Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/Geetima2021/PLL-IC-design-using-Open-Source-PDK-Google-Skywater-130nm
This repository in a walk through the entire process of PLL IC designing from the tools to the final tapeout.
https://github.com/Geetima2021/PLL-IC-design-using-Open-Source-PDK-Google-Skywater-130nm
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
This repository in a walk through the entire process of PLL IC designing from the tools to the final tapeout.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/Geetima2021/PLL-IC-design-using-Open-Source-PDK-Google-Skywater-130nm
- Owner: Geetima2021
- Created: 2021-07-31T03:18:44.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2022-02-16T05:38:14.000Z (almost 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-03T01:38:04.874Z (6 months ago)
- Homepage:
- Size: 142 KB
- Stars: 19
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# PLL IC design using Open Source PDK Google Skywater 130nm

# Table of contents
- [Overview](#overview)
- [Day 1 : PLL Theory and Lab set-up](#Day1)
- [Introduction to PLL](#PLL)
- [Introduction to Phase frequency detector](#PFD)
- [Introduction to charge pump](#CP)
- [Voltage control oscillator and Frequency Divider](#VCO)
- [Tool setup and design flow](#tool)
- [Introduction to PDK, specifications and pre-layout circuits](#PDK)
- [Day 2 : PLL Labs and Post Layout simulations](#lay)
- [PLL component circuit design](#des)
- [PLL component circuit simulation](#sim)
- [Steps to combine PLL sub circuits and PLL full design simulation](#sub)
- [Troubleshooting](#trou)
- [Layout design](#lay)
- [Layout walkthrough](#walk)
- [Tapeout theory](#tape)
- [Tapeout labs](#labs)
- [Acknoledgement](#Ack)
## Overview
This repository deals with the workshop which signinfies the beginning of a new era of “Design at $0” as visualize and materialize by the continuous effort of the entire VSD team and [Lakshmi Sathi](https://github.com/lakshmi-sathi/avsdpll_1v8). It is another of VSD standard VSD IAT cloud based 2 days workshop with 24 hrs accessibility of the platform to each participants. The VSD IAT platform provides all the necessary material including remote access of their ubuntu server for carrying on the labs with the pre-loaded tools required for the particular workshop. Assessment is also done through the multiple choice questions, including both the theoritical understanding and lab exercise. However, the installation procedure of the required tools viz ngspice and magic for use in our local system is covered. The snippet of the platform and lab instance is as shown below.


## Day 1 : PLL Theory and Lab set-up
Day1 is divided into two parts - PLL Theory section and the Lab set-up section. The approach taken by the instructor [Lakshmi Sathi](https://github.com/lakshmi-sathi/avsdpll_1v8) the designer herself, in designing the Phase-Locked Loop IC on Open-Source Google-Skywater 130nm node is an intuitive one where a simple PLL with extraordinarily little math and without diving into complex frequency domain analysis or control system theory is considered.
Now starting from the basic question:
Why PLL?
To get precise clock signal without frequency and phase noise. Also to have flexibility to work on frequency of choice. Now as quartz crystal provides superior spectral purity, fixed frequency and phase noise performance, VCO on the other hand has good flexibility and implemantable on SOC, hence the amalgamation of the two for designing a simple PLL IC is good enough. The Phase lock loop intution is based on the ability of the output signal to mimic the input reference signal and maintaining a constant phase difference. The block diagram of the PLL is as shown in figure below with a more detailed one next to it.


Phase frequency detector, works by comparing the reference frequency signal and the output frequency to bring about synchronization so that the phase difference is minimum, whose output is in digital form. Next the charge pump circuit converts the same into analog signal which the LPF smoothens and serves as input to the VCO. The Frequency divider circuit also known as clock muliiplier as it divides the entire circuit to a mulitiplier circuit. Say for example if the FD signal is divided by 8 then the VCO has to be adjusted so that the signal is 8 times that of the reference signal.
## Introduction to phase frequecy detector
Two cases are considered - one when the output frequeny is leading the reference frequency and the other when it is lagging. The two signals are then XORed and their output compared. From the XORed signal it is concluded that it is difficult to distinguish between the lagging and leading signal base on this method. The reference figure is included below.

Hence the concept of DOWN signal and UP signal is applied. Whenever the output signal is leading the DOWN signal is activated and vice versa incase of lagging signal and thereby the VCO signal is adjusted as per requirement to minimize the phase difference.

