Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/NazmusSayad/rype
Ultra-Fast Type-Optimized Data Validation
https://github.com/NazmusSayad/rype
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Ultra-Fast Type-Optimized Data Validation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/NazmusSayad/rype
- Owner: NazmusSayad
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-06-16T22:22:40.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-01-01T05:50:09.000Z (11 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-01-02T05:32:23.771Z (11 months ago)
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage: https://npmjs.com/package/rype
- Size: 410 KB
- Stars: 11
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
## Rype: Ultra-Fast Type-Optimized Data Validation
**Rype** is not just another validation package; it's a lightning-fast, type-optimized solution designed specifically for TypeScript projects. Unlike other libraries, Rype has been fine-tuned to fully harness the power of TypeScript, providing unparalleled performance and type safety.
### Requirements
- **TypeScript v5+**: Rype is optimized for TypeScript version 5 and above, ensuring compatibility with the latest TypeScript features and improvements.
- **"strictNullChecks": true**: To ensure robust type checking, please set `"strictNullChecks": true` inside your `tsconfig.json` configuration.
## Key Features
- **Blazing Speed**: Rype is optimized for speed, delivering rapid validation results.
- **Minimalistic**: With a compact footprint, it's easy to integrate into your project.
- **Robust Validation**: Comprehensive validation rules for precise data validation.
- **TypeScript Integration**: Rype's type system integration ensures type safety throughout your codebase.
- **Flexibility**: Adaptable to simple data structures or complex objects.
- **Intuitive API**: Developer-friendly API for defining validation schemas.
- **Type Safety**: Rype prioritizes type safety by minimizing the use of "any" types in the codebase, resulting in a more robust and bug-free experience.
## Why Rype?
In today's fast-paced development landscape, every millisecond counts, and type safety is paramount. Rype offers rapid validation with a small footprint, making it ideal for high-performance TypeScript applications, microservices, and projects where efficiency and type correctness are crucial. Elevate your project's performance while keeping your codebase lean and mean with Rype. Try it today and experience the future of type-optimized validation in TypeScript!
### Bundlephobia results:
- **Significantly Compact Size Compared to Alternatives**

Note: This information may be outdated; please refer to the latest version of [Bundlephobia(rype)](https://bundlephobia.com/package/rype@latest) for the most current data.
### Performance Comparison with Others
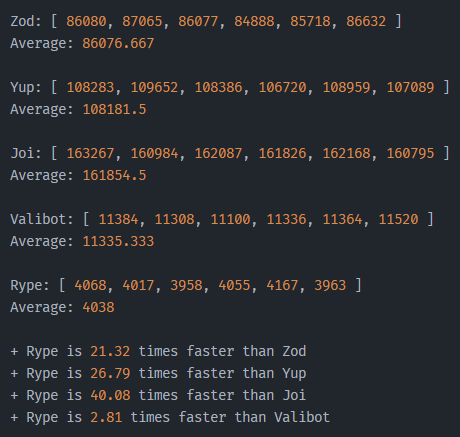
- **Env**: Github Codespace
- **Note**: This benchmark may not accurately represent real-world scenarios. Actual performance may vary, and in many cases, all packages have demonstrated similar speeds. It's worth highlighting that all packages are optimized for speed.
If you'd like to explore and verify these results yourself, you can find the test codes available in the following repository: [rype-benchmark](https://github.com/NazmusSayad/rype-benchmark). This way, you can run the tests and draw your own conclusions.
## Installation
- with npm
```shell
npm i rype
```
- with yarn
```shell
yarn add rype
```
- with pnpm
```shell
pnpm add rype
```
## Example
Here's a simple example demonstrating how to use Rype for data validation in TypeScript.
```ts
import { r } from 'rype'
// Define a schema for a string
const schema = r.string()
// Validate a string
const result1 = schema.parseTyped('My String') // Valid
// Attempt to validate a number (will result in a validation error)
const result2 = schema.parseTyped(100_100_100) // Error - In both runtime and TypeScript type level
```
### Example 1: Primitive
```ts
const schema = r.string('String')
const result = schema.parseTyped('My String')
// Error (TypeScript also provides type-level error)
// 'My String' is not assignable to 'String'
```
```ts
const schema = r.string('String', 'Your String')
const result = schema.parseTyped('My String')
// 'My String' is not assignable to 'String' | 'Your String'
```
Note:
**_You can apply similar checks to `r.number()` and `r.boolean()` as well_**
### Example 2: Object
```ts
const schema = r.object({
name: r.string(),
age: r.number(),
})
schema.parseTyped({
name: 'John Doe',
age: 10,
})
```
### Example 2.5: Record
```ts
const schema = r.record(r.string())
schema.parseTyped({
name: 'John Doe',
father: 'Parent Doe',
})
```
### Example 2.75: Instance
```ts
const schema = r.instance(Array)
schema.parseTyped(['string', 100])
```
### Example 3: Object with Array
```ts
const schema = r.object({
name: r.string(),
age: r.number(),
hobbies: r.array(r.string()),
someValues: r.array(r.string(), r.number()),
})
schema.parseTyped({
name: 'John Doe',
age: 10,
hobbies: ['Cricket', 'Football'],
someValues: ['Cricket', 100],
})
```
### Example 4: Object with Tuple
```ts
const schema = r.object({
name: r.string(),
age: r.number(),
unknown: r.tuple(r.string(), r.number()),
})
schema.parseTyped({
name: 'John Doe',
age: 10,
unknown: ['string', 100],
})
```
### Example 5: Object with Or
```ts
const schema = r.object({
name: r.string(),
age: r.number(),
country: r.or(
r.string('Bangladesh'),
r.object({ name: r.string(), coords: r.number() })
),
})
schema.parseTyped({
name: 'John Doe',
age: 10,
country: { name: 'Arab', coords: 100 },
})
```
### Example 6: Setting Default Values
You can use the `default` method to set default values for fields in your Rype schema.
