https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects
Clean up your controllers, slim up your models, handle more use cases
https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects
form-objects hexagonal-architecture rails ruby
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
Clean up your controllers, slim up your models, handle more use cases
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects
- Owner: FidMe
- Created: 2018-11-20T10:17:00.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-01-20T14:06:23.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-15T04:53:22.777Z (6 months ago)
- Topics: form-objects, hexagonal-architecture, rails, ruby
- Language: Ruby
- Size: 226 KB
- Stars: 15
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 4
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# ActiveFormObjects
[](https://travis-ci.org/FidMe/active_form_objects)
[](https://badge.fury.io/rb/active_form_objects)
Form objects are a great way to clean up your controllers and models.
Whenever your Rails application grows, you will eventually end up with bloated models and controllers. Even though Rails is awesome, it often leads you toward putting unnecessary logic in your controllers and models.
**Take the bull by the horns, use ActiveFormObjects, and start cleaning up your mess ! 💪**
A few benefits :
- Keep business logic out of the Controller and models
- Add validation support to plain Ruby object using ActiveModel
- Display data validation errors in the form
For more infos regarding this pattern, [see this blog post](https://medium.com/selleo/essential-rubyonrails-patterns-form-objects-b199aada6ec9)
## Menu
**Getting started**
- [Installation](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects#installation)
- [The Form Layer](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects#the-form-layer)
- [A basic example](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects#a-basic-example)
- [Usage](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects#usage)
**Documentation**
- [Resource](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects/blob/master/docs/Resource.md)
- [Attributes](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects/blob/master/docs/Attributes.md)
- [Relations](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects/blob/master/docs/Relations.md)
- [Polymorphs](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects/blob/master/docs/Polymorphs.md)
- [Scopes](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects/blob/master/docs/Scopes.md)
