https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/ride
Training wheels, side rails, and helicopter parent for your Deep Learning projects in PyTorch
https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/ride
ai artificial-intelligence deep-learning framework machine-learning python pytorch pytorch-lightning
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
Training wheels, side rails, and helicopter parent for your Deep Learning projects in PyTorch
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/ride
- Owner: LukasHedegaard
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2021-02-03T09:56:15.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2023-09-23T09:22:42.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-10T04:38:39.747Z (6 months ago)
- Topics: ai, artificial-intelligence, deep-learning, framework, machine-learning, python, pytorch, pytorch-lightning
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.42 MB
- Stars: 25
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

Training wheels, side rails, and helicopter parent for your Deep Learning projects in [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org).
```bash
pip install ride
```
## ZERO-boilerplate AI research
`Ride` provides a feature-rich, battle-tested boilerplate, so that you can focus on the model-building and research. 🧪
Out of the box, `Ride` gives you:
- __Training and testing methods__ 🏋️♂️
- __Checkpointing__ ✅
- __Metrics__ 📈
- __Finetuning schemes__ 👌
- __Feature extraction__ 📸
- __Visualisations__ 👁
- __Hyperparameter search__ 📊
- __Logging__ 📜
- __Command-line interface__ 💻
- __Multi-gpu, multi-node handling via__ 
- _... and more_
## Boilerplate inheritance
With `Ride`, we inject functionality by means of _inheritance_.
The same way, your network would usually inherit from `torch.nn.Module`, we can _mix in_ a plethora of functionality by inheriting from the `RideModule` (which also includes the `torch.nn.Module`).
In addition, boiler-plate for wiring up optimisers, metrics and datasets can be also _mixed in_ as seen below.
### Complete project definition
```python
# simple_classifier.py
import torch
import ride
import numpy as np
from .examples import MnistDataset
class SimpleClassifier(
ride.RideModule,
ride.SgdOneCycleOptimizer,
ride.TopKAccuracyMetric(1,3),
MnistDataset,
):
def __init__(self, hparams):
# `self.input_shape` and `self.output_shape` were injected via `MnistDataset`
self.l1 = torch.nn.Linear(np.prod(self.input_shape), self.hparams.hidden_dim)
self.l2 = torch.nn.Linear(self.hparams.hidden_dim, self.output_shape)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = torch.relu(self.l1(x))
x = torch.relu(self.l2(x))
return x
@staticmethod
def configs():
c = ride.Configs()
c.add(
name="hidden_dim",
type=int,
default=128,
strategy="choice",
choices=[128, 256, 512, 1024],
description="Number of hidden units.",
)
return c
if __name__ == "__main__":
ride.Main(SimpleClassifier).argparse()
```
The above is the __complete__ code for a simple classifier on the MNIST dataset.
All of the usual boiler-plate code has been _mixed in_ using multiple inheritance:
- `RideModule` is a base-module which includes `pl.LightningModule` and makes some behind-the-scenes python-magic work. For instance, it modifies your `__init__` function to automatically initiate all the mixins correctly. Moreover, it mixes in `training_step`, `validation_step`, and `test_step`.
- `SgdOneCycleOptimizer` mixes in a `configure_optimizers` functionality with SGD and [OneCycleLR scheduler](https://pytorch.org/vision/0.8/datasets.html#torchvision.datasets.MNIST).
- `TopKAccuracyMetric` adds top1acc and top3acc metrics, which can be used for checkpointing and benchmarking.
- `MnistDataset` mixes in `train_dataloader`, `val_dataloader`, and `test_dataloader` functions for the [MNIST dataset](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/co-rider). Dataset mixins always provide `input_shape` and `output_shape` attributes, which are handy for defining the networking structure as seen in `__init__`.
## Configs
In addition to inheriting lifecycle functions etc., the mixins also add `configs` to your module (powered by [co-rider](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/co-rider)).
These define all of the configurable (hyper)parameters including their
- _type_
- _default_ value
- _description_ in plain text (reflected in command-line interface),
- _choices_ defines accepted input range
- _strategy_ specifies how hyperparameter-search tackles the parameter.