## Introduction to charge pump
It converts the digital measure of phase/frequency difference into an analog signal to control the oscillator. The circuit diagram of the charge pump circuit is as shown below. It consists of a current stirring circuit whose output depends on whether the capacitor is charging or discharging based on the Up and Down signal. However, the charge pump has leakage issue.

Now in order to stabilize the output a loop filter (LPF) is added along with the capacitor. The value of the capacitor is change and its value is based on the thumb rule and with the loop filter bandwidth is as shown in the figure.

## Voltage control oscillator and Frequency Divider
The most common oscillator, Ring oscillator is used as a VCO. It consists of odd number of inverters connected in series, which has the same delay. The output flips after the delay and hence driving half of a period which is given twice the delay of the inverter and the inverter count viz `period = 2*delay(inverter)*inverter count` which bascically signifies that it has a fixed frequency. To have control over the frequency, a current starving mechanism is used over the ring oscillator circuit, where two supply of currect sources are provided to the top and bottom of the ring oscillator, which are controlled by the control voltage. The current sources in turn control the frequencies.It is necesary to design the VCO circuit properly to ensure that the desired range of frequency is obtained.

### Frequency Divider
As the output of the toggle flip flop is half the frequency of the input sigal. Hence, if we had a D-flip we can make into a toggle flip flop by adding an inverter to the ouput and input pin of the D flip flop. Hence, if the a signal with 10 ns period is supplied at the input, the ouput will a signal of 20 ns period as shown in figure below. For obtaining a 8x multiplier 3 such toggling flip flop can be used.

Some common terms used in PLL
- Lock range : The frequency the range the PLL is able to follow input frequency variations once locked.
- Capture range: The frequency range the PLL is able to lock-in when starting from an unlocked condition and it depends on the bandwidth of the loop filter.
- Settling time : The time the PLL requires to be in lock step from an unlocked state. It depends on how the charge pump reaches its stable value
## Tool setup and design flow
This section deals with the tool setup and the development flow. For using the required tools into local machine the open source tools ngspice and magic is to be installed along the Google skywater PDK - a 130 nm process. The details of the same can be found [here](https://github.com/lakshmi-sathi/avsdpll_1v8/blob/main/README.md#-Instruction).
### Development flow
The design/development flow for any IC includes the following steps
- Specification
- Spice level circuit simulation
- Pre-layout simulation
- Layout development
- Parasitic extraction
- Post layout simulation
## Introduction to PDK, specifications and pre-layout circuits
The Process design kit (PDK) used is the open source Google Skywater 130nm. PDK's are basically the foundry files which contains information about the transistor, their configuarion, timing information, area occupied, layout, verilog etc. However, in building the PLL IC all these information is not necessary as it is designed from scratch i.e from the transistor level. Also the PDK has diffrent process corners and in this case the TT corner is considered. The specications provided in designng the PLL IC are mentioned below and the per-layout and post-layout output obtained can be viewed in the [repository](https://github.com/lakshmi-sathi/avsdpll_1v8). Also the PDK provides different sets of libraries and in this case the primitive library as obtained from [here](https://github.com/google/skywater-pdk/tree/main/libraries/sky130_fd_pr) is used for spice simulation.
### Specifications for PLL design
| Parameters | Value |
| ------------- | ------------- |
| Supply voltage | 1.8V |
| Temperature | 27C |
| Corner | TT |
| Input Frequency |Fmin = 5MHz, Fmax = 12.5 MHz |
| Jitter | < 20ns |
| Duty cycle | 50% |
| Phase noise | < 10ns |
| Multiplier | 8x |
The first step to start the lab exercise is to git clone the avsdpll_1v8 repository using the git command followed by the url of the repository viz `git clone https://github.com/lakshmi-sathi/avsdpll_1v8.git`. Thus, a folder will be created which contains all the necessary files and folders required for the smooth functioning of the workshop.

Now, the necessary files required for the lab is to be collected in the same location and thereafter a file is to created with all the required libraries for used during execution of the ngspice programs. With respect to the specification given, the nfet and pfet configuration for 1.8v supply voltage, TT corner and room temperature, the required libraries are collected in the same location for ease in the operation. The snapshot of the list of the libraries considered is as shown below.

## Day 2 : PLL Labs and Post Layout simulations
During the Day 2, some of the labs of post layout simualtions are done for understanding of the procedure required and the changes to be done so that the pre-layout and post-layout simulations output matches.
## PLL component circuit design
Now the frequency divider spice file is checked and the proper location of the library file is mentioned for its execution. Also, the maximum allowable length for 130nm process is considered to be 150nm. As far as the width of the transistors the minimum width for nmos is 360nm and for pmos is 420nm. Base on the requirement of the design the width of the transistor are adjusted. The snippet of the FD.cir is included below.

## PLL component circuit simulation
Here the circuit simulation of the charge pump circuit is done as a part of lab assessment. For that the library file path is checked and modified, and therafter slight modification in the transient response ending time is done from 1us to 20us, inorder to find the voltage at the output due to leakage, which is 800uv. The snapshot of the assessment along with the output is included below.


## Steps to combine PLL sub circuits and PLL full design simulation
After individually designing the layout of the different components the next step is to combime the layouts into the final layout design. Thus a magic file is opened using the command `magic -T sky130A.tech`, where `sky130A.tech`, is the technology file provided by Google Skywater. Now the individual layouts are placed by clicking cells part and using the place instance as shown in the figure below. Initially blank box appears and to view the layout the 'i' key followed by the 'x' key is used. After properly placing the layouts, the next step is to connect them together using the input and the output metal layers and combining them together by appropriate via.



## Troubleshooting
It is important to troubleshoot/debug a design at the individual level prior connecting them together which saves from unwanted hiccups at later stage. In case of PLL IC design some of the issues face during Pre-layout simulation is mentioned below along with its debugging procedure.
- PreLayout-Sim: What to do if it doesn't work?
- Observe what kind of issue is faced
- Always debug individual component fully before moving to combined simulation
- Are some signals coming up flat? Or the siumalation is crashing? - Check connections
- The signals are right but mimicking not happening - Check wrong net name, capatilization issue or wrong parameter value
- For what range of frequencies, is the VCO working properly?
- Is the phase frequency detector able to detect small difference
- How is the response of Charge Pump?
- Whether the loop filter values ane working out?
## Layout design
Here some discussion on the magic design tool is done viz drawing a simple nmos transistor, using of the color pallete on the right hand side of the layout window which showcase the different layers required in layout design, selecting the entire design using the key `A`, moving the entire design to a different location using `M` key or simply copying it through `C` key. If drc error exists it can be viwed by using `?` in the tkcon window, and the error has to be rectified. Now here a lab execise is done to find the area of either charge pump/frequency detector. For that simply the a box is selected by left clicking say on the top left corner and right clicking on the bottom right corner thereafter simply th box command is used in tkcon window/editor of magic as shown in figure below.

## Layout walkthrough
The VCO layout design is considered, and the design is explained thoroughly and the figure of the VCO design is included below. The final layout of the PLL IC is also included below.
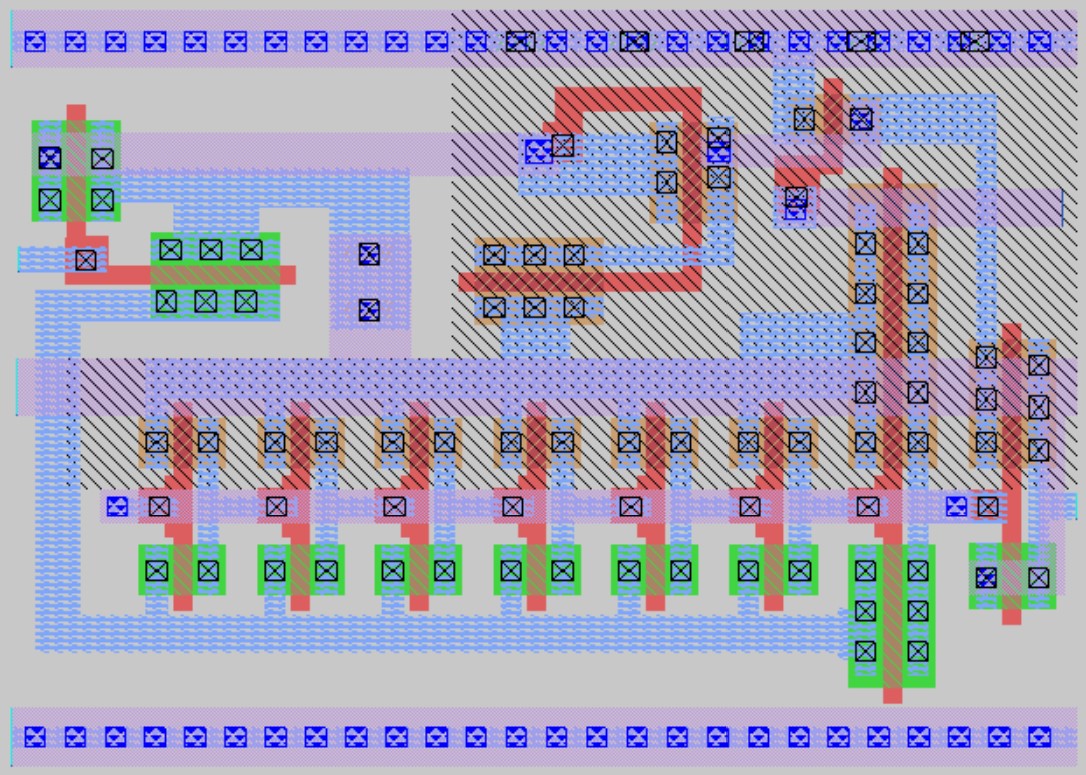

