https://github.com/CVxTz/medical_image_segmentation
Medical image segmentation ( Eye vessel segmentation)
https://github.com/CVxTz/medical_image_segmentation
convolutional-neural-networks keras medical-imaging segmentation
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
Medical image segmentation ( Eye vessel segmentation)
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/CVxTz/medical_image_segmentation
- Owner: CVxTz
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-03-13T19:02:56.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2020-04-16T07:42:19.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-15T18:38:04.740Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: convolutional-neural-networks, keras, medical-imaging, segmentation
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 21.5 KB
- Stars: 128
- Watchers: 7
- Forks: 46
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome_medical - medical_image_segmentation
README
# medical_image_segmentation
Medical image segmentation
Code for : https://towardsdatascience.com/vessel-segmentation-with-python-and-keras-722f9fb71b21
### Data
Available at https://www.isi.uu.nl/Research/Databases/DRIVE/
Unzip in ./input
# Vessel Segmentation With Python and Keras
### Motivation :
Automatic segmentation of medical images is an important step to extract useful
information that can help doctors make a diagnosis. For example, it can be used
to segment retinal vessels so that we can represent their structure and measure
their width which in turn can help diagnose retinal diseases.
In this post we will implement a Neural baseline that does image segmentation
applied to retinal vessel images.
### Dataset :
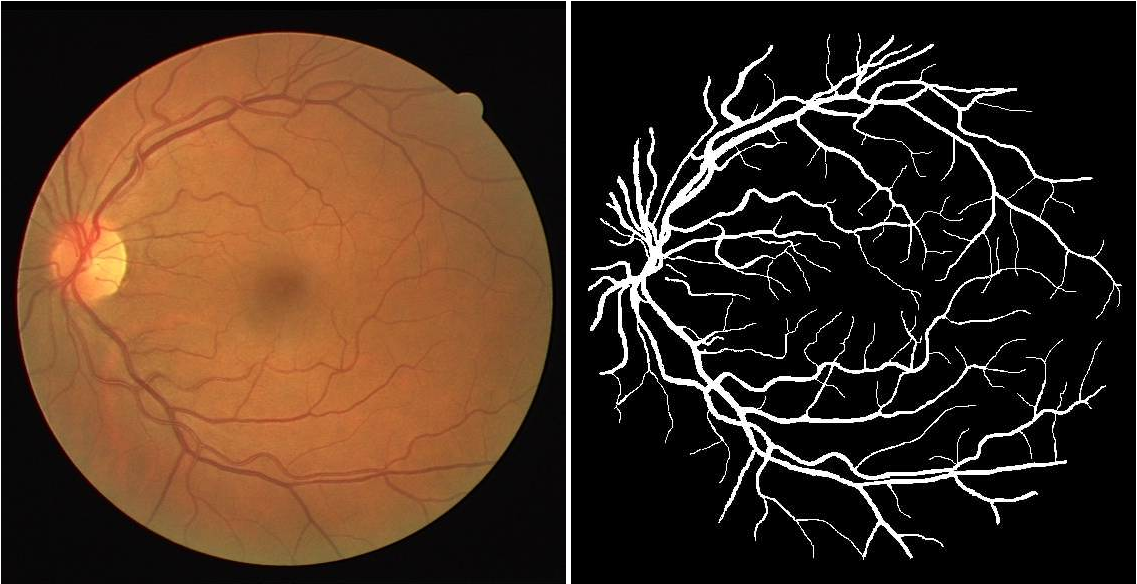
[http://www.isi.uu.nl/Research/Databases/DRIVE/browser.php](http://www.isi.uu.nl/Research/Databases/DRIVE/browser.php)
We use [DRIVE (Digital Retinal Images for Vessel
Extraction)](http://www.isi.uu.nl/Research/Databases/DRIVE/) data set for all
the experiments throughout the post. It is a data set of 40 retinal images ( 20
for training and 20 for testing ) where blood vessel were annotated at the pixel
level ( see example above) to mark the presence (1) or absence (0) of a blood
vessel at each pixel (i, j) of the image.
### Problem Setting :
**Problem** : We want to assign to each a pixel a “1” label if it is part of a
blood vessel in the image and “0” otherwise.
**Intuition**/**Hypothesis** :
The neighboring pixels values are important to make a prediction for each pixel
(i, j) so we should take into account context. The predictions do not depend on
the specific position on the image so the classifier should have some
translation invariance.