Configs specific to the SimpleClassifier can be added by overloading the `configs` methods as shown in the example.
The final piece of sorcery is the `Main` class, which adds a complete command-line interface.
## Command-line interface 💻
### Train and test
```shell
$ python simple_classifier.py --train --test --learning_rate 0.01 --hidden_dim 256 --max_epochs 1
```
- _Example output:_
```shell
lightning: Global seed set to 123
ride: Running on host HostName
ride: ⭐️ View project repository at https://github.com/UserName/project_name/tree/commit_hash
ride: Run data is saved locally at /Users/UserName/project_name/logs/run_logs/your_id/version_1
ride: Logging using Tensorboard
ride: 💾 Saving /Users/au478108/Projects/ride/logs/run_logs/your_id/version_1/hparams.yaml
ride: 🚀 Running training
ride: ✅ Checkpointing on val/loss with optimisation direction min
lightning: GPU available: False, used: False
lightning: TPU available: False, using: 0 TPU cores
lightning:
| Name | Type | Params
--------------------------------
0 | l1 | Linear | 200 K
1 | l2 | Linear | 2.6 K
--------------------------------
203 K Trainable params
0 Non-trainable params
203 K Total params
0.814 Total estimated model params size (MB)
lightning: Global seed set to 123
Epoch 0: 100%|████████| 3751/3751 [00:20<00:00, 184.89it/s, loss=0.785, v_num=9, step_train/loss=0.762]
lightning: Epoch 0, global step 3437: val/loss reached 0.77671 (best 0.77671), saving model to "/Users/UserName/project_name/logs/run_logs/your_id/version_1/checkpoints/epoch=0-step=3437.ckpt" as top 1
lightning: Saving latest checkpoint...
Epoch 0: 100%|████████| 3751/3751 [00:20<00:00, 184.65it/s, loss=0.785, v_num=9, step_train/loss=0.762]
ride: 🚀 Running evaluation on test set
Testing: 100%|████████| 625/625 [00:01<00:00, 358.86it/s]
-------------------------------------
DATALOADER:0 TEST RESULTS
{'loss': 0.7508705258369446,
'test/loss': 0.7508705258369446,
'test/top1acc': 0.7986000180244446,
'test/top3acc': 0.8528000116348267}
-------------------------------------
ride: 💾 Saving /Users/UserName/project_name/logs/run_logs/your_id/version_1/test_results.yaml
```
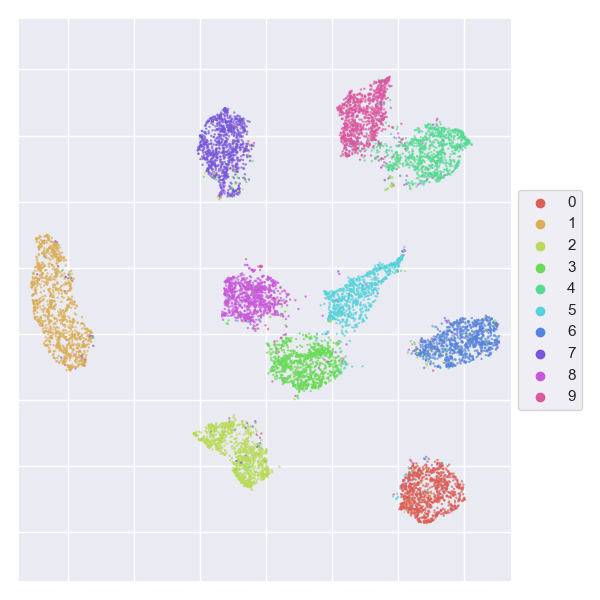
### Feature extraction and visualisation
Extract features after layer `l1` and visualise them with [UMAP](https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.03426).
