https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie
C++ implementation of a fast and memory efficient HAT-trie
https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie
c-plus-plus cpp data-structures hat-trie header-only trie
Last synced: 12 months ago
JSON representation
C++ implementation of a fast and memory efficient HAT-trie
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie
- Owner: Tessil
- License: mit
- Created: 2017-04-20T14:38:53.000Z (almost 9 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-02-10T15:03:55.000Z (about 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-02-16T07:36:58.197Z (about 2 years ago)
- Topics: c-plus-plus, cpp, data-structures, hat-trie, header-only, trie
- Language: C++
- Size: 957 KB
- Stars: 753
- Watchers: 36
- Forks: 114
- Open Issues: 8
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- fucking-awesome-cpp - hat-trie - C++ implementation of a fast and memory efficient HAT-trie. [MIT] (Containers)
- awesome-cpp - hat-trie - C++ implementation of a fast and memory efficient HAT-trie. [MIT] (Containers)
- awesome-cpp-with-stars - hat-trie - trie. [MIT] | 2025-11-11 | (Containers)
README
[](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie/actions/workflows/ci.yml)
## A C++ implementation of a fast and memory efficient HAT-trie
Trie implementation based on the "HAT-trie: A Cache-conscious Trie-based Data Structure for Strings." (Askitis Nikolas and Sinha Ranjan, 2007) paper. For now, only the pure HAT-trie has been implemented, the hybrid version may arrive later. Details regarding the HAT-trie data structure can be found [here](https://tessil.github.io/2017/06/22/hat-trie.html).
The library provides an efficient and compact way to store a set or a map of strings by compressing the common prefixes. It also allows to search for keys that match a prefix. Note though that the default parameters of the structure are geared toward optimizing exact searches, if you do a lot of prefix searches you may want to reduce the burst threshold through the `burst_threshold` method.
It's a well adapted structure to store a large number of strings.
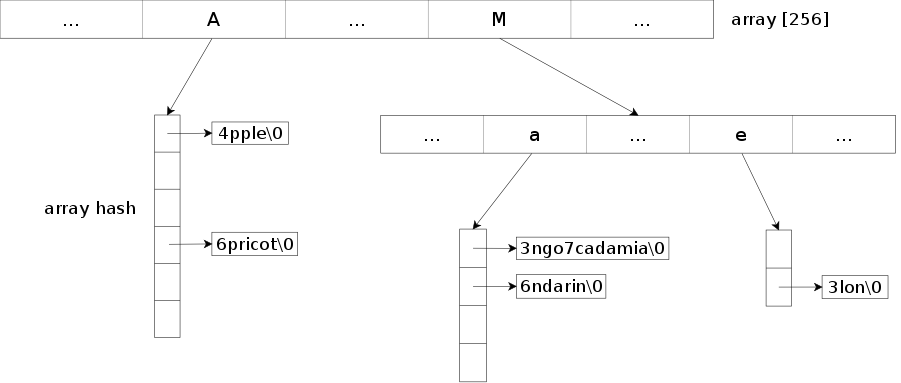
For the array hash part, the [array-hash](https://github.com/Tessil/array-hash) project is used and included in the repository.
The library provides two classes: `tsl::htrie_map` and `tsl::htrie_set`.
### Overview
- Header-only library, just add the [include](include/) directory to your include path and you are ready to go. If you use CMake, you can also use the `tsl::hat_trie` exported target from the [CMakeLists.txt](CMakeLists.txt).
- Low memory usage while keeping reasonable performances (see [benchmark](#benchmark)).
- Support prefix searches through `equal_prefix_range` (useful for autocompletion for example) and prefix erasures through `erase_prefix`.
- Support longest matching prefix searches through `longest_prefix`.
- Support for efficient serialization and deserialization (see [example](#serialization) and the `serialize/deserialize` methods in the [API](https://tessil.github.io/hat-trie/doc/html/classtsl_1_1htrie__map.html) for details).
- Keys are not ordered as they are partially stored in a hash map.