- [Hooks](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects/blob/master/docs/Hooks.md)
- [Debugging](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects/blob/master/docs/Debugging.md)
- [Error handling](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects/blob/master/docs/Errors.md)
- [Saving the form](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects/blob/master/docs/Savings.md)
- [ActiveModel](https://api.rubyonrails.org/classes/ActiveModel/Model.html)
## Installation
Add this line to your application's Gemfile:
```ruby
gem 'active_form_objects'
```
Execute
```bash
$ bundle install
```
Then, depending on your usage you may want to create an `app/forms` folder in your Rails application.
You will put all your forms inside of it.
A form is just a class that extends `ActiveFormObjects::Base`.
On top of all its features, `ActiveFormObjects` gives you access to the entire [Active Model](https://guides.rubyonrails.org/active_model_basics.html) stack.
## The Form layer
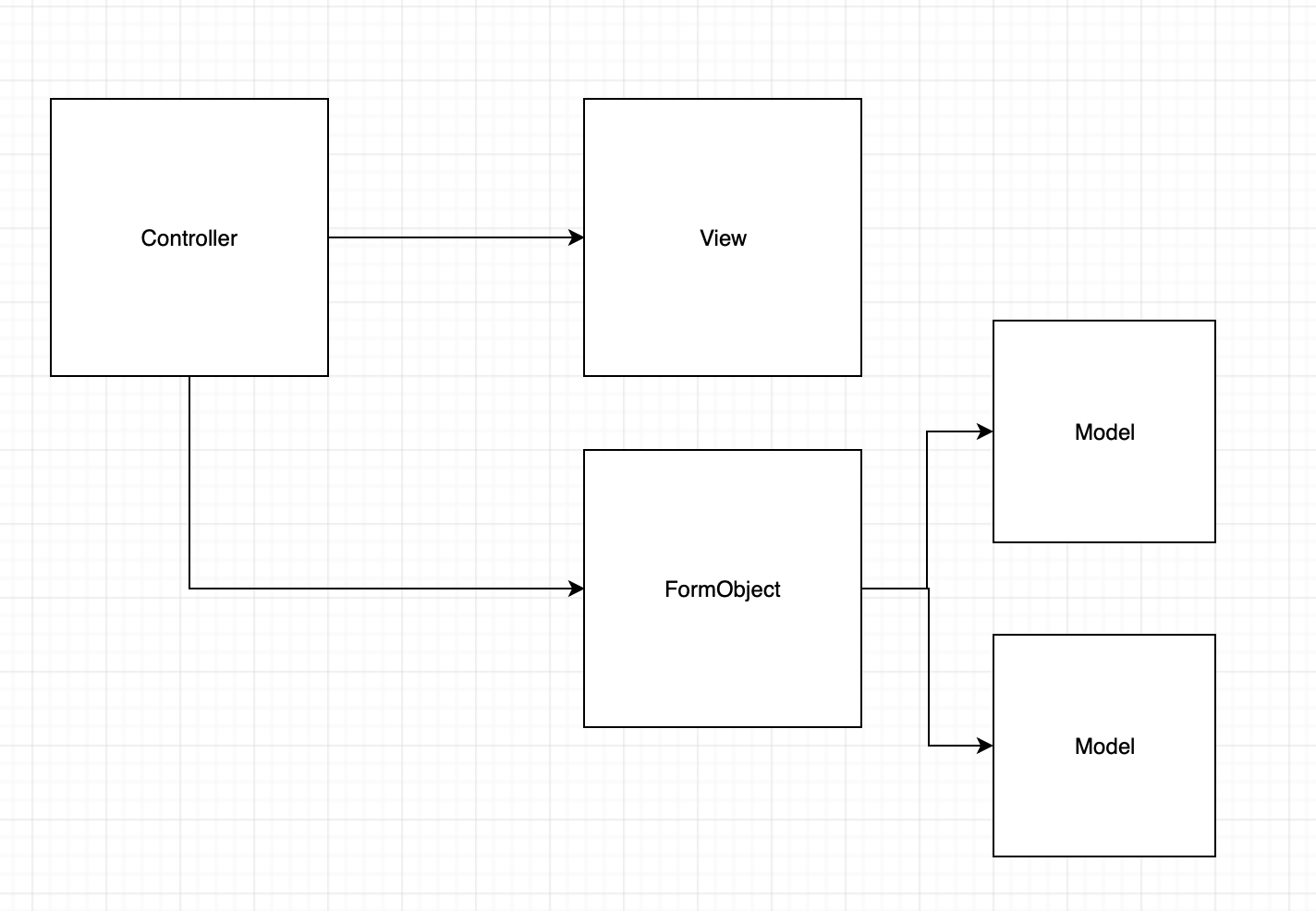
A form object can be decoupled into three parts.
- Params filtering and validating
- Any business logic
- Communication with model
Even though it seems to be a lot to handle for a single class, remember that most of it used to be (poorly done) in your controller.
### A basic example
You have a `User` model.
This model has a password field and on creation you want to verify that password and `password_confirm` match.
This logic does not belong to your `User` model.
Indeed, `User` only needs to know that the `User` has a password, furthemore, `User` does not have a `password_confirm` field, so you would need to add attr_accessor and custom validation into your `User` model.
Seems a bit to much to handle for a `User` model that is also used in a thousand other use cases...
`ActiveFormObjects` allows you to refactor this logic and put it where it belongs.
In this case :
```ruby
class RegistrationController
def create
RegistrationForm.new(params).save!
end
end
class RegistrationForm < ActiveFormObjects::Base
resource User
attributes :email, :password, :password_confirm
validate :confirmation_match
def confirmations_match
errors.add(:password, "must match password_confirm") if password != password_confirm
end
end
class User
validates :email, :password, presence: true
end
```
### Another example
Another great example where a `FormObject` becomes necessary is when you have several ways to create or update a model.
