https://github.com/aershov24/front-end-developer-interview-questions
Awesome list of front end developer interview questions from FullStack.Cafe
https://github.com/aershov24/front-end-developer-interview-questions
angular-interview-questions interview-questions interview-questions-solved javascript-interview-questions nodejs-interview-questions react-interview-questions
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Awesome list of front end developer interview questions from FullStack.Cafe
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/aershov24/front-end-developer-interview-questions
- Owner: aershov24
- Created: 2019-10-31T05:07:41.000Z (almost 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2019-10-31T07:24:39.000Z (almost 6 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-19T09:12:17.997Z (9 months ago)
- Topics: angular-interview-questions, interview-questions, interview-questions-solved, javascript-interview-questions, nodejs-interview-questions, react-interview-questions
- Homepage: https://www.fullstack.cafe
- Size: 202 KB
- Stars: 32
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 19
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
## Table of Contents
* [11 Painful Git Interview Questions You Will Cry On](#11PainfulGitInterviewQuestionsYouWillCryOn)
* [112+ Behavioral Interview Questions for Software Developers](#112+BehavioralInterviewQuestionsforSoftwareDevelopers)
* [13 Tricky CSS3 Interview Questions And Answers to Stand Out on Interview in 2018](#13TrickyCSS3InterviewQuestionsAndAnswerstoStandOutonInterviewin2018)
* [15 ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions And Answers (2019 Update)](#15ASP.NETWebAPIInterviewQuestionsAndAnswers(2019Update))
* [15 Amazon Web Services Interview Questions and Answers for 2018](#15AmazonWebServicesInterviewQuestionsandAnswersfor2018)
* [15 Best Continuous Integration Interview Questions (2018 Revision)](#15BestContinuousIntegrationInterviewQuestions(2018Revision))
* [15 Essential HTML5 Interview Questions to Watch Out in 2018](#15EssentialHTML5InterviewQuestionstoWatchOutin2018)
* [15+ Azure Interview Questions And Answers (2018 REVISIT)](#15+AzureInterviewQuestionsAndAnswers(2018REVISIT))
* [19+ Expert Node.js Interview Questions in 2018](#19+ExpertNode.jsInterviewQuestionsin2018)
* [20 .NET Core Interview Questions and Answers](#20.NETCoreInterviewQuestionsandAnswers)
* [20 Basic TypeScript Interview Questions (2018 Edition)](#20BasicTypeScriptInterviewQuestions(2018Edition))
* [20 Reactive Programming Interview Questions To Polish Up In 2019](#20ReactiveProgrammingInterviewQuestionsToPolishUpIn2019)
* [20 Senior .NET Developer Interview Questions to Ask in 2019](#20Senior.NETDeveloperInterviewQuestionstoAskin2019)
* [20 Vue.js Interview Questions And Answers (2018 Updated)](#20Vue.jsInterviewQuestionsAndAnswers(2018Updated))
* [20+ Agile Scrum Interview Questions for Software Developers in 2018](#20+AgileScrumInterviewQuestionsforSoftwareDevelopersin2018)
* [22 Essential WCF Interview Questions That'll Make You Cry](#22EssentialWCFInterviewQuestionsThat'llMakeYouCry)
* [22 Important JavaScript/ES6/ES2015 Interview Questions](#22ImportantJavaScript/ES6/ES2015InterviewQuestions)
* [22+ Angular 6 Interview Questions to Stand Out in 2018](#22+Angular6InterviewQuestionstoStandOutin2018)
* [23 Advanced JavaScript Interview Questions](#23AdvancedJavaScriptInterviewQuestions)
* [26 Top Angular 8 Interview Questions To Learn in 2019](#26TopAngular8InterviewQuestionsToLearnin2019)
* [29 Essential Blockchain Interview Questions You Will Suck On](#29EssentialBlockchainInterviewQuestionsYouWillSuckOn)
* [30 Best MongoDB Interview Questions and Answers (2018 Update)](#30BestMongoDBInterviewQuestionsandAnswers(2018Update))
* [30 Docker Interview Questions and Answers in 2019](#30DockerInterviewQuestionsandAnswersin2019)
* [32 jQuery Interview Questions You'll Simply Fail On](#32jQueryInterviewQuestionsYou'llSimplyFailOn)
* [33 Frequently Asked Node.js Interview Questions (2020 Update)](#33FrequentlyAskedNode.jsInterviewQuestions(2020Update))
* [35 LINQ Interview Questions and Answers in 2019](#35LINQInterviewQuestionsandAnswersin2019)
* [35 Microservices Interview Questions You Most Likely Can't Answer](#35MicroservicesInterviewQuestionsYouMostLikelyCan'tAnswer)
* [35 Top Angular 7 Interview Questions To Crack in 2019](#35TopAngular7InterviewQuestionsToCrackin2019)
* [37 ASP.NET Interview Questions You Must Know](#37ASP.NETInterviewQuestionsYouMustKnow)
* [39 Advanced React Interview Questions You Must Clarify (2020 Update)](#39AdvancedReactInterviewQuestionsYouMustClarify(2020Update))
* [40 Advanced OOP Interview Questions and Answers [2019 Update]](#40AdvancedOOPInterviewQuestionsandAnswers[2019Update])
* [40 Common ADO.NET Interview Questions to Know in 2019](#40CommonADO.NETInterviewQuestionstoKnowin2019)
* [42 Advanced Java Interview Questions For Senior Developers](#42AdvancedJavaInterviewQuestionsForSeniorDevelopers)
* [45 Important PHP Interview Questions That May Land You a Job](#45ImportantPHPInterviewQuestionsThatMayLandYouaJob)
* [5 Salary Negotiation Rules for Software Developers](#5SalaryNegotiationRulesforSoftwareDevelopers)
* [50 Common Front End Developer Interview Questions [2019 Edition]](#50CommonFrontEndDeveloperInterviewQuestions[2019Edition])
* [50 Common Web Developer Interview Questions [2020 Updated]](#50CommonWebDeveloperInterviewQuestions[2020Updated])
* [50 Junior Web Developer Interview Questions. The Ultimate 2018 Guide.](#50JuniorWebDeveloperInterviewQuestions.TheUltimate2018Guide.)
* [50 Senior Java Developer Interview Questions To Ask in 2020](#50SeniorJavaDeveloperInterviewQuestionsToAskin2020)
* [6 Web Security Interview Questions for Full Stack Developers](#6WebSecurityInterviewQuestionsforFullStackDevelopers)
* [60 Java and Spring Interview Questions You Must Know](#60JavaandSpringInterviewQuestionsYouMustKnow)
* [70 C# Interview Questions You Must Know [2019 Update]](#70C#InterviewQuestionsYouMustKnow[2019Update])
* [75+ JavaScript Interview Questions [ES6/ES2015 Update] in 2019](#75+JavaScriptInterviewQuestions[ES6/ES2015Update]in2019)
* [8 Common Full Stack Interview Questions To Brush Up (2018 Edition)](#8CommonFullStackInterviewQuestionsToBrushUp(2018Edition))
* [8 DevOps Interview Questions and Answers in 2018](#8DevOpsInterviewQuestionsandAnswersin2018)
* [8 GraphQL Interview Questions To Know (in 2018)](#8GraphQLInterviewQuestionsToKnow(in2018))
* [8 Performance Testing Interview Questions & Answers in 2018](#8PerformanceTestingInterviewQuestions&Answersin2018)
* [8 Steps to Increase Your Dev Resume Response Rate by 90%](#8StepstoIncreaseYourDevResumeResponseRateby90%)
* [9 Basic webpack Interview Questions And Answers in 2019](#9BasicwebpackInterviewQuestionsAndAnswersin2019)
* [9 Expert Design Patterns Interview Questions To Know (in 2018)](#9ExpertDesignPatternsInterviewQuestionsToKnow(in2018))
* [9 Questions Every Developer Should Ask On Interview](#9QuestionsEveryDeveloperShouldAskOnInterview)
* [9 Tricky Software Architecture Interview Questions ](#9TrickySoftwareArchitectureInterviewQuestions)
* [Angular Developer Resume Sample & Template (Download Word/PDF)](#AngularDeveloperResumeSample&Template(DownloadWord/PDF))
* [Front End Developer Resume Sample & Template (Word, PDF)](#FrontEndDeveloperResumeSample&Template(Word,PDF))
* [Guest Voice: The Solution For The CV Problem In IT Recruitment](#GuestVoice:TheSolutionForTheCVProblemInITRecruitment)
* [JavaScript Developer Resume Sample & Template (2019 Update)](#JavaScriptDeveloperResumeSample&Template(2019Update))
* [Node.js Error Handling: 7 Ways To Kill Them All](#Node.jsErrorHandling:7WaysToKillThemAll)
* [The Ultimate Guide to Transitioning to Remote Web Development](#TheUltimateGuidetoTransitioningtoRemoteWebDevelopment)
* [Top 26+ React Interview Questions (2018 Edition)](#Top26+ReactInterviewQuestions(2018Edition))
* [Top 60+ MEAN Stack Developer Interview Questions And Answers (2019 Edition)](#Top60+MEANStackDeveloperInterviewQuestionsAndAnswers(2019Edition))
## [[⬆]](#toc) 11 Painful Git Interview Questions You Will Cry On
> Originally published on 👉 11 Painful Git Interview Questions You Will Cry On | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Git fork? What is difference between fork, branch and clone? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* A **fork** is a remote, server-side copy of a repository, distinct from the original. A fork isn't a Git concept really, it's more a political/social idea.
* A **clone** is not a fork; a clone is a local copy of some remote repository. When you clone, you are actually copying the entire source repository, including all the history and branches.
* A **branch** is a mechanism to handle the changes within a single repository in order to eventually merge them with the rest of code. A branch is something that is within a repository. Conceptually, it represents a thread of development.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q2: What is the difference between "git pull" and "git fetch"? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In the simplest terms, `git pull` does a `git fetch` followed by a `git merge`.
* When you use `pull`, Git tries to automatically do your work for you. **It is context sensitive**, so Git will merge any pulled commits into the branch you are currently working in. `pull` **automatically merges the commits without letting you review them first**. If you don’t closely manage your branches, you may run into frequent conflicts.
