https://github.com/5cript/interval-tree
A C++ header only interval tree implementation.
https://github.com/5cript/interval-tree
cpp11 interval interval-tree intervals overlap red-black-tree
Last synced: 2 days ago
JSON representation
A C++ header only interval tree implementation.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/5cript/interval-tree
- Owner: 5cript
- License: cc0-1.0
- Created: 2017-03-24T12:56:50.000Z (almost 9 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-08-29T23:33:32.000Z (5 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-08-30T01:12:43.548Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: cpp11, interval, interval-tree, intervals, overlap, red-black-tree
- Language: C++
- Size: 201 KB
- Stars: 68
- Watchers: 7
- Forks: 18
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# interval-tree
A C++ header only interval tree implementation, which takes a red black tree as its base to inhibit degeneration to linked lists.
- [Interval Tree](#interval-tree)
- [How an interval tree looks like:](#how-an-interval-tree-looks-like)
- [Example](#example)
- [Compile & Run Testing](#compile--run-testing)
- [Free Functions](#free-functions)
- [Members of IntervalTree](#members-of-intervaltree)
- [Members of Interval](#members-of-interval)
## How an interval tree looks like:

## Example
```C++
// #include // to draw tree. this is not header only anymore.
#include
int main()
{
using namespace lib_interval_tree;
// interval_tree>; // closed by default
// interval_tree>;
// interval_tree>;
// interval_tree>;
// interval_tree>;
// interval_tree>; // counts adjacent intervals as overlapping
interval_tree_t tree;
tree.insert(make_safe_interval(21, 16)); // make_safe_interval swaps low and high if not in right order.
tree.insert({8, 9});
tree.insert({25, 30});
tree.insert({5, 8});
tree.insert({15, 23});
tree.insert({17, 19});
tree.insert({26, 26});
tree.insert({0, 3});
tree.insert({6, 10});
tree.insert({19, 20});
tree.deoverlap();
for (auto const& i : tree)
{
std::cout << "[" << i.low() << ", " << i.high() << "]\n";
}
// dynamic has some logic overhead.
interval_tree> dynamicIntervals;
dynamicIntervals.insert({0, 1, interval_border::closed, interval_border::open});
dynamicIntervals.insert({7, 5, interval_border::open, interval_border::closed_adjacent});
}
```
## Compile & Run Testing
Having googletest (find here on github) installed / built is a requirement to run the tests.
Create a build folder, navigate there, run cmake and build the tree-tests target.
You might have to adapt the linker line for gtest, if you built it yourself and didn't install it into your system.
If you want to generate the pretty drawings, install cairo, pull the submodule and pass INT_TREE_DRAW_EXAMPLES=on to the cmake command line to generate a drawings/make_drawings executeable.
Some features of this library require the presence of an optional type.
If you are using C++17 and up, it will be std::optional.
Otherwise you can specify INTERVAL_TREE_HAVE_BOOST_OPTIONAL to use boost::optional.
And if neither, a reduced version of optional is provided in the library, not perfectly exchangeable with std::optional, but sufficient for the library to work.
## Draw Dot Graph
This draws a dot graph of the tree:
```c++
#include
#include
int main()
{
using namespace lib_interval_tree;
interval_tree_t tree;
tree.insert(make_safe_interval(21, 16)); // make_safe_interval swaps low and high if not in right order.
tree.insert({8, 9});
tree.insert({25, 30});
tree.insert({5, 8});
tree.insert({15, 23});
tree.insert({17, 19});
tree.insert({26, 26});
tree.insert({0, 3});
tree.insert({6, 10});
tree.insert({19, 20});
draw_dot_graph(
std::cout,
tree,
{
// digraph or graph?