- All operations modifying the data structure (insert, emplace, erase, ...) invalidate the iterators.
- Support null characters in the key (you can thus store binary data in the trie).
- Support for any type of value as long at it's either copy-constructible or both nothrow move constructible and nothrow move assignable.
- The balance between speed and memory usage can be modified through the `max_load_factor` method. A lower max load factor will increase the speed, a higher one will reduce the memory usage. Its default value is set to 8.0.
- The default burst threshold, which is the maximum size of an array hash node before a burst occurs, is set to 16 384 which provides good performances for exact searches. If you mainly use prefix searches, you may want to reduce it to something like 1024 or lower for faster iteration on the results through the `burst_threshold` method.
- By default the maximum allowed size for a key is set to 65 535. This can be raised through the `KeySizeT` template parameter.
Thread-safety and exception guarantees are similar to the STL containers.
### Hash function
The default hash function used by the structure depends on the presence of `std::string_view`. If it is available, `std::hash` is used, otherwise a simple [FNV-1a](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fowler%E2%80%93Noll%E2%80%93Vo_hash_function#FNV-1a_hash) hash function is used to avoid any dependency.
If you can't use C++17 or later, we recommend to replace the hash function with something like [CityHash](https://github.com/google/cityhash), MurmurHash, [FarmHash](https://github.com/google/farmhash), ... for better performances. On the tests we did, CityHash64 offers a ~20% improvement on reads compared to FNV-1a.
```c++
#include
struct str_hash {
std::size_t operator()(const char* key, std::size_t key_size) const {
return CityHash64(key, key_size);
}
};
tsl::htrie_map map;
```
The `std::hash` can't be used efficiently as the structure doesn't store any `std::string` object. Any time a hash would be needed, a temporary `std::string` would have to be created.
### Benchmark
#### Wikipedia dataset
The benchmark consists in inserting all the titles from the main namespace of the Wikipedia archive into the data structure, check the used memory space after the insert (including potential memory fragmentation) and search for all the titles again in the data structure. The peak memory usage during the insert process is also measured with [time(1)](https://linux.die.net/man/1/time).
* Dataset: [enwiki-20170320-all-titles-in-ns0.gz](https://dumps.wikimedia.org/enwiki/20170320/)
* Size: 262.7 MiB
* Number of keys: 13 099 148
* Average key length: 19.90
* Median key length: 17
* Max key length: 251
Each title is associated with an int (32 bits). All the hash based structures use [CityHash64](https://github.com/google/cityhash) as hash function. For the tests marked *with reserve*, the `reserve` function is called beforehand to avoid any rehash.
Note that `tsl::hopscotch_map`, `std::unordered_map`, `google::dense_hash_map` and `spp::sparse_hash_map` use `std::string` as key which imposes a minimum size of 32 bytes (on x64) even if the key is only one character long. Other structures may be able to store one-character keys with 1 byte + 8 bytes for a pointer (on x64).
The benchmark was compiled with GCC 6.3 and ran on Debian Stretch x64 with an Intel i5-5200u and 8Go of RAM. Best of 20 runs was taken.
The code of the benchmark can be found on [Gist](https://gist.github.com/Tessil/72e11891fc155f5b2eb53de22cbc4053).
##### Unsorted
The *enwiki-20170320-all-titles-in-ns0.gz* dataset is alphabetically sorted. For this benchmark, we first shuffle the dataset through [shuf(1)](https://linux.die.net/man/1/shuf) to avoid a biased sorted dataset.