```shell
$ python simple_classifier.py --train --test --extract_features_after_layer = "l1" --visualise_features = "umap"
```
- _Example output:_
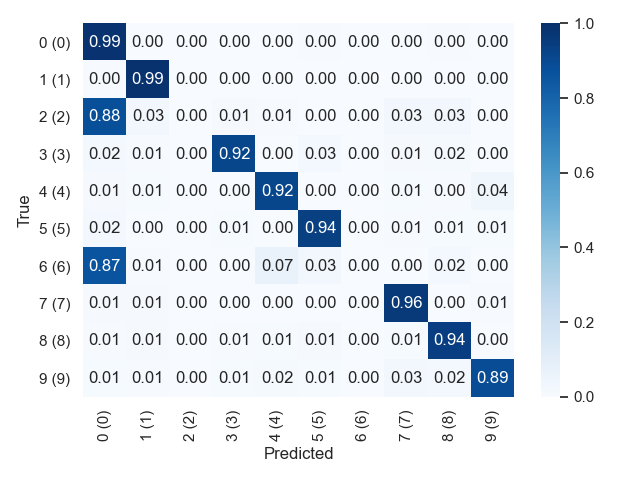
### Confusion matrix visualisation
Plot the confution matrix for the test set.
```shell
$ python simple_classifier.py --train --test --test_confusion_matrix 1
```
- _Example output:_
### Advanced model finetuning
Load model and finetune with [gradual unfreeze and discriminative learning rates](https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.06146)
```shell
$ python simple_classifier.py --train --finetune_from_weights your/path.ckpt --unfreeze_layers_initial 1 --unfreeze_epoch_step 1 --unfreeze_from_epoch 0 --discriminative_lr_fraction 0.1
```
### Hyperparameter optimization
If we want to perform __hyperparameter optimisation__ across four gpus, we can run:
```shell
$ python simple_classifier.py --hparamsearch --gpus 4
```
Curretly, we use [Ray Tune](https://docs.ray.io/en/master/tune.html) and the [ASHA](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.05934) algorithm under the hood.
### Profile model
You can check the __timing__ and __FLOPs__ of the model with:
```shell
$ python simple_classifier.py --profile_model
```
- _Example output:_
```shell
Results:
flops: 203530
machine:
cpu:
architecture: x86_64
cores:
physical: 6
total: 12
frequency: 2.60 GHz
model: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-9750H CPU @ 2.60GHz
gpus: null
memory:
available: 5.17 GB
total: 16.00 GB
used: 8.04 GB
system:
node: d40049
release: 19.6.0
system: Darwin
params: 203530
timing:
batch_size: 16
num_runs: 10000
on_gpu: false
samples_per_second: 88194.303 +/- 17581.377 [20177.049, 113551.377]
time_per_sample: 12.031us +/- 3.736us [8.807us, 49.561us]
```
### Additional options
For additional configuration options, check out the help:
```shell
$ python simple_classifier.py --help
```
- _Truncated output:_
```shell
Flow:
Commands that control the top-level flow of the programme.
--hparamsearch Run hyperparameter search. The best hyperparameters
will be used for subsequent lifecycle methods
--train Run model training
--validate Run model evaluation on validation set
--test Run model evaluation on test set
--profile_model Profile the model
General:
Settings that apply to the programme in general.
--id ID Identifier for the run. If not specified, the current
timestamp will be used (Default: 202101011337)
--seed SEED Global random seed (Default: 123)
--logging_backend {tensorboard,wandb}
Type of experiment logger (Default: tensorboard)
...
Pytorch Lightning:
Settings inherited from the pytorch_lightning.Trainer
...
--gpus GPUS number of gpus to train on (int) or which GPUs to
train on (list or str) applied per node
...
Hparamsearch:
Settings associated with hyperparameter optimisation
...
Module:
Settings associated with the Module
--loss {mse_loss,l1_loss,nll_loss,cross_entropy,binary_cross_entropy,...}
Loss function used during optimisation.
(Default: cross_entropy)
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
Dataloader batch size. (Default: 64)
--num_workers NUM_WORKERS
Number of CPU workers to use for dataloading.