* When you `fetch`, Git gathers any commits from the target branch that do not exist in your current branch and **stores them in your local repository**. However, **it does not merge them with your current branch**. This is particularly useful if you need to keep your repository up to date, but are working on something that might break if you update your files. To integrate the commits into your master branch, you use `merge`.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q3: What's the difference between a "pull request" and a "branch"? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* A **branch** is just a separate version of the code.
* A **pull request** is when someone take the repository, makes their own branch, does some changes, then tries to merge that branch in (put their changes in the other person's code repository).
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q4: How to revert previous commit in git? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Say you have this, where C is your HEAD and (F) is the state of your files.
```sh
(F)
A-B-C
↑
master
```
1. To nuke changes in the commit:
```sh
git reset --hard HEAD~1
```
Now B is the HEAD. Because you used --hard, your files are reset to their state at commit B.
2. To undo the commit but keep your changes:
```sh
git reset HEAD~1
```
Now we tell Git to move the HEAD pointer back one commit (B) and leave the files as they are and `git status` shows the changes you had checked into C.
3. To undo your commit but leave your files and your index
```sh
git reset --soft HEAD~1
```
When you do `git status`, you'll see that the same files are in the index as before.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q5: What is "git cherry-pick"? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The command git *cherry-pick* is typically used to introduce particular commits from one branch within a repository onto a different branch. A common use is to forward- or back-port commits from a maintenance branch to a development branch.
This is in contrast with other ways such as merge and rebase which normally apply many commits onto another branch.
Consider:
```sh
git cherry-pick
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q6: Explain the advantages of Forking Workflow ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **Forking Workflow** is fundamentally different than other popular Git workflows. Instead of using a single server-side repository to act as the “central” codebase, it gives every developer their own server-side repository. The Forking Workflow is most often seen in public open source projects.
The *main advantage* of the Forking Workflow is that contributions can be integrated without the need for everybody to push to a single central repository that leads to a clean project history. Developers push to their own server-side repositories, and only the project maintainer can push to the official repository.
When developers are ready to publish a local commit, they push the commit to their own public repository—not the official one. Then, they file a pull request with the main repository, which lets the project maintainer know that an update is ready to be integrated.
**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q7: Tell me the difference between HEAD, working tree and index, in Git? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* The **working tree/working directory/workspace** is the directory tree of (source) files that you see and edit.
* The **index/staging area** is a single, large, binary file in /.git/index, which lists all files in the current branch, their sha1 checksums, time stamps and the file name - it is not another directory with a copy of files in it.
* **HEAD** is a reference to the last commit in the currently checked-out branch.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q8: Could you explain the Gitflow workflow? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Gitflow workflow employs two parallel *long-running* branches to record the history of the project, `master` and `develop`:
* **Master** - is always ready to be released on LIVE, with everything fully tested and approved (production-ready).
* **Hotfix** - Maintenance or “hotfix” branches are used to quickly patch production releases. Hotfix branches are a lot like release branches and feature branches except they're based on `master` instead of `develop`.
* **Develop** - is the branch to which all feature branches are merged and where all tests are performed. Only when everything’s been thoroughly checked and fixed it can be merged to the `master`.
* **Feature** - Each new feature should reside in its own branch, which can be pushed to the `develop` branch as their parent one.

**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q9: When should I use "git stash"? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The `git stash` command takes your uncommitted changes (both staged and unstaged), saves them away for later use, and then reverts them from your working copy.
Consider:
```sh
$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
new file: style.css
Changes not staged for commit:
modified: index.html
$ git stash
Saved working directory and index state WIP on master: 5002d47 our new homepage
HEAD is now at 5002d47 our new homepage
$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
```
The one place we could use stashing is if we discover we forgot something in our last commit and have already started working on the next one in the same branch:
```sh
# Assume the latest commit was already done
# start working on the next patch, and discovered I was missing something
# stash away the current mess I made
$ git stash save
# some changes in the working dir
# and now add them to the last commit:
$ git add -u
$ git commit --ammend
# back to work!
$ git stash pop
```
**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q10: How to remove a file from git without removing it from your file system? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q11: When do you use "git rebase" instead of "git merge"? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 112+ Behavioral Interview Questions for Software Developers
> Originally published on 👉 112+ Behavioral Interview Questions for Software Developers | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: How do you spend your time outside work? ⭐
**Answer:**
## [[⬆]](#toc) 13 Tricky CSS3 Interview Questions And Answers to Stand Out on Interview in 2018
> Originally published on 👉 13 Tricky CSS3 Interview Questions And Answers to Stand Out on Interview in 2018 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: Describe floats and how they work ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Float* is a CSS positioning property. Floated elements remain a part of the flow of the web page. This is distinctly different than page elements that use absolute positioning. Absolutely positioned page elements are removed from the flow of the webpage.
```css
#sidebar {
float: right; // left right none inherit
}
```
The CSS clear property can be used to be positioned below `left`/`right`/`both` floated elements.
**Source:** _css-tricks.com_
#### Q2: How is responsive design different from adaptive design? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Both *responsive* and *adaptive* design attempt to optimize the user experience across different devices, adjusting for different viewport sizes, resolutions, usage contexts, control mechanisms, and so on.
**Responsive design** works on the principle of flexibility — a single fluid website that can look good on any device. Responsive websites use *media queries*, *flexible grids*, and *responsive images* to create a user experience that flexes and changes based on a multitude of factors. Like a single ball growing or shrinking to fit through several different hoops.
**Adaptive design** is more like the modern definition of progressive enhancement. Instead of one flexible design, adaptive design detects the device and other features, and then provides the appropriate feature and layout based on a *predefined set of viewport sizes* and other characteristics. The site detects the type of device used, and delivers the pre-set layout for that device. Instead of a single ball going through several different-sized hoops, you’d have several different balls to use depending on the hoop size.
**Source:** _codeburst.io_
#### Q3: How does CSS actually work (under the hood of browser)? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
When a browser displays a document, it must combine the document's content with its style information. It processes the document in two stages:
* The browser converts *HTML* and *CSS* into the *DOM (Document Object Model)*. The DOM represents the document in the computer's memory. It combines the document's content with its style.
* The browser displays the contents of the DOM.

**Source:** _developer.mozilla.org_
#### Q4: What does Accessibility (a11y) mean? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Accessibility (a11y)** is a measure of a computer system's accessibility is to all people, including those with disabilities or impairments. It concerns both software and hardware and how they are configured in order to enable a disabled or impaired person to use that computer system successfully.
Accessibility is also known as *assistive technology*.
**Source:** _techopedia.com_
#### Q5: Explain the purpose of clearing floats in CSS ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q6: How do you optimize your webpages for print? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q7: Can you explain the difference between coding a website to be responsive versus using a mobile-first strategy? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q8: Explain the basic rules of CSS Specificity ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q9: Is there any reason you'd want to use `translate()` instead of `absolute` positioning, or vice-versa? And why? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q10: What the code fragment has the greater CSS specificity? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider the three code fragments:
```html
// A
h1
// B
#content h1
// C
Headline
```
What the code fragment has the greater specificy?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q11: What clearfix methods do you know? Provide some examples. ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q12: How to style every element which has an adjacent item right before it? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: Write down a selector that will match any links end in .zip, .ZIP, .Zip etc... ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 15 ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions And Answers (2019 Update)
> Originally published on 👉 15 ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions And Answers (2019 Update) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is ASP.NET Web API? ⭐
**Answer:**
ASP.NET Web API is a framework that simplifies building HTTP services for broader range of clients (including browsers as well as mobile devices) on top of .NET Framework.
Using ASP.NET Web API, we can create non-SOAP based services like plain XML or JSON strings, etc. with many other advantages including:
* Create resource-oriented services using the full features of HTTP
* Exposing services to a variety of clients easily like browsers or mobile devices, etc.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q2: What are the Advantages of Using ASP.NET Web API? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Using ASP.NET Web API has a number of advantages, but core of the advantages are:
* It works the HTTP way using standard HTTP verbs like `GET`, `POST`, `PUT`, `DELETE`, etc. for all CRUD operations
* Complete support for routing
* Response generated in JSON or XML format using `MediaTypeFormatter`
* It has the ability to be hosted in IIS as well as self-host outside of IIS
* Supports Model binding and Validation
* Support for OData
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q3: Which status code used for all uncaught exceptions by default? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**500** – Internal Server Error
Consider:
```csharp
[Route("CheckId/{id}")]
[HttpGet]
public IHttpActionResult CheckId(int id)
{
if(id > 100)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException();
}
return Ok(id);
}
```
And the result:
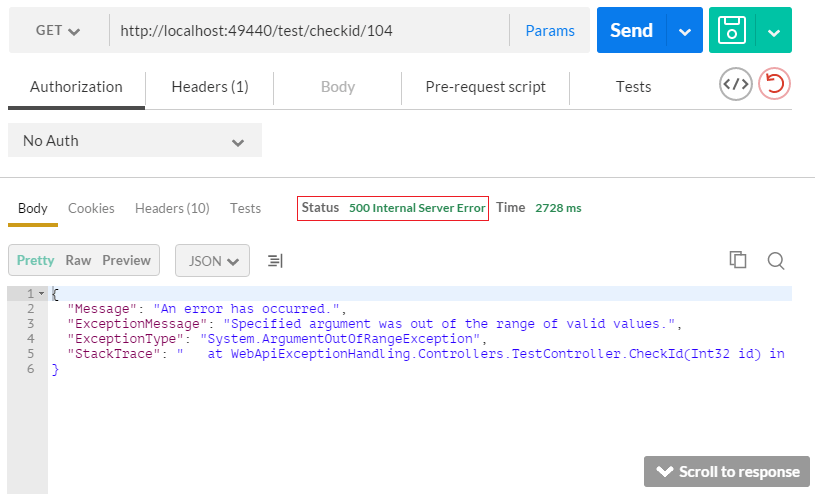
**Source:** _docs.microsoft.com_
#### Q4: What is the difference between ApiController and Controller? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Use **Controller** to render your normal views.
* **ApiController** action only return data that is serialized and sent to the client.