.digraph = true,
// graph name
.name = "G",
// extra node attributes
.extra_node_attributes = {"color=red"},
// extra graph statements
.extra_statements = {"rankdir=LR"},
// put space after comma of interval label? (a,b) vs (a, b)
.space_after_comma = false,
// left brace override enabled if not 0, otherwise determined from interval kind
.left_brace = '\0',
// right brace override enabled if not 0, otherwise determined from interval kind
.right_brace = '\0',
// edge attributes
.edge_attributes = {"color=blue"},
// indent characters
.indent = "\t",
}
);
}
```
## Free Functions
### interval make_safe_interval(NumericT border1, NumericT border2)
Creates an interval where the borders are sorted so the lower border is the first one.
### draw_dot_graph(std::ostream& os, interval_tree_t const& tree, DrawOptions const& options)
Draws a dot graph of the interval tree to the output stream.
Options are:
- digraph: bool
- name: std::string
- extra_node_attributes: std::vector\
- extra_statements: std::vector\
- space_after_comma: bool
- left_brace: char (0 = ignored, std::optional is c++17)
- right_brace: char (0 = ignored, std::optional is c++17)
- edge_attributes: std::vector\
- indent: std::string
## Members of IntervalTree
- [interval-tree](#interval-tree)
- [How an interval tree looks like:](#how-an-interval-tree-looks-like)
- [Example](#example)
- [Compile \& Run Testing](#compile--run-testing)
- [Draw Dot Graph](#draw-dot-graph)
- [Free Functions](#free-functions)
- [interval\ make\_safe\_interval(NumericT border1, NumericT border2)](#intervalnumerict-kind-make_safe_intervalnumerict-border1-numerict-border2)
- [draw\_dot\_graph(std::ostream\& os, interval\_tree\_t const\& tree, DrawOptions const\& options)](#draw_dot_graphstdostream-os-interval_tree_t-const-tree-drawoptions-const-options)
- [Members of IntervalTree](#members-of-intervaltree)
- [iterator insert(interval\_type const\& ival)](#iterator-insertinterval_type-const-ival)
- [Parameters](#parameters)
- [iterator insert\_overlap(interval\_type const\& ival, bool, bool)](#iterator-insert_overlapinterval_type-const-ival-bool-bool)
- [Parameters](#parameters-1)
- [iterator erase(iterator iter)](#iterator-eraseiterator-iter)
- [Parameters](#parameters-2)
- [size\_type size() const](#size_type-size-const)
- [(const)iterator find(interval\_type const\& ival)](#constiterator-findinterval_type-const-ival)
- [Parameters](#parameters-3)
- [(const)iterator find(interval\_type const\& ival, CompareFunctionT const\& compare)](#constiterator-findinterval_type-const-ival-comparefunctiont-const-compare)
- [Parameters](#parameters-4)
- [(const)iterator find\_all(interval\_type const\& ival, OnFindFunctionT const\& on\_find)](#constiterator-find_allinterval_type-const-ival-onfindfunctiont-const-on_find)
- [Parameters](#parameters-5)
- [Example](#example-1)
- [(const)iterator find\_all(interval\_type const\& ival, OnFindFunctionT const\& on\_find, CompareFunctionT const\& compare)](#constiterator-find_allinterval_type-const-ival-onfindfunctiont-const-on_find-comparefunctiont-const-compare)
- [Parameters](#parameters-6)
- [(const)iterator find\_next\_in\_subtree(iterator from, interval\_type const\& ival)](#constiterator-find_next_in_subtreeiterator-from-interval_type-const-ival)
- [Parameters](#parameters-7)
- [(const)iterator find\_next\_in\_subtree(iterator from, interval\_type const\& ival, CompareFunctionT const\& compare)](#constiterator-find_next_in_subtreeiterator-from-interval_type-const-ival-comparefunctiont-const-compare)
- [Parameters](#parameters-8)
- [(const)iterator overlap\_find(interval\_type const\& ival, bool exclusive)](#constiterator-overlap_findinterval_type-const-ival-bool-exclusive)
