of the activity, then ScrollView will not shrink. This is because the property forces ScrollView to be full screen. However, in the theme set android: fitsSystemWindows = "false" will also lead to adjustResize does not work
* After Android 4.0, in the Manifest.xml static registration of the broadcast, the program must be installed once to receive a broadcast, such as your application to monitor the boot-activated broadcast, you must run your program to be able to monitor
* Activity onDestory method call timing is uncertain (sometimes leave the interface for a long time after the call onDestory method), should be avoided through the onDestory method to release the resources associated with the Activity, otherwise it will lead to some random bug
* 2.X era Bitmap object is stored in the heap memory, but with a byte array to store its pixel information. The number of references to the pixel information is recorded by a counter. Some people think that this byte array in the native heap, but in fact it is also in the heap. Only after the user calls recycle (), the Bitmap object will release the pixel information before it will be destroyed by the garbage collection mechanism. Coupled with the DVM heap size has a strict threshold, so the use of a large number of picture resources, and its prone to OOM. The solution is generally to use a hash table to store the soft reference of the Bitmap object, as a memory cache, and at its proper time off its recycle (). 3.0 or later Bitmap object can be completely destroyed by the garbage collection mechanism, theoretically no need to call recycle ().
* .gitignore can only ignore those files that were not currently tracked, and if some files have been included in version management, the modified .gitignore is invalid. Then the solution is to first delete the local cache (changed to no track state), and then submit:
```
Git rm -r --cached.
Git add
Git commit -m 'update .gitignore'
```
* Timestamp Please use long or String type to receive, encountered the pit, because the project model is generated by a lot of GsonFormat, the server to the json timestamp is 10, resulting in GsonFormat automatically resolved into Int, when the testers select the time for 2100 when the timestamp is 4 at the beginning of the ten with the int type to receive cross-border, and lead to error
* For your app to add the default layout style, such as: each control need to write width and height attributes, but many of the control of the width and height attributes are wrap_content, then we can add the following style in the style file:
```
<Item name = "android: layout_width"> wrap_content </ item>
<Item name = "android: layout_height"> wrap_content </ item>
</ Style>
```
In this way, the control of the width of the default are wrap_content style friends.
* Style in the style written by the same as the parent tag to extend your style, so more efficient, where the official proposal is that only Android comes with the style tag with the parent, if it is a custom style, direct use. To connect on the line. Such as Fill.Height.
```
<Style name = "Fill">
<Item name = "android: layout_width"> fill_parent </ item>
<Item name = "android: layout_height"> fill_parent </ item>
</ Style>
<Style name = "Fill.Height">
<Item name = "android: orientation"> vertical </ item>
</ Style>
```
* Android application switching button is not listed in the application but Task, so you will see some applications in the switch view there are multiple tasks. These situations are suitable for multitasking if your application has logically independent parts, or if you want to show the two different parts of the application side by side in a multi-window environment. Use the manifest attribute (static) or intent flags (dynamic) to achieve this, see the video: http://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XMTU2ODk4NDg2NA==.html?f=26587294
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jiang111/awesome-android-tips/master/img/multy_task1.jpg" width = "50%" height="300px" /><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jiang111/awesome-android-tips/master/img/multy_task2.jpg" width = "50%" height="300px"/>
* When the app's theme is NoActionBar, but in the layout is still used when the toolbar, not in the style file fitsSystemWindows attribute, but in the use of the toolbar of the outermost layer plus fitsSystemWindows, or when you use EditText, In the millet phone long press EditText call up the system paste function, paste the layout of the layout will be dislocation.
* When WebView and ScrollView nested use, and WebView font zoom function, when switching webview fonts, webview height and can not be a good calculation, this time through the injection method, so that js calculate the height, Tested, this is the most reliable, code address: http://blog.csdn.net/jys1115/article/details/43525979
* The createPackageContext (packageName, flags) method in the Context class that can be used to get the Context object for the specified package name application.