Consider:
```csharp
public class TweetsController : Controller {
// GET: /Tweets/
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult Index() {
return Json(Twitter.GetTweets(), JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
}
```
or
```csharp
public class TweetsController : ApiController {
// GET: /Api/Tweets/
public List Get() {
return Twitter.GetTweets();
}
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q5: Name types of Action Results in Web API 2 ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A Web API controller action can return any of the following:
* void - Return empty 204 (No Content)
* HttpResponseMessage - Return empty 204 (No Content)
* IHttpActionResult - Call ExecuteAsync to create an HttpResponseMessage, then convert to an HTTP response message
* Some other type - Write the serialized return value into the response body; return 200 (OK).
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q6: Compare WCF vs ASP.NET Web API? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Windows Communication Foundation** is designed to exchange standard SOAP-based messages using variety of transport protocols like HTTP, TCP, NamedPipes or MSMQ, etc.
* On the other hand, **ASP.NET API** is a framework for building non-SOAP based services over HTTP only.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q7: Explain the difference between MVC vs ASP.NET Web API ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* The purpose of Web API framework is to generate HTTP services that reach more clients by generating data in raw format, for example, plain XML or JSON string. So, ASP.NET Web API creates simple HTTP services that renders raw data.
* On the other hand, ASP.NET MVC framework is used to develop web applications that generate Views (HTML) as well as data. ASP.NET MVC facilitates in rendering HTML easy.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q8: What is Attribute Routing in ASP.NET Web API 2.0? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ASP.NET Web API v2 now support _Attribute Routing_ along with _convention-based approach_. In convention-based routes, the route templates are already defined as follows:
```csharp
Config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "api/{Controller}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional }
);
```
So, any incoming request is matched against already defined _**routeTemplate**_ and further routed to matched controller action. But it’s really hard to support _**certain URI patterns**_ using conventional routing approach like nested routes on same controller. For example, _authors have books_ or _customers have orders_, _students have courses_ etc.
Such patterns can be defined using attribute routing i.e. adding an attribute to controller action as follows:
```csharp
[Route("books/{bookId}/authors")]
public IEnumerable GetAuthorsByBook(int bookId) { ..... }
```
**Source:** _webdevelopmenthelp.net_
#### Q9: How to Return View from ASP.NET Web API Method? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q10: Explain briefly CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q11: What's the difference between OpenID and OAuth? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q12: Why should I use IHttpActionResult instead of HttpResponseMessage? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: Explain briefly OWIN (Open Web Interface for .NET) Self Hosting? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q14: Could you clarify what is the best practice with Web API error management? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: What is difference between WCF and Web API and WCF REST and Web Service? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 15 Amazon Web Services Interview Questions and Answers for 2018
> Originally published on 👉 15 Amazon Web Services Interview Questions and Answers for 2018 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: Explain the key components of AWS? ⭐
**Answer:**
* **Simple Storage Service (S3)**: S3 is most widely used AWS storage web service.
* **Simple E-mail Service (SES)**: SES is a hosted transactional email service and allows one to fluently send deliverable emails using a RESTFUL API call or through a regular SMTP.
* **Identity and Access Management (IAM)**: IAM provides improved identity and security management for AWS account.
* **Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)**: EC2 is an AWS ecosystem central piece. It is responsible for providing on-demand and flexible computing resources with a “pay as you go” pricing model.
* **Elastic Block Store (EBS)**: EBS offers continuous storage solution that can be seen in instances as a regular hard drive.
* **CloudWatch**: CloudWatch allows the controller to outlook and gather key metrics and also set a series of alarms to be notified if there is any trouble.
**Source:** _whizlabs.com_
#### Q2: Is data stored in S3 is always encrypted? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
By default data on S3 is not encrypted, but all you could enable server-side encryption in your object metadata when you upload your data to Amazon S3. As soon as your data reaches S3, it is encrypted and stored.
**Source:** _aws.amazon.com_
#### Q3: What is the connection between AMI and Instance? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Many different types of *instances* can be launched from one *AMI*. The type of an instance generally regulates the hardware components of the host computer that is used for the instance. Each type of instance has distinct computing and memory efficacy.
Once an instance is launched, it casts as host and the user interaction with it is same as with any other computer but we have a completely controlled access to our instances. AWS developer interview questions may contain one or more AMI based questions, so prepare yourself for the AMI topic very well.
**Source:** _whizlabs.com_
#### Q4: How can I download a file from EC2? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Use scp:
```sh
scp -i ec2key.pem username@ec2ip:/path/to/file .
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q5: What do you mean by AMI? What does it include? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**AMI** stands for the term **Amazon Machine Image**. It’s an AWS template which provides the information (an application server, and operating system, and applications) required to perform the launch of an instance. This AMI is the copy of the AMI that is running in the cloud as a virtual server. You can launch instances from as many different AMIs as you need. AMI consists of the followings:
* A root volume template for an existing instance
* Launch permissions to determine which AWS accounts will get the AMI in order to launch the instances
* Mapping for block device to calculate the total volume that will be attached to the instance at the time of launch
**Source:** _whizlabs.com_
#### Q6: Can we attach single EBS to multiple EC2s same time? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
No. After you create a volume, you can attach it to any EC2 instance in the same Availability Zone. An EBS volume can be attached to **only one EC2 instance at a time**, but multiple volumes can be attached to a single instance.
**Source:** _docs.aws.amazon.com_
#### Q7: What is AWS Data Pipeline? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**AWS Data Pipeline** is a web service that you can use to automate the movement and transformation of data. With AWS Data Pipeline, you can define data-driven workflows, so that tasks can be dependent on the successful completion of previous tasks.
**Source:** _docs.aws.amazon.com_
#### Q8: How many storage options are there for EC2 Instance? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are four storage options for Amazon EC2 Instance:
* Amazon EBS
* Amazon EC2 Instance Store
* Amazon S3
* Adding Storage
**Source:** _whizlabs.com_
#### Q9: How to get the instance id from within an EC2 instance? ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
How can I find out the `instance id` of an ec2 instance from within the ec2 instance?
**Answer:**
Run:
```sh
wget -q -O - http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/instance-id
```
Or on Amazon Linux AMIs you can do:
```sh
$ ec2-metadata -i
instance-id: i-1234567890abcdef0
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q10: What is the difference between Amazon EC2 and AWS Elastic Beanstalk? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **EC2** is Amazon's service that allows you to create a server (AWS calls these instances) in the AWS cloud. You pay by the hour and only what you use. You can do whatever you want with this instance as well as launch n number of instances.
* **Elastic Beanstalk** is one layer of abstraction away from the EC2 layer. Elastic Beanstalk will setup an "environment" for you that can contain a number of EC2 instances, an optional database, as well as a few other AWS components such as a Elastic Load Balancer, Auto-Scaling Group, Security Group. Then Elastic Beanstalk will manage these items for you whenever you want to update your software running in AWS.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q11: When should one use the following: Amazon EC2, Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure and Salesforce.com? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q12: How would you implement vertical auto scaling of EC2 instance? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: What is the underlying hypervisor for EC2? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q14: Our EC2 micro instance occasionally runs out of memory. Other than using a larger instance size, what else can be done? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: How to safely upgrade an Amazon EC2 instance from t1.micro to large? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
I have an Amazon EC2 micro instance (t1.micro). I want to upgrade this instance to large. This is our production environment, so what is the best and risk-free way to do this?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 15 Best Continuous Integration Interview Questions (2018 Revision)
> Originally published on 👉 15 Best Continuous Integration Interview Questions (2018 Revision) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is meant by Continuous Integration? ⭐
**Answer:**
*Continuous Integration (CI)* is a development practice that requires developers to integrate code into a shared repository several times a day. Each check-in is then verified by an automated build, allowing teams to detect problems early.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q2: What are the success factors for Continuous Integration? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Maintain a code repository
* Automate the build
* Make the build self-testing
* Everyone commits to the baseline every day
* Every commit (to baseline) should be built
* Keep the build fast
* Test in a clone of the production environment
* Make it easy to get the latest deliverables
* Everyone can see the results of the latest build
* Automate deployment
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q3: What is the function of CI (Continuous Integration) server? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
CI server function is to continuously integrate all changes being made and committed to repository by different developers and check for compile errors. It needs to build code several times a day, preferably after every commit so it can detect which commit made the breakage if the breakage happens.
**Source:** _linoxide.com_
#### Q4: What's the difference between a blue/green deployment and a rolling deployment? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* In **Blue Green Deployment**, you have TWO complete environments.
One is Blue environment which is running and the Green environment to which you want to upgrade. Once you swap the environment from blue to green, the traffic is directed to your new green environment. You can delete or save your old blue environment for backup until the green environment is stable.
* In **Rolling Deployment**, you have only ONE complete environment. The code is deployed in the subset of instances of the same environment and moves to another subset after completion.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q5: What is the difference between resource allocation and resource provisioning? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Resource allocation is the process of reservation that demarcates a quantity of a resource for a tenant's use.
* Resource provision is the process of activation of a bundle of the allocated quantity to bear the tenant's workload.
Immediately after allocation, all the quantity of a resource is available. Provision removes a quantity of a resource from the available set. De-provision returns a quantity of a resource to the available set.
At any time:
```
Allocated quantity = Available quantity + Provisioned quantity
```
**Source:** _dev.to_
#### Q6: What are the differences between continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Developers practicing **continuous integration** merge their changes back to the main branch as often as possible. By doing so, you avoid the integration hell that usually happens when people wait for release day to merge their changes into the release branch.
* **Continuous delivery** is an extension of continuous integration to make sure that you can release new changes to your customers quickly in a sustainable way. This means that on top of having automated your testing, you also have automated your release process and you can deploy your application at any point of time by clicking on a button.
* **Continuous deployment** goes one step further than continuous delivery. With this practice, every change that passes all stages of your production pipeline is released to your customers. There's no human intervention, and only a failed test will prevent a new change to be deployed to production.
**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q7: Could you explain the Gitflow workflow? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Gitflow workflow employs two parallel *long-running* branches to record the history of the project, `master` and `develop`:
* **Master** - is always ready to be released on LIVE, with everything fully tested and approved (production-ready).
* **Hotfix** - Maintenance or “hotfix” branches are used to quickly patch production releases. Hotfix branches are a lot like release branches and feature branches except they're based on `master` instead of `develop`.
* **Develop** - is the branch to which all feature branches are merged and where all tests are performed. Only when everything’s been thoroughly checked and fixed it can be merged to the `master`.