- [Parameters](#parameters-9)
- [(const)iterator overlap\_find\_all(interval\_type const\& ival, OnFindFunctionT const\& on\_find, bool exclusive)](#constiterator-overlap_find_allinterval_type-const-ival-onfindfunctiont-const-on_find-bool-exclusive)
- [Parameters](#parameters-10)
- [Example](#example-2)
- [(const)iterator overlap\_find\_next\_in\_subtree(interval\_type const\& ival, bool exclusive)](#constiterator-overlap_find_next_in_subtreeinterval_type-const-ival-bool-exclusive)
- [Parameters](#parameters-11)
- [interval\_tree\& deoverlap()](#interval_tree-deoverlap)
- [After deoverlap](#after-deoverlap)
- [interval\_tree deoverlap\_copy()](#interval_tree-deoverlap_copy)
- [interval\_tree punch(interval\_type const\& ival)](#interval_tree-punchinterval_type-const-ival)
- [Before punching (closed intervals)](#before-punching-closed-intervals)
- [After punching (with \[-10, 60\])](#after-punching-with--10-60)
- [interval\_tree punch()](#interval_tree-punch)
- [bool empty() const noexcept](#bool-empty-const-noexcept)
- [iterator begin()](#iterator-begin)
- [iterator end()](#iterator-end)
- [iterator cbegin()](#iterator-cbegin)
- [iterator cend()](#iterator-cend)
- [reverse\_iterator rbegin()](#reverse_iterator-rbegin)
- [reverse\_iterator rend()](#reverse_iterator-rend)
- [reverse\_iterator crbegin()](#reverse_iterator-crbegin)
- [reverse\_iterator crend()](#reverse_iterator-crend)
- [void erase\_range(interval\_type const\& ival)](#void-erase_rangeinterval_type-const-ival)
- [void erase\_range(interval\_type const\& ival, bool retainSlices)](#void-erase_rangeinterval_type-const-ival-bool-retainslices)
- [Members of Interval](#members-of-interval)
- [using value\_type](#using-value_type)
- [using interval\_kind](#using-interval_kind)
- [friend bool operator==(interval const\& lhs, interval const\& other)](#friend-bool-operatorinterval-const-lhs-interval-const-other)
- [friend bool operator!=(interval const\& lhs, interval const\& other)](#friend-bool-operatorinterval-const-lhs-interval-const-other-1)
- [value\_type low() const](#value_type-low-const)
- [value\_type high() const](#value_type-high-const)
- [DEPRECATED bool overlaps(value\_type l, value\_type h) const](#deprecated-bool-overlapsvalue_type-l-value_type-h-const)
- [bool overlaps\_exclusive(value\_type l, value\_type h) const](#bool-overlaps_exclusivevalue_type-l-value_type-h-const)
- [bool overlaps(interval const\& other) const](#bool-overlapsinterval-const-other-const)
- [bool overlaps\_exclusive(interval const\& other) const](#bool-overlaps_exclusiveinterval-const-other-const)
- [bool within(value\_type value) const](#bool-withinvalue_type-value-const)
- [bool within(interval const\& other) const](#bool-withininterval-const-other-const)
- [value\_type operator-(interval const\& other) const](#value_type-operator-interval-const-other-const)
- [value\_type size() const](#value_type-size-const)
- [interval join(interval const\& other) const](#interval-joininterval-const-other-const)
- [slice\_type slice(interval const\& other) const](#slice_type-sliceinterval-const-other-const)
### iterator insert(interval_type const& ival)
Adds an interval into the tree.
#### Parameters
* `ival` An interval
**Returns**: An iterator to the inserted element.
---
### iterator insert_overlap(interval_type const& ival, bool, bool)
Inserts an interval into the tree if no other interval overlaps it.
Otherwise merge the interval with the one being overlapped.
#### Parameters
* `ival` An interval
* `exclusive` Exclude borders from overlap check. Defaults to false.
