https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShellEditorServices
A common platform for PowerShell development support in any editor or application!
https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShellEditorServices
debugger intellisense language-server-protocol powershell
Last synced: 12 months ago
JSON representation
A common platform for PowerShell development support in any editor or application!
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShellEditorServices
- Owner: PowerShell
- License: mit
- Created: 2015-05-21T18:54:08.000Z (almost 11 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-18T21:19:17.000Z (12 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-22T10:01:42.277Z (12 months ago)
- Topics: debugger, intellisense, language-server-protocol, powershell
- Language: C#
- Homepage:
- Size: 8.32 MB
- Stars: 671
- Watchers: 57
- Forks: 231
- Open Issues: 179
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
- Codeowners: .github/CODEOWNERS
- Security: SECURITY.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-starred-test - PowerShell/PowerShellEditorServices - A common platform for PowerShell development support in any editor or application! (C# #)
README
# PowerShell Editor Services
[](https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShellEditorServices/actions/workflows/ci-test.yml)
[](https://aka.ms/psdiscord)
[](https://gitter.im/PowerShell/PowerShellEditorServices?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge)
**PowerShell Editor Services** is a PowerShell module that provides common
functionality needed to enable a consistent and robust PowerShell development
experience in almost any editor or integrated development environment (IDE).
## [Language Server Protocol](https://microsoft.github.io/language-server-protocol/) clients using PowerShell Editor Services:
The functionality in PowerShell Editor Services is available in the following editor extensions:
- [PowerShell for Visual Studio Code](https://github.com/PowerShell/vscode-powershell), also available in Azure Data Studio
- [lsp-pwsh](https://github.com/emacs-lsp/lsp-mode/blob/master/clients/lsp-pwsh.el), an Emacs PowerShell plugin
- [intellij-powershell](https://github.com/ant-druha/intellij-powershell), adds PowerShell language support to IntelliJ-based IDEs
- [coc-powershell](https://github.com/yatli/coc-powershell), a Vim and Neovim plugin
- [powershell.nvim](https://github.com/TheLeoP/powershell.nvim) a Neovim plugin
Please note that other than PowerShell for Visual Studio Code, these clients are community maintained and may be very out of date.
It is recommended that you simply use an LSP plugin for your editor and configure it as demonstrated [below](#Usage).
## Features
- The Language Service provides common editor features for the PowerShell language:
- Code navigation actions (find references, go to definition)
- Statement completions (IntelliSense)
- Real-time semantic analysis of scripts using PowerShell Script Analyzer
- The Debugging Service simplifies interaction with the PowerShell debugger (breakpoints, variables, call stack, etc.)
- The [$psEditor API](docs/guide/extensions.md) enables scripting of the host editor
- A full, Extension Terminal experience for interactive development and debugging
## Usage
If you're looking to integrate PowerShell Editor Services into your [Language Server Protocol](https://microsoft.github.io/language-server-protocol/) compliant editor or client,
we support two ways of connecting.
### Named Pipes / Unix Domain Sockets
If you're looking for a more feature-rich experience,
named pipes (AKA sockets) are the way to go.
They give you all the benefits of the Language Server Protocol with extra capabilities that you can take advantage of:
- The PowerShell Extension Terminal
- Debugging using the [Debug Adapter Protocol](https://microsoft.github.io/debug-adapter-protocol/)
The typical command to start PowerShell Editor Services using named pipes / sockets is as follows:
```powershell
pwsh -NoLogo -NoProfile -Command "./PowerShellEditorServices/Start-EditorServices.ps1 -SessionDetailsPath ./session.json"
```
The start script, `Start-EditorServices.ps1`, is found in the `PowerShellEditorServices` folder instead the `PowerShellEditorServices.zip` downloaded from the GitHub releases.
The session details (which named pipes were created) will be written to the given session details path,
and the client needs to point to these in order to connect.
The Visual Studio Code, Vim, Neovim, and IntelliJ extensions use named pipes.
### Standard Input and Output
Alternatively, the `-SessionDetailsPath ./session.json` argument can be replaced with just `-Stdio`.
The use of stdio is the _simplest_ way to connect with most LSP clients,
but will limit some features, such as the debugger and Extension Terminal.
This is because because these two features require their own IO streams and stdio only provides a single pair of streams.
Please see the [emacs-simple-test.el](test/emacs-simple-test.el),
[emacs-test.el](test/emacs-test.el),
[vim-simple-test.vim](test/vim-simple-test.vim) and [vim-test.vim](test/vim-test.vim) for examples of end-to-end tested configurations.
They use [eglot for Emacs](https://github.com/joaotavora/eglot) and [LanguageClient-neovim](https://github.com/autozimu/LanguageClient-neovim).
