https://github.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator
CRD and Operator to access your Kubernetes Deployment over the Internet
https://github.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator
go kubebuilder kubernetes operator
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
CRD and Operator to access your Kubernetes Deployment over the Internet
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator
- Owner: abhirockzz
- Created: 2021-09-18T15:56:35.000Z (almost 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-09-18T18:14:27.000Z (almost 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-24T00:24:28.031Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: go, kubebuilder, kubernetes, operator
- Language: Go
- Homepage: https://itnext.io/kubexpose-a-kubernetes-operator-for-fun-and-profit-f528586eee07
- Size: 67.4 KB
- Stars: 48
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Kubexpose: Access your Kubernetes Deployment over the Internet
[Kubexpose](https://github.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator) makes it easy to access a Kubernetes `Deployment` over a public URL. It's a [Kubernetes Operator](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/extend-kubernetes/operator/) backed by a [Custom Resource Definition](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/extend-kubernetes/api-extension/custom-resources/).
> `Kubexpose` is an experimental project built using [kubebuilder](kubebuilder.io)
## Quick start
Any Kubernetes cluster will work (`minikube`, `kind`, Docker Desktop, on the cloud, whatever...).
To deploy the operator and required components:
```bash
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator/master/kubexpose-all-in-one.yaml
# check CRD
kubectl get crd
```
Make sure Operator is up and running:
```bash
export OPERATOR_NAMESPACE=kubexpose-operator-system
# check Pods
kubectl get pods -n $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE
# check logs
kubectl logs -f $(kubectl get pods --namespace $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE -o=jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -c manager -n $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE
```
Create `nginx` Deployment (this is the one you want to expose over the internet using a public URL) and `kubexpose` resource (which will help you do that!):
```
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator/master/quickstart/nginx.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator/master/quickstart/kubexpose.yaml
```
Wait for a few seconds and check the public URL at which the Nginx `Deployment` can be accessed:
```bash
kubectl get kubexpose/kubexpose-test -o=jsonpath='{.status.url}'
```
> Access the publlic URL using your browser or test it using `curl`
Confirm that the `Service` and `Deployment` have been created as well:
```bash
kubectl get svc/nginx-test-svc-kubexpose-test
kubectl get deployment/nginx-test-expose-kubexpose-test
```
> You can try out other scenarios such as trying to `Deployment` and/or `Service` - the Operator will reconcile or bring things back to the state as specified in the resource.
To delete the `kubexpose` resource:
```bash
kubectl delete kubexpose/kubexpose-test
```
> This will also delete the `Service` and `Deployment` which were created for this resource
Delete the Nginx deployment:
```bash
kubectl delete deployment/nginx-test
```
To uninstall the Operator:
```bash
kubectl delete -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator/master/kubexpose-all-in-one.yaml
```
> This will delete the CRD, `kubexpose` operator and other resources.
## How does it work?
Behind the scenes, `Kubexpose` uses the awesome [ngrok](https://ngrok.com/) project to get the job done!
When you create a `kubexpose` resource, the operator:
- Creates a `ClusterIP` type `Service` for the `Deployment` you want to access (naming format: `-svc-`)
- Creates a `Deployment` (using this [ngrok Docker image](https://hub.docker.com/r/wernight/ngrok/)) that runs `ngrok` - which is configured to point to the `Service` (naming format: `-expose-`). It's equivalent to starting `ngrok` as such: `ngrok http foo-svc-bar 80`
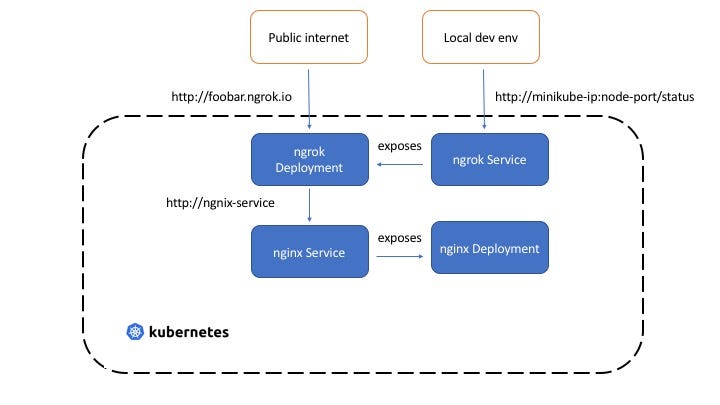
> The `Deployment` and `Service` and owned and managed by the Kubexpose resource instance.
## Build from source
You need to have [kubebuilder installed](https://book.kubebuilder.io/quick-start.html#installation) on your machine. If you don't want to do that, simply leverage the [devcontainer config](.devcontainer) that comes with the project to [setup the entire environment](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/remote/containers#_quick-start-open-an-existing-folder-in-a-container) in just a few clicks.
Clone the repository:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator
```
First, build a Docker image and push it to a registry of your choice:
```bash
export IMG=
docker login
make docker-build docker-push IMG=$IMG
```
You can now setup the operator and associated resources on the Kubernetes cluster:
```bash
export IMG=
make deploy IMG=$IMG
```
This single command will create a bunch of resources, such as the `Kubexpose` Custom Resource Definition (CRD), `Kubexpose` Operator `Deployment`, RBAC policies etc.
Check the output for details:
```bash
/workspaces/kubexpose-operator/bin/controller-gen "crd:trivialVersions=true,preserveUnknownFields=false" rbac:roleName=manager-role webhook paths="./..." output:crd:artifacts:config=config/crd/bases
cd config/manager && /workspaces/kubexpose-operator/bin/kustomize edit set image controller=abhirockzz/kubexpose
/workspaces/kubexpose-operator/bin/kustomize build config/default | kubectl apply -f -
namespace/kubexpose-operator-system created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kubexposes.kubexpose.kubexpose.io created
serviceaccount/kubexpose-operator-controller-manager created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-leader-election-role created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-manager-role created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-metrics-reader created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-proxy-role created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-leader-election-rolebinding created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-manager-rolebinding created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-proxy-rolebinding created
configmap/kubexpose-operator-manager-config created
service/kubexpose-operator-controller-manager-metrics-service created
deployment.apps/kubexpose-operator-controller-manager created
```
> The operator runs in a different namespace - `kubexpose-operator-system`
To check the operator `Deployment`:
```bash
export OPERATOR_NAMESPACE=kubexpose-operator-system
# wait for Pod to come up
kubectl get pods -n $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE -w
# check logs
kubectl logs -f $(kubectl get pods --namespace $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE -o=jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -c manager -n $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE
```