| Library | Data structure | Peak memory (MiB) | Memory (MiB) | Insert (ns/key) | Read (ns/key) |
|---------|----------------|------------------:|-------------:|----------------:|--------------:|
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie) | HAT-trie | **405.22** | **402.25** | 643.10 | 250.87 |
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie)
max_load_factor=4 | HAT-trie | 471.85 | 468.50 | 638.66 | 212.90 |
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie)
max_load_factor=2 | HAT-trie | 569.76 | 566.52 | 630.61 | 201.10 |
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie)
max_load_factor=1 | HAT-trie | 713.44 | 709.81 | 645.76 | 190.87 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) | Double-array trie | 1269.68 | 1254.41 | 1102.93 | 557.20 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) ORDERED=false | Double-array trie | 1269.80 | 1254.41 | 1089.78 | 570.13 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) | Double-array reduced trie | 1183.07 | 1167.79 | 1076.68 | 645.79 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) ORDERED=false | Double-array reduced trie | 1183.14 | 1167.85 | 1065.43 | 641.98 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) | Double-array prefix trie | 498.69 | 496.54 | 1096.90 | 628.01 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) ORDERED=false | Double-array prefix trie | 498.65 | 496.60 | 1048.40 | 628.94 |
| [hat-trie](https://github.com/dcjones/hat-trie)1 (C) | HAT-trie | 504.07 | 501.50 | 917.49 | 261.00 |
| [qp trie](https://github.com/fanf2/qp) (C) | QP trie | 941.23 | 938.17 | 1349.25 | 1281.46 |
| [crit-bit trie](https://github.com/fanf2/qp) (C) | Crit-bit trie | 1074.96 | 1071.98 | 2930.42 | 2869.74 |
| [JudySL](http://judy.sourceforge.net/) (C) | Judy array | 631.09 | 628.37 | 884.29 | 803.58 |
| [JudyHS](http://judy.sourceforge.net/) (C) | Judy array | 723.44 | 719.47 | 476.79 | 417.15 |
| [tsl::array_map](https://github.com/Tessil/array-hash) | Array hash table | 823.54 | 678.73 | 603.94 | 138.24 |
| [tsl::array_map](https://github.com/Tessil/array-hash)
with reserve | Array hash table | 564.26 | 555.91 | 249.52 | 128.28 |
| [tsl::hopscotch_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hopscotch-map) | Hash table | 1325.83 | 1077.99 | 368.26 | **119.49** |
| [tsl::hopscotch_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hopscotch-map)
with reserve | Hash table | 1080.51 | 1077.98 | **240.58** | 119.91 |
| [google::dense_hash_map](https://github.com/sparsehash/sparsehash) | Hash table | 2319.40 | 1677.11 | 466.60 | 138.87 |
| [google::dense_hash_map](https://github.com/sparsehash/sparsehash)
with reserve | Hash table | 1592.51 | 1589.99 | 259.56 | 120.40 |
| [spp::sparse_hash_map](https://github.com/greg7mdp/sparsepp) | Sparse hash table | 918.67 | 917.10 | 769.00 | 175.59 |
| [spp::sparse_hash_map](https://github.com/greg7mdp/sparsepp)
with reserve | Sparse hash table | 913.35 | 910.65 | 427.22 | 159.08 |
| [std::unordered_map](http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/unordered_map) | Hash table | 1249.05 | 1246.60 | 590.88 | 173.58 |
| [std::unordered_map](http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/unordered_map)
with reserve | Hash table | 1212.23 | 1209.71 | 350.33 | 178.70 |
1. As the hash function can't be passed in parameter, the code of the library itself is modified to use CityHash64.
##### Sorted
The key are inserted and read in alphabetical order.
