https://github.com/Thinklab-SJTU/ThinkMatch
A research protocol for deep graph matching.
https://github.com/Thinklab-SJTU/ThinkMatch
combinatorial-optimization graph-matching neural-graph-matching quadratic-assignment-problem
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
A research protocol for deep graph matching.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/Thinklab-SJTU/ThinkMatch
- Owner: Thinklab-SJTU
- License: other
- Created: 2019-09-06T17:07:08.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-04-08T16:03:20.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-05-06T00:03:30.109Z (12 months ago)
- Topics: combinatorial-optimization, graph-matching, neural-graph-matching, quadratic-assignment-problem
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/
- Size: 2.16 MB
- Stars: 792
- Watchers: 20
- Forks: 119
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
- Citation: CITATION.cff
Awesome Lists containing this project
- StarryDivineSky - Thinklab-SJTU/ThinkMatch
README
# Think Match
[](https://github.com/Thinklab-SJTU/ThinkMatch/releases)
[](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/runzhongwang/thinkmatch/tags)
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/runzhongwang/thinkmatch/tags)
[](https://discord.gg/8m6n7rRz9T)
[](https://qm.qq.com/cgi-bin/qm/qr?k=QolXYJn_M5ilDEM9e2jEjlPnJ02Ktabd&jump_from=webapi&authKey=6zG6D/Js4YF5h5zj778aO5MDKOXBwPFi8gQ4LsXJN8Hn1V8uCVGV81iT4J/FjPGT)
[](https://GitHub.com/Thinklab-SJTU/ThinkMatch/stargazers/)
_ThinkMatch_ is developed and maintained by [ThinkLab](http://thinklab.sjtu.edu.cn) at Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
This repository is developed for the following purposes:
* **Providing modules** for developing deep graph matching algorithms to facilitate future research.
* **Providing implementation** of state-of-the-art deep graph matching methods.
* **Benchmarking** existing deep graph matching algorithms under different dataset & experiment settings, for the purpose of fair comparison.
Official documentation: https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io
Source code: https://github.com/Thinklab-SJTU/ThinkMatch
