https://github.com/16eagle/movevis
An R package providing tools to visualize movement data (e.g. from GPS tracking) and temporal changes of environmental data (e.g. from remote sensing) by creating video animations.
https://github.com/16eagle/movevis
animal-behavior animal-environment animal-movement animal-tracking animation movement-ecology movement-video r remote-sensing visualization
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
An R package providing tools to visualize movement data (e.g. from GPS tracking) and temporal changes of environmental data (e.g. from remote sensing) by creating video animations.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/16eagle/movevis
- Owner: 16EAGLE
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2017-05-17T22:19:41.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-04-26T14:37:29.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-12-12T01:50:40.674Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: animal-behavior, animal-environment, animal-movement, animal-tracking, animation, movement-ecology, movement-video, r, remote-sensing, visualization
- Language: R
- Homepage: http://www.movevis.org
- Size: 31.3 MB
- Stars: 131
- Watchers: 15
- Forks: 20
- Open Issues: 41
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: NEWS.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
[](https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=moveVis)
[](https://16eagle.r-universe.dev/moveVis)
[](https://github.com/r-universe/16eagle/actions/workflows/build.yml)
[](https://github.com/16EAGLE/moveVis/actions)
[](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/16EAGLE/moveVis)
[](https://app.codecov.io/gh/16EAGLE/moveVis)
## Introduction
`moveVis` provides tools to visualize movement data (e.g. from GPS tracking) and temporal changes of environmental data (e.g. from remote sensing) by creating video animations. It works with `move2` and `terra` class inputs and turns them into `ggplot2`-based frames that can be further customized. `moveVis` uses `gifski` (wrapping the gifski cargo crate) and `av` (binding to FFmpeg) to render frames into animated GIF or video files.
