https://github.com/adbrosaci/vue-lang-router
Vue language routing with (optional) localized URLs.
https://github.com/adbrosaci/vue-lang-router
Last synced: 8 months ago
JSON representation
Vue language routing with (optional) localized URLs.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/adbrosaci/vue-lang-router
- Owner: adbrosaci
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-05-13T09:49:06.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-07-07T23:09:31.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-15T03:54:56.968Z (8 months ago)
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.11 MB
- Stars: 64
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 8
- Open Issues: 17
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-vue - vue-lang-router - Vue language routing with (optional) localized URLs. (UI Utilities [🔝](#readme))
- awesome-vue - vue-lang-router - Vue.js 2 & 3 language routing with (optional) URL localization. (Components & Libraries / UI Utilities)
README
# :earth_africa: Vue Language Router
Language routing and URL localization made easy.
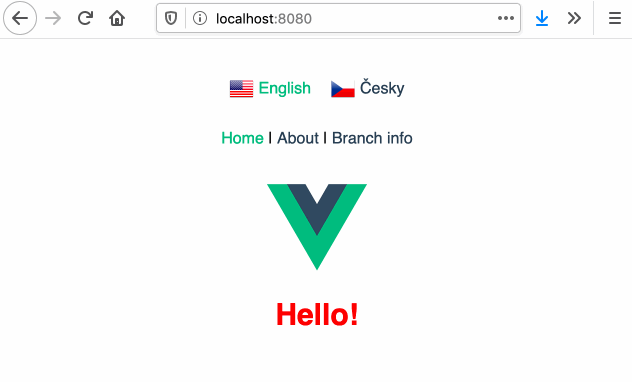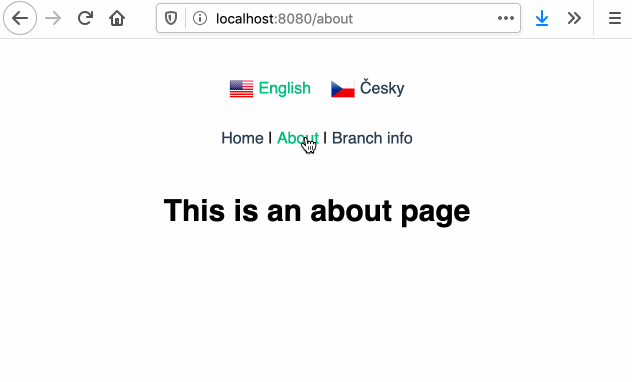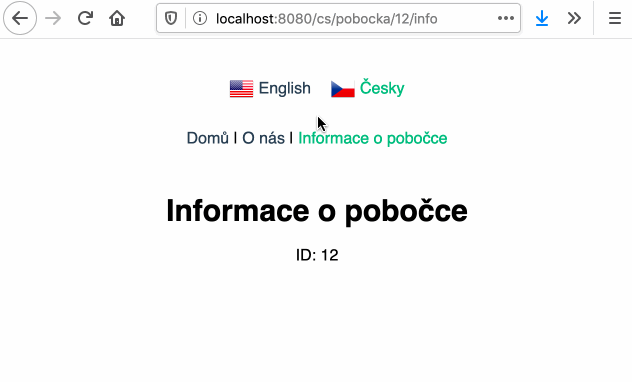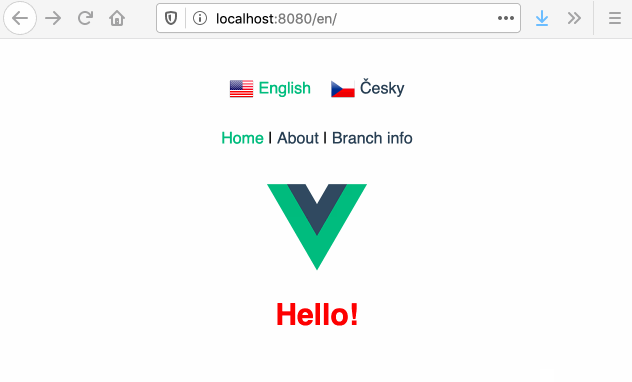
Built on top of :vertical_traffic_light: [Vue Router](https://router.vuejs.org/) and :globe_with_meridians: [Vue I18n](https://kazupon.github.io/vue-i18n/).
## Demo
You can play with demo at [Code Sandbox](https://codesandbox.io/s/vue-2-example-zy7ou).
## Features
:hourglass_flowing_sand: Asynchronous translation loading
:performing_arts: URL localization
:classical_building: Default language (no language prefix in URL)
:baby: Supports variables and children in routes
:car: :bike: Supports both history and hash mode
:books: Sets user-preferred language on first visit
:memo: Loads last used language when visiting site again
:fast_forward: No extra router setup
## Version information
This version is compatible with [Vue 2](https://vuejs.org/). If you need [Vue 3](https://v3.vuejs.org) compatible version, please check out [v2](https://github.com/adbrosaci/vue-lang-router/tree/vue-3) of this project.