* **Feature** - Each new feature should reside in its own branch, which can be pushed to the `develop` branch as their parent one.

**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q8: Explain usage of NODE_ENV ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q9: What is LTS releases of Node.js why should you care? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q10: What Is Sticky Session Load Balancing? What Do You Mean By "Session Affinity"? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Sticky session* or a *session affinity technique* is another popular load balancing technique that requires a user session to be always served by an allocated machine.
In a load balanced server application where user information is stored in session it will be required to keep the session data available to all machines. This can be avoided by always serving a particular user session request from one machine. The machine is associated with a session as soon as the session is created. All the requests in a particular session are always redirected to the associated machine. This ensures the user data is only at one machine and load is also shared.
This is typically done by using SessionId cookie. The cookie is sent to the client for the first request and every subsequent request by client must be containing that same cookie to identify the session.
** What Are The Issues With Sticky Session?**
There are few issues that you may face with this approach
* The client browser may not support cookies, and your load balancer will not be able to identify if a request belongs to a session. This may cause strange behavior for the users who use no cookie based browsers.
* In case one of the machine fails or goes down, the user information (served by that machine) will be lost and there will be no way to recover user session.
**Source:** _fromdev.com_
#### Q11: Explain Blue-Green Deployment Technique ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Blue-green deployment** is a technique that reduces downtime and risk by running two identical production environments called Blue and Green. At any time, only one of the environments is live, with the live environment serving all production traffic. For this example, Blue is currently live and Green is idle.
As you prepare a new version of your software, deployment and the final stage of testing takes place in the environment that is not live: in this example, Green. Once you have deployed and fully tested the software in Green, you switch the router so all incoming requests now go to Green instead of Blue. Green is now live, and Blue is idle.
This technique can eliminate downtime due to application deployment. In addition, blue-green deployment reduces risk: if something unexpected happens with your new version on Green, you can immediately roll back to the last version by switching back to Blue.
**Source:** _cloudfoundry.org_
#### Q12: Why layering your application is important? Provide some bad layering example. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: Are you familiar with The Twelve-Factor App principles? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 15 Essential HTML5 Interview Questions to Watch Out in 2018
> Originally published on 👉 15 Essential HTML5 Interview Questions to Watch Out in 2018 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: Explain meta tags in HTML ⭐
**Answer:**
- **Meta tags** always go inside **head tag** of the HTML page
- **Meta tags** is always passed as name/value pairs
- **Meta tags** are not displayed on the page but intended for the browser
- **Meta tags** can contain information about **character encoding**, **description**, **title** of the document etc,
**Example**:
```html
Home Page
```
**Source:** _github.com/FuelFrontend_
#### Q2: What is an optional tag? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In HTML, some elements have optional tags. In fact, both the opening and closing tags of some elements may be completely removed from an HTML document, even though the elements themselves are required.
Three required HTML elements whose start and end tags are optional are the `html`, `head`, and `body` elements.
**Source:** _computerhope.com_
#### Q3: Can a web page contain multiple elements? What about elements? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Yes to both. The W3 documents state that the tags represent the header(``) and footer(``) areas of their nearest ancestor "section". So not only can the page `` contain a header and a footer, but so can every `` and `` element.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q4: What is the DOM? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The *DOM (Document Object Model)* is a cross-platform API that treats HTML and XML documents as a tree structure consisting of nodes. These nodes (such as elements and text nodes) are objects that can be programmatically manipulated and any visible changes made to them are reflected live in the document. In a browser, this API is available to JavaScript where DOM nodes can be manipulated to change their styles, contents, placement in the document, or interacted with through event listeners.
* The DOM was designed to be independent of any particular programming language, making the structural representation of the document available from a single, consistent API.
* The DOM is constructed progressively in the browser as a page loads, which is why scripts are often placed at the bottom of a page, in the `` with a `defer` attribute, or inside a `DOMContentLoaded` event listener. Scripts that manipulate DOM nodes should be run after the DOM has been constructed to avoid errors.
* `document.getElementById()` and `document.querySelector()` are common functions for selecting DOM nodes.
* Setting the `innerHTML` property to a new value runs the string through the HTML parser, offering an easy way to append dynamic HTML content to a node.
**Source:** _developer.mozilla.org_
#### Q5: Discuss the differences between an HTML specification and a browser’s implementation thereof. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
HTML specifications such as `HTML5` define a set of rules that a document must adhere to in order to be “valid” according to that specification. In addition, a specification provides instructions on how a browser must interpret and render such a document.
A browser is said to “support” a specification if it handles valid documents according to the rules of the specification. As of yet, no browser supports all aspects of the `HTML5` specification (although all of the major browser support most of it), and as a result, it is necessary for the developer to confirm whether the aspect they are making use of will be supported by all of the browsers on which they hope to display their content. This is why cross-browser support continues to be a headache for developers, despite the improved specificiations.
* `HTML5` defines some rules to follow for an invalid `HTML5` document (i.e., one that contains syntactical errors)
* However, invalid documents may contain anything, so it's impossible for the specification to handle all possibilities comprehensively.
* Thus, many decisions about how to handle malformed documents are left up to the browser.
**Source:** _w3.org_
#### Q6: What is HTML5 Web Storage? Explain `localStorage` and `sessionStorage`. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
With HTML5, web pages can store data locally within the user’s browser.
The data is stored in name/value pairs, and a web page can only access data stored by itself.
**Differences between `localStorage` and `sessionStorage` regarding lifetime:**
* Data stored through `localStorage` is permanent: it does not expire and remains stored on the user’s computer until a web app deletes it or the user asks the browser to delete it.
* `sessionStorage` has the same lifetime as the top-level window or browser tab in which the data got stored. When the tab is permanently closed, any data stored through `sessionStorage` is deleted.
**Differences between `localStorage` and `sessionStorage` regarding storage scope:**
Both forms of storage are scoped to the document origin so that documents with different origins will never share the stored objects.
* `sessionStorage` is also scoped on a per-window basis. Two browser tabs with documents from the same origin have separate `sessionStorage` data.
* Unlike in `localStorage`, the same scripts from the same origin can't access each other's `sessionStorage` when opened in different tabs.
**Source:** _w3schools.com_
#### Q7: What's new in HTML 5? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
HTML 5 adds a lot of new features to the HTML specification
**New Doctype**
Still using that pesky, impossible-to-memorize XHTML doctype?
```html
```
If so, why? Switch to the new HTML5 doctype. You'll live longer -- as Douglas Quaid might say.
```html
```
**New Structure**
- `` - to define sections of pages
- `` - defines the header of a page
- `` - defines the footer of a page
- `` - defines the navigation on a page
- `` - defines the article or primary content on a page
- `` - defines extra content like a sidebar on a page
- `` - defines images that annotate an article
**New Inline Elements**
These inline elements define some basic concepts and keep them semantically marked up, mostly to do with time:
- `` - to indicate content that is marked in some fashion
- `
**New Form Types**
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
**New Elements**
There are a few exciting new elements in HTML 5:
- `` - an element to give you a drawing space in JavaScript on your Web pages. It can let you add images or graphs to tool tips or just create dynamic graphs on your Web pages, built on the fly.
- `` - add video to your Web pages with this simple tag.
- `` - add sound to your Web pages with this simple tag.
**No More Types for Scripts and Links**
You possibly still add the `type` attribute to your `link` and `script` tags.
```html
```
This is no longer necessary. It's implied that both of these tags refer to stylesheets and scripts, respectively. As such, we can remove the `type` attribute all together.
```html
```
**Make your content editable**
The new browsers have a nifty new attribute that can be applied to elements, called `contenteditable`. As the name implies, this allows the user to edit any of the text contained within the element, including its children. There are a variety of uses for something like this, including an app as simple as a to-do list, which also takes advantage of local storage.
```html
To-Do List
- Break mechanical cab driver.
- Drive to abandoned factory
- Watch video of self
```
**Attributes**
- `require` to mention the form field is required
- `autofocus` puts the cursor on the input field
**Source:** _github.com/FuelFrontend_
#### Q8: HTML Markup Validity ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q9: What are the building blocks of HTML5? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q10: What is progressive rendering? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q11: Why to use HTML5 semantic tags? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q12: What's the difference between Full Standard, Almost Standard and Quirks Mode? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: Could you generate a public key in HTML? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q14: What is accessibility & ARIA role means in a web application? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: What are Web Components? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 15+ Azure Interview Questions And Answers (2018 REVISIT)
> Originally published on 👉 15+ Azure Interview Questions And Answers (2018 REVISIT) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Azure Cloud Service? ⭐
**Answer:**
By creating a cloud service, you can deploy a multi-tier web application in Azure, defining multiple roles to distribute processing and allow flexible scaling of your application. A cloud service consists of one or more web roles and/or worker roles, each with its own application files and configuration. Azure Websites and Virtual Machines also enable web applications on Azure. The main advantage of cloud services is the ability to support more complex multi-tier architectures
**Source:** _mindmajix.com_
#### Q2: What is Azure Functions? ⭐
**Answer:**
Azure Functions is a solution for easily running small pieces of code, or "functions," in the cloud. We can write just the code we need for the problem at hand, without worrying about a whole application or the infrastructure to run it and use language of our choice such as C#, F#, Node.js, Java, or PHP. Azure Functions lets us develop serverless applications on Microsoft Azure.
#### Q3: What is Azure Resource Group? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Resource groups (RG) in Azure is an approach to group a collection of assets in logical groups for easy or even automatic provisioning, monitoring, and access control, and for more effective management of their costs. The underlying technology that powers resource groups is the Azure Resource Manager (ARM).
**Source:** _onlinetech.com_
#### Q4: What is Kudu? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Every Azure App Service web application includes a "hidden" service site called **Kudu**.
Kudu Console for example is a debugging service for Azure platform which allows you to explore your web app and surf the bugs present on it, like deployment logs, memory dump, and uploading files to your web app, and adding JSON endpoints to your web apps, etc.
#### Q5: What is Azure Blob Storage? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Azure Blob storage* is Microsoft's object storage solution for the cloud. Blob storage is optimized for storing massive amounts of unstructured data, such as text or binary data. Azure Storage offers three types of blobs:
* **Block blobs** store text and binary data, up to about 4.7 TB. Block blobs are made up of blocks of data that can be managed individually.