## Introduction to Graph Matching
Graph Matching (GM) is a fundamental yet challenging problem in computer vision, pattern recognition and data mining. GM aims to find node-to-node correspondence among multiple graphs, by solving an NP-hard combinatorial problem named Quadratic Assignment Problem (QAP). Recently, there is growing interest in developing deep learning based graph matching methods.
Graph matching techniques have been applied to the following applications:
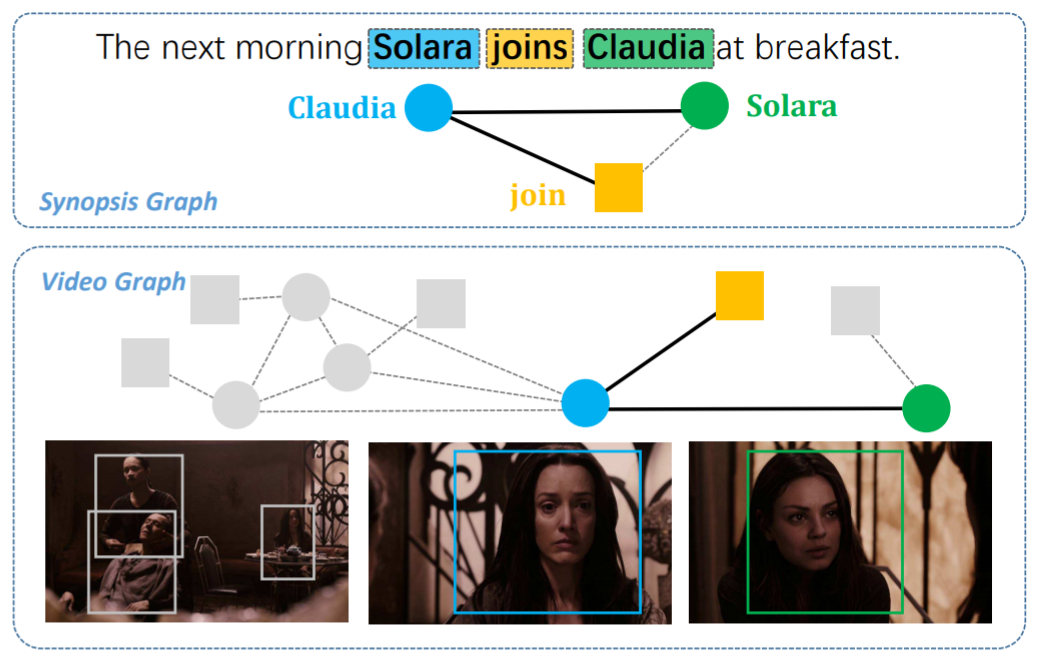
* [Bridging movie and synopses](https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/Xiong_A_Graph-Based_Framework_to_Bridge_Movies_and_Synopses_ICCV_2019_paper.pdf)
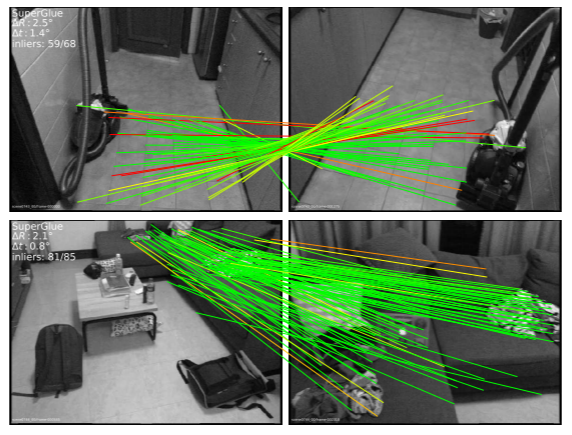
* [Image correspondence](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.11763.pdf)
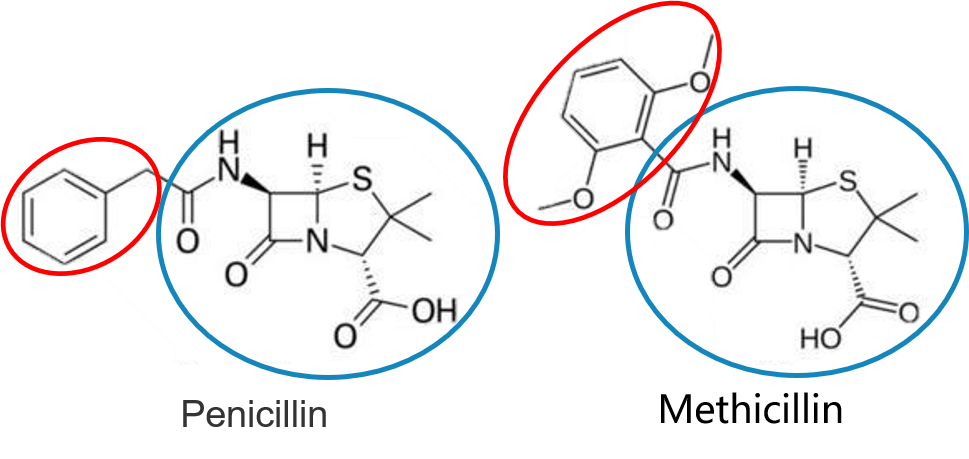
* [Molecules matching](https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2021/papers/Wang_Combinatorial_Learning_of_Graph_Edit_Distance_via_Dynamic_Embedding_CVPR_2021_paper.pdf)
* and more...
In this repository, we mainly focus on image keypoint matching because it is a popular testbed for existing graph matching methods.
Readers are referred to the following survey for more technical details about graph matching:
* Junchi Yan, Xu-Cheng Yin, Weiyao Lin, Cheng Deng, Hongyuan Zha, Xiaokang Yang. "A Short Survey of Recent Advances in Graph Matching."
_ICMR 2016_.
## Deep Graph Matching Algorithms
_ThinkMatch_ currently contains pytorch source code of the following deep graph matching methods:
* [**GMN**](/models/GMN)
* Andrei Zanfir and Cristian Sminchisescu. "Deep Learning of Graph Matching." _CVPR 2018_.
[[paper]](http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/html/Zanfir_Deep_Learning_of_CVPR_2018_paper.html)
* [**PCA-GM & IPCA-GM**](/models/PCA)
* Runzhong Wang, Junchi Yan and Xiaokang Yang. "Combinatorial Learning of Robust Deep Graph Matching: an Embedding based Approach." _TPAMI 2020_.
[[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9128045/), [[project page]](https://thinklab.sjtu.edu.cn/IPCA_GM.html)
* Runzhong Wang, Junchi Yan and Xiaokang Yang. "Learning Combinatorial Embedding Networks for Deep Graph Matching." _ICCV 2019_.