* The setKeyListener (KeyListener) method of the TextView class;
Where DigitsKeyListener class, using the getInstance (String accepted) method to specify EditText to enter a character set;
* Recommended data structure in Android:
```
ArrayMap <K, V> in place of HashMap <K, V>
ArraySet <K, V> in place of HashSet <K, V>
SparseArray <V> in place of HashMap <Integer, V>
SparseBooleanArray in place of HashMap <Integer, Boolean>
SparseIntArray in place of HashMap <Integer, Integer>
SparseLongArray in place of HashMap <Integer, Long>
LongSparseArray <V> in place of HashMap <Long, V>
```
* Generate GUID (because java can only generate UUID, so here to change):
```
Return UUID.randomUUID (). ToString (). ToUpperCase (). ReplaceAll ("-", "");
```
* Business scenarios: the need to regularly scan the database background, upload local photos to the cloud, the timing of the task using what mode:
1. Handler or Timer timing is generally a second-level task, Timer will start additional threads, and Handler can not.
2. Both Handler and Timer need to rely on the process to survive
3. Handler implementation of the task of the class: HandlerTimer
4. If the time is long, you need to use the AlarmManager
5. In addition, we should prioritize whether such business can be based on event notification.
6. If you are adding files to the media library, we can use the registerContentObserver to monitor media library file changes.
* Activity as a parameter passed to a static method, will affect the normal destruction of the Activity?
1. Memory leaks are independent of whether or not the method is static or not, and is related to the internal method body implementation.
2. Memory leaks can be easily understood as: the long life cycle of the object is not properly held holding a short life cycle of the object, resulting in short life cycle of the object can not be recycled.
3. For example, the Activity instance is held by the Application object, and the Activity instance is held by the static variable.
* In the assert folder to store a single file size can not exceed 1M, if the read more than 1M file will be reported "Data exceeds UNCOMPRESS_DATA_MAX (1314625 vs 1048576)" IOException. If you have to store, you can split the file, go to merge the file
* In the Android library can not use the switch-case statement to access the resource ID, because the case branch followed by the parameters must be constant, and library of each resource ID are not declared as final.
* The current Activity's onPause method is executed after the implementation of the next Activity onCreate method, so in the onPause method is not suitable for long time-consuming work, which will affect the efficiency of the jump between the pages;
* Do not pass bulk data via Bundle, otherwise it will report a TransactionTooLargeException exception
* (AnimationDrawable in Android5.0 and above version has been significantly optimized) try not to use AnimationDrawable, it will be in the initialization of all the pictures will be loaded into memory, in particular, memory, and can not be released, the next time after the release Reloading;
* .9 Figure can not be compressed by tinypng, otherwise there will be problems;
* Genymotion simulator is fast because it is based on the x86 architecture, if your application used so, but no x86 architecture so, can only give up the use of it; Android Studio simulator is the same;
* When using Toast, it is recommended to define a global Toast object, which can avoid the continuous display Toast can not cancel the last Toast message (if you have a continuous pop-up Toast, avoid the use of Toast.makeText);
* Try to avoid setting the background to the window and the Activity at the same time, which will cause the transition to be drawn. You can reduce the layer by changing the windowBackground background when you set the theme to the Activity. Sometimes it will be blank or white in order to avoid entering the Activity. Screen (and the theme), will set the theme in the Activity to set the background to the window, if the case to the Activity also set the background, is to double the memory:
```
<Item name = "android: windowBackground">@null</ item>
```
* Settings to change the font for the large and the like will affect the app font style, the solution is: 1. All fonts used to replace the unit dp, no longer use sp. This is not very tricky, not everyone can do it.
2.
```
Configuration configuration = getResources (). GetConfiguration ();
Configuration.fontScale = (float) 1;
/ Medium.85 small, 1 standard size, 1.15 large, 1.3 large, 1.45 large
DisplayMetrics metrics = new DisplayMetrics ();
GetWindowManager (). GetDefaultDisplay (). GetMetrics (metrics);
Metrics.scaledDensity = configuration.fontScale * metrics.density;
GetBaseContext (). GetResources (). UpdateConfiguration (configuration, metrics);
// (except ps: dialog popupwindow, these two need to re-set the fontScale in the control)
```
* Android in the introduction of new alternative annotations are IntDef and StringDef, here to IntDef example to illustrate.