* **Append blobs** are made up of blocks like block blobs, but are optimized for append operations. Append blobs are ideal for scenarios such as logging data from virtual machines.
* **Page blobs** store random access files up to 8 TB in size. Page blobs store the VHD files that back VMs.
**Source:** _docs.microsoft.com_
#### Q6: What are stateful and stateless microservices for Service Fabric? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Service Fabric* enables you to build applications that consist of microservices:
* Stateless microservices (such as protocol gateways and web proxies) do not maintain a mutable state outside a request and its response from the service. Azure Cloud Services worker roles are an example of a stateless service.
* Stateful microservices (such as user accounts, databases, devices, shopping carts, and queues) maintain a mutable, authoritative state beyond the request and its response.
**Source:** _quora.com_
#### Q7: What is key vault in Azure? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Microsoft **Azure Key Vault** is a cloud-hosted management service that allows users to encrypt keys and small secrets by using keys that are protected by hardware security modules (HSMs). Small secrets are data less than 10 KB like passwords and .PFX files.
**Source:** _searchwindowsserver.techtarget.com_
#### Q8: What is Azure MFA? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)** is Microsoft's two-step verification solution. It delivers strong authentication via a range of verification methods, including phone call, text message, or mobile app verification.
**Source:** _docs.microsoft.com_
#### Q9: What is Azure Table Storage? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Azure Table storage* is a service that stores structured NoSQL data in the cloud, providing a key/attribute store with a schemaless design. Because Table storage is schemaless, it's easy to adapt your data as the needs of your application evolve. Access to Table storage data is fast and cost-effective for many types of applications, and is typically lower in cost than traditional SQL for similar volumes of data.
**Source:** _docs.microsoft.com_
#### Q10: What is Azure Resource Manager and why we need to use one? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **Azure Resource Manager (ARM)** is the service used to provision resources in your Azure subscription. ARM provides us a way to describe resources in a resource group using JSON documents (ARM Template). by using the ARM Template you have a fully repeatable configuration of a given deployment and this is extremely valuable for Production environments but especially so for Dev/Test deployments. By having a set template, we can ensure that anytime a new Dev or Test deployment is required (which happens all the time), it can be achieved in moments and safe in the knowledge that it will be identical to the previous environments.
**Source:** _codeisahighway.com_
#### Q11: What do you know about Azure WebJobs? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**WebJobs** is a feature of Azure App Service that enables you to run a program or script in the same context as a web app, API app, or mobile app. There is no additional cost to use WebJobs.
The Azure WebJobs SDK is a framework that simplifies the task of writing background processing code that runs in Azure WebJobs. It includes a declarative binding and trigger system that works with Azure Storage Blobs, Queues and Tables as well as Service Bus. You could also trigger Azure WebJob using Kudu API.
**Source:** _github.com/Azure_
#### Q12: Is it possible to create a Virtual Machine using Azure Resource Manager in a Virtual Network that was created using classic deployment? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: What is Azure VNET? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q14: How are Azure Marketplace subscriptions priced? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: What VPN types are supported by Azure? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 19+ Expert Node.js Interview Questions in 2018
> Originally published on 👉 19+ Expert Node.js Interview Questions in 2018 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Node.js? ⭐
**Answer:**
Node.js is a web application framework built on Google Chrome's JavaScript Engine (V8 Engine).
Node.js comes with runtime environment on which a Javascript based script can be interpreted and executed (It is analogus to JVM to JAVA byte code). This runtime allows to execute a JavaScript code on any machine outside a browser. Because of this runtime of Node.js, JavaScript is now can be executed on server as well.
*Node.js = Runtime Environment + JavaScript Library*
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q2: What is global installation of dependencies? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Globally installed packages/dependencies are stored in ****/npm directory. Such dependencies can be used in CLI (Command Line Interface) function of any node.js but can not be imported using require() in Node application directly. To install a Node project globally use -g flag.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q3: What is an error-first callback? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Error-first callbacks* are used to pass errors and data. The first argument is always an error object that the programmer has to check if something went wrong. Additional arguments are used to pass data.
```js
fs.readFile(filePath, function(err, data) {
if (err) {
//handle the error
}
// use the data object
});
```
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q4: What are the benefits of using Node.js? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Following are main benefits of using Node.js
* **Aynchronous and Event Driven** - All APIs of Node.js library are aynchronous that is non-blocking. It essentially means a Node.js based server never waits for a API to return data. Server moves to next API after calling it and a notification mechanism of Events of Node.js helps server to get response from the previous API call.
* **Very Fast** - Being built on Google Chrome's V8 JavaScript Engine, Node.js library is very fast in code execution.
* **Single Threaded but highly Scalable** - Node.js uses a single threaded model with event looping. Event mechanism helps server to respond in a non-bloking ways and makes server highly scalable as opposed to traditional servers which create limited threads to handle requests. Node.js uses a single threaded program and same program can services much larger number of requests than traditional server like Apache HTTP Server.
* **No Buffering** \- Node.js applications never buffer any data. These applications simply output the data in chunks.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q5: If Node.js is single threaded then how it handles concurrency? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Node provides a single thread to programmers so that code can be written easily and without bottleneck. Node internally uses multiple POSIX threads for various I/O operations such as File, DNS, Network calls etc.
When Node gets I/O request it creates or uses a thread to perform that I/O operation and once the operation is done, it pushes the result to the event queue. On each such event, event loop runs and checks the queue and if the execution stack of Node is empty then it adds the queue result to execution stack.
This is how Node manages concurrency.
**Source:** _codeforgeek.com_
#### Q6: How can you avoid callback hells? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
To do so you have more options:
* **modularization**: break callbacks into independent functions
* use _Promises_
* use `yield` with _Generators_ and/or _Promises_
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q7: What's the event loop? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**The event loop** is what allows Node.js to perform non-blocking I/O operations — despite the fact that JavaScript is single-threaded — by offloading operations to the system kernel whenever possible.

Every I/O requires a callback - once they are done they are pushed onto the event loop for execution. Since most modern kernels are multi-threaded, they can handle multiple operations executing in the background. When one of these operations completes, the kernel tells Node.js so that the appropriate callback may be added to the poll queue to eventually be executed.
**Source:** _blog.risingstack.com_
#### Q8: How Node prevents blocking code? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
By providing callback function. Callback function gets called whenever corresponding event triggered.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q9: What is Event Emmitter? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
All objects that emit events are members of EventEmitter class. These objects expose an `eventEmitter.on()` function that allows one or more functions to be attached to named events emitted by the object.
When the EventEmitter object emits an event, all of the functions attached to that specific event are called synchronously.
```js
const EventEmitter = require('events');
class MyEmitter extends EventEmitter {}
const myEmitter = new MyEmitter();
myEmitter.on('event', () => {
console.log('an event occurred!');
});
myEmitter.emit('event');
```
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q10: What tools can be used to assure consistent code style? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q11: Provide some example of config file separation for dev and prod environments ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q12: Explain usage of NODE_ENV ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: What are the timing features of Node.js? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q14: Explain what is Reactor Pattern in Node.js? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: Consider following code snippet ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider following code snippet:
```js
{
console.time("loop");
for (var i = 0; i < 1000000; i += 1) {
// Do nothing
}
console.timeEnd("loop");
}
```
The time required to run this code in Google Chrome is considerably more than the time required to run it in Node.js Explain why this is so, even though both use the v8 JavaScript Engine.
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: What is LTS releases of Node.js why should you care? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: Why should you separate Express 'app' and 'server'? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: What is the difference between process.nextTick() and setImmediate() ? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: Rewrite the code sample without try/catch block ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider the code:
```js
async function check(req, res) {
try {
const a = await someOtherFunction();
const b = await somethingElseFunction();
res.send("result")
} catch (error) {
res.send(error.stack);
}
}
```
Rewrite the code sample without try/catch block.
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 20 .NET Core Interview Questions and Answers
> Originally published on 👉 20 .NET Core Interview Questions and Answers | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is .NET Core? ⭐
**Answer:**
The .NET Core platform is a new .NET stack that is optimized for open source development and agile delivery on NuGet.
.NET Core has two major components. It includes a small runtime that is built from the same codebase as the .NET Framework CLR. The .NET Core runtime includes the same GC and JIT (RyuJIT), but doesn’t include features like Application Domains or Code Access Security. The runtime is delivered via NuGet, as part of the ASP.NET Core package.
.NET Core also includes the base class libraries. These libraries are largely the same code as the .NET Framework class libraries, but have been factored (removal of dependencies) to enable to ship a smaller set of libraries. These libraries are shipped as `System.*` NuGet packages on NuGet.org.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q2: What is the difference between .NET Core and Mono? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
To be simple:
* Mono is third party implementation of .Net Framework for Linux/Android/iOs
* .Net Core is Microsoft's own implementation for same.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q3: What are some characteristics of .NET Core? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Flexible deployment**: Can be included in your app or installed side-by-side user- or machine-wide.
* **Cross-platform**: Runs on Windows, macOS and Linux; can be ported to other OSes. The supported Operating Systems (OS), CPUs and application scenarios will grow over time, provided by Microsoft, other companies, and individuals.
* **Command-line tools**: All product scenarios can be exercised at the command-line.
* **Compatible**: .NET Core is compatible with .NET Framework, Xamarin and Mono, via the .NET Standard Library.
* **Open source**: The .NET Core platform is open source, using MIT and Apache 2 licenses. Documentation is licensed under CC-BY. .NET Core is a .NET Foundation project.
* **Supported by Microsoft**: .NET Core is supported by Microsoft, per .NET Core Support
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q4: What's the difference between SDK and Runtime in .NET Core? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* The SDK is all of the stuff that is needed/makes developing a .NET Core application easier, such as the CLI and a compiler.
* The runtime is the "virtual machine" that hosts/runs the application and abstracts all the interaction with the base operating system.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q5: What is CTS? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **Common Type System (CTS)** standardizes the data types of all programming languages using .NET under the umbrella of .NET to a common data type for easy and smooth communication among these .NET languages.