* `recursive` If the result of interval::join is a collection of intervals, shall each be inserted with more overlap searches? If the result is a single interval, shall it be inserted via insert_overlap or insert? Defaults to false. recursive=true picks insert_overlap. Also be careful to not produce overlapping merge sets when doing recursive insertion, or it will recurse endlessly.
**Returns**: An iterator to the inserted element.
---
### iterator erase(iterator iter)
Removes the interval given by iterator from the tree.
(does not invalidate iterators).
#### Parameters
* `iter` A valid non-end iterator
**Returns**: An iterator to the next element.
---
### size_type size() const
Returns the amount of nodes in the tree.
**Returns**: The amount of tree nodes.
---
### (const)iterator find(interval_type const& ival)
Finds the first interval in the interval tree that has an exact match.
**WARNING**: There is no special handling for floats.
#### Parameters
* `ival` The interval to find.
**Returns**: An iterator to the found element, or std::end(tree).
---
### (const)iterator find(interval_type const& ival, CompareFunctionT const& compare)
Finds the first interval in the interval tree that has the following statement evaluate to true: compare(interval_in_tree, ival);
Allows for propper float comparisons.
#### Parameters
* `ival` The interval to find.
* `compare` The compare function to compare intervals with. Function is called like so: compare(interval_in_tree, ival).
**Returns**: An iterator to the found element, or std::end(tree).
---
### (const)iterator find_all(interval_type const& ival, OnFindFunctionT const& on_find)
Find all intervals in the tree matching ival.
#### Parameters
* `ival` The interval to find.
* `on_find` A function of type bool(iterator) that is called when an interval was found.
Return true to continue, false to preemptively abort search.
#### Example
```c++
tree.insert({3, 7});
tree.insert({3, 7});
tree.insert({8, 9});
tree.find_all({3, 7}, [](auto iter) /* iter will be const_iterator if tree is const */ {
// will find all intervals that are exactly {3,7} here.
return true; // continue
});
```
**Returns**: An iterator to the found element, or std::end(tree).
---
### (const)iterator find_all(interval_type const& ival, OnFindFunctionT const& on_find, CompareFunctionT const& compare)
Find all intervals in the tree that the compare function returns true for.
#### Parameters
* `ival` The interval to find.
* `compare` The compare function to compare intervals with. Function is called like so: compare(interval_in_tree, ival).
* `on_find` A function of type bool(iterator) that is called when an interval was found.
Return true to continue, false to preemptively abort search.
**Returns**: An iterator to the found element, or std::end(tree).
---
### (const)iterator find_next_in_subtree(iterator from, interval_type const& ival)
Finds the next exact match EXCLUDING from in the subtree originating from "from".
You cannot find all matches this way, use find_all for that.
#### Parameters
* `from` The iterator to start from. (including this iterator!)
* `ival` The interval to find.
**Returns**: An iterator to the found element, or std::end(tree).
---
### (const)iterator find_next_in_subtree(iterator from, interval_type const& ival, CompareFunctionT const& compare)
Finds the next exact match EXCLUDING from in the subtree originating from "from".
You cannot find all matches this way, use find_all for that.
#### Parameters
* `from` The iterator to start from (including this iterator!)
* `ival` The interval to find.
* `compare` The compare function to compare intervals with. Function is called like so: compare(interval_in_tree, ival).
**Returns**: An iterator to the found element, or std::end(tree).
---
### (const)iterator overlap_find(interval_type const& ival, bool exclusive)
Finds the first interval in the interval tree that overlaps the given interval.
#### Parameters
* `ival` The interval to find an overlap for.
* `exclusive` Exclude borders from overlap check. Defaults to false.
**Returns**: An iterator to the found element, or std::end(tree).
---
### (const)iterator overlap_find_all(interval_type const& ival, OnFindFunctionT const& on_find, bool exclusive)
Finds all intervals in the interval tree that overlaps the given interval.
#### Parameters
* `ival` The interval to find an overlap for.
* `on_find` A function of type bool(iterator) that is called when an interval was found.
Return true to continue, false to preemptively abort search.
