https://github.com/Oblosys/react-lifecycle-visualizer
Real-time visualizer for React lifecycle methods
https://github.com/Oblosys/react-lifecycle-visualizer
lifecycle-methods react reactjs trace visualizer
Last synced: 11 months ago
JSON representation
Real-time visualizer for React lifecycle methods
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/Oblosys/react-lifecycle-visualizer
- Owner: Oblosys
- License: mit
- Created: 2018-04-18T15:04:10.000Z (almost 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-05-05T17:11:44.000Z (almost 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-10-15T21:42:06.812Z (over 1 year ago)
- Topics: lifecycle-methods, react, reactjs, trace, visualizer
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage: https://codesandbox.io/s/github/Oblosys/react-lifecycle-visualizer/tree/master/examples/parent-child-demo?file=/src/samples/New.js
- Size: 11.4 MB
- Stars: 1,336
- Watchers: 20
- Forks: 38
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-list - react-lifecycle-visualizer - time visualizer for React lifecycle methods | Oblosys | 1246 | (JavaScript)
README
# React Lifecycle Visualizer [](https://www.npmjs.com/package/react-lifecycle-visualizer) [](https://github.com/Oblosys/react-lifecycle-visualizer/actions/workflows/build-test.yml?query=branch/master)
An npm package ([`react-lifecycle-visualizer`](https://www.npmjs.com/package/react-lifecycle-visualizer)) for tracing & visualizing lifecycle methods of React class components. (For function components and hooks, check out [`react-hook-tracer`](https://github.com/Oblosys/react-hook-tracer#readme) instead.)
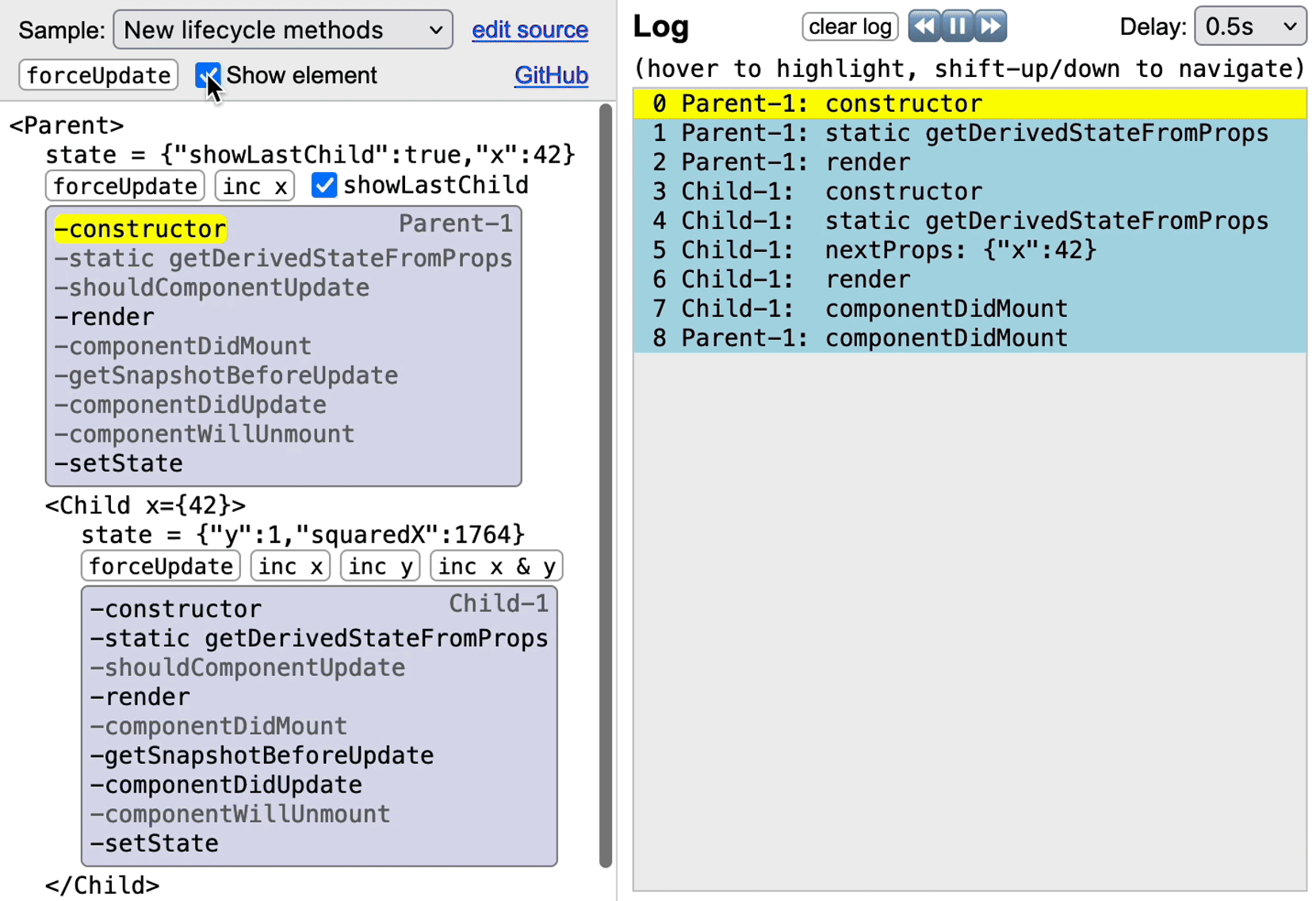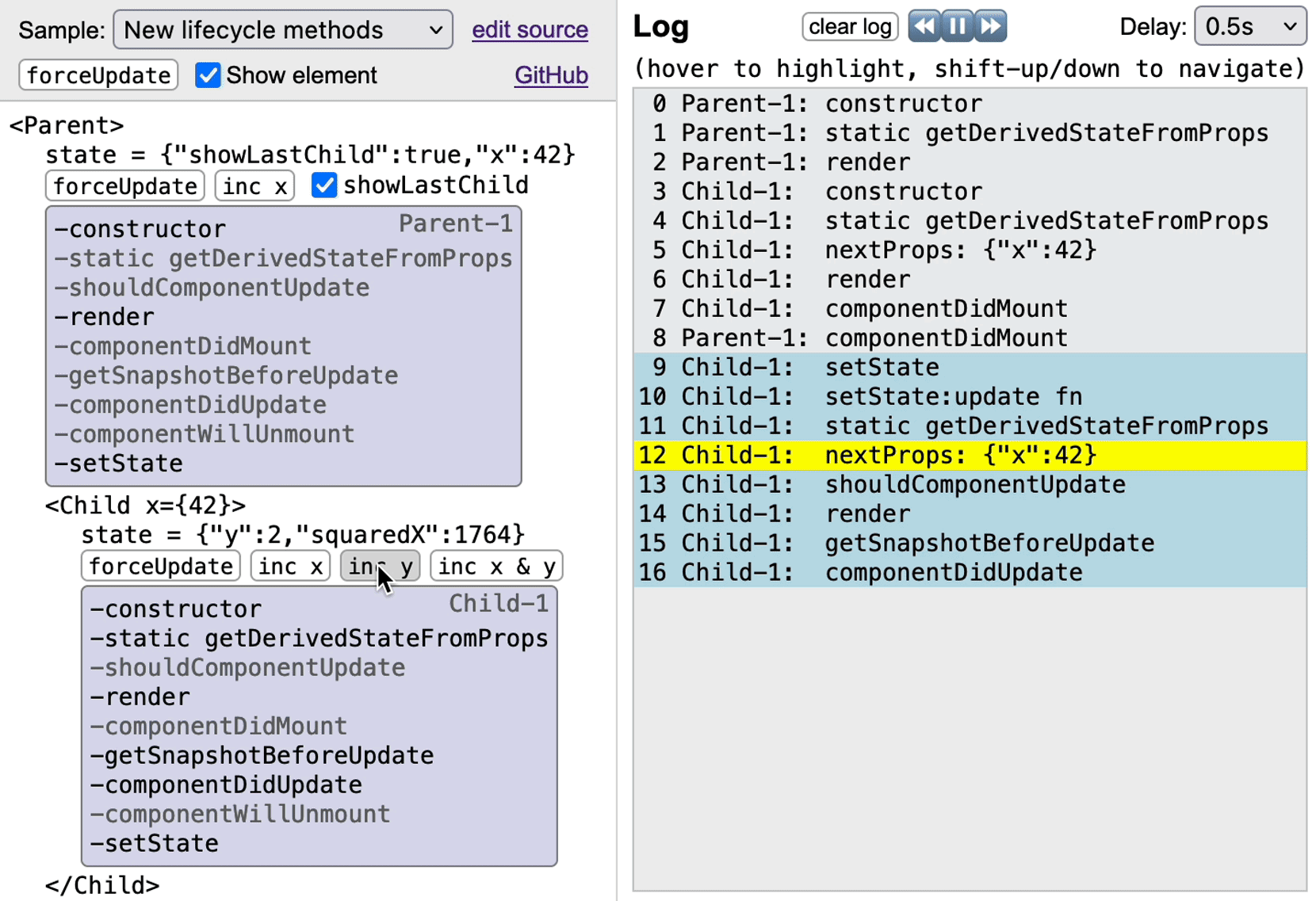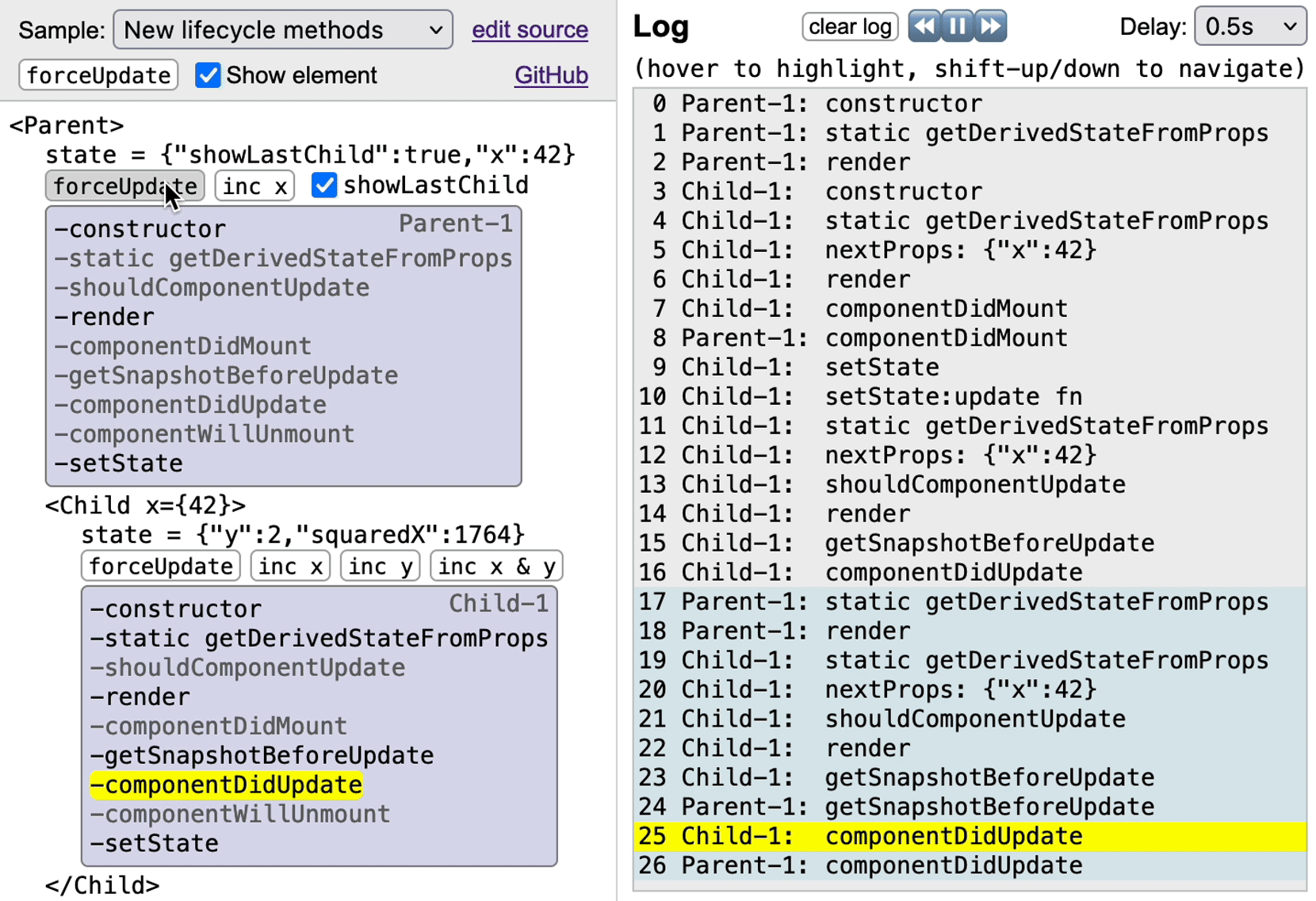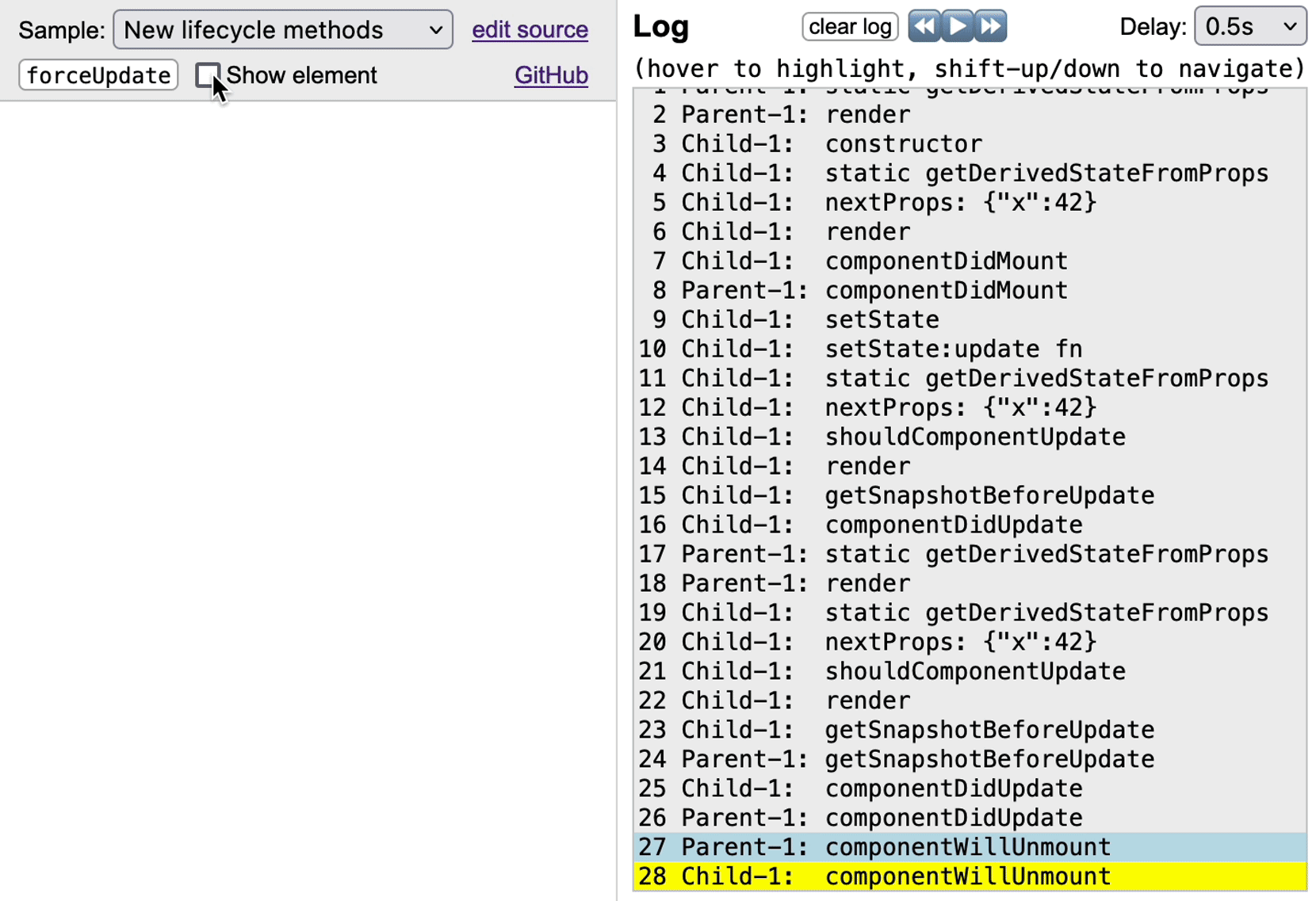
To trace a component, apply the higher-order component `traceLifecycle` to it, and all its lifecycle-method calls will show up in a replayable log component. Additionally, traced components may include a `` element in their rendering to show a panel with lifecycle methods, which are highlighted when the corresponding log entry is selected.
## Usage
The easiest way to get started is to
open the [CodeSandbox playground](https://codesandbox.io/s/github/Oblosys/react-lifecycle-visualizer/tree/master/examples/parent-child-demo?file=/src/samples/New.js) and edit the sample components in `src/samples`. (For a better view of the log, press the 'Open in New Window' button in the top-right corner.)
The panel shows the new React 16.3 lifecycle methods, unless the component defines at least one legacy method and no new methods. On a component that has both legacy and new methods, React ignores the legacy methods, so the panel shows the new methods.