CTS is designed as a singly rooted object hierarchy with `System.Object` as the base type from which all other types are derived. CTS supports two different kinds of types:
1. **Value Types**: Contain the values that need to be stored directly on the stack or allocated inline in a structure. They can be built-in (standard primitive types), user-defined (defined in source code) or enumerations (sets of enumerated values that are represented by labels but stored as a numeric type).
2. **Reference Types**: Store a reference to the value‘s memory address and are allocated on the heap. Reference types can be any of the pointer types, interface types or self-describing types (arrays and class types such as user-defined classes, boxed value types and delegates).
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q6: What is Kestrel? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Kestrel is a cross-platform web server built for ASP.NET Core based on libuv – a cross-platform asynchronous I/O library.
* It is a default web server pick since it is used in all ASP.NET Core templates.
* It is really fast.
* It is secure and good enough to use it without a reverse proxy server. However, it is still recommended that you use IIS, Nginx or Apache or something else.
**Source:** _talkingdotnet.com_
#### Q7: What is difference between .NET Core and .NET Framework? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
.NET as whole now has 2 flavors:
* .NET Framework
* .NET Core
*.NET Core* and the *.NET Framework* have (for the most part) a subset-superset relationship. .NET Core is named “Core” since it contains the core features from the .NET Framework, for both the runtime and framework libraries. For example, .NET Core and the .NET Framework share the GC, the JIT and types such as `String` and `List`.
.NET Core was created so that .NET could be open source, cross platform and be used in more resource-constrained environments.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q8: Explain what is included in .NET Core? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* A .NET runtime, which provides a type system, assembly loading, a garbage collector, native interop and other basic services.
* A set of framework libraries, which provide primitive data types, app composition types and fundamental utilities.
* A set of SDK tools and language compilers that enable the base developer experience, available in the .NET Core SDK.
* The 'dotnet' app host, which is used to launch .NET Core apps. It selects the runtime and hosts the runtime, provides an assembly loading policy and launches the app. The same host is also used to launch SDK tools in much the same way.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q9: What's the difference between .NET Core, .NET Framework, and Xamarin? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **.NET Framework** is the "full" or "traditional" flavor of .NET that's distributed with Windows. Use this when you are building a desktop Windows or UWP app, or working with older ASP.NET 4.6+.
* **.NET Core** is cross-platform .NET that runs on Windows, Mac, and Linux. Use this when you want to build console or web apps that can run on any platform, including inside Docker containers. This does not include UWP/desktop apps currently.
* **Xamarin** is used for building mobile apps that can run on iOS, Android, or Windows Phone devices.

Xamarin usually runs on top of Mono, which is a version of .NET that was built for cross-platform support before Microsoft decided to officially go cross-platform with .NET Core. Like Xamarin, the Unity platform also runs on top of Mono.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q10: What is CoreCLR? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
CoreCLR is the .NET execution engine in .NET Core, performing functions such as garbage collection and compilation to machine code.
Consider:

**Source:** _blogs.msdn.microsoft.com_
#### Q11: Explain the difference between Task and Thread in .NET ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Thread** represents an actual OS-level thread, with its own stack and kernel resources. Thread allows the highest degree of control; you can Abort() or Suspend() or Resume() a thread, you can observe its state, and you can set thread-level properties like the stack size, apartment state, or culture. ThreadPool is a wrapper around a pool of threads maintained by the CLR.
* The **Task class** from the Task Parallel Library offers the best of both worlds. Like the ThreadPool, a task does not create its own OS thread. Instead, tasks are executed by a TaskScheduler; the default scheduler simply runs on the ThreadPool. Unlike the ThreadPool, Task also allows you to find out when it finishes, and (via the generic Task) to return a result.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q12: What is JIT compiler? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Before a computer can execute the source code, special programs called compilers must rewrite it into machine instructions, also known as object code. This process (commonly referred to simply as “compilation”) can be done explicitly or implicitly.
Implicit compilation is a two-step process:
* The first step is converting the source code to intermediate language (IL) by a language-specific compiler.
* The second step is converting the IL to machine instructions. The main difference with the explicit compilers is that only executed fragments of IL code are compiled into machine instructions, at runtime. The .NET framework calls this compiler the **JIT (Just-In-Time) compiler**.
**Source:** _telerik.com_
#### Q13: What are the benefits of explicit compilation? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Ahead of time (AOT)** delivers faster start-up time, especially in large applications where much code executes on startup. But it requires more disk space and more memory/virtual address space to keep both the IL and precompiled images. In this case the JIT Compiler has to do a lot of disk I/O actions, which are quite expensive.
**Source:** _telerik.com_
#### Q14: When should we use .NET Core and .NET Standard Class Library project types? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Use a **.NET Standard** library when you want to increase the number of apps that will be compatible with your library, and you are okay with a decrease in the .NET API surface area your library can access.
* Use a **.NET Core** library when you want to increase the .NET API surface area your library can access, and you are okay with allowing only .NET Core apps to be compatible with your library.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q15: What's the difference between RyuJIT and Roslyn? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: What is the difference between AppDomain, Assembly, Process, and a Thread? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: Explain Finalize vs Dispose usage? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: How many types of JIT Compilations do you know? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: Can ASP.NET Core work with the .NET framework? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Yes. This might surprise many, but ASP.NET Core works with .NET framework and this is officially supported by Microsoft.
ASP.NET Core works with:
* .NET Core framework
* .NET framework
**Source:** _talkingdotnet.com_
#### Q20: What is the equivalent of WebForms in ASP.NET Core? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 20 Basic TypeScript Interview Questions (2018 Edition)
> Originally published on 👉 20 Basic TypeScript Interview Questions (2018 Edition) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is TypeScript and why would I use it in place of JavaScript? ⭐
**Details:**
**Answer:**
**TypeScript** is a superset of JavaScript which primarily provides optional static typing, classes and interfaces. One of the big benefits is to enable IDEs to provide a richer environment for spotting common errors as *you type the code*. For a large JavaScript project, adopting TypeScript might result in more robust software, while still being deployable where a regular JavaScript application would run.
In details:
* TypeScript supports new ECMAScript standards and compiles them to (older) ECMAScript targets of your choosing. This means that you can use features of ES2015 and beyond, like modules, lambda functions, classes, the spread operator, destructuring, today.
* JavaScript code is valid TypeScript code; TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript.
* TypeScript adds type support to JavaScript. The type system of TypeScript is relatively rich and includes: interfaces, enums, hybrid types, generics, union and intersection types, access modifiers and much more. TypeScript makes typing a bit easier and a lot less explicit by the usage of type inference.
* The development experience with TypeScript is a great improvement over JavaScript. The IDE is informed in real-time by the TypeScript compiler on its rich type information.
* With strict null checks enabled (`--strictNullChecks` compiler flag) the TypeScript compiler will not allow undefined to be assigned to a variable unless you explicitly declare it to be of nullable type.
* To use TypeScript you need a build process to compile to JavaScript code. The TypeScript compiler can inline source map information in the generated .js files or create separate .map files. This makes it possible for you to set breakpoints and inspect variables during runtime directly on your TypeScript code.
* TypeScript is open source (Apache 2 licensed, see github) and backed by Microsoft. *Anders Hejlsberg*, the lead architect of C# is spearheading the project.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q2: Explain generics in TypeScript ⭐
**Answer:**
Generics are able to create a component or function to work over a variety of types rather than a single one.
```js
/** A class definition with a generic parameter */
class Queue {
private data = [];
push = (item: T) => this.data.push(item);
pop = (): T => this.data.shift();
}
const queue = new Queue();
queue.push(0);
queue.push("1"); // ERROR : cannot push a string. Only numbers allowed
```
**Source:** _basarat.gitbooks.io_
#### Q3: Does TypeScript support all object oriented principles? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The answer is **YES**. There are 4 main principles to Object Oriented Programming:
* Encapsulation,
* Inheritance,
* Abstraction, and
* Polymorphism.
TypeScript can implement all four of them with its smaller and cleaner syntax.
**Source:** _jonathanmh.com_
#### Q4: How could you check null and undefined in TypeScript? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Just use:
```js
if (value) {
}
```
It will evaluate to `true` if `value` is not:
* `null`
* `undefined`
* `NaN`
* empty string `''`
* `0`
* `false`
TypesScript includes JavaScript rules.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q5: How to implement class constants in TypeScript? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In TypeScript, the `const` keyword cannot be used to declare class properties. Doing so causes the compiler to an error with "A class member cannot have the 'const' keyword." TypeScript 2.0 has the `readonly` modifier:
```js
class MyClass {
readonly myReadonlyProperty = 1;
myMethod() {
console.log(this.myReadonlyProperty);
}
}
new MyClass().myReadonlyProperty = 5; // error, readonly
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q6: What is a TypeScript Map file? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`.map` files are source map files that let tools map between the emitted JavaScript code and the TypeScript source files that created it. Many debuggers (e.g. Visual Studio or Chrome's dev tools) can consume these files so you can debug the TypeScript file instead of the JavaScript file.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q7: What is getters/setters in TypeScript? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
TypeScript supports **getters/setters** as a way of intercepting accesses to a member of an object. This gives you a way of having finer-grained control over how a member is accessed on each object.
```js
class foo {
private _bar:boolean = false;
get bar():boolean {
return this._bar;
}
set bar(theBar:boolean) {
this._bar = theBar;
}
}
var myBar = myFoo.bar; // correct (get)
myFoo.bar = true; // correct (set)
```
**Source:** _typescriptlang.org_
#### Q8: Could we use TypeScript on backend and how? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Typescript doesn’t only work for browser or frontend code, you can also choose to write your backend applications. For example you could choose Node.js and have some additional type safety and the other abstraction that the language brings.
1. Install the default Typescript compiler
```sh
npm i -g typescript
```
2. The TypeScript compiler takes options in the shape of a tsconfig.json file that determines where to put built files and in general is pretty similar to a babel or webpack config.
```sh
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es5",
"module": "commonjs",
"declaration": true,
"outDir": "build"
}
}
```
3. Compile ts files
```sh
tsc
```
4. Run
```js
node build/index.js
```
**Source:** _jonathanmh.com_
#### Q9: What are different components of TypeScript? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are mainly 3 components of TypeScript .
1. **Language** – The most important part for developers is the new language. The language consist of new syntax, keywords and allows you to write TypeScript.