* `exclusive` Exclude borders from overlap check. Defaults to false.
#### Example
```c++
tree.insert({0, 5});
tree.insert({5, 10});
tree.insert({10, 15});
tree.overlap_find_all({5, 5}, [](auto iter) /* iter will be const_iterator if tree is const */ {
// called with {0, 5} and {5, 10} in unspecified order.
return true; // continue
});
```
**Returns**: An iterator to the found element, or std::end(tree).
---
### (const)iterator overlap_find_next_in_subtree(interval_type const& ival, bool exclusive)
Finds the next interval in the subtree originating in ival that overlaps the given interval.
You cannot find all matches this way, use overlap_find_all for that.
#### Parameters
* `ival` The interval to find an overlap for.
* `exclusive` Exclude borders from overlap check. Defaults to false.
**Returns**: An iterator to the found element, or std::end(tree).
---
### interval_tree& deoverlap()
Merges all overlapping intervals within the tree. After calling deoverlap, the tree will only contain disjoint intervals.
**Returns**: *this
### After deoverlap

### interval_tree deoverlap_copy()
Same as deoverlap, but not inplace
---
### interval_tree punch(interval_type const& ival)
Cuts the intervals of the tree out of the given interval. Like a cookie cutter cuts out of dough.
This will return a new interval_tree containing the gaps between the intervals in the tree and the given interval.
Closed adjacent intervals are treated as exclusive on the borders. [0,5]a[6,10]a will not produce another interval between 5 and 6 as they are considered within the intervals and nothing fits inbetween.
Regular closed intervals will not behave like this, so [0,5][6,10] will produce a new interval [5,6].
Open intervals with integral numbers will also not produce the gap (5, 6), because (5, 6) is empty for integers, not for floats.
**IMPORTANT! The tree must be deoverlapped, or the result is undefined.**
`ival` can be any subrange of the tree, including encompassing the whole tree.
**Returns**: A new interval_tree containing the gaps.
### Before punching (closed intervals)
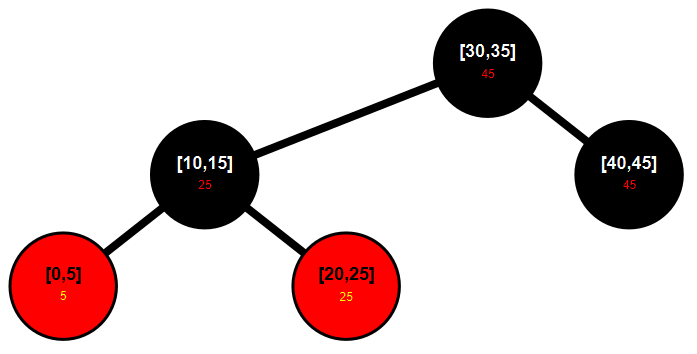
### After punching (with [-10, 60])

---
### interval_tree punch()
Same as punch(interval_type const& ival), but with ival = [lowest_lower_bound, highest_upper_bound], resulting in only
the gaps between existing intervals.
---
### bool empty() const noexcept
Returns whether or not the tree is empty.
**Returns**: Is this tree empty?
---
### iterator begin()
Returns the iterator of the interval with the lowest lower_bound.
**Returns**: begin iterator.
---
### iterator end()
Returns a past the end iterator.
**Returns**: past the end iterator.
---
### iterator cbegin()
Returns the const_iterator of the interval with the lowest lower_bound.
**Returns**: begin iterator.
---
### iterator cend()
Returns a past the end const_iterator.
**Returns**: past the end const_iterator.
---
### reverse_iterator rbegin()
Returns the iterator of the interval with the highest lower_bound.
**Returns**: rbegin iterator.
---
### reverse_iterator rend()
Returns a past the end iterator in reverse.
**Returns**: past the end iterator.
---
### reverse_iterator crbegin()
Returns the const_iterator of the interval with the highest lower_bound.