[[paper]](http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/Wang_Learning_Combinatorial_Embedding_Networks_for_Deep_Graph_Matching_ICCV_2019_paper.pdf)
* [**NGM & NGM-v2**](/models/NGM)
* Runzhong Wang, Junchi Yan, Xiaokang Yang. "Neural Graph Matching Network: Learning Lawler's Quadratic Assignment Problem with Extension to Hypergraph and Multiple-graph Matching." _TPAMI 2021_.
[[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9426408), [[project page]](http://thinklab.sjtu.edu.cn/project/NGM/index.html)
* [**CIE-H**](/models/CIE)
* Tianshu Yu, Runzhong Wang, Junchi Yan, Baoxin Li. "Learning deep graph matching with channel-independent embedding and Hungarian attention." _ICLR 2020_.
[[paper]](https://openreview.net/forum?id=rJgBd2NYPH)
* [**GANN**](/models/GANN)
* Runzhong Wang, Junchi Yan and Xiaokang Yang. "Graduated Assignment for Joint Multi-Graph Matching and Clustering with Application to Unsupervised Graph Matching Network Learning." _NeurIPS 2020_.
[[paper]](https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2020/hash/e6384711491713d29bc63fc5eeb5ba4f-Abstract.html)
* Runzhong Wang, Junchi Yan and Xiaokang Yang. "Unsupervised Learning of Graph Matching with Mixture of Modes via Discrepancy Minimization." _TPAMI 2023_.
[[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10073537), [[project page]](https://thinklab.sjtu.edu.cn/project/GANN-GM/index.html)
* [**BBGM**](/models/BBGM)
* Michal Rolínek, Paul Swoboda, Dominik Zietlow, Anselm Paulus, Vít Musil, Georg Martius. "Deep Graph Matching via Blackbox Differentiation of Combinatorial Solvers." _ECCV 2020_.
[[paper]](https://www.ecva.net/papers/eccv_2020/papers_ECCV/papers/123730409.pdf)
* [**GCAN**](/models/GCAN)
* Zheheng Jiang, Hossein Rahmani, Plamen Angelov, Sue Black, Bryan M. Williams. "Graph-Context Attention Networks for Size-Varied Deep Graph Matching." _CVPR 2022_.
[[paper]](https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2022/papers/Jiang_Graph-Context_Attention_Networks_for_Size-Varied_Deep_Graph_Matching_CVPR_2022_paper.pdf)
* [**AFAT**](/models/AFAT)
* Runzhong Wang, Ziao Guo, Shaofei Jiang, Xiaokang Yang, Junchi Yan. "Deep Learning of Partial Graph Matching via Differentiable Top-K." _CVPR 2023_.
[[paper]](https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2023/html/Wang_Deep_Learning_of_Partial_Graph_Matching_via_Differentiable_Top-K_CVPR_2023_paper.html)
* [**LinSAT**](/models/LinSAT)
* Runzhong Wang, Yunhao Zhang, Ziao Guo, Tianyi Chen, Xiaokang Yang, Junchi Yan. "LinSATNet: The Positive Linear Satisfiability Neural Networks." _ICML 2023_.
[[paper]](https://openreview.net/forum?id=D2Oaj7v9YJ)
* [**COMMON**](/models/COMMON)
* Yijie Lin, Mouxing Yang, Jun Yu, Peng Hu, Changqing Zhang, Xi Peng. "Graph Matching with Bi-level Noisy
Correspondence." _ICCV 2023_.
[[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.04085.pdf), [[project page]](https://github.com/Lin-Yijie/Graph-Matching-Networks/tree/main/COMMON)
## When to use ThinkMatch
ThinkMatch is designed as a research protocol for deep graph matching. It is recommended if you have any of the
following demands:
* Developing new algorithms and publishing new graph matching papers;
* Understanding the details of deep graph matching models;
* Playing around with the hyperparameters and network details;
* Benchmarking deep graph matching networks.
### When not to use ThinkMatch
You may find the environment setup in ThinkMatch complicated and the details of graph matching hard to understand.
``pygmtools`` offers a user-friendly API, and is recommended for the following cases:
* If you want to integrate graph matching as a step of your pipeline (either learning or non-learning,
with ``numpy``/``pytorch``/``jittor``/``paddle``/``mindspore``/``tensorflow``).
