https://github.com/PAIR-code/lit
The Learning Interpretability Tool: Interactively analyze ML models to understand their behavior in an extensible and framework agnostic interface.
https://github.com/PAIR-code/lit
machine-learning natural-language-processing visualization
Last synced: 11 months ago
JSON representation
The Learning Interpretability Tool: Interactively analyze ML models to understand their behavior in an extensible and framework agnostic interface.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/PAIR-code/lit
- Owner: PAIR-code
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2020-07-28T13:07:26.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-10-29T11:46:49.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-10-29T14:51:41.548Z (over 1 year ago)
- Topics: machine-learning, natural-language-processing, visualization
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage: https://pair-code.github.io/lit
- Size: 202 MB
- Stars: 3,482
- Watchers: 67
- Forks: 355
- Open Issues: 116
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-xai - LIT
- Awesome-explainable-AI - https://github.com/PAIR-code/lit - code/lit?style=social) (Python Libraries(sort in alphabeta order) / Evaluation methods)
- awesome-list - Language Interpretability Tool - Interactively analyze NLP models for model understanding in an extensible and framework agnostic interface. (Natural Language Processing / Others)
- awesome-ai-research-tools - LIT (Language Interpretability Tool)
- awesome-list - lit - code | 2627 | (TypeScript)
- awesome-python-machine-learning-resources - GitHub - 37% open · ⏱️ 15.03.2022): (模型的可解释性)
- StarryDivineSky - PAIR-code/lit
README
# 🔥 Learning Interpretability Tool (LIT)
The Learning Interpretability Tool (🔥LIT, formerly known as the Language
Interpretability Tool) is a visual, interactive ML model-understanding tool that
supports text, image, and tabular data. It can be run as a standalone server, or
inside of notebook environments such as Colab, Jupyter, and Google Cloud Vertex
AI notebooks.
LIT is built to answer questions such as:
* **What kind of examples** does my model perform poorly on?
* **Why did my model make this prediction?** Can this prediction be attributed
to adversarial behavior, or to undesirable priors in the training set?
* **Does my model behave consistently** if I change things like textual style,
verb tense, or pronoun gender?
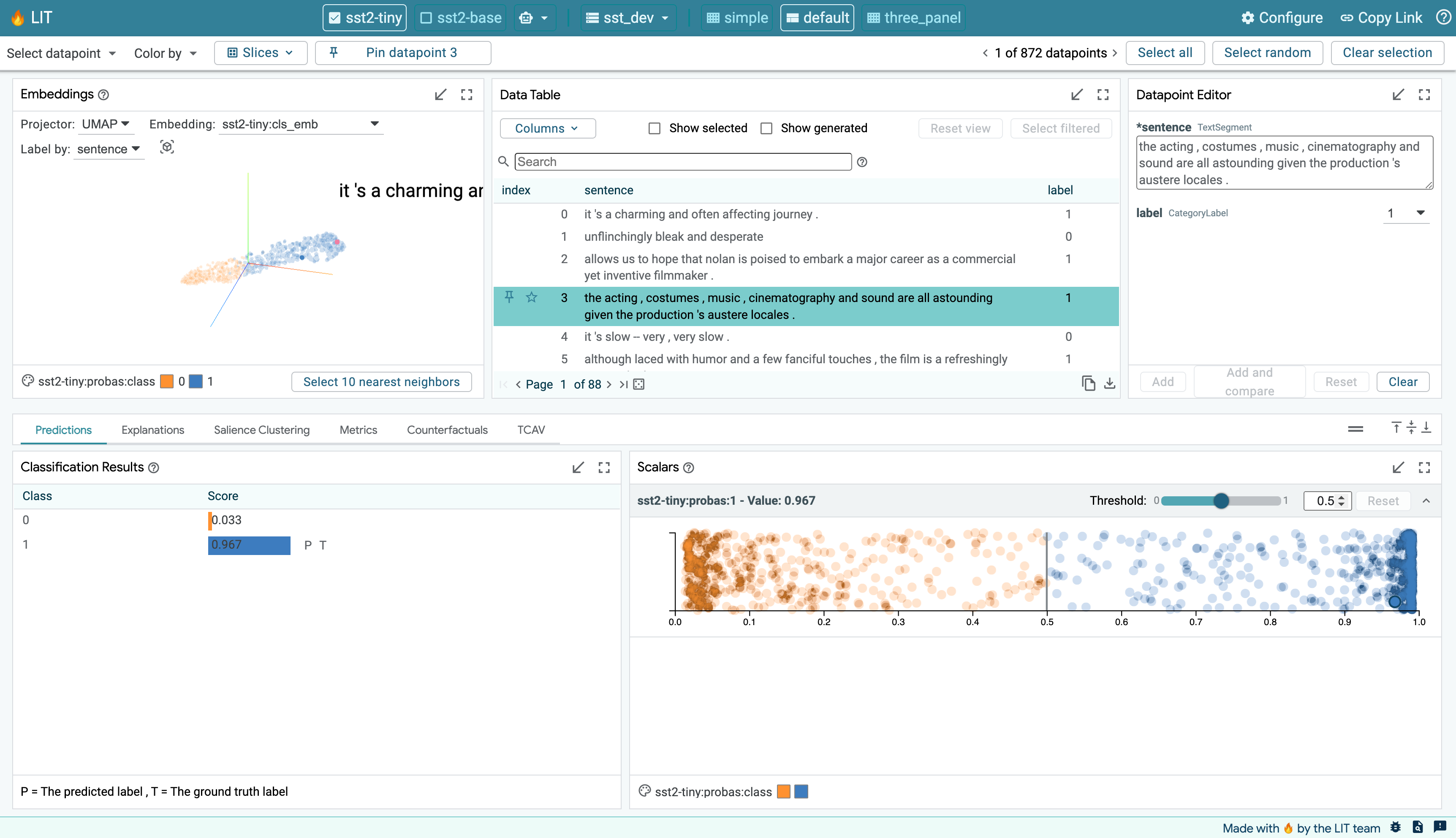
LIT supports a variety of debugging workflows through a browser-based UI.
Features include:
* **Local explanations** via salience maps and rich visualization of model
predictions.
* **Aggregate analysis** including custom metrics, slicing and binning, and
visualization of embedding spaces.
* **Counterfactual generation** via manual edits or generator plug-ins to
dynamically create and evaluate new examples.
* **Side-by-side mode** to compare two or more models, or one model on a pair
of examples.
* **Highly extensible** to new model types, including classification,
regression, span labeling, seq2seq, and language modeling. Supports