| Library | Data structure | Peak memory (MiB) | Memory (MiB) | Insert (ns/key) | Read (ns/key) |
|---------|----------------|------------------:|-------------:|----------------:|--------------:|
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie) | HAT-trie | **396.10** | **393.22** | 255.76 | 68.08 |
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie)
max_load_factor=4 | HAT-trie | 465.02 | 461.80 | 248.88 | 59.23 |
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie)
max_load_factor=2 | HAT-trie | 543.99 | 541.21 | 230.13 | 53.50 |
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie)
max_load_factor=1 | HAT-trie | 692.29 | 689.70 | 243.84 | **49.22** |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) | Double-array trie | 1269.58 | 1254.41 | 278.51 | 54.72 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) ORDERED=false | Double-array trie | 1269.66 | 1254.41 | 264.43 | 56.02 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) | Double-array reduced trie | 1183.01 | 1167.78 | 254.60 | 69.18 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) ORDERED=false | Double-array reduced trie | 1183.03 | 1167.78 | 241.45 | 69.67 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) | Double-array prefix trie | 621.59 | 619.38 | 246.88 | 57.83 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) ORDERED=false | Double-array prefix trie | 621.59 | 619.38 | **187.98** | 58.56 |
| [hat-trie](https://github.com/dcjones/hat-trie)2 (C) | HAT-trie | 521.25 | 518.52 | 503.01 | 86.40 |
| [qp trie](https://github.com/fanf2/qp) (C) | QP trie | 940.65 | 937.66 | 392.86 | 190.19 |
| [crit-bit trie](https://github.com/fanf2/qp) (C) | Crit-bit trie | 1074.87 | 1071.98 | 430.04 | 347.60 |
| [JudySL](http://judy.sourceforge.net/) (C) | Judy array | 616.95 | 614.27 | 279.07 | 114.47 |
| [JudyHS](http://judy.sourceforge.net/) (C) | Judy array | 722.29 | 719.47 | 439.66 | 372.25 |
| [tsl::array_map](https://github.com/Tessil/array-hash) | Array hash table | 826.98 | 682.99 | 612.31 | 139.16 |
| [tsl::array_map](https://github.com/Tessil/array-hash)
with reserve | Array hash table | 565.37 | 555.35 | 246.55 | 126.32 |
| [tsl::hopscotch_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hopscotch-map) | Hash table | 1331.87 | 1078.02 | 375.19 | 118.08 |
| [tsl::hopscotch_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hopscotch-map)
with reserve | Hash table | 1080.51 | 1077.97 | 238.93 | 117.20 |
| [google::dense_hash_map](https://github.com/sparsehash/sparsehash) | Hash table | 2325.27 | 1683.07 | 483.95 | 137.09 |
| [google::dense_hash_map](https://github.com/sparsehash/sparsehash)
with reserve | Hash table | 1592.54 | 1589.99 | 257.22 | 113.71 |
| [spp::sparse_hash_map](https://github.com/greg7mdp/sparsepp) | Sparse hash table | 920.96 | 918.70 | 772.03 | 176.64 |
| [spp::sparse_hash_map](https://github.com/greg7mdp/sparsepp)
with reserve | Sparse hash table | 914.84 | 912.47 | 422.85 | 158.73 |
| [std::unordered_map](http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/unordered_map) | Hash table | 1249.09 | 1246.65 | 594.85 | 173.54 |
| [std::unordered_map](http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/unordered_map)
with reserve | Hash table | 1212.21 | 1209.71 | 347.40 | 176.49 |
2. As the hash function can't be passed in parameter, the code of the library itself is modified to use CityHash64.
#### Dr. Askitis dataset
The benchmark consists in inserting all the words from the "Distinct Strings" dataset of Dr. Askitis into the data structure, check the used memory space and search for all the words from the "Skew String Set 1" dataset (where a string can be present multiple times) in the data structure. Note that the strings in this dataset have a quite short average and median key length (which may not be a realistic use case compared to the Wikipedia dataset used above). It's similar to the one on the [cedar](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) homepage.
* Dataset: [distinct_1](http://web.archive.org/web/20120206015921/http://www.naskitis.com/) (write) / [skew1_1](http://web.archive.org/web/20120206015921/http://www.naskitis.com/) (read)
* Size: 290.45 MiB / 1 029.46 MiB
* Number of keys: 28 772 169 / 177 999 203
* Average key length: 9.59 / 5.06
* Median key length: 8 / 4
* Max key length: 126 / 62
The benchmark protocol is the same as for the [Wikipedia dataset](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie#wikipedia-dataset).
