https://github.com/ETS-PoliTO/esp32-sniffer
ESP32 firmware that sniffs PROBE REQUEST packets sent from smartphones looking for a Wi-Fi connection in order to extract different types of information
https://github.com/ETS-PoliTO/esp32-sniffer
component esp32 esp32-idf esp32-spiffs esp32-wroom filesystem framework iot mqtt multithreading probe-requests real-time-location smartphones sniffer sntp spiffs task-management tasks tracking-system wifi-connection
Last synced: 11 months ago
JSON representation
ESP32 firmware that sniffs PROBE REQUEST packets sent from smartphones looking for a Wi-Fi connection in order to extract different types of information
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/ETS-PoliTO/esp32-sniffer
- Owner: ETS-PoliTO
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2018-12-07T10:47:17.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-12-18T22:52:06.000Z (about 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-07T11:44:33.680Z (over 1 year ago)
- Topics: component, esp32, esp32-idf, esp32-spiffs, esp32-wroom, filesystem, framework, iot, mqtt, multithreading, probe-requests, real-time-location, smartphones, sniffer, sntp, spiffs, task-management, tasks, tracking-system, wifi-connection
- Language: C
- Homepage: https://j4nn0.github.io/doc/ets_presentation.pdf
- Size: 457 KB
- Stars: 194
- Watchers: 11
- Forks: 31
- Open Issues: 5
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# ESP32 Sniffer

This project is using [Espressif IoT Development Framework](https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf) (ESP-IDF) and has been tested on ESP-WROOM-32 module and esp-idf `v3.2`.
An overview of the full project (i.e. ESP32 firmware, server and GUI) can be found [here](https://j4nn0.github.io/doc/ets_presentation.pdf).
This firmware is written with the purpose to sniff Probe Request packets sent by smartphones that are looking for Wi-Fi connection. When the Wi-Fi connection is active on a smartphone, it will send in broadcast (in all channels frequencies) a probe request messagge asking if there are any free Wi-Fi or some known ones (i.e. the smartphone knows the password for that Wi-Fi). The ESP32 will sniff it and extract different types of information.
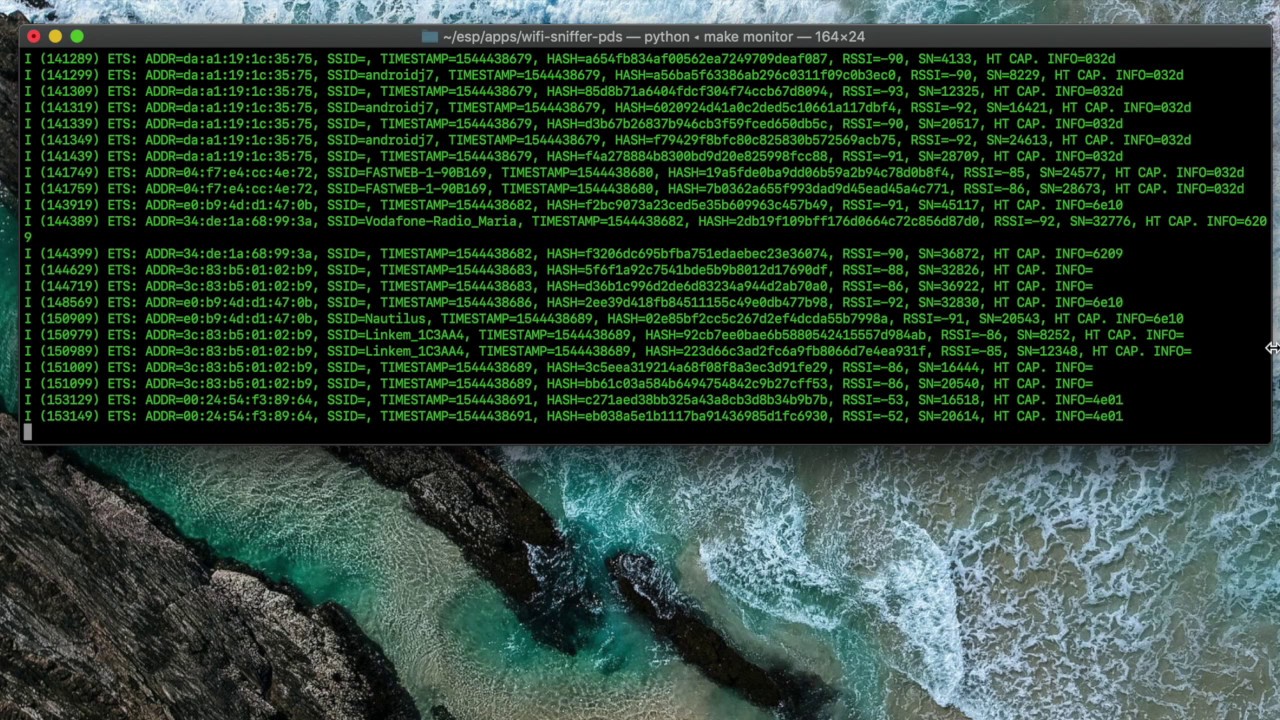
The following information is taken from each sniffed packet:
- MAC of the smartphone that has sent the request
- SSID of the wifi to which the request is sent
- The Timestamp of when the request was sent
- Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)
- Sequence Number (SN)
- HT Capabilities Info
After each minute these informations are sent to a [server](https://github.com/ETS-PoliTO/ETS-Server) and processed. Finally, it is possible to see the processed informations (smartphones real time location, smartphone frequency, etc.) through a [GUI](https://github.com/ETS-PoliTO/GUI-Application).
### Demo
[](https://youtu.be/NMywky9Ts_w)
# Table of Contents
- [Firmware Overview](#firmware-overview)
- [ESP-IDF Environment Configuration](#esp-idf-environment-configuration)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [File Configuration](#file-configuration)
- [Variables Configuration](#variables-configuration)
- [Add Customised Menu](#add-customised-menu)
- [Components](#components)
- [Resources](#resources)
# Firmware Overview
The firmware consits in two main threads/tasks:
- Sniffer Task
- Sniff Probe Request packet and save infomation described above into a file.
- Wi-Fi Task
- Each minute, take the information saved by the **Sniffer Task** and send it to the server.
- A `lock` is used in order to manage critical section for I/O operations in the file.
The ESP32 is configured in `WIFI_MODE_APSTA` mode: i.e. it creates "*soft-AP and station control block*" and starts "*soft-AP and station*". Thanks to this, the ESP32 is able to sniff and send informations to the server at the same time avoiding to lose packets information while sending data.
Here is the full list of information fields that can be in a Probe Request (source IEEE 802.11-2012):