* If you want a quick benchmarking and profiling of the graph matching solvers available in ``pygmtools``.
* If you do not want to dive too deep into the algorithm details and do not need to modify the algorithm.
You can simply install the user-friendly package by
```shell
$ pip install pygmtools
```
Official documentation: https://pygmtools.readthedocs.io
Source code: https://github.com/Thinklab-SJTU/pygmtools
## Deep Graph Matching Benchmarks
### PascalVOC - 2GM
| model | year | aero | bike | bird | boat | bottle | bus | car | cat | chair | cow | table | dog | horse | mbkie | person | plant | sheep | sofa | train | tv | mean |
| ------------------------------------------------------------ | ---- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
| [GMN](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#gmn) | 2018 | 0.4163 | 0.5964 | 0.6027 | 0.4795 | 0.7918 | 0.7020 | 0.6735 | 0.6488 | 0.3924 | 0.6128 | 0.6693 | 0.5976 | 0.6106 | 0.5975 | 0.3721 | 0.7818 | 0.6800 | 0.4993 | 0.8421 | 0.9141 | 0.6240 |
| [PCA-GM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#pca-gm) | 2019 | 0.4979 | 0.6193 | 0.6531 | 0.5715 | 0.7882 | 0.7556 | 0.6466 | 0.6969 | 0.4164 | 0.6339 | 0.5073 | 0.6705 | 0.6671 | 0.6164 | 0.4447 | 0.8116 | 0.6782 | 0.5922 | 0.7845 | 0.9042 | 0.6478 |
| [NGM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2019 | 0.5010 | 0.6350 | 0.5790 | 0.5340 | 0.7980 | 0.7710 | 0.7360 | 0.6820 | 0.4110 | 0.6640 | 0.4080 | 0.6030 | 0.6190 | 0.6350 | 0.4560 | 0.7710 | 0.6930 | 0.6550 | 0.7920 | 0.8820 | 0.6413 |
| [NHGM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2019 | 0.5240 | 0.6220 | 0.5830 | 0.5570 | 0.7870 | 0.7770 | 0.7440 | 0.7070 | 0.4200 | 0.6460 | 0.5380 | 0.6100 | 0.6190 | 0.6080 | 0.4680 | 0.7910 | 0.6680 | 0.5510 | 0.8090 | 0.8870 | 0.6458 |
| [IPCA-GM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#pca-gm) | 2020 | 0.5378 | 0.6622 | 0.6714 | 0.6120 | 0.8039 | 0.7527 | 0.7255 | 0.7252 | 0.4455 | 0.6524 | 0.5430 | 0.6724 | 0.6790 | 0.6421 | 0.4793 | 0.8435 | 0.7079 | 0.6398 | 0.8380 | 0.9083 | 0.6770 |
| [CIE-H](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#cie-h) | 2020 | 0.5250 | 0.6858 | 0.7015 | 0.5706 | 0.8207 | 0.7700 | 0.7073 | 0.7313 | 0.4383 | 0.6994 | 0.6237 | 0.7018 | 0.7031 | 0.6641 | 0.4763 | 0.8525 | 0.7172 | 0.6400 | 0.8385 | 0.9168 | 0.6892 |
| [BBGM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#bbgm) | 2020 | 0.6187 | 0.7106 | 0.7969 | 0.7896 | 0.8740 | 0.9401 | 0.8947 | 0.8022 | 0.5676 | 0.7914 | 0.6458 | 0.7892 | 0.7615 | 0.7512 | 0.6519 | 0.9818 | 0.7729 | 0.7701 | 0.9494 | 0.9393 | 0.7899 |
| [NGM-v2](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2021 | 0.6184 | 0.7118 | 0.7762 | 0.7875 | 0.8733 | 0.9363 | 0.8770 | 0.7977 | 0.5535 | 0.7781 | 0.8952 | 0.7880 | 0.8011 | 0.7923 | 0.6258 | 0.9771 | 0.7769 | 0.7574 | 0.9665 | 0.9323 | 0.8011 |
| [NHGM-v2](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2021 | 0.5995 | 0.7154 | 0.7724 | 0.7902 | 0.8773 | 0.9457 | 0.8903 | 0.8181 | 0.5995 | 0.8129 | 0.8695 | 0.7811 | 0.7645 | 0.7750 | 0.6440 | 0.9872 | 0.7778 | 0.7538 | 0.9787 | 0.9280 | 0.8040 |