| Library | Data structure | Peak memory (MiB) | Memory (MiB) | Insert (ns/key) | Read (ns/key) |
|---------|----------------|------------------:|-------------:|----------------:|--------------:|
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie) | HAT-trie | **604.76** | **601.79** | 485.45 | 77.80 |
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie)
max_load_factor=4 | HAT-trie | 768.10 | 764.98 | 491.78 | 75.48 |
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie)
max_load_factor=2 | HAT-trie | 1002.42 | 999.34 | 496.78 | 72.53 |
| [tsl::htrie_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie)
max_load_factor=1 | HAT-trie | 1344.98 | 1341.97 | 520.66 | 72.45 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) | Double-array trie | 1105.45 | 1100.05 | 682.25 | 71.98 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) ORDERED=false | Double-array trie | 1105.47 | 1100.05 | 668.75 | 71.95 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) | Double-array reduced trie | 941.16 | 926.04 | 684.38 | 79.11 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) ORDERED=false | Double-array reduced trie | 941.16 | 925.98 | 672.14 | 79.02 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) | Double-array prefix trie | 714.58 | 712.59 | 831.71 | 75.83 |
| [cedar::da](http://www.tkl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ynaga/cedar/) ORDERED=false | Double-array prefix trie | 714.66 | 712.31 | 786.93 | 75.89 |
| [hat-trie](https://github.com/dcjones/hat-trie)3 (C) | HAT-trie | 786.93 | 784.32 | 743.34 | 93.58 |
| [qp trie](https://github.com/fanf2/qp) (C) | QP trie | 1800.02 | 1797.21 | 987.95 | 428.51 |
| [crit-bit trie](https://github.com/fanf2/qp) (C) | Crit-bit trie | 2210.52 | 2207.64 | 1986.19 | 1109.88 |
| [JudySL](http://judy.sourceforge.net/) (C) | Judy array | 1025.59 | 1023.11 | 535.02 | 202.36 |
| [JudyHS](http://judy.sourceforge.net/) (C) | Judy array | 1002.50 | 999.97 | 456.09 | 148.36 |
| [tsl::array_map](https://github.com/Tessil/array-hash) | Array hash table | 1308.08 | 1031.67 | 545.82 | 46.41 |
| [tsl::array_map](https://github.com/Tessil/array-hash)
with reserve | Array hash table | 979.44 | 921.363 | 244.19 | 45.74 |
| [tsl::hopscotch_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hopscotch-map) | Hash table | 2336.39 | 1611.54 | 288.70 | 47.05 |
| [tsl::hopscotch_map](https://github.com/Tessil/hopscotch-map)
with reserve | Hash table | 1614.22 | 1611.64 | **220.67** | 46.39 |
| [google::dense_hash_map](https://github.com/sparsehash/sparsehash) | Hash table | 3913.64 | 2636.31 | 317.66 | 43.62 |
| [google::dense_hash_map](https://github.com/sparsehash/sparsehash)
with reserve | Hash table | 2638.19 | 2635.68 | 227.58 | **43.09** |
| [spp::sparse_hash_map](https://github.com/greg7mdp/sparsepp) | Sparse hash table | 1419.69 | 1417.61 | 586.26 | 56.00 |
| [spp::sparse_hash_map](https://github.com/greg7mdp/sparsepp)
with reserve | Sparse hash table | 1424.21 | 1421.69 | 392.76 | 55.73 |
| [std::unordered_map](http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/unordered_map) | Hash table | 2112.66 | 2110.19 | 554.02 | 105.05 |
| [std::unordered_map](http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/unordered_map)
with reserve | Hash table | 2053.95 | 2051.67 | 309.06 | 109.89 |
3. As the hash function can't be passed in parameter, the code of the library itself is modified to use CityHash64.
### Installation
To use the library, just add the [include](include/) directory to your include path. It is a **header-only** library.
If you use CMake, you can also use the `tsl::hat_trie` exported target from the [CMakeLists.txt](CMakeLists.txt) with `target_link_libraries`.
```cmake
# Example where the hat-trie project is stored in a third-party directory
add_subdirectory(third-party/hat-trie)
target_link_libraries(your_target PRIVATE tsl::hat_trie)
```
The code should work with any C++11 standard-compliant compiler and has been tested with GCC 4.8.4, Clang 3.5.0 and Visual Studio 2015.
To run the tests you will need the Boost Test library and CMake.
```bash
git clone https://github.com/Tessil/hat-trie.git
cd hat-trie/tests
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
cmake --build .
./tsl_hat_trie_tests
```
### Usage
The API can be found [here](https://tessil.github.io/hat-trie/doc_without_string_view/html). If `std::string_view` is available, the API changes slightly and can be found [here](https://tessil.github.io/hat-trie/doc/html/).
### Example
```c++
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main() {
/*
* Map of strings to int having char as character type.
* There is no support for wchar_t, char16_t or char32_t yet,
* but UTF-8 strings will work fine.
*/
tsl::htrie_map map = {{"one", 1}, {"two", 2}};
map["three"] = 3;
map["four"] = 4;
map.insert("five", 5);
map.insert_ks("six_with_extra_chars_we_ignore", 3, 6);
map.erase("two");
/*
* Due to the compression on the common prefixes, the letters of the string
* are not always stored contiguously. When we retrieve the key, we have to
* construct it.
*
* To avoid a heap-allocation at each iteration (when SSO doesn't occur),
* we reuse the key_buffer to construct the key.
*/
std::string key_buffer;
for(auto it = map.begin(); it != map.end(); ++it) {
it.key(key_buffer);
std::cout << "{" << key_buffer << ", " << it.value() << "}" << std::endl;
}
/*
* If you don't care about the allocation.
*/
for(auto it = map.begin(); it != map.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << "{" << it.key() << ", " << *it << "}" << std::endl;
}
tsl::htrie_map map2 = {{"apple", 1}, {"mango", 2}, {"apricot", 3},
{"mandarin", 4}, {"melon", 5}, {"macadamia", 6}};
// Prefix search
auto prefix_range = map2.equal_prefix_range("ma");
// {mandarin, 4} {mango, 2} {macadamia, 6}
for(auto it = prefix_range.first; it != prefix_range.second; ++it) {
std::cout << "{" << it.key() << ", " << *it << "}" << std::endl;
}
// Find longest match prefix.
auto longest_prefix = map2.longest_prefix("apple juice");
if(longest_prefix != map2.end()) {
// {apple, 1}
std::cout << "{" << longest_prefix.key() << ", "
<< *longest_prefix << "}" << std::endl;
}
// Prefix erase
map2.erase_prefix("ma");
// {apricot, 3} {melon, 5} {apple, 1}
for(auto it = map2.begin(); it != map2.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << "{" << it.key() << ", " << *it << "}" << std::endl;
}
tsl::htrie_set set = {"one", "two", "three"};
set.insert({"four", "five"});
// {one} {two} {five} {four} {three}
for(auto it = set.begin(); it != set.end(); ++it) {
it.key(key_buffer);
std::cout << "{" << key_buffer << "}" << std::endl;
}
}
```
#### Serialization
The library provides an efficient way to serialize and deserialize a map or a set so that it can be saved to a file or send through the network.
To do so, it requires the user to provide a function object for both serialization and deserialization.
```c++
struct serializer {
// Must support the following types for U: std::uint64_t, float and T if a map is used.
template
void operator()(const U& value);
void operator()(const CharT* value, std::size_t value_size);
};
```
```c++
struct deserializer {
// Must support the following types for U: std::uint64_t, float and T if a map is used.
template
U operator()();
void operator()(CharT* value_out, std::size_t value_size);
};
```
Note that the implementation leaves binary compatibility (endianness, float binary representation, size of int, ...) of the types it serializes/deserializes in the hands of the provided function objects if compatibility is required.
More details regarding the `serialize` and `deserialize` methods can be found in the [API](https://tessil.github.io/hat-trie/doc/html/classtsl_1_1htrie__map.html).