```
Public class Colors {
@IntDef ({RED, GREEN, YELLOW})
// declare the necessary int constants, decorate LightColors with @IntDef, set the arguments to the set to be enumerated
@Retention (RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
// use @Retention (RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) to specify annotations that exist only in the source code and not in the class file
Public @interface LightColors {}
// declare a comment for LightColors
Public static final int RED = 0;
Public static final int GREEN = 1;
Public static final int YELLOW = 2;
}
//usage
Private void setColor (@ Colors.LightColors int color) {
Log.d ("MainActivity", "setColor color =" + color);
}
// call this method when
SetColor (Colors.GREEN);
```
* PathInterpolatorCompat is very easy to use it to create a variety of interpolation curve, give a very simple example:
```
Path path = new Path ();
Path.cubicTo (0.2f, 0f, 0.1f, 1f, 0.5f, 1f);
Path.lineTo (1f, 1f);
ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat (view, View.TRANSLATION_X, 500);
Animator.setInterpolator (PathInterpolatorCompat.create (path));
Animator.start ();
```
* Detect whether the current network can access the remote server (domestic detection by Baidu Baidu)
```
Public static boolean isNetWorkAvailable (final context context) {
Try {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime ();
Process pingProcess = runtime.exec ("/ system / bin / ping -c 1 www.baidu.com");
Int exitCode = pingProcess.waitFor (); // 0 stands for connectivity, 2 is unreachable
Return (exitCode == 0);
} Catch (Exception e) {
E.printStackTrace ();
}
Return false
}
```
* Intercept system to return key (onBackPressed ()), so that App does not exit, but into the background
```
@Override
Public void onBackPressed () {
MoveTaskToBack (false);
}
```
* View.performClick () automatically calls the View Click event. Normally buttons and other controls can only trigger a click event when the user clicks, which can trigger simulated user click behavior by some special conditions. There are also similar performLongClick () methods.
* Linkify.addLinks () through the android: autoLink attribute can be added to them, such as web, phone and other fixed template hyperlink event. But after all, the system template is limited, and the use of Linkify.addLinks () method can add some in-app custom templates, such as Sina microblogging "@XXX" format hyperlink jump, etc., can be customized by regular expression Match processing.
* GetWindow (). AddFlags (WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SECURE) Set the security window to disable the system screenshots. To prevent some of the interface in the App screen was screened and displayed in other equipment caused by information leakage. (Common mobile device system screenshots: press the power button and volume keys.)
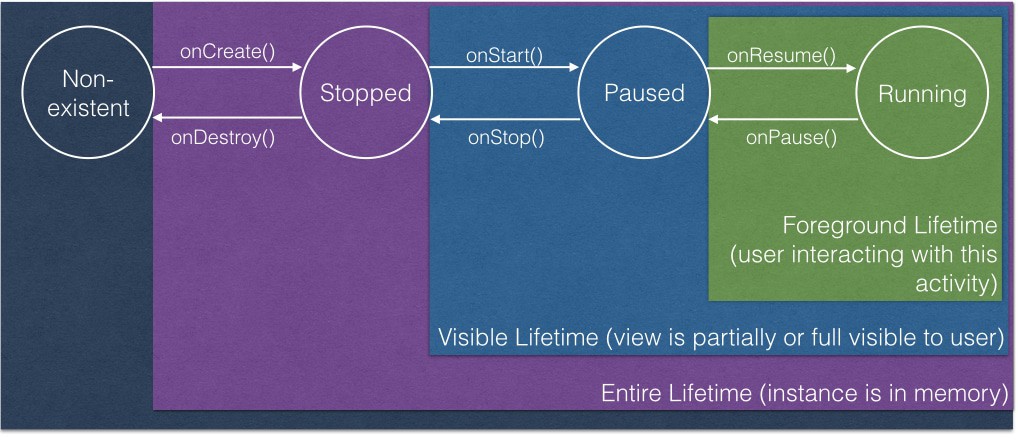
* Activity lifecycle ([Ref Link](https://www.bignerdranch.com/blog/android-activity-lifecycle-onStop/))
* 
* RecyclerView calls notifyItem () when there is a default animation, you can call ((SimpleItemAnimator)recyclerView.getItemAnimator()).SetSupportsChangeAnimations(false); to remove the default animation.
#### From [the following address](https://github.com/jiang111/awesome-android-tips/blob/master/Authors.md)
### Donation
If you think this item is helpful to you, please ask the author [a cup of coffee](https://paypal.me/jyuesong). <br /> <br />

### License
Copyright 2016 NewTab
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.