https://github.com/Liu-xiandong/How_to_optimize_in_GPU
This is a series of GPU optimization topics. Here we will introduce how to optimize the CUDA kernel in detail. I will introduce several basic kernel optimizations, including: elementwise, reduce, sgemv, sgemm, etc. The performance of these kernels is basically at or near the theoretical limit.
https://github.com/Liu-xiandong/How_to_optimize_in_GPU
elementwise gpu-acceleration high-performance-computing hpc reduce sgemm sgemv
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
This is a series of GPU optimization topics. Here we will introduce how to optimize the CUDA kernel in detail. I will introduce several basic kernel optimizations, including: elementwise, reduce, sgemv, sgemm, etc. The performance of these kernels is basically at or near the theoretical limit.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/Liu-xiandong/How_to_optimize_in_GPU
- Owner: Liu-xiandong
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2021-10-17T14:19:27.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-07-29T05:52:37.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-13T19:45:36.165Z (about 1 year ago)
- Topics: elementwise, gpu-acceleration, high-performance-computing, hpc, reduce, sgemm, sgemv
- Language: Cuda
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.25 MB
- Stars: 825
- Watchers: 13
- Forks: 131
- Open Issues: 6
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-cuda-and-hpc - Liu-xiandong/How_to_optimize_in_GPU - xiandong/How_to_optimize_in_GPU?style=social"/> : This is a series of GPU optimization topics. Here we will introduce how to optimize the CUDA kernel in detail. I will introduce several basic kernel optimizations, including: elementwise, reduce, sgemv, sgemm, etc. The performance of these kernels is basically at or near the theoretical limit. (Learning Resources)
README
# How to optimize in GPU
This is a series of GPU optimization topics. Here we will introduce how to optimize the program on the GPU in detail. Here, I will introduce several basic kernel optimizations, including: elementwise, reduce, sgemv, sgemm, etc. All the following performance data are run on V100 and tested by nsight.
If you have any questions, you can directly contact: xiandong_liu@foxmail.com
## 1. elementwise
For elementwise kernel, the optimization techniques that can be used are mainly vectorized memory access. I compared the three memory access methods of float, float2, and float4. The performance is as follows:
| Type | Bandwiths | Ratio |
| :------------: | :------------: | :------------: |
| float | 827 | 91.9% |
| float2 | 838 | 93.1% |
| float4 | 844 | 93.8% |
## 2. reduce
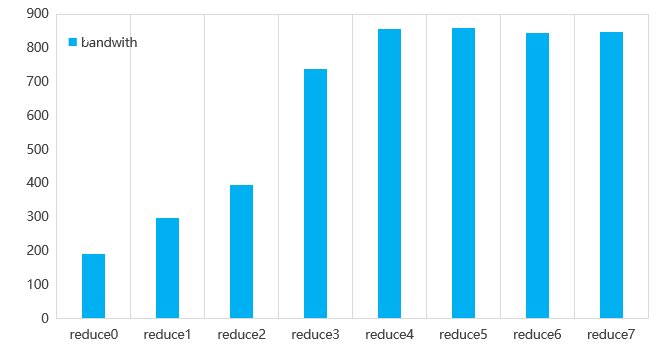
Seven optimization methods were used to optimize reduce operator, and the performance of different optimization methods was tested on V100. The bandwidth of **858GB/s** is obtained, and the bandwidth utilization rate is: **858/900=95.3%**. The figure below shows the performance of the 7 optimization techniques.
## 3. sgemv
The core of sgemv kernel optimization lies in the design of blocks and threads, and it is necessary to avoid the situation of thread idle as much as possible.
There are different optimization techniques for different data shapes. I designed 3 different optimization methods for 3 different situations, namely: n=32, n<32, and n>32. The corresponding performance is as follows:
| sgemv | M | N | my_sgemv time(ns) | cublas(ns) | my_sgemv/cublas |
| :------------: | :------------: | :------------: | :------------: | :------------: | :------------: |
| v0 | 16384 | 32 | 10341 | 8386 | 81.1% |
| v1 | 16384 | 128 | 14284 | 15848 | 110.9% |
| v2 | 16384 | 16 | 6903 | 7576 | 109.7% |
## 4. sgemm
The optimization of sgemm is divided into two levels, namely CUDA
C-level optimization and optimization of SASS code.
Regarding CUDA C-level optimizations, the final code is sgemm_v3. On a large matrix of 4096 (M=N=K), our sgemm can achieve **96.8%** performance of cublas, with a peak floating point efficiency of 93.6%, basically reaching the limit of CUDA C code optimization. The figure below shows the performance of sgemm_v3.

Regarding the optimization of SASS code, CuAssembler is used for tuning. There are two main optimization techniques in this part, namely register remapping and instruction rearrangement to obtain better .reuse flag layout.
## License
All the source codes of this repo are released under [Apache 2.0](http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0).