### Advanced Usage
If you are trying to automate the service in PowerShell, you can also run it under `Start-Process` to prevent hanging your script.
It also gives you access to process automation features like `$process.Close()` or `$process.Kill()`.
The `Start-EditorServices.ps1` script takes many more optional arguments, but they no longer _need_ to be specified.
```powershell
$command = @(
"$PSES_BUNDLE_PATH/PowerShellEditorServices/Start-EditorServices.ps1",
"-BundledModulesPath $PSES_BUNDLE_PATH",
"-LogPath ./logs",
"-SessionDetailsPath ./session.json",
"-FeatureFlags @()",
"-AdditionalModules @()",
"-HostName 'My Client'",
"-HostProfileId 'myclient'",
"-HostVersion 1.0.0",
"-LogLevel Diagnostic"
) -join " "
$pwsh_arguments = "-NoLogo -NoProfile -Command $command"
$process = Start-Process pwsh -ArgumentList $arguments -PassThru
...
$process.Close(); #$process.Kill();
```
Once the command is run,
PowerShell Editor Services will wait until the client connects to the named pipe.
The `session.json` will contain the paths of the named pipes that you will connect to.
There will be one you immediately connect to for Language Server Protocol messages,
and once you connect to when you launch the debugger for Debug Adapter Protocol messages.
### PowerShell Extension Terminal
The PowerShell Extension Terminal uses the host process' stdio streams for console input and output.
Please note that this is mutually exclusive from using stdio for the Language Server Protocol messages.
If you want to take advantage of the PowerShell Extension Terminal,
you must include the `-EnableConsoleRepl` switch when calling `Start-EditorServices.ps1`.
This is typically used if your client can create arbitrary terminals in the editor like below:
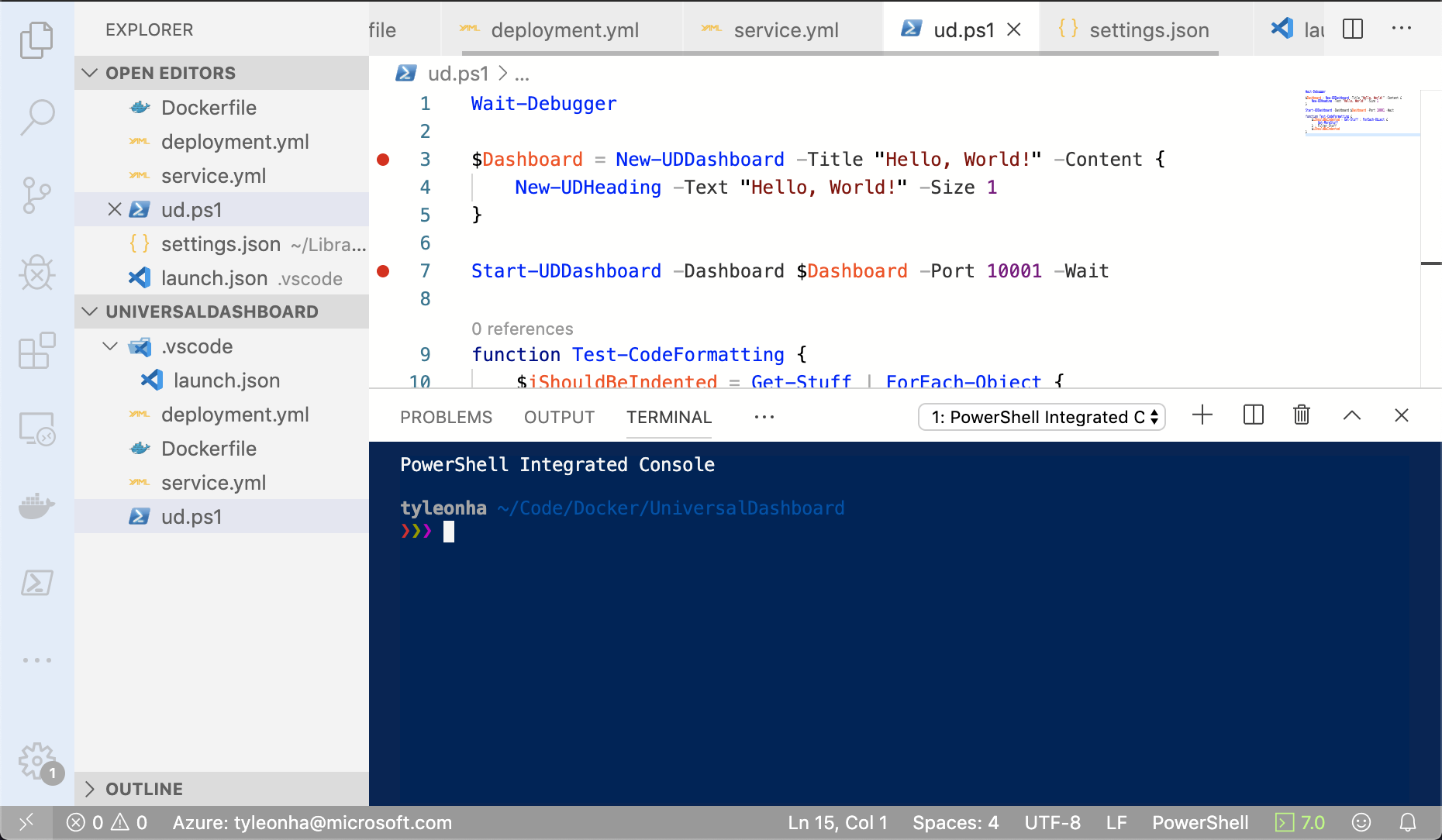
The Visual Studio Code, Vim, and IntelliJ extensions currently use the PowerShell Extension Terminal.
