https://github.com/abstractalgo/react-browser-extension
starter repo for building web browser extensions (MV3) with React v18 and Typescript
https://github.com/abstractalgo/react-browser-extension
browser-extension chrome chrome-extension extension react typescript
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
starter repo for building web browser extensions (MV3) with React v18 and Typescript
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/abstractalgo/react-browser-extension
- Owner: abstractalgo
- Created: 2022-01-03T13:01:15.000Z (almost 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-03-23T20:46:39.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-06T05:12:56.408Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: browser-extension, chrome, chrome-extension, extension, react, typescript
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 404 KB
- Stars: 52
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 7
- Open Issues: 7
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Web Extensions React starter
A starter repo for building browser extensions with React and Typescript.
Here's what you get:
- :atom_symbol: content scripts, popup and options page as three separate React (v18.2+) apps
- 𝙏𝙎 Typescript (v5.0+) on all apps and other scripts
- 💬 a common communication channel and storage for all these apps and scripts
- 🧩 works with Manifest V3 (i.e. works with all Chromium-based browsers and soon Firefox)
## developing your own extension
Short version:
```bash
# install dependencies in all apps thanks to Yarn workspaces
yarn
# run
cd content_scripts/app && yarn start
cd options && yarn start
cd popup && yarn start
# to build
yarn build
# to package into an archive
yarn zip
```
More details:
- learn more about WebExtensions and Manifest files (see [resources](#resources) section)
- update information inside `manifest.json` (name, description, homepage,...) and update icons
- code and test your React apps within `/content_scripts/app`, `/options` and `/popup`
- all three folders are regular React apps bundled via [Vite](https://vitejs.dev/), so just refer to their `package.json` and `vite.config.js` for config, and write code like you would for any other React app
- if you don't need some of these apps or scripts, simply remove them from the project and remove their build steps in the build pipeline (inside `./build.sh`)
- build/compile your extension by running `yarn build` from the root folder (this executes `./build.sh`), load it in the browser and try it there
- you can use generated `./build` folder to load the "unpacked" version of the extension in the browser and test it locally (see how [for Chrome](https://developer.chrome.com/docs/extensions/mv3/getstarted/#manifest) or [for Firefox](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Mozilla/Add-ons/WebExtensions/Your_first_WebExtension#trying_it_out))
- pack the extension into a single archive
- run `yarn zip` from the root folder
- publish it on the web stores
- instructions for [publishing to Chrome Web Store](https://developer.chrome.com/docs/extensions/mv3/hosting/)
- instructions for [publishing to Firefox Add-ons](https://extensionworkshop.com/documentation/publish/)
## resources
Docs and guides:
- [Chrome API reference](https://developer.chrome.com/docs/extensions/reference/)
- [MV3 architecture overview](https://developer.chrome.com/docs/extensions/mv3/architecture-overview/) (Chrome)
- [Manifest V3 file format](https://developer.chrome.com/docs/extensions/mv3/manifest/)
- [Anatomy of a Web Extension](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Mozilla/Add-ons/WebExtensions/Anatomy_of_a_WebExtension) (Firefox)
- [Building a cross-browser extension](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Mozilla/Add-ons/WebExtensions/Build_a_cross_browser_extension)
- [Porting a Google Chrome extension](https://extensionworkshop.com/documentation/develop/porting-a-google-chrome-extension/)
Useful code repos:
- [mozilla/webextension-polyfill](https://github.com/mozilla/webextension-polyfill)
- [mozilla/web-ext](https://github.com/mozilla/web-ext)
- [GoogleChrome/chrome-extensions-samples](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/chrome-extensions-samples) (non-React)
## how it works
Web extensions, and thus this repo, consist of four large parts, plus the manifest file specifying each of those and some additional meta-information. The parts are: content scripts, action/popup, options page and background scripts. A single web extension can have any combination of these, neither of all of them (i.e. all are optional); only the manifest is mandatory.
- The root folder (`./`) holds basic meta-information about the extension, i.e. its manifest and icons.
- `/content_scripts` is a place for the extra JS and CSS that gets injected into the pages that you view while your extension is installed and enabled. `/app` folder within it holds the React app where you basically write the entirety of logic, and the remaining files are there to create a container for your React root (similar to how `div#root` exists in `public/index.html` when using a regular CRA).
- `/popup` is a place for another React app that gets displayed as a popup/dropdown when clicking on the extension's icon displayed near the address bar in the browser.
- `/options` hosts a React app that serves an Options page for the extension where you can configure and persists whatever some common options.
- `/worker` is a place for a service worker (MV3) or a background script (MV2). These scripts can never have any UI as a part of it, so it consists only of TS/JS files, and they run in the background.
By having a very predictable build output (a single JS bundle) for each part of our extension, we can hardcode their script files inside `manifest.json` and that's it - always the same output, always the same entry points and script files, i.e. no need for [programmatic injection](https://developer.chrome.com/docs/extensions/mv3/content_scripts/#programmatic), dynamic loading or anything complex.
This is a build output:
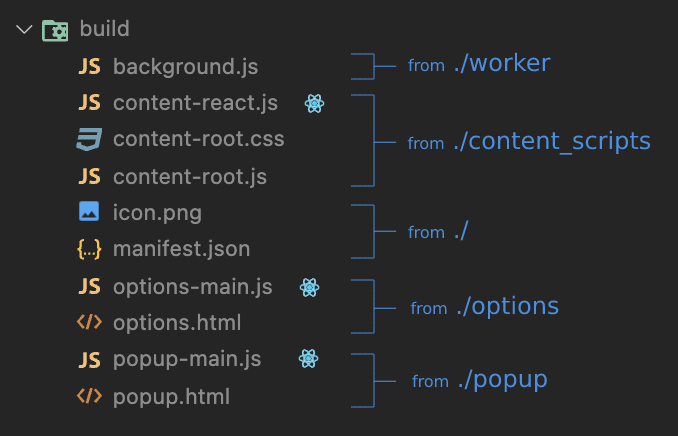
You can see how that exactly matches the files specified inside of `manifest.json`:
