https://github.com/HoudiniProject/houdini
Free and open source fundraising infrastructure for nonprofits and NGOs
https://github.com/HoudiniProject/houdini
crowdfunding donation-management nonprofit
Last synced: 4 months ago
JSON representation
Free and open source fundraising infrastructure for nonprofits and NGOs
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/HoudiniProject/houdini
- Owner: houdiniproject
- License: other
- Created: 2018-03-19T22:01:26.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-17T18:10:51.000Z (4 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-17T19:26:46.839Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: crowdfunding, donation-management, nonprofit
- Language: Ruby
- Homepage: https://houdiniproject.org
- Size: 18.5 MB
- Stars: 195
- Watchers: 10
- Forks: 94
- Open Issues: 183
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Houdini
[](https://github.com/houdiniproject/houdini/discussions)
[](https://crowdin.com/project/houdiniproject)
> *Note*: This is the latest version (pre-2.0) of Houdini and
> is currently in HEAVY development. You may want
> to use
> [v1](https://github.com/houdiniproject/houdini/tree/1-0-stable)
> instead.
The Houdini Project is free and open source fundraising infrastructure. It includes...
- Crowdfunding campaigns
- Donate widget page and generator
- Fundraising events
- Nonprofit Profiles
- Nonprofit payment history and payouts dashboard
- Nonprofit recurring donation management dashboard
- Nonprofit metrics overview / business intelligence dashboard
- Nonprofit supporter relationship management dashboard (CRM)
- Nonprofit org user account management
- Simple donation management for donors
The frontend is written in a few custom frameworks, the largest of which is
called Flimflam.
We endeavor to migrate to React as quickly as possible to increase development
comfort and speed.
All new backend code and React components should be well tested.
## Supported operating systems
- Ubuntu 18.04, 20.04, 22.04 or equivalent
## Prerequisites
- Node.js 16 (we require 16 because we want the full internationalization built-in)
- Yarn
- PostgreSQL 12 (10 probably works)
- Ruby 2.7
- Ubuntu 18.04, 20.04, 22.04 or equivalent
> Note: All tools will be installed in the Dev Setup.
## Get involved
Houdini's success depends on you!
### Join our Discussions chat
[https://github.com/houdiniproject/houdini/discussions]
### Help with translations
Check our [translation guide](docs/translations.md) to translate Houdini to other
languages.
### Help with usability tests
Check on [contribution_guide_usability_testing.md](docs/contribution_guide_usability_testing.md)
and create an issue with your test design or run test sessions for
[opened usability testing issues](https://github.com/houdiniproject/houdini/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+%5BUX%5D+).
## Dev Setup
### Installation prep
Houdini requires a few pieces of software be installed as mentioned in
Prerequisites above, as well as some optional pieces which make development much
easier. The optional tools include:
- RBENV - rbenv is a version manager tool for the Ruby programming language on
Unix-like systems. It is useful for switching between multiple Ruby versions on
the same machine and for ensuring that each project you are working on always
runs on the correct Ruby version.
- Automatic Version Switching for Node (AVN) - similar to RVM, AVN makes it
simple to switch between versions of Node. When properly configured,
it automatically switches version at the console when you change to a directory
for a project prepared for AVN, like Houdini.
### One-time setup
#### Postgres installation
You'll want to run the next commands as root or via sudo (for Ubuntu 18.04 users
or anyone running ProgresSQL 10, change "postgresql-12" below to "postgresql-10").
You could do this by typing `sudo /bin/sh` running the commands from there.
#### Curl install
```bash
apt update
apt install curl -yy
```
#### Node and Yarn install
```bash
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_16.x | bash -
curl -sS https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | apt-key add -
echo "deb https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/ stable main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.list
apt update
```
#### Postgres install
```bash
apt install git postgresql-12 libpq-dev libjemalloc-dev libvips42 yarn -yy
```
You'll run the next commands as your normal user.
> *Note*: in the case of a production instance, this might be
> your web server's user.
> *Note*: We use [RBENV](https://https://github.com/rbenv/rbenv.io) inside the
project folder to have more control over the exact version of Ruby.
> *Tip*: To get out of the root shell, run `exit`
Run the following command as the `postgres` user and then enter your houdini_user
password at the prompt.
**Note: For development, Houdini expects the password to be 'password'.**
**This would be terrible for production but for development, it's likely not a**
**huge issue.**
#### Create user account for the database connection
```bash
sudo -u postgres createuser houdini_user -s -d -P
```
Now that we have all of our prerequisites prepared, we need to get the Houdini code.