### Debugging
Debugging support is also exposed with PowerShell Editor Services.
It is handled within the same process as the Language Server Protocol.
This provides a more integrated experience for end users but is something to note as not many other language servers work in the same way.
If you want to take advantage of debugging,
your client must support the [Debug Adapter Protocol](https://microsoft.github.io/debug-adapter-protocol/).
Your client should use the path to the debug named pipe found in the `session.json` file talked about above.
The debugging functionality in PowerShell Editor Services is available in the following editor extensions:
- [PowerShell for Visual Studio Code](https://github.com/PowerShell/vscode-powershell)
- [nvim-dap-powershell for Neovim](https://github.com/Willem-J-an/nvim-dap-powershell)
- [powershell.nvim for Neovim](https://github.com/TheLeoP/powershell.nvim)
- [intellij-powershell](https://github.com/ant-druha/intellij-powershell)
## API Usage
Please note that we only consider the following as stable APIs that can be relied on:
- Language Server Protocol connection
- Debug Adapter Protocol connection
- Start-up mechanism
The types of PowerShell Editor Services can change at any moment and should not be linked against in a production environment.
## Development
> NOTE: The easiest way to manually test changes you've made in PowerShellEditorServices is to follow the [vscode-powershell development doc](https://github.com/PowerShell/vscode-powershell/blob/main/docs/development.md) to get a local build of the VS Code extension to use your local build of PowerShellEditorServices.
### 1. Install PowerShell 7+
Install PowerShell 7+ with [these instructions](https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell#get-powershell).
### 2. Clone the GitHub repository
```powershell
git clone https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShellEditorServices.git
```
### 3. Install [Invoke-Build](https://github.com/nightroman/Invoke-Build)
```powershell
Install-Module InvokeBuild -Scope CurrentUser
Install-Module platyPS -Scope CurrentUser
```
### 4. Delete `NuGet.Config`
Our NuGet configuration points to a private feed necessary for secure builds,
and it must be committed to the repo as it is.
The easiest way to build without access to that private feed is to delete the file:
```powershell
Remove-Item NuGet.Config
```
Please be careful not to commit this change in a PR.
Now you're ready to build the code.
You can do so in one of two ways:
### Building the code from PowerShell
```powershell
PS C:\path\to\PowerShellEditorServices> Invoke-Build Build
```
### Building the code from Visual Studio Code
Open the PowerShellEditorServices folder that you cloned locally and press Ctrl+Shift+B
(or Cmd+Shift+B on macOS).
## Code of Conduct
Please see our [Code of Conduct](CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md) before participating in this project.
## Contributions Welcome
We would love to incorporate community contributions into this project. If you would like to
contribute code, documentation, tests, or bug reports, please read our [Contribution Guide](CONTRIBUTING.md) to learn more.
## Security Note
For any security issues, please see [here](SECURITY.md).
## Maintainers
- Andy Jordan - [@andyleejordan](https://github.com/andyleejordan)
- Patrick Meinecke - [@SeeminglyScience](https://github.com/SeeminglyScience)
- Sydney Smith - [@SydneyhSmith](https://github.com/SydneyhSmith)
- Justin Grote - [@JustinGrote](https://github.com/JustinGrote)
### Emeriti
- Rob Holt - [@rjmholt](https://github.com/rjmholt)
- Tyler Leonhardt - [@TylerLeonhardt](https://github.com/TylerLeonhardt)
- David Wilson - [@daviwil](https://github.com/daviwil)
## License
This project is [licensed under the MIT License](LICENSE). Please see the
[third-party notices](NOTICE.txt) file for details on the third-party
binaries that we include with releases of this project.