| [COMMON](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.04085.pdf) | 2023 | 0.6560 | 0.7520 | 0.8080 | 0.7950 |0.8930 | 0.9230 | 0.9010 | 0.8180 | 0.6160 | 0.8070| 0.9500 | 0.8200 | 0.8160 | 0.7950 | 0.6660 | 0.9890 | 0.7890 | 0.8090 | 0.9930 | 0.9380 | 0.8270 |
### Willow Object Class - 2GM & MGM
| model | year | remark | Car | Duck | Face | Motorbike | Winebottle | mean |
| ------------------------------------------------------------ | ---- | --------------- | ------ | ------ | ------ | --------- | ---------- | ------ |
| [GMN](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#gmn) | 2018 | - | 0.6790 | 0.7670 | 0.9980 | 0.6920 | 0.8310 | 0.7934 |
| [PCA-GM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#pca-gm) | 2019 | - | 0.8760 | 0.8360 | 1.0000 | 0.7760 | 0.8840 | 0.8744 |
| [NGM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2019 | - | 0.8420 | 0.7760 | 0.9940 | 0.7680 | 0.8830 | 0.8530 |
| [NHGM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2019 | - | 0.8650 | 0.7220 | 0.9990 | 0.7930 | 0.8940 | 0.8550 |
| [NMGM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2019 | - | 0.7850 | 0.9210 | 1.0000 | 0.7870 | 0.9480 | 0.8880 |
| [IPCA-GM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#pca) | 2020 | - | 0.9040 | 0.8860 | 1.0000 | 0.8300 | 0.8830 | 0.9006 |
| [CIE-H](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#cie-h) | 2020 | - | 0.8581 | 0.8206 | 0.9994 | 0.8836 | 0.8871 | 0.8898 |
| [BBGM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#bbgm) | 2020 | - | 0.9680 | 0.8990 | 1.0000 | 0.9980 | 0.9940 | 0.9718 |
| [GANN-MGM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#gann) | 2020 | self-supervised | 0.9600 | 0.9642 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9879 | 0.9906 |
| [NGM-v2](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2021 | - | 0.9740 | 0.9340 | 1.0000 | 0.9860 | 0.9830 | 0.9754 |
| [NHGM-v2](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2021 | - | 0.9740 | 0.9390 | 1.0000 | 0.9860 | 0.9890 | 0.9780 |
| [NMGM-v2](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2021 | - | 0.9760 | 0.9447 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9902 | 0.9822 |
| [COMMON](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.04085.pdf) | 2023 | - | 0.9760 | 0.9820 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9960 | 0.9910 |
### SPair-71k - 2GM
| model | year | aero | bike | bird | boat | bottle | bus | car | cat | chair | cow | dog | horse | mtbike | person | plant | sheep | train | tv | mean |
| ------------------------------------------------------------ | ---- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
| [GMN](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#gmn) | 2018 | 0.5991 | 0.5099 | 0.7428 | 0.4672 | 0.6328 | 0.7552 | 0.6950 | 0.6462 | 0.5751 | 0.7302 | 0.5866 | 0.5914 | 0.6320 | 0.5116 | 0.8687 | 0.5787 | 0.6998 | 0.9238 | 0.6526 |
| [PCA-GM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#pca-gm) | 2019 | 0.6467 | 0.4571 | 0.7811 | 0.5128 | 0.6381 | 0.7272 | 0.6122 | 0.6278 | 0.6255 | 0.6822 | 0.5906 | 0.6115 | 0.6486 | 0.5773 | 0.8742 | 0.6042 | 0.7246 | 0.9283 | 0.6595 |