#### Cloning project
```bash
git clone https://github.com/HoudiniProject/houdini
```
This will download the latest Houdini code.
Let's run the Houdini project setup and we'll be ready to go!
#### Get the latest rbenv
```bash
git clone https://github.com/rbenv/rbenv.git ~/.rbenv
```
#### Add rbenv to bashrc
```bash
echo 'eval "$(~/.rbenv/bin/rbenv init - bash)"' >> ~/.bashrc
```
> *Note*: close and reopen your terminal.
#### Download the rbenv install feature
```bash
git clone https://github.com/rbenv/ruby-build.git "$(rbenv root)"/plugins/ruby-build
```
#### Ruby install
```bash
rbenv install 3.0.7
```
#### Setup project
```bash
cd houdini
bin/setup
```
> *Note*: The .env file holds your environment variables for development;
on production you might
> have these set somewhere else other than this file.
> *Tip*: On Heroku, the environment variables are set in your Dashboard.
Also, you should set the STRIPE_API_KEY and STRIPE_API_PUBLIC
environment variables which you'd get from the Stripe
dashboard. On your development environment,
make sure to use test keys. If you don't, you're
going to be charged real money!
### Stripe keys setup
#### Get Stripe keys
Go to [Stripe](https://stripe.com), create an account or just log in with you
already have one. Access the stripe dashboard and copy both publishable and
secret keys.
> make sure to use test keys. If you don't, you're
going to be charged real money!
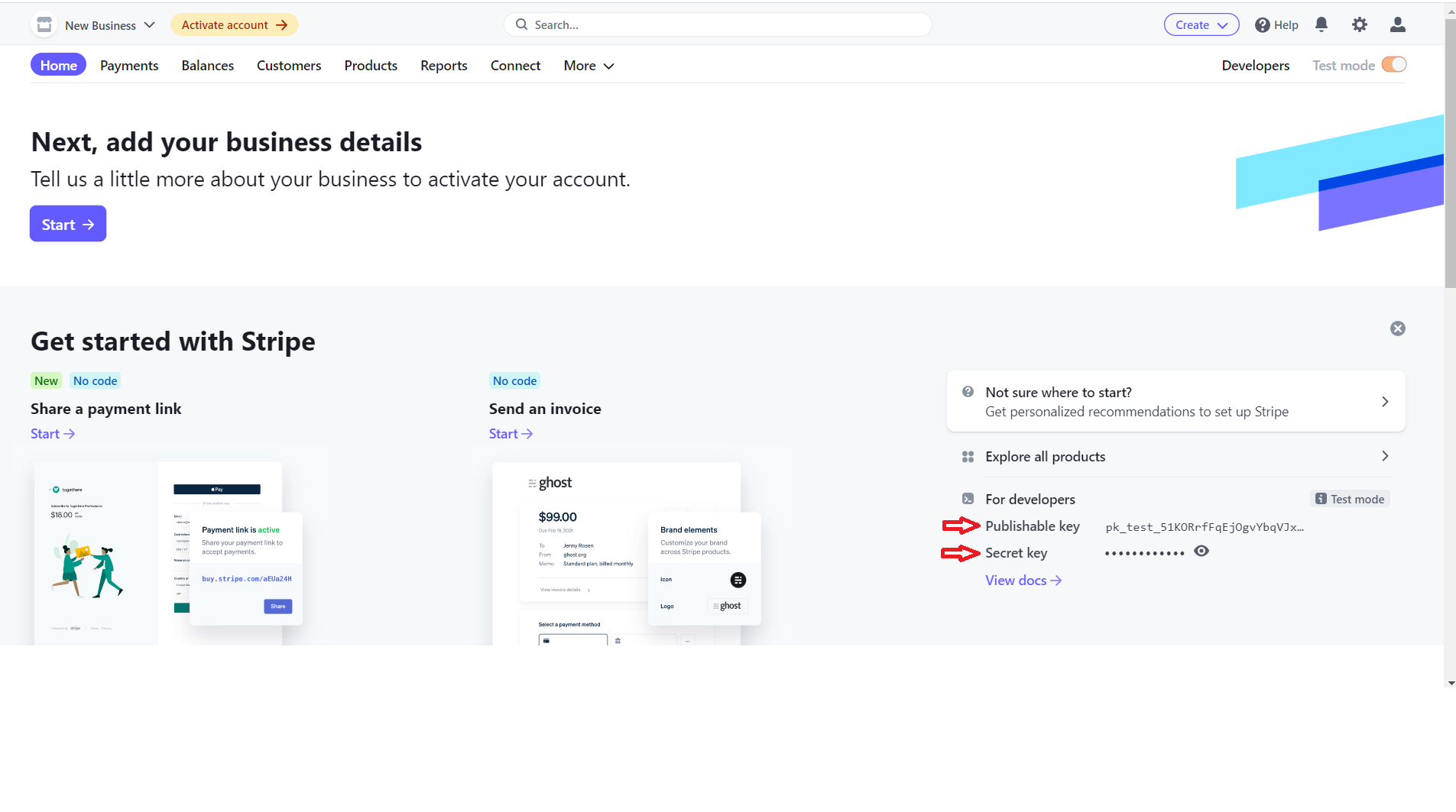
#### Configure the .env file
Then after retrieving both keys copy them into your .env file on these lines:
```bash
export STRIPE_API_KEY='REPLACE' # use your test private key from your stripe account
export STRIPE_API_PUBLIC='REPLACE' # use your test public key from your stripe account
```
### Testing
To verify everying is set up correctly, you can try running through the Ruby
test cases:
```bash
bin/rails spec
```
(You can also run `bin/rspec`, which provides the full feature set of rspec such
as `--next-failure` and `--only-failures`, but does not set up a test database
when it doesn't exist.)