multi-head models and multiple input features out of the box.
* **Framework-agnostic** and compatible with TensorFlow, PyTorch, and more.
LIT has a [website](https://pair-code.github.io/lit) with live demos, tutorials,
a setup guide and more.
Stay up to date on LIT by joining the
[lit-announcements mailing list](https://groups.google.com/g/lit-annoucements).
For a broader overview, check out [our paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.05122) and the
[user guide](https://pair-code.github.io/lit/documentation/ui_guide).
## Documentation
* [Documentation index](https://pair-code.github.io/lit/documentation/)
* [FAQ](https://pair-code.github.io/lit/documentation/faq)
* [Release notes](./RELEASE.md)
## Download and Installation
LIT can be installed via `pip` or built from source. Building from source is
necessary if you want to make code changes.
### Install from PyPI with pip
```sh
pip install lit-nlp
```
The default `pip` installation will install all required packages to use the LIT
Python API, built-in interpretability components, and web application. To
install dependencies for the provided demos or test suite, install LIT with the
appropriate optional dependencies.
```sh
# To install dependencies for the discriminative AI examples (GLUE, Penguin)
pip install 'lit-nlp[examples-discriminative-ai]'
# To install dependencies for the generative AI examples (Prompt Debugging)
pip install 'lit-nlp[examples-generative-ai]'
# To install dependencies for all examples plus the test suite
pip install 'lit-nlp[test]'
```
### Install from source
Clone the repo:
```sh
git clone https://github.com/PAIR-code/lit.git
cd lit
```
Note: be sure you are running Python 3.9+. If you have a different version on
your system, use the `conda` instructions below to set up a Python 3.9
environment.
Set up a Python environment with `venv` (or your preferred environment manager).
Note that these instructions assume you will be making code changes to LIT and
includes the full requirements for all examples and the test suite. See the
other optional dependency possibilities in the install with pip section.
```sh
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
python -m pip install -e '.[test]'
```
The LIT repo does not include a distributable version of the LIT app. You must
build it from source.
```sh
(cd lit_nlp; yarn && yarn build)
```
Note: if you see [an error](https://github.com/yarnpkg/yarn/issues/2821)
running `yarn` on Ubuntu/Debian, be sure you have the
[correct version installed](https://yarnpkg.com/en/docs/install#linux-tab).
## Running LIT
Explore a collection of hosted demos on the
[demos page](https://pair-code.github.io/lit/demos).
### Using container images
See the [containerization guide](https://pair-code.github.io/lit/documentation/docker) for instructions on using LIT
locally in Docker, Podman, etc.
LIT also provides pre-built images that can take advantage of accelerators,
making Generative AI and LLM use cases easier to work with. Check out the
[LIT on GCP docs](https://codelabs.developers.google.com/codelabs/responsible-ai/lit-on-gcp)
for more.