```c++
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
class serializer {
public:
serializer(const char* file_name) {
m_ostream.exceptions(m_ostream.badbit | m_ostream.failbit);
m_ostream.open(file_name);
}
template::value>::type* = nullptr>
void operator()(const T& value) {
m_ostream.write(reinterpret_cast(&value), sizeof(T));
}
void operator()(const char* value, std::size_t value_size) {
m_ostream.write(value, value_size);
}
private:
std::ofstream m_ostream;
};
class deserializer {
public:
deserializer(const char* file_name) {
m_istream.exceptions(m_istream.badbit | m_istream.failbit | m_istream.eofbit);
m_istream.open(file_name);
}
template::value>::type* = nullptr>
T operator()() {
T value;
m_istream.read(reinterpret_cast(&value), sizeof(T));
return value;
}
void operator()(char* value_out, std::size_t value_size) {
m_istream.read(value_out, value_size);
}
private:
std::ifstream m_istream;
};
int main() {
const tsl::htrie_map map = {{"one", 1}, {"two", 2},
{"three", 3}, {"four", 4}};
const char* file_name = "htrie_map.data";
{
serializer serial(file_name);
map.serialize(serial);
}
{
deserializer dserial(file_name);
auto map_deserialized = tsl::htrie_map::deserialize(dserial);
assert(map == map_deserialized);
}
{
deserializer dserial(file_name);
/**
* If the serialized and deserialized map are hash compatibles (see conditions in API),
* setting the argument to true speed-up the deserialization process as we don't have
* to recalculate the hash of each key. We also know how much space each bucket needs.
*/
const bool hash_compatible = true;
auto map_deserialized =
tsl::htrie_map::deserialize(dserial, hash_compatible);
assert(map == map_deserialized);
}
}
```
##### Serialization with Boost Serialization and compression with zlib
It's possible to use a serialization library to avoid some of the boilerplate if the types to serialize are more complex.
The following example uses Boost Serialization with the Boost zlib compression stream to reduce the size of the resulting serialized file.
```c++
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
template
struct serializer {
Archive& ar;
template
void operator()(const T& val) { ar & val; }
template
void operator()(const CharT* val, std::size_t val_size) {
ar.save_binary(reinterpret_cast(val), val_size*sizeof(CharT));
}
};
template
struct deserializer {
Archive& ar;
template
T operator()() { T val; ar & val; return val; }
template
void operator()(CharT* val_out, std::size_t val_size) {
ar.load_binary(reinterpret_cast(val_out), val_size*sizeof(CharT));
}
};
namespace boost { namespace serialization {
template
void serialize(Archive & ar, tsl::htrie_map& map, const unsigned int version) {
split_free(ar, map, version);
}
template
void save(Archive & ar, const tsl::htrie_map& map, const unsigned int version) {
serializer serial{ar};
map.serialize(serial);
}
template
void load(Archive & ar, tsl::htrie_map& map, const unsigned int version) {
deserializer deserial{ar};
map = tsl::htrie_map::deserialize(deserial);
}
}}
int main() {
const tsl::htrie_map map = {{"one", 1}, {"two", 2},
{"three", 3}, {"four", 4}};
const char* file_name = "htrie_map.data";
{
std::ofstream ofs;
ofs.exceptions(ofs.badbit | ofs.failbit);
ofs.open(file_name, std::ios::binary);
boost::iostreams::filtering_ostream fo;
fo.push(boost::iostreams::zlib_compressor());
fo.push(ofs);
boost::archive::binary_oarchive oa(fo);
oa << map;
}
{
std::ifstream ifs;
ifs.exceptions(ifs.badbit | ifs.failbit | ifs.eofbit);
ifs.open(file_name, std::ios::binary);
boost::iostreams::filtering_istream fi;
fi.push(boost::iostreams::zlib_decompressor());
fi.push(ifs);
boost::archive::binary_iarchive ia(fi);
tsl::htrie_map map_deserialized;
ia >> map_deserialized;
assert(map == map_deserialized);
}
}
```
### License
The code is licensed under the MIT license, see the [LICENSE file](LICENSE) for details.