2. **Compiler** – The TypeScript compiler is open source, cross-platform and open specification, and is written in TypeScript. Compiler will compile your TypeScript into JavaScript. And it will also emit error, if any. It can also help in concating different files to single output file and in generating source maps.
3. **Language Service** – TypeScript language service which powers the interactive TypeScript experience in Visual Studio, [VS Code](http://www.talkingdotnet.com/what-is-visual-studio-code-and-difference-between-visual-studio-2015/), Sublime, the TypeScript playground and other editor.
**Source:** _talkingdotnet.com_
#### Q10: Is that TypeScript code valid? Explain why. ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider:
```js
class Point {
x: number;
y: number;
}
interface Point3d extends Point {
z: number;
}
let point3d: Point3d = {x: 1, y: 2, z: 3};
```
**Answer:**
Yes, the code is valid. A class declaration creates two things: a *type* representing instances of the class and a *constructor function*. Because classes create types, you can use them in the same places you would be able to use interfaces.
**Source:** _typescriptlang.org_
#### Q11: Explain how and why we could use property decorators in TS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Decorators can be used to modify the behavior of a class or become even more powerful when integrated into a framework. For instance, if your framework has methods with restricted access requirements (just for admin), it would be easy to write an `@admin` method decorator to deny access to non-administrative users, or an `@owner` decorator to only allow the owner of an object the ability to modify it.
```ts
class CRUD {
get() { }
post() { }
@admin
delete() { }
@owner
put() { }
}
```
**Source:** _www.sitepen.com_
#### Q12: Are strongly-typed functions as parameters possible in TypeScript? ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider the code:
```js
class Foo {
save(callback: Function) : void {
//Do the save
var result : number = 42; //We get a number from the save operation
//Can I at compile-time ensure the callback accepts a single parameter of type number somehow?
callback(result);
}
}
var foo = new Foo();
var callback = (result: string) : void => {
alert(result);
}
foo.save(callback);
```
Can you make the result parameter in `save` a type-safe function? Rewrite the code to demonstrate.
**Answer:**
In TypeScript you can declare your **callback type** like:
```js
type NumberCallback = (n: number) => any;
class Foo {
// Equivalent
save(callback: NumberCallback): void {
console.log(1)
callback(42);
}
}
var numCallback: NumberCallback = (result: number) : void => {
console.log("numCallback: ", result.toString());
}
var foo = new Foo();
foo.save(numCallback)
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q13: How can you allow classes defined in a module to accessible outside of the module? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Classes define in a module are available within the module. Outside the module you can’t access them.
```js
module Vehicle {
class Car {
constructor (
public make: string,
public model: string) { }
}
var audiCar = new Car("Audi", "Q7");
}
// This won't work
var fordCar = Vehicle.Car("Ford", "Figo");
```
As per above code, `fordCar` variable will give us compile time error. To make classes accessible outside module use `export` keyword for classes.
```js
module Vehicle {
export class Car {
constructor (
public make: string,
public model: string) { }
}
var audiCar = new Car("Audi", "Q7");
}
// This works now
var fordCar = Vehicle.Car("Ford", "Figo");
```
**Source:** _http://www.talkingdotnet.com_
#### Q14: Does TypeScript supports function overloading? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Yes, TypeScript does support function overloading but the implementation is a bit different if we compare it to OO languages. We are creating just one function and a number of declarations so that TypeScript doesn't give compile errors. When this code is compiled to JavaScript, the concrete function alone will be visible. As a JavaScript function can be called by passing multiple arguments, it just works.
```js
class Foo {
myMethod(a: string);
myMethod(a: number);
myMethod(a: number, b: string);
myMethod(a: any, b?: string) {
alert(a.toString());
}
}
```
**Source:** _typescriptlang.org_
#### Q15: Explain why that code is marked as WRONG? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```js
/* WRONG */
interface Fetcher {
getObject(done: (data: any, elapsedTime?: number) => void): void;
}
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: How would you overload a class constructor in TypeScript? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: What is the difference between "interface vs type" statements? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```js
interface X {
a: number
b: string
}
type X = {
a: number
b: string
};
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: Explain when to use "declare" keyword in TypeScript ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: What are Ambients in TypeScripts and when to use them? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: Is it possible to generate TypeScript declaration files from JS library? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 20 Reactive Programming Interview Questions To Polish Up In 2019
> Originally published on 👉 20 Reactive Programming Interview Questions To Polish Up In 2019 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is the difference between BehaviorSubject vs Observable? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q2: What is the Reactive Manifesto? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **Reactive Manifesto** is a document that defines the core principles of reactive programming. It was first released in 2013 by a group of developers led by a man called Jonas Boner. The Reactive Manifesto underpins the principles of reactive programming.
**Source:** _reactivemanifesto.org_
#### Q3: What is Reactive Programming? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Reactive programming is programming with asynchronous data streams.** Event buses or your typical click events are really an asynchronous event stream, on which you can observe and do some side effects. Reactive is that idea on steroids. You are able to create data streams of anything, not just from click and hover events. Streams are cheap and ubiquitous, anything can be a stream: variables, user inputs, properties, caches, data structures, etc. For example, imagine your Twitter feed would be a data stream in the same fashion that click events are. You can listen to that stream and react accordingly.
**Source:** _github.com_
#### Q4: What is Stream? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **stream** is a sequence of ongoing events ordered in time. It can emit three different things: a value (of some type), an error, or a "completed" signal.
**Source:** _github.com_
#### Q5: What Are Some Advantages of Reactive Programming? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Here’s a short list of advantages :
* avoid “callback hell”
* a lot simpler to do async / threaded work
* a lot of operators that simplify work
* very simple to compose streams of data
* complex threading becomes very easy
* you end up with a more cleaner, readable code base
* easy to implement back-pressure
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q6: What Does Asynchrony Mean in the Context of Reactive Systems? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The Oxford Dictionary defines asynchronous as “not existing or occurring at the same time”. In the context of Reactive Sysytems, it means that the processing of a request occurs at an arbitrary point in time, sometime after it has been transmitted from client to service. The client cannot directly observe, or synchronize with, the execution that occurs within the service. This is the antonym of synchronous processing which implies that the client only resumes its own execution once the service has processed the request.
**Source:** _reactivemanifesto.org_
#### Q7: What is Back-Pressure? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
When one component is struggling to keep-up, the system as a whole needs to respond in a sensible way. It is unacceptable for the component under stress to fail catastrophically or to drop messages in an uncontrolled fashion. Since it can’t cope and it can’t fail it should communicate the fact that it is under stress to upstream components and so get them to reduce the load. This **back-pressure is an important feedback mechanism that allows systems to gracefully respond to load rather than collapse under it**. The back-pressure may cascade all the way up to the user, at which point responsiveness may degrade, but this mechanism will ensure that the system is resilient under load, and will provide information that may allow the system itself to apply other resources to help distribute the load.
**Source:** _reactivemanifesto.org_
#### Q8: What is Elasticity (in contrast to Scalability)? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Elasticity** means that the throughput of a system scales up or down automatically to meet varying demand as resource is proportionally added or removed. The system needs to be scalable to allow it to benefit from the dynamic addition, or removal, of resources at runtime. Elasticity therefore builds upon scalability and expands on it by adding the notion of automatic resource management.
**Source:** _reactivemanifesto.org_
#### Q9: Explain the Term Non-Blocking ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**In concurrent programming an algorithm is considered non-blocking if threads competing for a resource do not have their execution indefinitely postponed by mutual exclusion protecting that resource**. In practice this usually manifests as an API that allows access to the resource if it is available otherwise it immediately returns informing the caller that the resource is not currently available or that the operation has been initiated and not yet completed. A non-blocking API to a resource allows the caller the option to do other work rather than be blocked waiting on the resource to become available. This may be complemented by allowing the client of the resource to register for getting notified when the resource is available or the operation has completed.
**Source:** _reactivemanifesto.org_
#### Q10: What is Actor Model? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
All Actor model says that your concurrency primitives are actors, which can:
* receive a message and decide what to do next depending on the content of the message, including:
* send messages to any actors they know about
* create new actors
and provides certain guarantees, e.g.:
* any actor will only handle a single message at a time
* messages sent by actor X to actor Y will arrive in the order thay were sent
**Source:** _github.com_
#### Q11: Describe Difference Between Reactive Programming vs Imperative Programming ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In reactive programming, Observables emit data, and send it to the subscribers. This can be seen as data being _PUSHed_ in reactive programming, as opposed to data being _PULLed_ in imperative programming, where you explicitly request data (iterating over collection, requesting data from the DB, etc).
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q12: What Does It Mean to be Resilient for a Reactive System? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: What Does It Mean to be Elastic for a Reactive System? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q14: Explain Failure in Contrast to Error ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: What is Difference Between Observer Pattern and Reactive Programming? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: Imperative vs Functional vs Reactive Programming. Explain. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: What does Amdahl's Law mean? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: Explain Message-Driven vs Event-Driven Approaches ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: What are the core principles of Redux? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Redux follows three fundamental principles:
1. **Single source of truth:** The state of your whole application is stored in an object tree within a single store. The single state tree makes it easier to keep track of changes over time and debug or inspect the application.
2. **State is ready only:** The only way to change the state is to emit an action, an object describing what happened. This ensures that neither the views nor the network callbacks will ever write directly to the state.
3. **Changes are made with pure functions:** To specify how the state tree is transformed by actions, you write pure reducers(Reducers are just pure functions that take the previous state and an action, and return the next state).
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q20: Are there any similarities between Redux and RxJS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
These libraries are very different for very different purposes, but there are some vague similarities.
* **Redux** is a tool for managing state throughout the application. It is usually used as an architecture for UIs. Think of it as an alternative to (half of) Angular.
* **RxJS** is a reactive programming library. It is usually used as a tool to accomplish asynchronous tasks in JavaScript. Think of it as an alternative to Promises.
Redux uses the Reactive paradigm little bit because the Store is reactive. The Store observes actions from a distance, and changes itself. RxJS also uses the Reactive paradigm, but instead of being an architecture, it gives you basic building blocks, Observables, to accomplish this "observing from a distance" pattern.