A peer-reviewed open-access paper accompanying `moveVis` has been published in *Methods in Ecology and Evolution*.
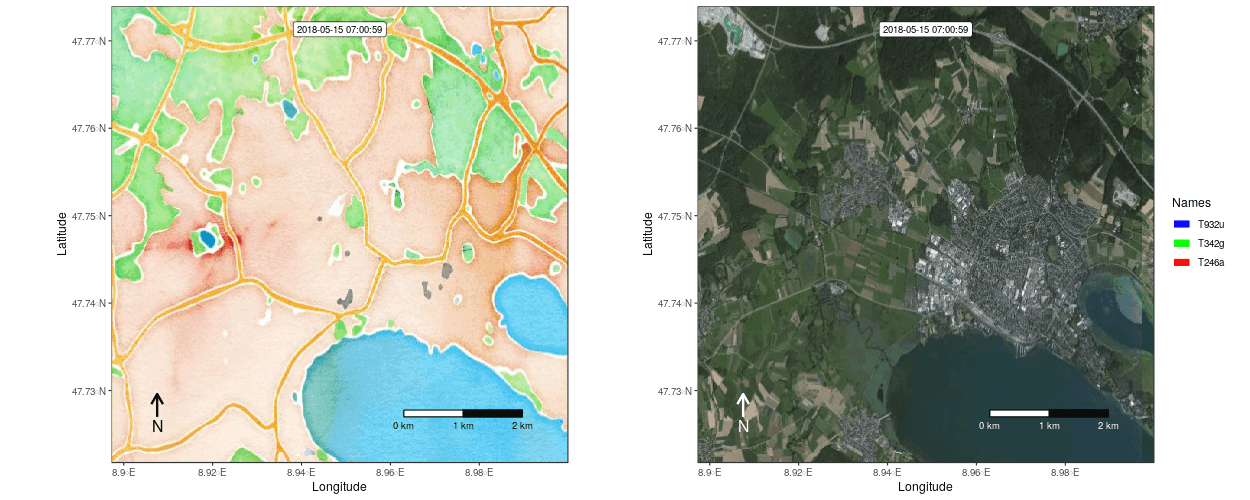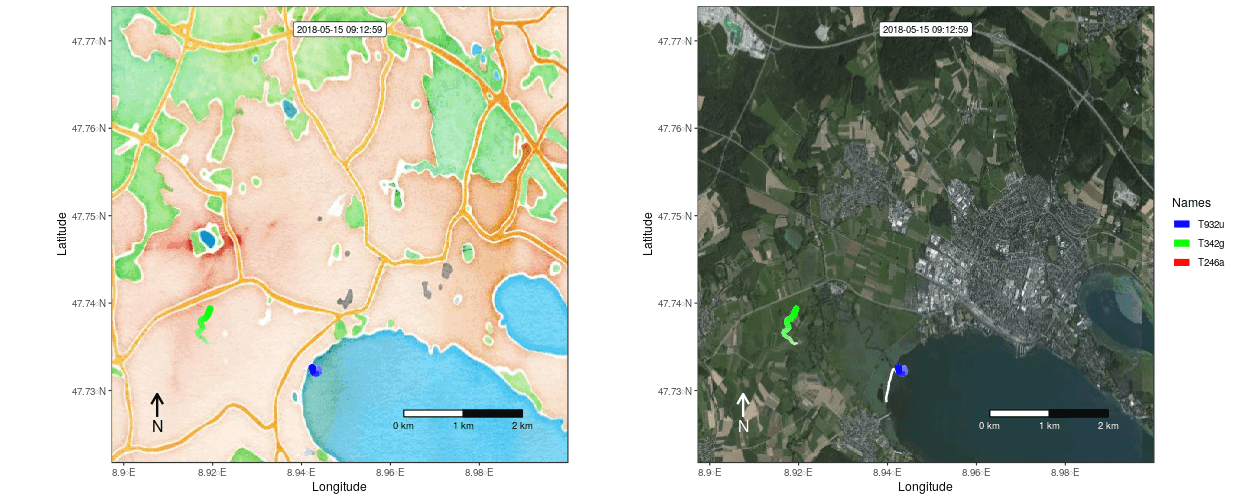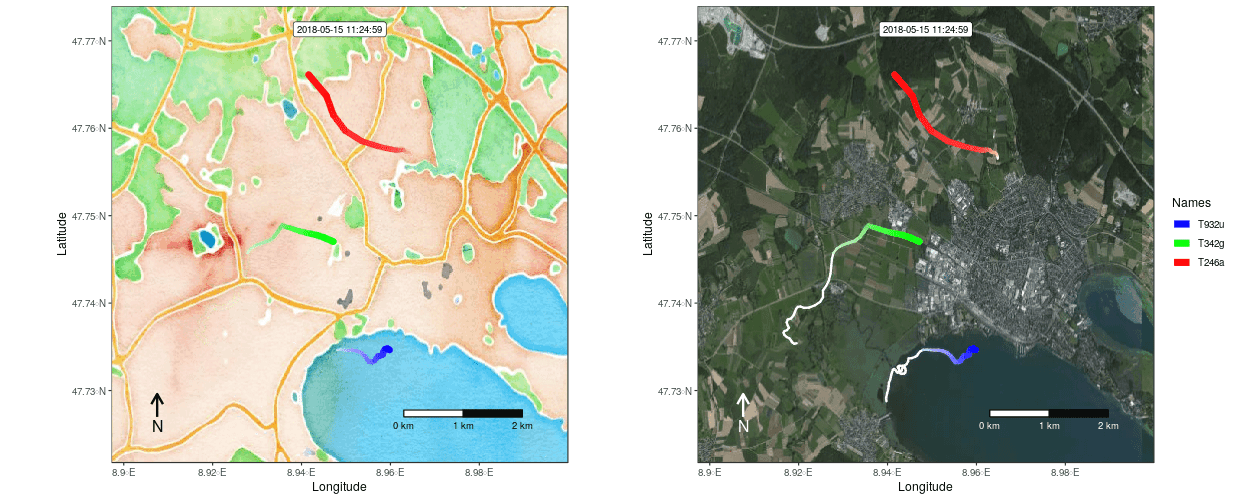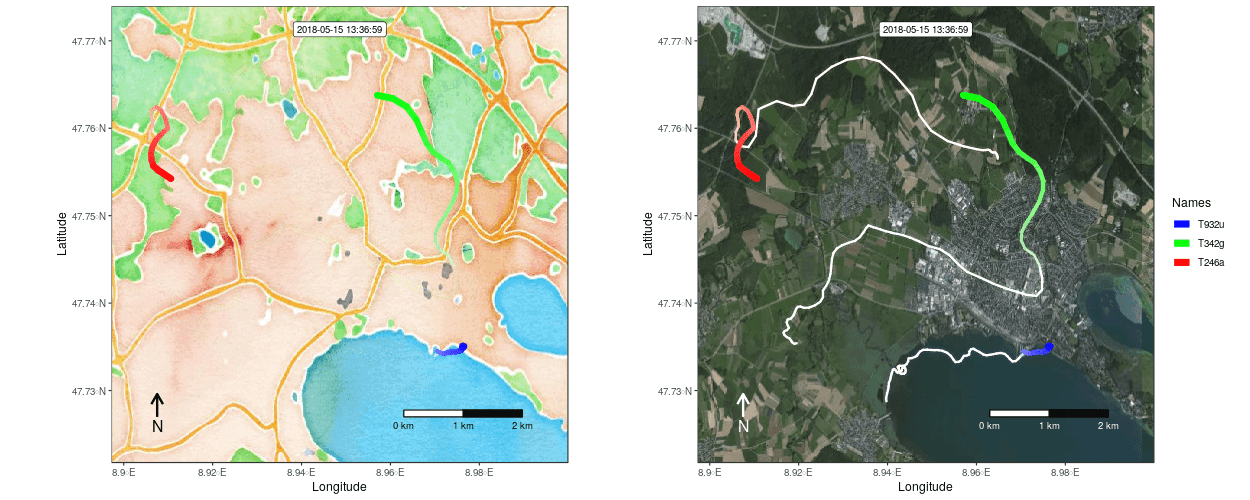
Figure 1: Example movement tracks nearby Lake of Constance on top of a OSM watercolor and a mapbox satellite base map
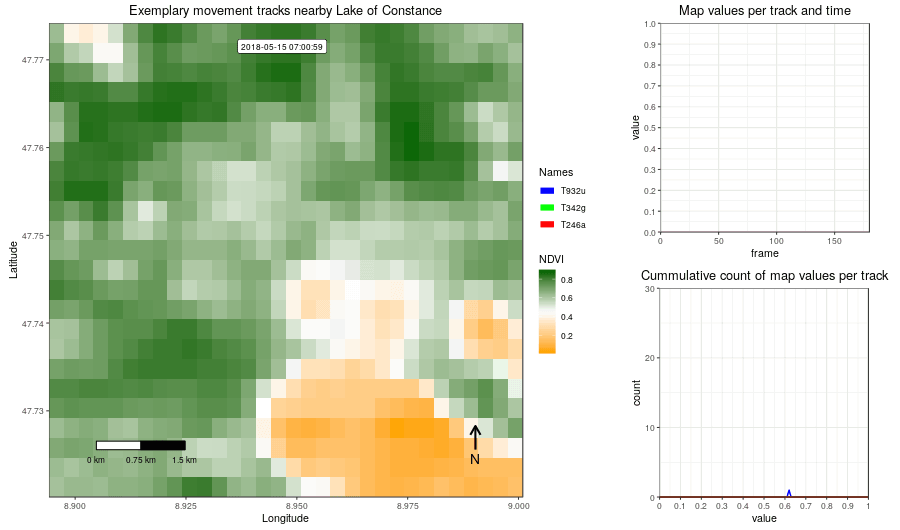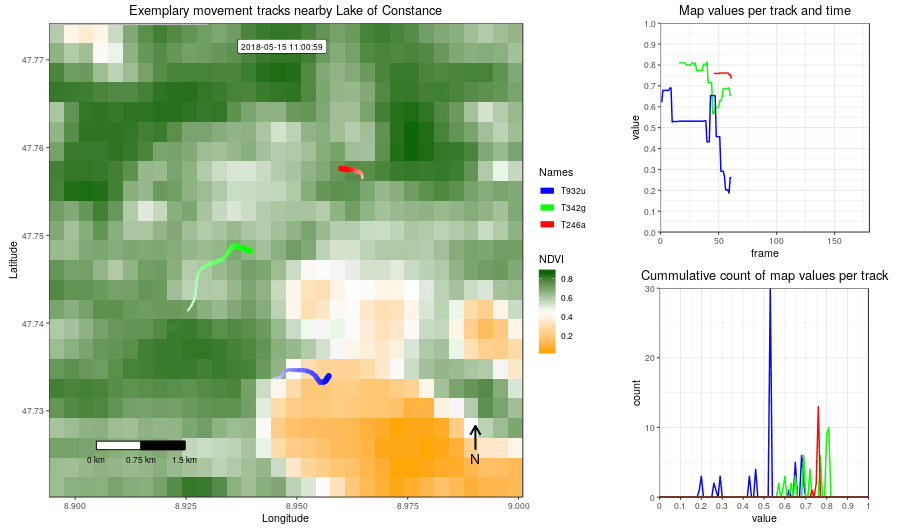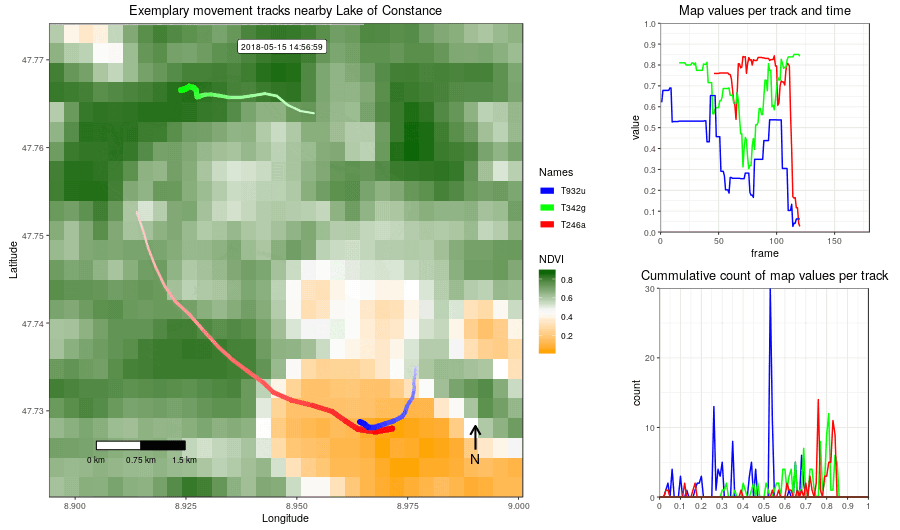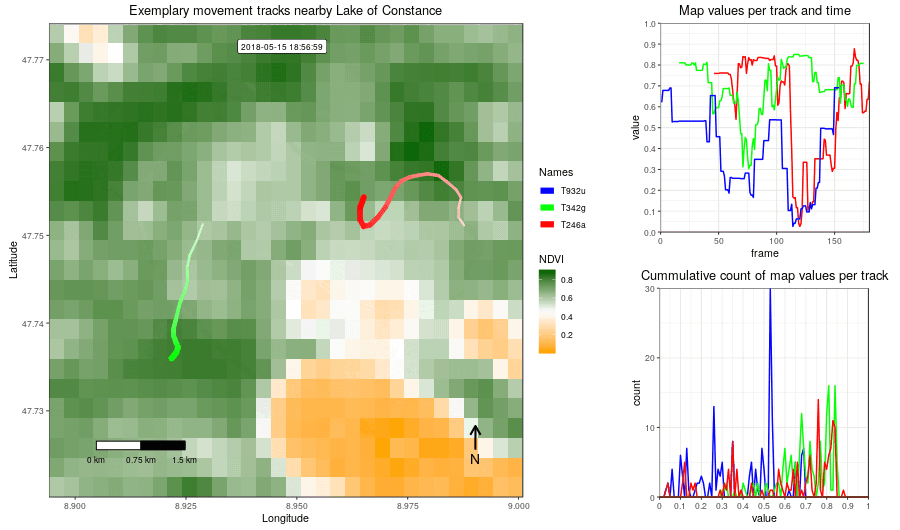
Figure 2: Example movement tracks nearby Lake of Constance and a gradient base layer faded over time
## Installation
Install the latest stable release of `moveVis` from CRAN (*currently unavailable*):
```r
install.packages("moveVis", repos = 'https://cloud.r-project.org')
```
Install the latest tested development builds of `moveVis` from r-universe:
```r
install.packages("moveVis", repos = '16eagle.r-universe.dev')
```
Install the latest tested development version of `moveVis` from source via GitHub:
```r
remotes::install_github("16EAGLE/moveVis")
