https://github.com/adulau/malwareclassifier
Malware Classifier From Network Captures
https://github.com/adulau/malwareclassifier
malware malware-classifier network-capture python tshark visualization
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
Malware Classifier From Network Captures
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/adulau/malwareclassifier
- Owner: adulau
- Created: 2015-01-10T18:49:03.000Z (over 10 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2017-01-27T20:42:26.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-08T01:42:36.711Z (2 months ago)
- Topics: malware, malware-classifier, network-capture, python, tshark, visualization
- Language: Python
- Size: 528 KB
- Stars: 82
- Watchers: 6
- Forks: 13
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Malware Classifier From Network Capture
*Malware Classifier* is a simple free software project done during an [university workshop of 4 hours](http://www.foo.be/cours/dess-20142015/Redis-Introduction.pdf). The objective of the 4 hours workshop was to introduce network forensic and simple techniques to classify malware network capture (from their execution in a virtual machine). So the software was kept very simple while using and learning existing tools ([networkx](https://networkx.github.io/), [redis](http://www.redis.io/) and [Gephi](http://gephi.github.io/)).
## Requirements
* Python 2.7
* networkx and redis modules (pip install -r REQUIREMENTS)
* tshark (part of Wireshark)
* a Redis server
# How to use the Malware Classifier
You'll need of a set of network packet captures. In the workshop, we use a dataset with more than 5000 pcap files generated from the execution of malware in virtual machines.
```
...
0580c82f6f90b75fcf81fd3ac779ae84.pcap
05a0f4f7a72f04bda62e3a6c92970f6e.pcap
05b4a945e5f1f7675c19b74748fd30d1.pcap
05b57374486ce8a5ce33d3b7d6c9ba48.pcap
05bbddc8edac3615754f93139cf11674.pcap
...
```
The filename includes the MD5 malware executed in the virtual machine.
If you want to classify malware communications based on the Server HTTP headers of the (potential) C&C communication.
```shell
cd capture
ls -1 . | parallel --gnu "cat {1} | tshark -E header=yes -E separator=, -Tfields -e http.server -r {1} | python ./bin/import.py -f {1} "
```
You can add additional attributes like any fields from the dissectors available within tshark (tshark -G fields). You can add additional fields in the command above. This will update the redis data structure. Then when you have enough attributes, you can dump a graph out of the relationships between the attributes and the malware packet captures.
```shell
python ./bin/graph.py
```
graph.py generates a GEXF file that you can import in [gephi](https://gephi.org).
The output in Gephi can look like this:

## Redis data structure
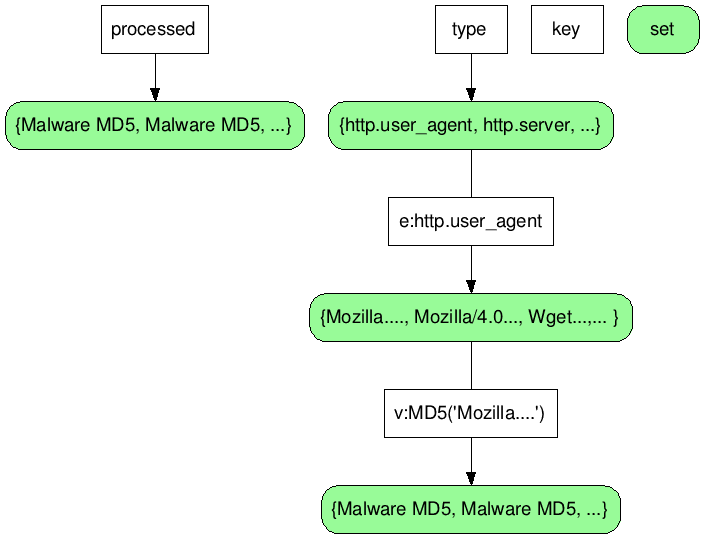
## Notes for the student
Check the git log and the commits, these include the steps performed during the workshop especially regarding the improvement of the Python scripts.
## Slides of the training session
[Classifying malware using network traffic analysis. Or how to learn Redis, git, tshark and Python in 4 hours.](https://www.foo.be/cours/dess-20162017/pub/Redis-Introduction.pdf)