| [NGM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2019 | 0.6644 | 0.5262 | 0.7696 | 0.4960 | 0.6766 | 0.7878 | 0.6764 | 0.6827 | 0.5917 | 0.7364 | 0.6391 | 0.6066 | 0.7074 | 0.6089 | 0.8754 | 0.6387 | 0.7979 | 0.9150 | 0.6887 |
| [IPCA-GM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#pca) | 2020 | 0.6901 | 0.5286 | 0.8037 | 0.5425 | 0.6653 | 0.8001 | 0.6847 | 0.7136 | 0.6136 | 0.7479 | 0.6631 | 0.6514 | 0.6956 | 0.6391 | 0.9112 | 0.6540 | 0.8291 | 0.9750 | 0.7116 |
| [CIE-H](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#cie-h) | 2020 | 0.7146 | 0.5710 | 0.8168 | 0.5672 | 0.6794 | 0.8246 | 0.7339 | 0.7449 | 0.6259 | 0.7804 | 0.6872 | 0.6626 | 0.7374 | 0.6604 | 0.9246 | 0.6717 | 0.8228 | 0.9751 | 0.7334 |
| [BBGM](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#bbgm) | 2020 | 0.7250 | 0.6455 | 0.8780 | 0.7581 | 0.6927 | 0.9395 | 0.8859 | 0.7992 | 0.7456 | 0.8315 | 0.7878 | 0.7710 | 0.7650 | 0.7634 | 0.9820 | 0.8554 | 0.9678 | 0.9931 | 0.8215 |
| [NGM-v2](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2021 | 0.6877 | 0.6331 | 0.8677 | 0.7013 | 0.6971 | 0.9467 | 0.8740 | 0.7737 | 0.7205 | 0.8067 | 0.7426 | 0.7253 | 0.7946 | 0.7340 | 0.9888 | 0.8123 | 0.9426 | 0.9867 | 0.8020 |
| [NHGM-v2](https://thinkmatch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guide/models.html#ngm) | 2021 | 0.6202 | 0.5781 | 0.8642 | 0.6846 | 0.6872 | 0.9335 | 0.8081 | 0.7656 | 0.6919 | 0.7987 | 0.6623 | 0.7171 | 0.7812 | 0.6953 | 0.9824 | 0.8444 | 0.9316 | 0.9926 | 0.7799 |
| [COMMON](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.04085.pdf) | 2023 | 0.7730 | 0.6820 | 0.9200 | 0.7950 | 0.7040 | 0.9750 | 0.9160 | 0.8250 | 0.7220 | 0.8800 | 0.8000| 0.7410 | 0.8340 | 0.8280 | 0.9990 | 0.8440 | 0.9820 | 0.9980| 0.8450 |
_ThinkMatch_ includes the flowing datasets with the provided benchmarks:
* **PascalVOC-Keypoint**
* **Willow-Object-Class**
* **CUB2011**
* **SPair-71k**
* **IMC-PT-SparseGM**
**TODO** We also plan to include the following datasets in the future:
* **Synthetic data**
_ThinkMatch_ also supports the following graph matching settings:
* **2GM** namely **Two**-**G**raph **M**atching where every time only a pair of two graphs is matched.
* **MGM** namely **M**ulti-**G**raph **M**atching where more than two graphs are jointly matched.
* **MGM3** namely **M**ulti-**G**raph **M**atching with a **M**ixture of **M**odes, where multiple graphs are jointly considered, and at the same time the graphs may come from different categories.
## Get Started
### Docker (RECOMMENDED)
Get the recommended docker image by
```bash
docker pull runzhongwang/thinkmatch:torch1.6.0-cuda10.1-cudnn7-pyg1.6.3-pygmtools0.5.1
```
Other combinations of torch and cuda are also available. See available images at [docker hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/runzhongwang/thinkmatch/tags).
See details in [ThinkMatch-runtime](https://github.com/Thinklab-SJTU/ThinkMatch-runtime).
### Manual configuration (for Ubuntu)
This repository is developed and tested with Ubuntu 16.04, Python 3.7, Pytorch 1.6, cuda10.1, cudnn7 and torch-geometric 1.6.3.