You should expect to see the output of the test execution,
including messages about pending test cases, and
eventually get the output to the effect of below:
```text
Finished in 6 minutes 25 seconds (files took 10.35 seconds to load)
2433 examples, 0 failures, 42 pending
Coverage report generated for RSpec to .../houdini/coverage. 10552 / 12716 LOC
(82.98%) covered.
```
The important thing to look for is that the number of
failures is zero.
We also recommend you run through the javascript test cases by running:
```bash
yarn test:js
```
Lastly, you can use [Storybook](https://storybook.js.org/) to experiment with
the various new React components.
```bash
yarn storybook
```
If you create a new React component, make sure you add a storybook and jest
tests for that component!
#### Creating your first nonprofits and user
To create a nonprofit, use the command line to run the following command and fill
in the questions with the required information:
```bash
bin/rails houdini:nonprofit:create
```
There are available arguments that add configurations on the nonprofit's creation:
```bash
# Make the nonprofit admin a super user (they can access any nonprofit's dashboards)
-s, [--super-admin], [--no-super-admin]
# Autoconfirm the admin instead of waiting for them to click the email link
# Default: true
[--confirm-admin], [--no-confirm-admin]
```
Additionally, it is possible to provide arguments to fill in the fields for the
nonprofit creation without coming across the questions:
```bash
# Provide the nonprofit's name
[--nonprofit-name=NONPROFIT_NAME]
# Provide the nonprofit' state code
[--state-code=STATE_CODE]
# Provide the nonprofit's city
[--city=CITY]
# [OPTIONAL] Provide the nonprofit public website
[--nonprofit-website=NONPROFIT_WEBSITE]
# [OPTIONAL] Provide the nonprofit public email
[--nonprofit-email=NONPROFIT_EMAIL]
# [OPTIONAL] Provide the nonprofit's 's phone
[--nonprofit-phone=NONPROFIT_PHONE]
# Provide the nonprofit's admin's name
[--user-name=USER_NAME]
# Provide the nonprofit's admin's email address(It'll be used for logging in)
[--user-email=USER_EMAIL]
# Provide the nonprofit's admin's password
[--user-password=USER_PASSWORD]
```
You can use this in the future for creating additional nonprofits.
### Startup
`bin/rails server`
You can connect to your server at [http://localhost:5000]
#### Super admin
There is a way to set your user as a super_admin. This role lets you access any
of the nonprofits
on your Houdini instance. Additionally, it gives you access to the super admin
control panel to search all supporters and
nonprofits, which is located at `/admin` url.
To create the super user, go to the rails console by calling:
`bin/rails console`
In the console, run the following:
```ruby
admin=User.find(1) #or the id of the user you want to add the role
role=Role.create(user:admin,name: "super_admin")
```
#### Code Analysis
We use `Rubocop` to perform static code analysis:
```bash
rubocop
```
## Additional documentation
We have some additional documentation describing some implementations, definitions
and other guides on the [docs folder](docs).
## Known issues
For a list of [how to solve known issues](docs/known_issues.md)
## Run in production
You will likely want to make a few changes in your configuration of Houdini before
running in production as you
would for any Rails project. For details, see [production deployment](docs/production_deployment.md).