```
## Get started
The following example shows how to make a simple animation using a default basemap by first aligning your movement data to a uniform time scale, creating frames that can be viewed or modified using `ggplot2` or `add*()` functions and turning these frames into an animated `GIF`:
```R
library(moveVis)
library(move2)
data("move_data", package = "moveVis") # move2 class object
# align move_data to a uniform time scale
m <- align_move(move_data, res = units::set_units(4, "min"))
# create spatial frames with an OpenStreetMap basemap
frames <- frames_spatial(
m, path_colours = c("blue", "cyan", "purple"),
map_service = "osm", map_type = "topographic", alpha = 0.5) %>%
add_labels(x = "Longitude", y = "Latitude") %>% # add some customizations, such as axis labels
add_northarrow() %>%
add_scalebar() %>%
add_timestamps(type = "label") %>%
add_progress()
frames[[100]] # preview one of the frames, e.g. the 100th frame
# animate frames
animate_frames(frames, out_file = "moveVis.gif")
```
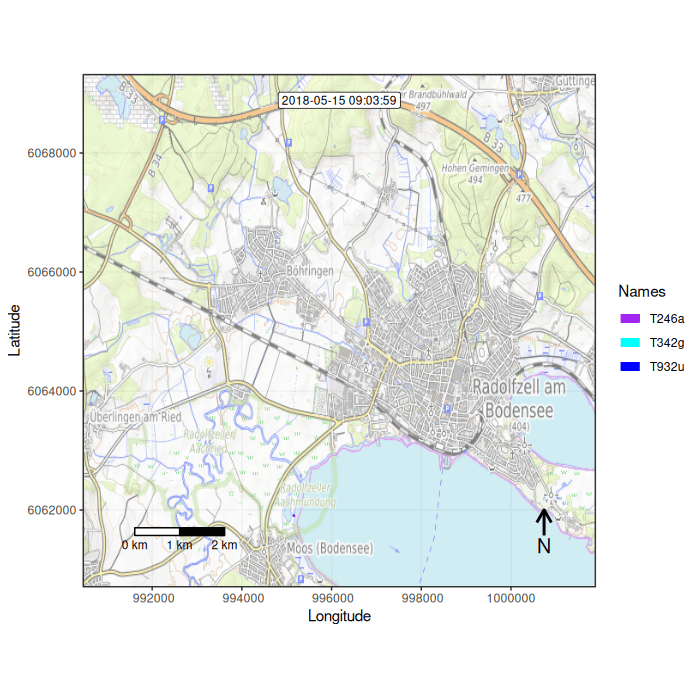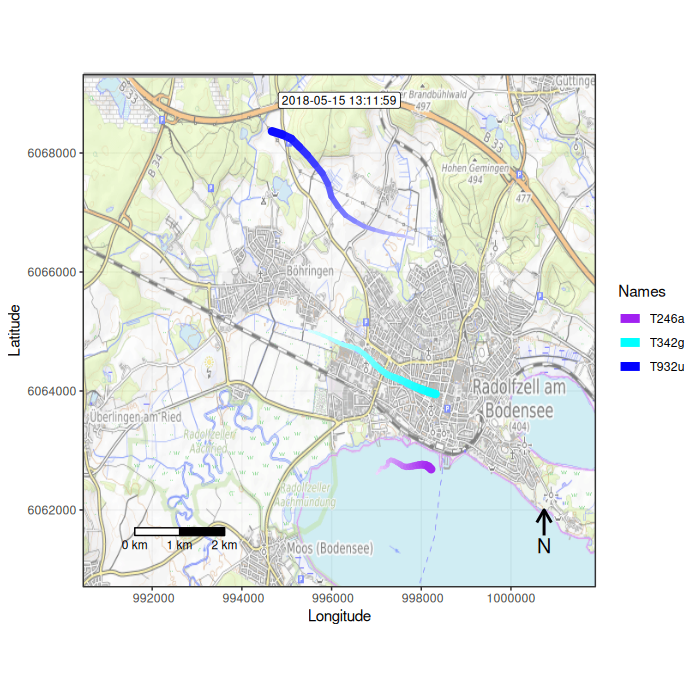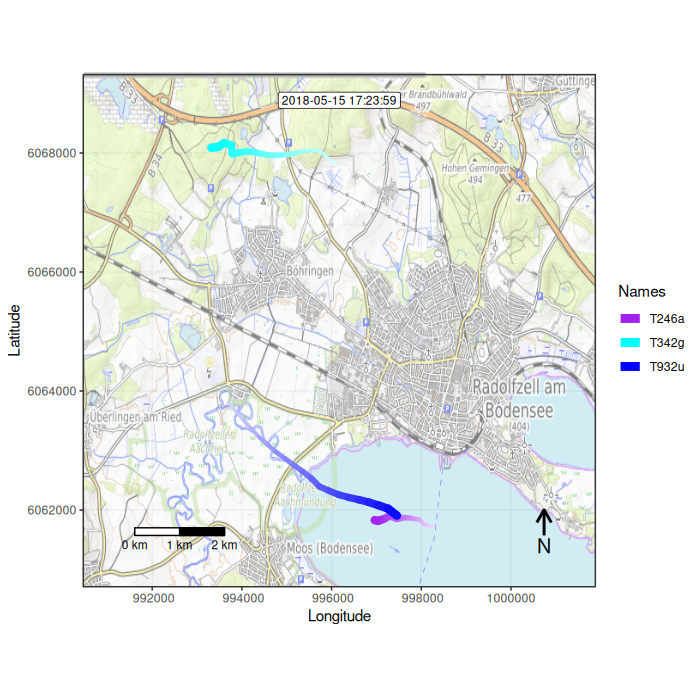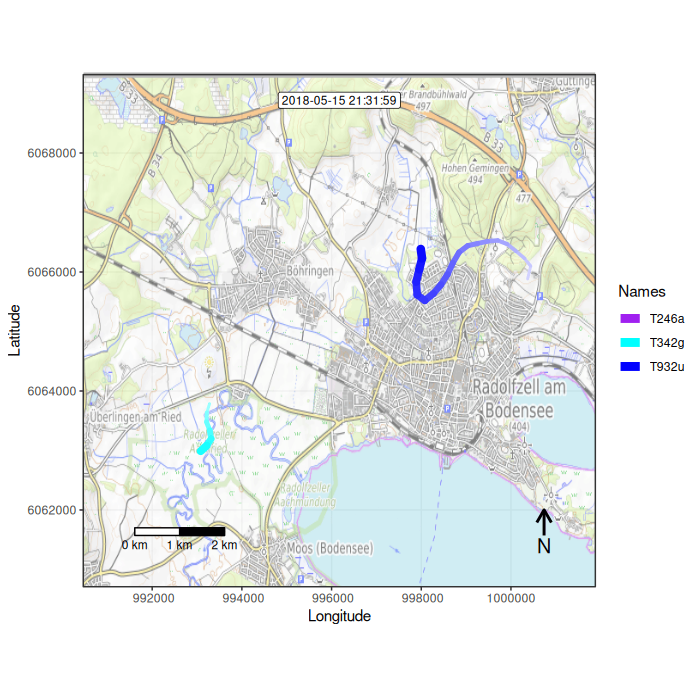
## Function overview
`moveVis` includes the following functions, sorted by the order they would be applied to create an animation from movement and environmental data:
#### Preparing movement tracks
* `align_move()` aligns single and multi-individual movement data to a uniform time scale with a uniform temporal resolution needed for creating an animation from it. Use this function to prepare your movement data for animation depending on the temporal resolution that suits your data.
#### Creating frames
* `get_maptypes()` returns available map services and types that can be used with `frames_spatial()`. This function is reexported from the basemaps package.
* `frames_spatial()` creates `moveVis` frames from movement and map/raster data, displaying movement-environment interactions spatio-temporally. Frames are returned as an object of class `moveVis` and can be subsetted, viewed (see `render_frame()`), modified (see `add_gg()`} and associated functions) and animated (see `animate_frames()`).