1. Install and configure Pytorch 1.6 (with GPU support).
1. Install ninja-build: ``apt-get install ninja-build``
1. Install python packages:
```bash
pip install tensorboardX scipy easydict pyyaml xlrd xlwt pynvml pygmtools
```
1. Install building tools for LPMP:
```bash
apt-get install -y findutils libhdf5-serial-dev git wget libssl-dev
wget https://github.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/download/v3.19.1/cmake-3.19.1.tar.gz && tar zxvf cmake-3.19.1.tar.gz
cd cmake-3.19.1 && ./bootstrap && make && make install
```
1. Install and build LPMP:
```bash
python -m pip install git+https://[email protected]/rogerwwww/lpmp.git
```
You may need ``gcc-9`` to successfully build LPMP. Here we provide an example installing and configuring ``gcc-9``:
```bash
apt-get update
apt-get install -y software-properties-common
add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntu-toolchain-r/test
apt-get install -y gcc-9 g++-9
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-9 60 --slave /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-9
```
1. Install torch-geometric:
```bash
export CUDA=cu101
export TORCH=1.6.0
/opt/conda/bin/pip install torch-scatter==2.0.5 -f https://pytorch-geometric.com/whl/torch-${TORCH}+${CUDA}.html
/opt/conda/bin/pip install torch-sparse==0.6.8 -f https://pytorch-geometric.com/whl/torch-${TORCH}+${CUDA}.html
/opt/conda/bin/pip install torch-cluster==1.5.8 -f https://pytorch-geometric.com/whl/torch-${TORCH}+${CUDA}.html
/opt/conda/bin/pip install torch-spline-conv==1.2.0 -f https://pytorch-geometric.com/whl/torch-${TORCH}+${CUDA}.html
/opt/conda/bin/pip install torch-geometric==1.6.3
```
1. If you have configured ``gcc-9`` to build LPMP, be sure to switch back to ``gcc-7`` because this code repository is based on ``gcc-7``. Here is also an example:
```bash
update-alternatives --remove gcc /usr/bin/gcc-9
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-7 60 --slave /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-7
```
### Available datasets
Note: All following datasets can be automatically downloaded and unzipped by `pygmtools`, but you can also download the dataset yourself if a download failure occurs.
1. PascalVOC-Keypoint
1. Download [VOC2011 dataset](http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/voc2011/index.html) and make sure it looks like ``data/PascalVOC/TrainVal/VOCdevkit/VOC2011``
1. Download keypoint annotation for VOC2011 from [Berkeley server](https://www2.eecs.berkeley.edu/Research/Projects/CS/vision/shape/poselets/voc2011_keypoints_Feb2012.tgz) or [google drive](https://drive.google.com/open?id=1D5o8rmnY1-DaDrgAXSygnflX5c-JyUWR) and make sure it looks like ``data/PascalVOC/annotations``
1. The train/test split is available in ``data/PascalVOC/voc2011_pairs.npz``. **This file must be added manually.**
Please cite the following papers if you use PascalVOC-Keypoint dataset:
```
@article{EveringhamIJCV10,
title={The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge},
author={Everingham, Mark and Van Gool, Luc and Williams, Christopher KI and Winn, John and Zisserman, Andrew},
journal={International Journal of Computer Vision},
volume={88},
pages={303–338},
year={2010}
}
@inproceedings{BourdevICCV09,
title={Poselets: Body part detectors trained using 3d human pose annotations},
author={Bourdev, L. and Malik, J.},
booktitle={International Conference on Computer Vision},
pages={1365--1372},
year={2009},
organization={IEEE}
}
```
1. Willow-Object-Class
1. Download Willow-ObjectClass dataset from [the official site](http://www.di.ens.fr/willow/research/graphlearning/WILLOW-ObjectClass_dataset.zip) or [hugging face](https://huggingface.co/heatingma/pygmtools/resolve/main/WILLOW-ObjectClass_dataset.zip)
1. Unzip the dataset and make sure it looks like ``data/WillowObject/WILLOW-ObjectClass``
Please cite the following paper if you use Willow-Object-Class dataset:
```
@inproceedings{ChoICCV13,
author={Cho, Minsu and Alahari, Karteek and Ponce, Jean},
title = {Learning Graphs to Match},
booktitle = {International Conference on Computer Vision},
pages={25--32},
year={2013}
}
```
1. CUB2011
1. Download [CUB-200-2011 dataset](http://www.vision.caltech.edu/visipedia-data/CUB-200-2011/CUB_200_2011.tgz).
1. Unzip the dataset and make sure it looks like ``data/CUB_200_2011/CUB_200_2011``
Please cite the following report if you use CUB2011 dataset:
```
@techreport{CUB2011,
Title = {{The Caltech-UCSD Birds-200-2011 Dataset}},
Author = {Wah, C. and Branson, S. and Welinder, P. and Perona, P. and Belongie, S.},
Year = {2011},
Institution = {California Institute of Technology},
Number = {CNS-TR-2011-001}
}
```
1. IMC-PT-SparseGM
1. Download the IMC-PT-SparseGM dataset from [google drive](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1C3xl_eWaCG3lL2C3vP8Fpsck88xZOHtg/view?usp=sharing) or [baidu drive (code: g2cj)](https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ZQ3AMqoHtE_uA86GPf2h4w) or [hugging face](https://huggingface.co/datasets/esflfei/IMC-PT-SparseGM).