A typical use case would be as follow :
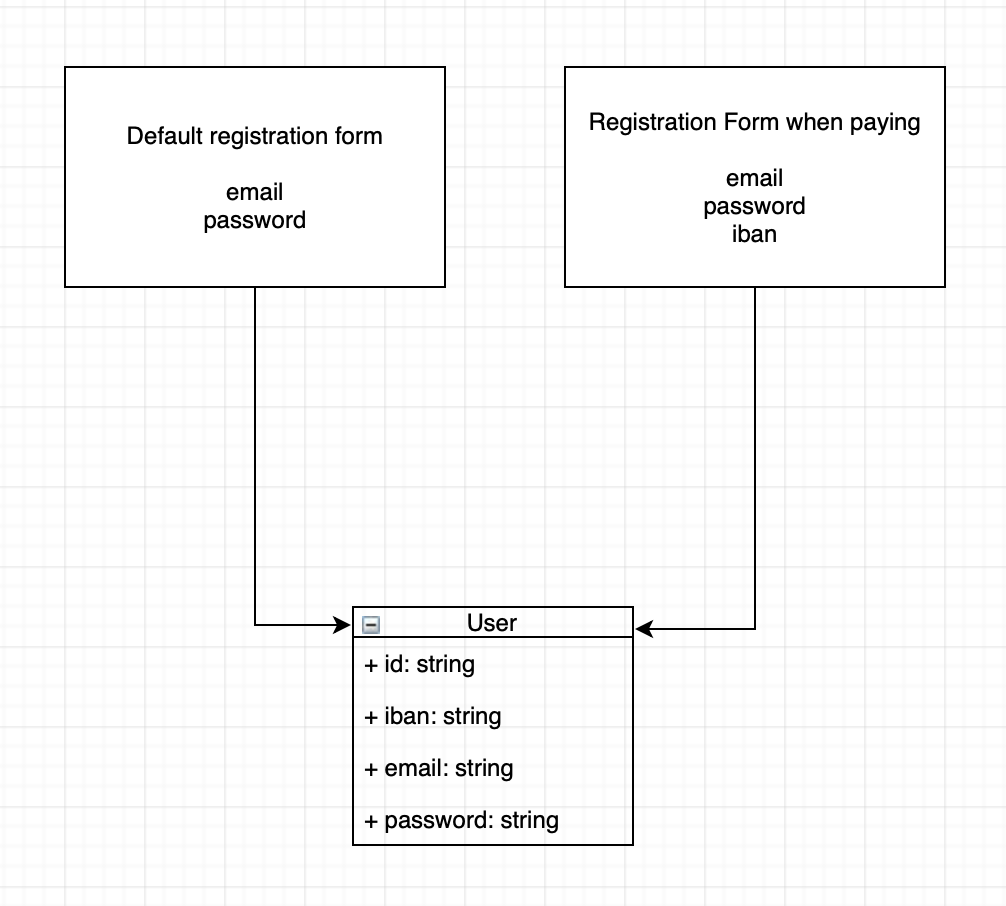
In the above example, you have two distinct ways of creating your User.
Therefore you need distinct validations to handle those cases, and your model must not handle them.
## Usage
Using a declarated form is very simple.
Consider this form :
```ruby
class ExampleForm < ActiveFormObjects::Base
resource Example
attributes :name
before_save :capitalize_name
def capitalize_name
name.capitalize!
end
end
```
You have two ways of using it :
**Without resource**
```ruby
form = ExampleForm.new(name: 'Michael')
# Will create an instance of Example
@user = form.save!
# => Example#{ name: 'Michael' }
```
**With resource**
```ruby
form = ExampleForm.new({ name: 'Nicolas' }, @user)
# Will update the given resource
form.save!
# => Example#{ name: 'Nicolas' }
```
Note that you can of course override the `save!` method
```ruby
class ExampleForm < ActiveFormObjects::Base
def save!
# do nothing
end
end
```
The provided `save!` method is just a helper that does
- validate!
- Uses ActiveRecord::Base.transaction
- Returns the resource
For more informations on saving, please [read the dedicated section](https://github.com/FidMe/active_form_objects/blob/master/docs/Savings.md)
## Anything is missing ?
File an issue