**Solution** : Use CNNs ! We will use the
[U-net](https://duckduckgo.com/?q=U-net&t=canonical&atb=v134-5__&ia=web)
architecture to do blood vessel segmentation. It is an architecture that is
widely used for semantic segmentation tasks especially in the medical domain.
### Model :
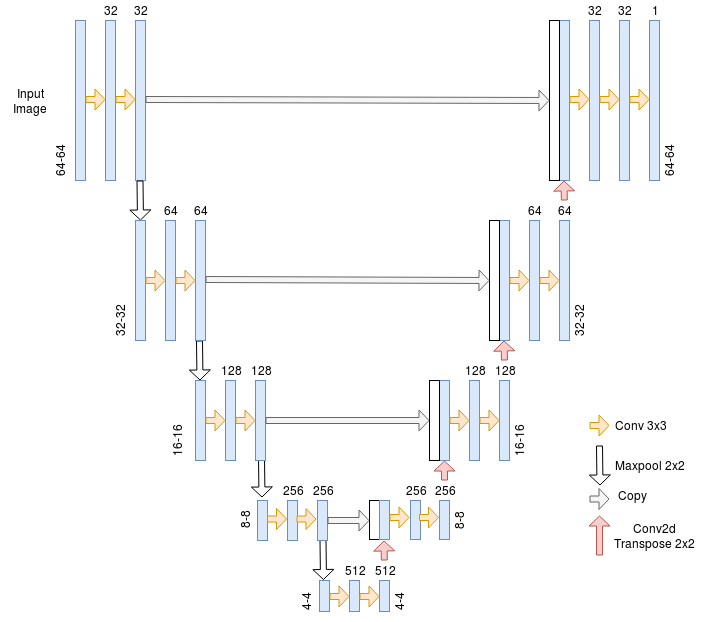
U-net
The U-net Architecture is an encoder-decoder with some skip connections between
the encoder and the decoder. The major advantage of this architecture is its
ability to take into account a wider context when making a prediction for a
pixel. This is thanks to the large number of channels used in the up-sampling
operation.
#### **Input image processing :**
We apply this sequence of processing steps before feeding it to the CNN.
* Normalization : we divide pixel intensities by 255 so they are in the 0–1 range.
* Cropping : The network expects each dimension of the input image to be divisible
by 2⁴ because of the pooling operations so we take a random crop of 64*64 from
each image.
* Data augmentation : Random flip (Horizontal or vertical or both), Random Shear,
Random translation (Horizontal or vertical or both), Random Zoom. Performed
during training only.
We train three variations of the model :
* Pre-trained on ImageNet VGG encoder + data augmentation.
* Trained from scratch + data augmentation.
* Trained from scratch without data augmentation.
We will compare those three models using AUC ROC metric and we will only
consider the pixels inside the retinal mask in the evaluation (meaning the black