## Installation
### Vue CLI plugin (recommended)
The easiest way to install Language Router is using [Vue CLI plugin for Language Router](https://github.com/adbrosaci/vue-cli-plugin-lang-router#readme). The plugin will modify your router file, setup translation files and more.
Use this command to add Language Router to your Vue.js project:
```sh
$ vue add lang-router
```
### Manually
#### 1. Install Language Router
```sh
$ npm i vue-lang-router
```
#### 2. Create translations in your app.
> Note: This example uses Czech and English translations.
Example file structure:
```sh
src
└── lang
└── translations
├── cs.json
├── en.json
└── index.js
```
Create `JSON` files for all desired languages and reference them in `index.js`. Translations are loaded on demand.
```javascript
/* src/lang/translations/en.json */
{
"hello": "Hello!",
"about": {
"example": "This is an About page."
}
}
```
```javascript
/* src/lang/translations/cs.json */
{
"hello": "Ahoj!",
"about": {
"example": "Tohle je stránka O nás."
}
}
```
```javascript
/* src/lang/translations/index.js */
export default {
en: {
name: 'English',
load: () => { return import('./en.json'); },
},
cs: {
name: 'Česky',
load: () => { return import('./cs.json'); },
},
};
```
In case you do not want to load translations asynchronously, you can provide `messages` object with translations instead of `load` function. For example:
```javascript
export default {
en: {
name: 'English',
messages: {
hello: 'Hello!',
},
},
};
```
#### 3. Create localized URLs in your app.
> Note: Localized URLs are optional.
Example file structure:
```sh
src
└── lang
└── localized-urls
├── cs.json
└── index.js
```
Create `JSON` files for all desired languages and `import` them in `index.js`. Localized URLs need to be imported before router instantiation.
```javascript
/* src/lang/localized-urls/cs.json */
{
"about": "o-nas"
}
```
```javascript
/* src/lang/localized-urls/index.js */
import cs from './cs.json';
export default { cs };
```
Language router will parse any given path and attempt to localize its segments based on this configuration. If no match is found, the original path segment is retained.
#### 4. Modify your router file
- Import `LangRouter` and use it instead of `VueRouter`.
- Import translations and localized URLs and pass them to `LangRouter` plugin.
- Create new router instance. All the options are the same as in `VueRouter`.
```javascript
/* src/router/index.js */
import Vue from 'vue';
import LangRouter from 'vue-lang-router';
import translations from '../lang/translations';
import localizedURLs from '../lang/localized-urls';
Vue.use(LangRouter, {
defaultLanguage: 'en',
translations,
localizedURLs,
});
const routes = [ /* Your routes here */ ];
const router = new LangRouter({
routes,
mode: 'history',
});
```
#### 5. Modify your main file
Import `i18n` and use it in your `Vue` instance.
```javascript
import Vue from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
import router from './router';
import { i18n } from 'vue-lang-router';
new Vue({
router,
i18n,
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app');
```
## How to use
### Using translations
To use any translated string, use `$t('stringName')` in your code. For more information check out [`Vue I18n`](http://kazupon.github.io/vue-i18n/).
### Using links
Use `` component. It localizes given router path based on current language. It's a simple, yet powerful component, which takes a hassle out of generating proper links on your site.
It accepts the same options as [``](https://router.vuejs.org/api/#router-link-props).
```html
John Smith
```
The above code will generate a link with `href` value depending on various factors. Here are a few examples:
```javascript
/*
Default language: "en"
Current language: "en"
Localized URLs "en": {}
Current URL: /
*/
href="/user/john-smith"
/*
Default language: "en"
Current language: "en"
Localized URLs "en": { "user": "u" }
Current URL: /en/example
*/
href="/en/u/john-smith"
/*
Default language: "en"
Current language: "cs"
Localized URLs "cs": { "user": "uzivatel" }
Current URL: /
*/
href="/cs/uzivatel/john-smith"
```
### Switching language
Use `` component for this. The component will loop over all available languages and generate `links` array with properties, which you can use to create your own menu.
The wrapper element will have `router-language-switcher` class.
#### Examples:
```html
![]()
{{ link.langName }}
```
```html
{{ link.langIndex }}
```
#### Properties:
- **url** : The localized path to the current/specified page in iterated language.
- **langIndex** : The index of the iterated language provided in `translations`.
- **langName** : The name of the iterated language provided in `translations`.
- **activeClass** : Returns the active class when iterated language equals current language, otherwise empty.
#### Accepted attributes:
- **tag** : Use this attribute to specify which tag should be used as a wrapper element. The default is `div`.
- **url** : Provides a specific path to generate translation links for. If omitted, current path is used.
- **active-class** : Defines the name of class to provide when language of the link equals current language. The default is `router-active-language`.
### Vue I18n customization
In case you'd like to pass in custom `vue-i18n` options, you can do so using `i18nOptions` property, for example:
```javascript
/* src/router/index.js */
Vue.use(LangRouter, {
defaultLanguage: 'en',
translations,
localizedURLs,
i18nOptions: {
dateTimeFormats: { ... },
pluralizationRules: { ... },
}
});
```