* `frames_graph()` creates `moveVis` frames displaying movement-environment interaction graphs. Frames can be viewed or modified individually and animated using `animate_frames()`.
#### Adapting frames
* `add_gg()` adds `ggplot2` expressions (e.g. to add layers such as points, polygons, lines, or to change scales etc.) to frames created with `frames_spatial()` or `frames_graph()`.
* `add_labels()` adds character labels such as title or axis labels to frames created with `frames_spatial()` or `frames_graph()`.
* `add_scalebar()` adds a scale bar to frames created with `frames_spatial()` or `frames_graph()`.
* `add_northarrow()` adds a north arrow to frames created with `frames_spatial()` or `frames_graph()`.
* `add_progress()` adds a progress bar to frames created with `frames_spatial()` or `frames_graph()`.
* `add_timestamps()` adds timestamps to frames created with `frames_spatial()` or `frames_graph()`.
* `add_text()` adds static or dynamically changing text to frames created with `frames_spatial()` or `frames_graph()`.
* `add_colourscale()` adjusts the colour scales of frames created with `frames_spatial()` and custom map imagery.
* `join_frames()` side-by-side two or more sets of frames of equal lengths into one set of frames using `patchwork::wrap_plots()`, e.g. to combine spatial frames returned by `frames_spatial()` with graph frames returned by `frames_graph()`.
* `get_frametimes()` extracts the timestamps associated with each frame of frames created using `frames_spatial()` or `frames_graph()` and returns them as a vector.
#### Animating frames (as GIF or video)
* `suggest_formats()` returns a selection of suggested file formats that can be used with `out_file` of `animate_frames()` on your system.
* `animate_frames()` creates an animation from `moveVis` frames, e.g as `.gif` or `.mov` video file.
#### Viewing movement tracks
* `render_frame()` renders an individual frame. It yields the same result as if an individual frame is extracted using `[[`.
* `view_spatial()` displays movement tracks on an interactive `mapview` or `leaflet` map.
#### Methods
* `[` extracts individual frames or a sequence of frames from a `moveVis` frames object.