edges around the circle of the image won’t count).
#### Results :
* Trained from scratch + data augmentation AUC ROC : **0.9820**
* Trained from scratch without augmentation AUC ROC : 0.9806
* Pre-trained encoder + data augmentation AUC ROC : *0.9811*
The performance is close for the three variations but it seems pretraining does
not help in this case while data augmentation does a little bit.
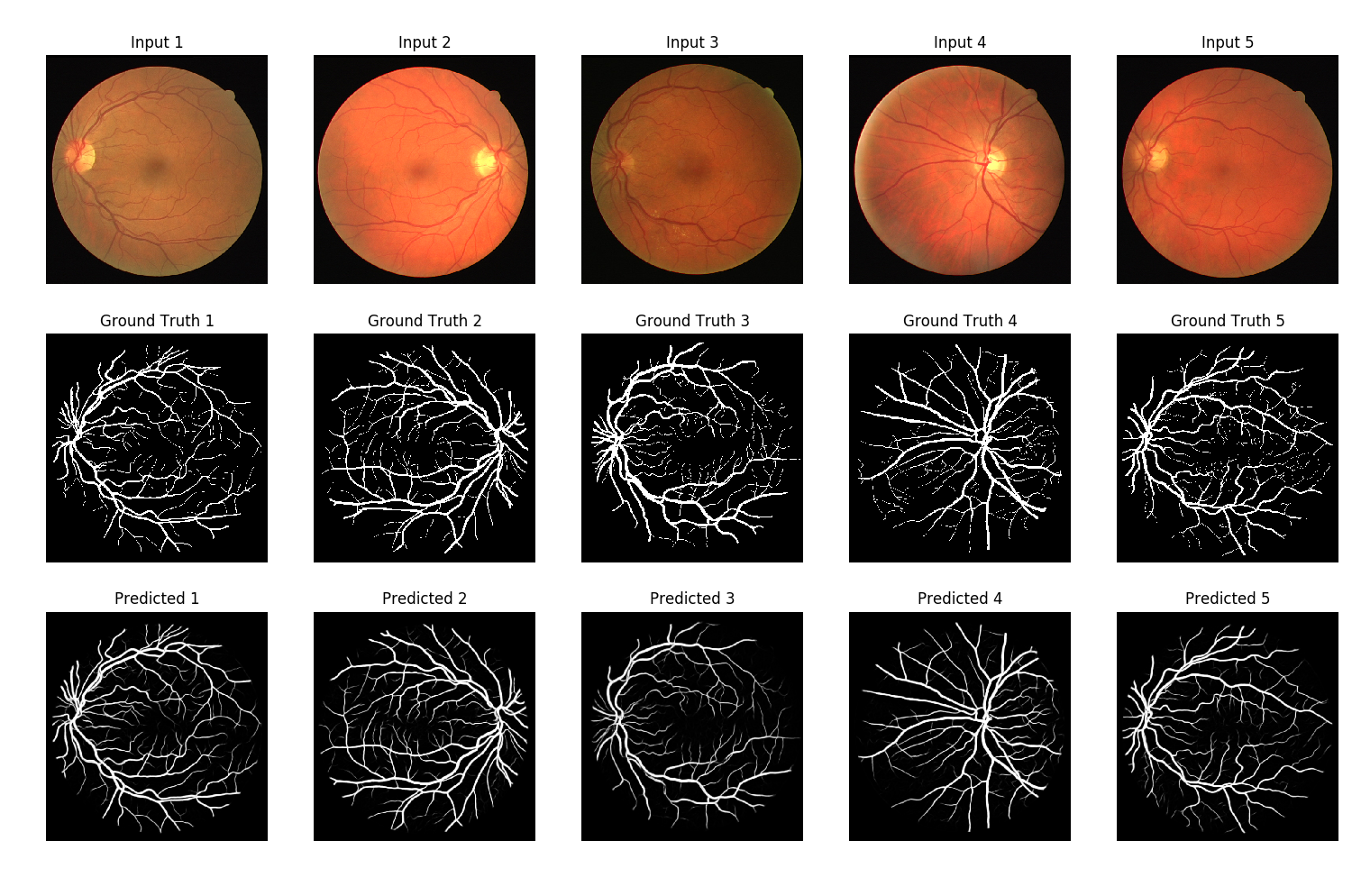
Best model predictions
The predictions in the figure above look pretty cool ! 😄
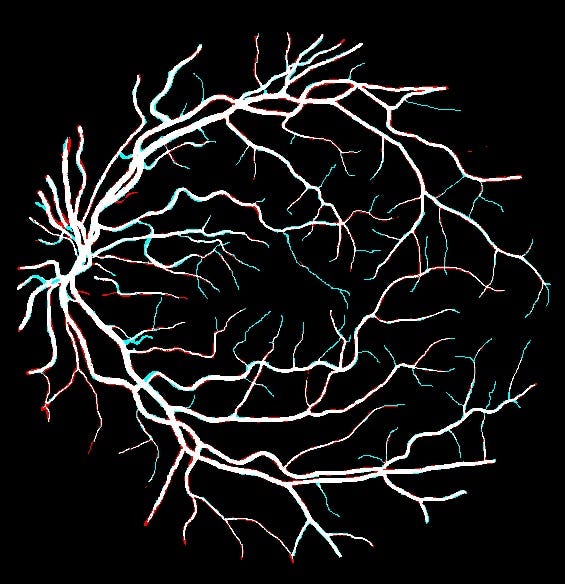
Predictions on top of ground Truth
We also plot the differences between the predictions and the ground truth :
False negatives in blue and false positives in red. We can see that the model
have some difficulties predicting fine vessels that are just one or two pixels
wide.
### Conclusion :
In this post we implemented a neural network to do image segmentation applied to
blood vessel detection in retinal images. We obtained an AUC ROC of **0.9820
**which is pretty close to the state of the art (
[https://paperswithcode.com/search?q=vessel](https://paperswithcode.com/search?q=vessel)
). What I find most interesting about the results of the experiments is that for
some tasks like this one we can train a deep neural network on as little as 20
images and still obtain a nice performance and pretty cool results.
Code to reproduce the results is available here :
[https://github.com/CVxTz/medical_image_segmentation](https://github.com/CVxTz/medical_image_segmentation)