**Returns**: begin iterator.
---
### reverse_iterator crend()
Returns a past the end const_iterator in reverse.
**Returns**: past the end const_iterator.
### void erase_range(interval_type const& ival)
Removes all intervals overlapping ival from the tree
### void erase_range(interval_type const& ival, bool retainSlices)
Removes all intervals overlapping ival from the tree, but retains the overlap beyond the erase interval.
## Members of Interval
___You can implement your own interval if you provide the same functions, except (slice, operator-, size, operator!=).___
There are 6 types of intervals:
- open: (a, b)
- left_open: (a, b]
- right_open: [a, b)
- closed: [a, b]
- closed_adjacent: [a, b] (counts adjacent intervals as overlapping)
- dynamic: Can be any of the above, depending on the input. Not supported for floating point.
Which can be picked with the second template parameter of interval:
`lib_interval_tree::interval`
- [Members of Interval](#members-of-interval)
- [using value_type](#using-value_type)
- [using interval_kind](#using-interval_kind)
- [friend bool operator==(interval const& lhs, interval const& other)](#friend-bool-operatorinterval-const-lhs-interval-const-other)
- [friend bool operator!=(interval const& lhs, interval const& other)](#friend-bool-operatorinterval-const-lhs-interval-const-other-1)
- [value_type low() const](#value_type-low-const)
- [value_type high() const](#value_type-high-const)
- [DEPRECATED bool overlaps(value_type l, value_type h) const](#bool-overlapsvalue_type-l-value_type-h-const)
- [bool overlaps_exclusive(value_type l, value_type h) const](#bool-overlaps_exclusivevalue_type-l-value_type-h-const)
- [bool overlaps(interval const& other) const](#bool-overlapsinterval-const-other-const)
- [bool overlaps_exclusive(interval const& other) const](#bool-overlaps_exclusiveinterval-const-other-const)
- [bool within(value_type value) const](#bool-withinvalue_type-value-const)
- [bool within(interval const& other) const](#bool-withininterval-const-other-const)
- [value_type operator-(interval const& other) const](#value_type-operator-interval-const-other-const)
- [value_type size() const](#value_type-size-const)
- [interval join(interval const& other) const](#interval-joininterval-const-other-const)
- [slice\_type slice(interval const\& other) const](#slice_type-sliceinterval-const-other-const)
### using value_type
The underlying interval numerical type
### using interval_kind
The interval kind. You dont need to provides this typedef in your interval class.
### friend bool operator==(interval const& lhs, interval const& other)
Comparison operator.
### friend bool operator!=(interval const& lhs, interval const& other)
Comparison operator.
### value_type low() const
Lower bound.
### value_type high() const
Upper bound.
### DEPRECATED bool overlaps(value_type l, value_type h) const
Overlap these bounds with this interval?
Is deprecated because the overlapping does not work with the dynamic interval type.
### bool overlaps_exclusive(value_type l, value_type h) const
Overlap these bounds with this interval excluding borders?
### bool overlaps(interval const& other) const
Like overlaps with lower and upper bound.
### bool overlaps_exclusive(interval const& other) const
Like overlaps with lower and upper bound.
### bool within(value_type value) const
Is the value within the interval?
### bool within(interval const& other) const
Is the interval within the interval?
### value_type operator-(interval const& other) const
Calculates the distance between the two intervals.
Overlapping intervals have 0 distance.
### value_type size() const
Returns The amount of elements in the interval when integral, or the distance between the 2 bounds when floating point.
### interval join(interval const& other) const
Joins 2 intervals and whatever is inbetween.
### slice_type slice(interval const& other) const
Removes other from this interval returning what is remaining.
The range of other going beyond the range of this is ignored.
Returns a struct with 2 members: left_slice and right_slice.
```
[ this interval ]
[left][other][right]
```
When the intervals are closed_adjacent, adjacent results are differenty by 1.
[0, 9].slice([5, 19]) => left: [0, 4], right: nullopt