* `[[` renders an individual frame.
* `c()` combines multiple `moveVis` frames.
* `tail()` and `head()` return `n` last or first frames of a `moveVis` frames object.
* `length()` returns the length of `moveVis` frames, i.e. number of frames.
* `print()` shows basic information about a `moveVis` frames object, i.e. number of frames, extent and more.
* `rev()` reverses the order of a `moveVis` frames object.
#### Processing settings
* `use_multicore()` enables multi-core usage for computational expensive processing steps.
* `use_disk()` enables the usage of disk space for creating frames, which can prevent memory overload when creating frames for very large animations.
#### Example data
* `data("move_data")` returns a `move2` object representing coordinates and acquisition times of three simulated movement tracks, covering a location nearby Lake of Constance, Germany.
* `data("whitestork_data")` returns a `data.frame` and a `move2` object, both representing coordinates and acquisition times of 15 White Storks, migrating from Lake of Constance, SW Germany, to Africa.
* `readRDS(example_data(file = "basemap_data.rds"))` returns a `SpatRasterDataset`, representing simulated NDVI images covering the Lake of Constance area, as well as invented dates and times that simulate acquisition times.
The majority of these functions can be used with the forward pipe operator `%>%`, which is re-exported by `moveVis`.
## Examples
You can find code examples on how to use `moveVis` here:
Example 1: Creating a simple movement animation
Example 3: Using a mapbox satellite base map
Example 4: View movement tracks
Real-data example using White Storks (*Ciconia ciconia*) migration movement data [.docx]
## Code snippets
These commented `moveVis` code snippets, addressing specific issues or questions, could also be helpful to you:
How to display the full traces of each path using trace_show and trace_colour with frames_spatial()
How to colour paths based on a continuous variable
How to assign multiple path colours per individual, e.g. to indicate behavioral segments
How to adapt the path legend of frames created with frames_spatial()
How to create a data.frame containing each track coordinate per frame
How to overlay frames with additional transparent rasters changing over time (hacky, not a very optimal solution)
## Further resources
Detailed code examples explaining how to use specific functions are provided at the function help pages. User contributions such as code examples or tutorials are very welcome and are linked below as soon as they have been spotted somewhere on the web:
Animating animal tracks from multiple years over a common year with moveVis: An example with Blue Whale Argos tracks on Movebank by Daniel M. Palacios, Marine Mammal Institute, Oregon State University
Reproducible example of how to combine animal tracking data, tidal water height data and a heightmap to visualize animal movement with moveVis by Henk-Jan van der Kolk, The Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW)
How to build animated tracking maps using tracking data in Movebank and environmental covariates in track and raster annotations from EnvDATA with moveVis by Sarah C. Davidson, Data Curator at Movebank
## Mentions
Blog post: Featured article in Issue 11.5: Our May issue is now online! by Methods in Ecology and Evolution
## Related packages
Other R packages that might interest you:
* basemaps, a package to download and cache spatial basemaps from open sources such as *OpenStreetMap*, *Stamen*, *Thunderforest*, *Carto*, *Mapbox* and others,
* getSpatialData, a package to query, preview and download satellite data,
* RStoolbox, a package providing a wide range of tools for every-day remote sensing processing needs,
## Acknowledgements
This initiative was part of the Opt4Environment project and had been funded by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) on behalf of the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi) with the research grant 50 EE 1403.
## Citation
An open-access paper accompanying the `moveVis` R package has been peer-reviewed by and published in *'Methods in Ecology and Evolution'* (see https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13374). Please cite moveVis, e.g. when you use it in publications or presentations, using the output of `citation("moveVis")` or as follows:
Schwalb-Willmann, J.; Remelgado, R.; Safi, K.; Wegmann, M. (2020). moveVis: Animating movement trajectories in synchronicity with static or temporally dynamic environmental data in R. *Methods Ecol Evol*. 2020; 11: 664–669. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13374