1. Unzip the dataset and make sure it looks like ``data/IMC-PT-SparseGM/annotations`` for 50 anchor points and ``data/IMC-PT-SparseGM/annotations_100`` for 100 anchor points
Please cite the following papers if you use IMC-PT-SparseGM dataset:
```
@article{JinIJCV21,
title={Image Matching across Wide Baselines: From Paper to Practice},
author={Jin, Yuhe and Mishkin, Dmytro and Mishchuk, Anastasiia and Matas, Jiri and Fua, Pascal and Yi, Kwang Moo and Trulls, Eduard},
journal={International Journal of Computer Vision},
pages={517--547},
year={2021}
}
@InProceedings{WangCVPR23,
author = {Wang, Runzhong and Guo, Ziao and Jiang, Shaofei and Yang, Xiaokang and Yan, Junchi},
title = {Deep Learning of Partial Graph Matching via Differentiable Top-K},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2023}
}
```
1. SPair-71k
1. Download [SPair-71k dataset](http://cvlab.postech.ac.kr/research/SPair-71k/)
1. Unzip the dataset and make sure it looks like ``data/SPair-71k``
Please cite the following papers if you use SPair-71k dataset:
```
@article{min2019spair,
title={SPair-71k: A Large-scale Benchmark for Semantic Correspondence},
author={Juhong Min and Jongmin Lee and Jean Ponce and Minsu Cho},
journal={arXiv prepreint arXiv:1908.10543},
year={2019}
}
@InProceedings{min2019hyperpixel,
title={Hyperpixel Flow: Semantic Correspondence with Multi-layer Neural Features},
author={Juhong Min and Jongmin Lee and Jean Ponce and Minsu Cho},
booktitle={ICCV},
year={2019}
}
```
For more information, please see [pygmtools](https://pypi.org/project/pygmtools/).
## Run the Experiment
Run training and evaluation
```bash
python train_eval.py --cfg path/to/your/yaml
```
and replace ``path/to/your/yaml`` by path to your configuration file, e.g.
```bash
python train_eval.py --cfg experiments/vgg16_pca_voc.yaml
```
Default configuration files are stored in``experiments/`` and you are welcomed to try your own configurations. If you find a better yaml configuration, please let us know by raising an issue or a PR and we will update the benchmark!
## Pretrained Models
_ThinkMatch_ provides pretrained models. The model weights are available via [google drive](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/11xAQlaEsMrRlIVc00nqWrjHf8VOXUxHQ?usp=sharing)
To use the pretrained models, firstly download the weight files, then add the following line to your yaml file:
```yaml
PRETRAINED_PATH: path/to/your/pretrained/weights
```
## Chat with the Community
If you have any questions, or if you are experiencing any issues, feel free to raise an issue on GitHub.
We also offer the following chat rooms if you are more comfortable with them:
* Discord (for English users):
[](https://discord.gg/8m6n7rRz9T)
* QQ Group (for Chinese users)/QQ群(中文用户): 696401889
[](https://qm.qq.com/cgi-bin/qm/qr?k=NlPuwwvaFaHzEWD8w7jSOTzoqSLIM80V&jump_from=webapi&authKey=chI2htrWDujQed6VtVid3V1NXEoJvwz3MVwruax6x5lQIvLsC8BmpmzBJOCzhtQd)
## Citing ThinkMatch
If you find any of the models useful in your research, please cite the corresponding papers (BibTeX citations are available for each model in the [``models/``](https://github.com/Thinklab-SJTU/ThinkMatch/tree/master/models) directory).
If you like this framework, you may also cite the underlying library ``pygmtools`` which is called during training & testing:
```
@article{wang2024pygm,
author = {Runzhong Wang and Ziao Guo and Wenzheng Pan and Jiale Ma and Yikai Zhang and Nan Yang and Qi Liu and Longxuan Wei and Hanxue Zhang and Chang Liu and Zetian Jiang and Xiaokang Yang and Junchi Yan},
title = {Pygmtools: A Python Graph Matching Toolkit},
journal = {Journal of Machine Learning Research},
year = {2024},
volume = {25},
number = {33},
pages = {1-7},
url = {https://jmlr.org/papers/v25/23-0572.html},
}
```