```ts
const schema = r.object({
name: r.string(),
age: r.number().default(18),
})
const result = schema.parseTyped({
name: 'John Doe',
})
/* Result:
{
name: 'John Doe',
age: 18 // Default value applied
}
*/
```
Note:
- **Works Everywhere**: You can use the `default` method in various situations.
- **Enhanced Type Support**: Type support is seamlessly integrated with the default method.
- **Runtime Consideration**: While Rype generally doesn't examine default values right away, remember that for `object` and `tuple` types, a runtime validation takes place during data parsing. Keep in mind, this validation occurs when you're **parsing data**, not when you **initially set the default value**.
### Example 7: Adding Custom Validation Logic
You can employ the `validate` method to incorporate custom validation logic.
```ts
const schema = r
.object({
name: r.string(),
password: r.string(),
confirmPassword: r.string(),
})
.validate((data) => {
if (data.password !== data.confirmPassword) {
return "Password doesn't matched"
}
})
const result = schema.parseTyped({
name: 'John Doe',
password: 'password',
confirmPassword: 'another',
})
// Error: Password doesn't matched
```
### Example 8: Customizing Error Messages
You can easily set custom error messages for specific cases during runtime checking using Rype.
#### Set custom error when invalid type error occurs
```ts
const schema = r.object({
name: r.string().setTypeErrMsg('Name for user is invalid'),
age: r.number().default(18),
})
const result = schema.parseTyped({ name: 0 })
// Error: Name for user is invalid
```
#### Set custom error when input is null or undefined
```ts
const schema = r.object({
name: r.string().setRequiredErrMsg('User must have a name'),
age: r.number().default(18),
score: r.number().default(() => 100),
})
const result = schema.parseTyped({})
// Error: User must have a name
```
### Available Schema Types
```ts
r.string()
r.number()
r.boolean()
r.tuple()
r.array()
r.object()
r.record()
r.instance()
r.or()
```
### Different Parsing Methods
Rype offers a range of parsing methods that allow you to tailor your data validation process to various scenarios. These methods provide flexibility in handling validation errors and extracting validated data.
#### `.parse`: Runtime Error on Type Mismatch or Missing Schema Type
```ts
const result1 = schema.parse('My String') // Generates a runtime error if types don't match
const result2 = schema.parseTyped('My String') // Generates both runtime and type errors
```
- The `.parse` method triggers a runtime error if there is a type mismatch between the validated value and the schema, or if a type is specified in the schema but the input doesn't match it.
- The `.parseTyped` method additionally provides TypeScript type checking, ensuring type correctness in your codebase.
#### `.filter`: Returns Matched Value or Undefined on Validation Failure
```ts
const result3 = schema.filter('My String') // Returns the validated value or undefined on failure
const result4 = schema.filterTyped('My String') // Generates only a type error
```
- The `.filter` method returns the value if it matches the schema, and returns `undefined` if validation fails for a specific field.
- The `.filterTyped` method performs type checking, providing a TypeScript type error if the validation fails.
#### `.safeParse`: Returns Array with Data and Error
```ts
const result3 = schema.safeParse('My String') // Returns [data, undefined] on success
const result4 = schema.safeParseTyped('My String') // Generates only a type error
```
- The `.safeParse` method returns an array where the first element is the validated data and the second element is `undefined` on successful validation.
- If validation fails, the second element becomes the error output, and the first element is `undefined`.
- The `.safeParseTyped` method provides TypeScript type checking for error handling.
#### `.safeParseList`: Returns Array with Data and Errors
```ts
const result3 = schema.safeParseList('My String') // Returns [data, undefined] on success
const result4 = schema.safeParseListTyped('My String') // Generates only a type error
```
- The `.safeParseList` method returns an array where the first element is the validated data and the second element is `undefined` on successful validation.
- If validation fails, the second element becomes the error output as an array of `RypeError`, and the first element is `undefined`.
- The `.safeParseListTyped` method provides TypeScript type checking for error handling.
These parsing methods empower you to choose the appropriate approach for your validation needs, enhancing the precision and control over your data validation process.
### Complex Example
⚠️: Wear glasses before watching this
```ts
import { r } from 'rype'
r.object({
name: r.string('John Doe'),
age: r.number().optional(),
hobbies: r.tuple(r.string('Play')),
intro: r.object({ address: r.string('BD') }),
jobs: r.tuple(r.object({ name: r.number(200) })),
asdf: r.tuple(r.string()),
}).parseTyped({
age: 0,
name: 'John Doe',
hobbies: ['Play'],
intro: { address: 'BD' },
jobs: [{ name: 200 }],
asdf: ['Boom'],
})
```
# 🚧 More will be added soon
Stay tuned for updates as we enhance and improve the Schema Core library. We appreciate your support in making this tool more powerful and user-friendly.