Though technically not lifecycle methods, `setState` & `render` are also traced. A single `setState(update, [callback])` call may generate up to three log entries:
1. `'setState'` for the call itself.
2. If `update` is a function instead of an object, `'setState:update fn'` is logged when that function is evaluated.
3. If a `callback` function is provided, `'setState:callback'` is logged when it's called.
To save space, the lifecycle panel only contains `setState`, which gets highlighted on any of the three events above.
## Run the demo locally
To run a local copy of the CodeSandbox demo, simply clone the repo, and run `npm install` & `npm start`:
```
git clone git@github.com:Oblosys/react-lifecycle-visualizer.git
cd react-lifecycle-visualizer
npm install
npm start
```
The demo runs on http://localhost:8000/.
## Using the npm package
```sh
$ npm i react-lifecycle-visualizer
```
#### Setup
To set up tracing, wrap the root or some other ancestor component in a `` and include the `` component somewhere. For example:
```jsx
import { Log, VisualizerProvider } from 'react-lifecycle-visualizer';
ReactDom.render(
,
document.getElementById('root')
);
```
If you're using a WebPack dev-server with hot reloading, you can include a call to `resetInstanceIdCounters` in the module where you set up hot reloading:
```jsx
import { resetInstanceIdCounters } from 'react-lifecycle-visualizer';
..
resetInstanceIdCounters(); // reset instance counters on hot reload
..
```
This isn't strictly necessary, but without it, instance counters will keep increasing on each hot reload, making the log less readable.
#### Tracing components
To trace a component (e.g. `ComponentToTrace`,) apply the `traceLifecycle` HOC to it. This is most easily done with a decorator.
```jsx
import { traceLifecycle } from 'react-lifecycle-visualizer';
..
@traceLifecycle
class ComponentToTrace extends React.Component {
..
render() {
return (
..
..
);
}
}
```
Alternatively, apply `traceLifecycle` directly to the class, like this:
```jsx
const ComponentToTrace = traceLifecycle(class ComponentToTrace extends React.Component {...});
```
or
```jsx
class ComponentToTraceOrg extends React.Component {...}
const ComponentToTrace = traceLifecycle(ComponentToTraceOrg);
```
#### Traced component props: `LifecyclePanel` and `trace`
The traced component receives two additional props: `LifecyclePanel` and `trace`. The `LifecyclePanel` prop is a component that can be included in the rendering with `` to display the lifecycle methods of the traced component.
```jsx
render() {
return (
..
..
);
}
```
The `trace` prop is a function of type `(msg: string) => void` that can be used to log custom messages:
```jsx
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
this.props.trace('prevProps: ' + JSON.stringify(prevProps));
}
```
In the constructor we can use `this.props.trace` after the call to `super`, or access `trace` on the `props` parameter:
```jsx
constructor(props) {
props.trace('before super(props)');
super(props);
this.props.trace('after super(props)');
}
```
In the static `getDerivedStateFromProps` we cannot use `this` to refer to the component instance, but we can access `trace` on the `nextProps` parameter:
```jsx
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) {
nextProps.trace('nextProps: ' + JSON.stringify(nextProps));
..
}
```
## TypeScript
There's no need to install additional TypeScript typings, as these are already included in the package. The interface `TraceProps` declares the `trace` and `LifecyclePanel` props. Its definition is
```typescript
export interface TraceProps {
trace: (msg: string) => void,
LifecyclePanel : React.SFC
}
```
With the exception of tracing a component, the TypeScript setup is the same as the JavaScript setup above. Here's an example of a traced component in TypeScript:
```jsx
import { traceLifecycle, TraceProps } from 'react-lifecycle-visualizer';
..
interface ComponentToTraceProps extends TraceProps {}; // add trace & LifecyclePanel props
interface ComponentToTraceState {}
class ComponentToTrace extends React.Component {
constructor(props: ComponentToTraceProps, context?: any) {
props.trace('before super(props)');
super(props, context);
this.props.trace('after super(props)');
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps : ComponentToTraceProps, nextState: ComponentToTraceState) {
nextProps.trace('deriving');
return null;
}
render() {
return ;
}
}
```
The only difference is that we cannot use `traceLifecycle` as a decorator in TypeScript, because it changes the signature of the parameter class (see this [issue](https://github.com/DefinitelyTyped/DefinitelyTyped/issues/20796)). Instead, we simply apply it as a function:
```tsx
const TracedComponent = traceLifecycle(ComponentToTrace);
```