## Parasitic extraction
For extracting the parasitic capacitance and resistance after layout design the following command are used in the tkcon window.
```
extract all
```
it extracts a .ext file
```
ext2spice cthresh 0 rthresh 0
```
extracts the parasitics from the 0'th value itself.
```
ext2spice
```
generates a spice file
After extraction of the spice file, all the parasitics are included in it along with other parameters (ad,as,pd,ps) and some changes occurs in the spice program. The first thing which changes is the scale for the transistor sizing and hence it should be changed to the required scale. Now the parasitic extraction of the PFD file is done and the spice file is checked and it is found that a total of 43 parasitics capacitance is extracted nad the highest capacitive value is of capacitor C35 = 3.76fF, across the VDD and GND pin which is observe as a part of lab exercise. The snapshot of the same is included below.

Next exercise is to instantiate the subckt to the newly generated PFD spice file and make a phase difference of 0.25ns between the reference clock signal and the feedback clock signal and to obsere the output generated. It is observed that the up signal is short and is capable of detecting the small phase difference between the two signal.

Finally after removing the drc errors any verifing the proper functioning of the design, the next step is to create the gds file of the final PLL design, using magic. Go to file in the layout window and simply `write gds`, a gds file is created which is used for the final tapeout.
## Tapeout theory
Tapeout is he process of adding the final design to the FAB after we prepare it. The preparing stage consists of number of steps.
- Inclusion of I/O pads
- Peripherals for serial connection
- Memory
- Testing mechanism
- Others
However, in the open source world this has been made easy by Efabless through its MPW open shuttle program which is sponsored by Google. Efabless provides a Caravel SOC where anyone can use it for their design fabrication. For this a user project area is defined where the designer places his/her design based on the pins placement and makes the necessary connection. The Caravel SOC along with its details is as shown in figure below. The details of the Efables MPW shuttle 2 program can be viewed [here](https://efabless.com/open_shuttle_program/2).

## Tapeout Labs
- The first step is to go to the efabless caravel github [link](https://github.com/efabless/caravel) and from the gds folder download `user_analog_project_wrapper_empty.gds.gz` and extract it.
- Next open the `user_analog_project_wrapper_empty.gds.gz` in magic using the command `magic -T sky130A.tech user_analog_project_wrapper_empty.gds.gz` and place the PLL design in the used define area. By zooming in the pins available in the SOC can be viewed. The PLL has 5 pins, 1 each for voltage and ground, 2 digital IO pins for Ref_Clk and out_clk pins and an analog pin for the output VCO. The PLL IC is placed in the user defined area based on the pin placement and the connections are done properly, thus the final processing of the PLL IC is completed and it is ready for tapeout. However, the proper tapeout process is clearly documented in the avsdpll_1v8 github [link](https://github.com/lakshmi-sathi/avsdpll_1v8) of the designer.
## Acknowledgment
- [Kunal Ghosh](https://github.com/kunalg123), Co-founder, VSD Corp. Pvt. Ltd.
- [Lakshmi Sathi,8x PLL Clock Multipler IP on Google-skywater 130nm node](https://github.com/lakshmi-sathi/avsdpll_1v8).