(Default: 10)
--learning_rate LEARNING_RATE
Learning rate. (Default: 0.1)
--weight_decay WEIGHT_DECAY
Weight decay. (Default: 1e-05)
--momentum MOMENTUM Momentum. (Default: 0.9)
--hidden_dim HIDDEN_DIM {128, 256, 512, 1024}
Number of hidden units. (Defualt: 128)
--extract_features_after_layer EXTRACT_FEATURES_AFTER_LAYER
Layer name after which to extract features. Nested
layers may be selected using dot-notation, e.g.
`block.subblock.layer1` (Default: )
--visualise_features {,umap,tsne,pca}
Visualise extracted features using selected
dimensionality reduction method. Visualisations are
created only during evaluation. (Default: )
--finetune_from_weights FINETUNE_FROM_WEIGHTS
Path to weights to finetune from. Allowed extension
include {'.ckpt', '.pyth', '.pth', '.pkl',
'.pickle'}. (Default: )
--unfreeze_from_epoch UNFREEZE_FROM_EPOCH
Number of epochs to wait before starting gradual
unfreeze. If -1, unfreeze is omitted. (Default: -1)
--test_confusion_matrix {0,1}
Create and save confusion matrix for test data.
(Default: 0)
...
```
Though the above `--help` printout was truncated for readibility, there's still a lot going on!
The general structure is a follows:
First, there are flags for controlling the programme flow (e.g. whether to run hparamsearch or training), then some general parameters (id, seed, etc.), all the parameters from Pytorch Lightning, hparamsearch-related arguments, and finally the Module-specific arguments, which we either specified in the `SimpleClassifier` or inherited from the RideModule and mixins.
## Environment
Per default, `Ride` projects are oriented around the current working directory and will save logs in the `~/logs folders`, and cache to `~/.cache`.
This behaviour can be overloaded by changing of the following environment variables (defaults noted):
```bash
ROOT_PATH="~/"
CACHE_PATH=".cache"
DATASETS_PATH="datasets" # Dir relative to ROOT_PATH
LOGS_PATH="logs" # Dir relative to ROOT_PATH
RUN_LOGS_PATH="run_logs" # Dir relative to LOGS_PATH
TUNE_LOGS_PATH="tune_logs"# Dir relative to LOGS_PATH
LOG_LEVEL="INFO" # One of "DEBUG", "INFO", "WARNING", "ERROR", "CRITICAL"
```
## Examples
### Library Examples
- [SimpleClassifier](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/ride/blob/main/examples/simple_classifier.py)
- [MNIST Dataloader](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/ride/blob/main/examples/mnist_dataset.py)
### Community Examples
Video-based human action recognition:
- [I3D](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/co3d/tree/main/models/i3d)
- [R(2+1)D](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/co3d/tree/main/models/r2plus1d)
- [SlowFast](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/co3d/tree/main/models/slowfast)
- [CoSlow](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/co3d/tree/main/models/coslow)
- [X3D](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/co3d/tree/main/models/x3d)
- [CoX3D](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/co3d/tree/main/models/cox3d)
Skeleton-based human action recognition:
- [ST-GCN](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/continual-skeletons/blob/main/models/st_gcn/st_gcn.py)
- [CoST-GCN](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/continual-skeletons/blob/main/models/cost_gcn/cost_gcn.py)
- [A-GCN](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/continual-skeletons/blob/main/models/a_gcn/a_gcn.py)
- [CoA-GCN](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/continual-skeletons/blob/main/models/coa_gcn/coa_gcn.py)
- [S-Tr](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/continual-skeletons/blob/main/models/s_tr/s_tr.py)
- [CoS-Tr](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/continual-skeletons/blob/main/models/cos_tr/cos_tr.py)
## Citation
### BibTeX
If you use `Ride` for your research and feel like citing it, here's a BibTex:
```bibtex
@article{hedegaard2021ride,
title={Ride},
author={Lukas Hedegaard},
journal={GitHub. Note: https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/ride},
year={2021}
}
```
.MD
```md
[](https://github.com/LukasHedegaard/ride)
```