### Quick-start: classification and regression
To explore classification and regression models tasks from the popular
[GLUE benchmark](https://gluebenchmark.com/):
```sh
python -m lit_nlp.examples.glue.demo --port=5432 --quickstart
```
Navigate to http://localhost:5432 to access the LIT UI.
Your default view will be a
[small BERT-based model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.08962) fine-tuned on the
[Stanford Sentiment Treebank](https://nlp.stanford.edu/sentiment/treebank.html),
but you can switch to
[STS-B](http://ixa2.si.ehu.es/stswiki/index.php/STSbenchmark) or
[MultiNLI](https://cims.nyu.edu/~sbowman/multinli/) using the toolbar or the
gear icon in the upper right.
And navigate to http://localhost:5432 for the UI.
### Notebook usage
Colab notebooks showing the use of LIT inside of notebooks can be found at
[lit_nlp/examples/notebooks](./lit_nlp/examples/notebooks).
We provide a simple
[Colab demo](https://colab.research.google.com/github/PAIR-code/lit/blob/main/lit_nlp/examples/notebooks/LIT_sentiment_classifier.ipynb).
Run all the cells to see LIT on an example classification model in the notebook.
### More Examples
See [lit_nlp/examples](./lit_nlp/examples). Most are run similarly to the
quickstart example above:
```sh
python -m lit_nlp.examples..demo --port=5432 [optional --args]
```
## User Guide
To learn about LIT's features, check out the [user guide](https://pair-code.github.io/lit/documentation/ui_guide), or
watch this [video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CuRI_VK83dU).
## Adding your own models or data
You can easily run LIT with your own model by creating a custom `demo.py`
launcher, similar to those in [lit_nlp/examples](./lit_nlp/examples). The
basic steps are:
* Write a data loader which follows the [`Dataset` API](https://pair-code.github.io/lit/documentation/api#datasets)
* Write a model wrapper which follows the [`Model` API](https://pair-code.github.io/lit/documentation/api#models)
* Pass models, datasets, and any additional
[components](https://pair-code.github.io/lit/documentation/api#interpretation-components) to the LIT server class
For a full walkthrough, see
[adding models and data](https://pair-code.github.io/lit/documentation/api#adding-models-and-data).
## Extending LIT with new components
LIT is easy to extend with new interpretability components, generators, and
more, both on the frontend or the backend. See our [documentation](https://pair-code.github.io/lit/documentation/) to get
started.
## Pull Request Process
To make code changes to LIT, please work off of the `dev` branch and
[create pull requests](https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests/creating-a-pull-request)
(PRs) against that branch. The `main` branch is for stable releases, and it is
expected that the `dev` branch will always be ahead of `main`.
[Draft PRs](https://github.blog/2019-02-14-introducing-draft-pull-requests/) are
encouraged, especially for first-time contributors or contributors working on
complex tasks (e.g., Google Summer of Code contributors). Please use these to
communicate ideas and implementations with the LIT team, in addition to issues.
Prior to sending your PR or marking a Draft PR as "Ready for Review", please run
the Python and TypeScript linters on your code to ensure compliance with
Google's [Python](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html) and
[TypeScript](https://google.github.io/styleguide/tsguide.html) Style Guides.
```sh
# Run Pylint on your code using the following command from the root of this repo
(cd lit_nlp; pylint)
# Run ESLint on your code using the following command from the root of this repo
(cd lit_nlp; yarn lint)
```
## Citing LIT
If you use LIT as part of your work, please cite the
[EMNLP paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.05122) or the
[Sequence Salience paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.07498)
```BibTeX
@misc{tenney2020language,
title={The Language Interpretability Tool: Extensible, Interactive Visualizations and Analysis for {NLP} Models},
author={Ian Tenney and James Wexler and Jasmijn Bastings and Tolga Bolukbasi and Andy Coenen and Sebastian Gehrmann and Ellen Jiang and Mahima Pushkarna and Carey Radebaugh and Emily Reif and Ann Yuan},
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations",
year = "2020",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
pages = "107--118",
url = "https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.emnlp-demos.15",
}
```
```BibTeX
@article{tenney2024interactive,
title={Interactive prompt debugging with sequence salience},
author={Tenney, Ian and Mullins, Ryan and Du, Bin and Pandya, Shree and Kahng, Minsuk and Dixon, Lucas},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.07498},
year={2024}
}
```
## Disclaimer
This is not an official Google product.
LIT is a research project and under active development by a small team. We want
LIT to be an open platform, not a walled garden, and would love your suggestions
and feedback – please
[report any bugs](https://github.com/pair-code/lit/issues) and reach out on the
[Discussions page](https://github.com/PAIR-code/lit/discussions/landing).