And here below a packet sniffed with Wireshark in which you can see, for each field, the number of bits and their position within the packet:

# ESP-IDF Environment Configuration
This section might be outdated, checkout the [official site](https://esp-idf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get-started/index.html) for more info and for the latest guide on how to get started with ESP-IDF.
1. Setup Toolchain
- [Windows](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/get-started/windows-setup.html)
- [Linux](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/get-started/linux-setup.html)
- [Mac OS](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/get-started/macos-setup.html)
2. Get ESP-IDF
Besides the toolchain (that contains programs to compile and build the application), you also need ESP32 specific API / libraries.
cd ~/esp
git clone --recursive https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf.git
3. Checkout to version `v3.x`
cd esp-idf
git checkout release/v3.2
4. Setup path to ESP-IDF
The toolchain programs access ESP-IDF using `IDF_PATH` environment variable.
This variable should be set up on your PC, otherwise projects will not build.
- [Windows](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/get-started/add-idf_path-to-profile.html#add-idf-path-to-profile-windows)
- [Linux & Mac OS](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/get-started/add-idf_path-to-profile.html#add-idf-path-to-profile-linux-macos)
5. Install the Required Python Packages
python -m pip install --user -r $IDF_PATH/requirements.txt
# Usage
1. Make sure you have exported the path
export IDF_PATH=~/esp/esp-idf
export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/esp/xtensa-esp32-elf/bin
2. Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/ETS-PoliTO/esp32-sniffer.git
cd esp32-sniffer
3. Establish serial connection between ESP32 and your PC
make menuconfig
Go to `Serial flasher config`, then `Default serial port` and set the port in which ESP32 is connected
Note that, if you are using a bridge, probably you need to download some driver:
- [CP210x](https://www.silabs.com/products/development-tools/software/usb-to-uart-bridge-vcp-drivers)
- [FTDI](https://www.ftdichip.com/Drivers/VCP.htm)
[This](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/get-started/establish-serial-connection.html) provides a guide on how establish serial connection between ESP32 and PC.
4. Build code and flash the ESP32
make all && make flash
5. See logs
make monitor
# File Configuration
The file `/main/Kconfig.projbuild` contains two different menus:
- SPIFFS (SPI Flash File System)
It contains some important information about the SPIFFS partion:
- SPIFFS Base address
- SPIFFS Size
- SPIFFS Logical block size
- SPIFFS Logical page size
[SPIFFS](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/api-reference/storage/spiffs.html) is a file system that supports wear leveling, file system consistency checks and more.
- Configurations
It contains different variables:
- `ESP32_ID`: ID of the ESP32
- `WIFI_SSID`: SSID of WiFi (network name)
- `WIFI_PASS`: WiFi password (WPA or WPA2)
- `BROKER_ADDR`: IP of the MQTT broker
- `BROKER_PSW`: password of the MQTT broker
- `BROKER_PORT`: port of the MQTT broker
- `CHANNEL`: channel in which ESP32 will sniff PROBE REQUEST
- `SNIFFING_TIME`: time of sniffing
- etc...
### Variables Configuration
In order to configure the variables above:
1. Open your terminal within the project folder and run
make menuconfig
2. Select the menu you want to modify
3. Edit variables as you like
### Add Customised Menu
You can also add different menus with different variables:
1. Open `Kconfig.projbuild`
2. Start a new menu
menu YOUR_MENU_NAME
3. Add the variables you need
4. End menu
endmenu
# Components
- SPIFFS
You need to create a [partition table](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/api-guides/partition-tables.html).
[SPIFFS components](https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf/tree/master/components/spiffs)
- ESP32 MQTT
It has been used ESP32 MQTT Library.
[MQTT documentation](https://github.com/espressif/esp-mqtt/tree/c5ff6dd05fd357803f419916aa98ad7dd0f8e535)
- MD5
Hash function used on sniffed packets in order to get a unique identifier.
# Resources
- Official [esp-idf git repo](https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf) to see some examples and information about the used data structure.
- Latest Documentation version for [Espressif IoT Development Framework](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/).
- [ESP32 forum](https://esp32.com/) to ask questions and find community resources.
- [ESP32-IDF Documentation](http://esp32.info/docs/esp_idf/html/index.html) for browseable modules, namespaces, data structures and files.
Check also this demonstration [video](https://youtu.be/NMywky9Ts_w) to see how ESP32 works.
###### Seneca
> Longum iter est per praecepta, breve et efficax per exempla