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
## [[⬆]](#toc) 20 Senior .NET Developer Interview Questions to Ask in 2019
> Originally published on 👉 20 Senior .NET Developer Interview Questions to Ask in 2019 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is .NET Standard? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* .NET Standard solves the code sharing problem for .NET developers across all platforms by bringing all the APIs that you expect and love across the environments that you need: desktop applications, mobile apps & games, and cloud services
* .NET Standard is a set of APIs that all .NET platforms have to implement. This unifies the .NET platforms and prevents future fragmentation.
* .NET Standard 2.0 will be implemented by .NET Framework, .NET Core, and Xamarin. For .NET Core, this will add many of the existing APIs that have been requested.
* .NET Standard 2.0 includes a compatibility shim for .NET Framework binaries, significantly increasing the set of libraries that you can reference from your .NET Standard libraries.
* .NET Standard will replace Portable Class Libraries (PCLs) as the tooling story for building multi-platform .NET libraries.
**Source:** _talkingdotnet.com_
#### Q2: Explain the difference between Task and Thread in .NET ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Thread** represents an actual OS-level thread, with its own stack and kernel resources. Thread allows the highest degree of control; you can Abort() or Suspend() or Resume() a thread, you can observe its state, and you can set thread-level properties like the stack size, apartment state, or culture. ThreadPool is a wrapper around a pool of threads maintained by the CLR.
* The **Task class** from the Task Parallel Library offers the best of both worlds. Like the ThreadPool, a task does not create its own OS thread. Instead, tasks are executed by a TaskScheduler; the default scheduler simply runs on the ThreadPool. Unlike the ThreadPool, Task also allows you to find out when it finishes, and (via the generic Task) to return a result.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q3: Explain Finalize vs Dispose usage? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q4: What is difference between WCF and Web API and WCF REST and Web Service? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q5: What do you know about Azure WebJobs? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**WebJobs** is a feature of Azure App Service that enables you to run a program or script in the same context as a web app, API app, or mobile app. There is no additional cost to use WebJobs.
The Azure WebJobs SDK is a framework that simplifies the task of writing background processing code that runs in Azure WebJobs. It includes a declarative binding and trigger system that works with Azure Storage Blobs, Queues and Tables as well as Service Bus. You could also trigger Azure WebJob using Kudu API.
**Source:** _github.com/Azure_
#### Q6: What is difference between constants and readonly? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Constant variables are declared and initialized at compile time. The value can't be changed afterwards. Readonly is used only when we want to assign the value at run time.
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q7: Refactor the code ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```csharp
class ClassA
{
public ClassA() { }
public ClassA(int pValue) { }
}
// client program
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ClassA refA = new ClassA();
}
}
```
Is there a way to modify `ClassA` so that you can you call the constructor with parameters, when the Main method is called, without creating any other new instances of the `ClassA`?
**Answer:**
The `this` keyword is used to call other constructors, to initialize the class object. The following shows the implementation:
```csharp
class ClassA
{
public ClassA() : this(10)
{ }
public ClassA(int pValue)
{ }
}
```
**Source:** _toptal.com_
#### Q8: What is lambda expressions in C#? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **lambda expression** is an anonymous function that you can use to create delegates or _expression tree_ types. By using lambda expressions, you can write local functions that can be passed as arguments or returned as the value of function calls. Lambda expressions are particularly helpful for writing LINQ query expressions.
**Source:** _docs.microsoft.com_
#### Q9: What is Indexer in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q10: What is the "yield" keyword used for in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider:
```csharp
IEnumerable FilteredList()
{
foreach( object item in FullList )
{
if( IsItemInPartialList( item )
yield return item;
}
}
```
Could you explain what does the `yield` keyword do there?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q11: Can you create sealed abstract class in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q12: Implement the "Where" method in C# ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: What is Facade pattern? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Facade pattern** hides the complexities of the system and provides an interface to the client using which the client can access the system. This type of design pattern comes under *structural pattern* as this pattern adds an interface to existing system to hide its complexities.

This pattern involves a single class which provides simplified methods required by client and delegates calls to methods of existing system classes.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q14: What's the difference between the Dependency Injection and Service Locator patterns? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: Define what is Let clause? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In a query expression, it is sometimes useful to store the result of a sub-expression in order to use it in subsequent clauses. You can do this with the `let` keyword, which creates a new range variable and initializes it with the result of the expression you supply.
Consider:
```csharp
var names = new string[] { "Dog", "Cat", "Giraffe", "Monkey", "Tortoise" };
var result =
from animalName in names
let nameLength = animalName.Length
where nameLength > 3
orderby nameLength
select animalName;
```
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q16: Name some advantages of LINQ over Stored Procedures ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: Why do we use MSMQ? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Microsoft Message Queuing**, or MSMQ, is technology for asynchronous messaging. Whenever there's need for two or more applications (processes) to send messages to each other without having to immediately know results, MSMQ can be used. MSMQ can communicate between remote machines, even over Internet. It's free and comes with Windows, but is not installed by default.
This mainly addresses the common use case of asynchronous message processing: you have a service `Service1` that communicates (send messages) with another part of your software architecture, say `Service2`.
Main problem: what if `Service2` becomes suddenly unavailable? Will messages be lost?
If you use MSMQ it won't: `Service1` will send messages into a queue, and `Service2` will dequeue when it is available.
MSMQ will resolve following common issues:
- temporary unavailability of a service: messages are persisted on the disk and will be dequeued when the service becomes available again, so **no messages are lost**
- as it's fully asynchronous, it'll help a lot in case of **punctual peak load**: your `Service2` won't die under the heavy load, it'll just dequeue and process messages, one after one
**Source:** _cogin.com_
#### Q18: Explain the Single Responsibility Principle? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Single responsibility** is the concept of a Class doing one specific thing (responsibility) and not trying to do more than it should, which is also referred to as _High Cohesion_.
Classes don't often start out with Low Cohesion, but typically after several releases and different developers adding onto them, suddenly you'll notice that it became a monster or **God** class as some call it. So the class should be refactored.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q19: What is GOD class and why should we avoid it? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: When would you use Duplex WCF service? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 20 Vue.js Interview Questions And Answers (2018 Updated)
> Originally published on 👉 20 Vue.js Interview Questions And Answers (2018 Updated) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Vue.js? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Vue js** is progressive javascript script used to create dynamic user interfaces.Vue js is very easy to learn.In order to work with Vue js you just need to add few dynamic features to a website.You don’t need to install any thing to use Vue js just need add Vue js library in your project.
**Source:** _onlineinterviewquestions.com_
#### Q2: How to create an instance of Vue.js? ⭐
**Answer:**
Every Vue application starts by creating a new Vue instance with the Vue function:
```js
var vm = new Vue({
// options
})
```
**Source:** _onlineinterviewquestions.com_
#### Q3: Explain the differences between one-way data flow and two-way data binding? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In one-way data flow the view(UI) part of application does not updates automatically when data Model is change we need to write some custom code to make it updated every time a data model is changed. In Vue js **v-bind** is used for one-way data flow or binding.
In two-way data binding the view(UI) part of application automatically updates when data Model is changed. In Vue.js **v-model** directive is used for two way data binding.
**Source:** _onlineinterviewquestions.com_
#### Q4: How to create Two-Way Bindings in Vue.js? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`v-model` directive is used to create Two-Way Bindings in Vue js.In Two-Way Bindings data or model is bind with DOM and Dom is binded back to model.
In below example you can see how Two-Way Bindings is implemented.
```html
{{message}}
var message = 'Vue.js is rad';
new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message } });
```
**Source:** _onlineinterviewquestions.com_
#### Q5: What are components props? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Every component instance has its own isolated scope. This means you cannot (and should not) directly reference parent data in a child component’s template. Data can be passed down to child components using **props**. Props are custom attributes you can register on a component. When a value is passed to a prop attribute, it becomes a property on that component instance.
```js
Vue.component('blog-post', {
// camelCase in JavaScript
props: ['postTitle'],
template: '
{{ postTitle }}
'})
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q6: How to deploy Vue.js app? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
If you've created your project like this:
```sh
vue init webpack myproject
```
Now you can run
```sh
npm run build
```
Then copy index.html and /dist/ folder into your website root directory. Done.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q7: What are Components in Vue.js? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Components* are one of most powerful features of Vue js.In Vue components are custom elements that help extend basic HTML elements to encapsulate reusable code.
Following is the way to register a Vue component inside another component:
```js
export default {
el: '#your-element'
components: {
'your-component'
}
}
```
**Source:** _onlineinterviewquestions.com_
#### Q8: What is filters in Vue.js? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Vue.js allows you to define **filters** that can be used to apply common text formatting. Filters are usable in two places: mustache interpolations and v-bind expressions (the latter supported in 2.1.0+). Filters should be appended to the end of the JavaScript expression, denoted by the “pipe” symbol:
```html
{{ message | capitalize }}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q9: How can you redirect to another page in Vue.js? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
If you are using `vue-router`, you should use `router.go(path)` to navigate to any particular route. The router can be accessed from within a component using `this.$router`. `router.go()` changed in VueJS 2.0. You can use `router.push({ name: "yourroutename"})`or just `router.push("yourroutename")` now to redirect.
#### Q10: Explain the basic logical Vue.js app organisation ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **Vue.js application** consists of a root Vue instance created with new Vue, optionally organized into a tree of nested, reusable components. For example, a todo app’s component tree might look like this:
```sh
Root Instance
└─ TodoList
├─ TodoItem
│ ├─ DeleteTodoButton
│ └─ EditTodoButton
└─ TodoListFooter
├─ ClearTodosButton
└─ TodoListStatistics
```
All Vue components are also Vue instances.
**Source:** _vuejs.org_
#### Q11: List some features of Vue.js ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Vue js comes with following features
* Templates
* Reactivity
* Components
* Transitions
* Routing
**Source:** _onlineinterviewquestions.com_
#### Q12: How can I fetch query parameters in Vue.js? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
You have access to a `$route` object from your components, that expose what we need.
```js
//from your component
console.log(this.$route.query.test)
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q13: What is the difference v-bind and v-model? Provide some code example. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`v-model` is a **two-way binding for form inputs**. It combines `v-bind`, which **_brings a js value_ **into the markup, and `v-on:input` to **_update the js value_**.
Consider:
```html
```
and it's just syntactic sugar for:
```html
```
`v-model` works with all the basic HTML input types (text, textarea, number, radio, checkbox, select). You can use `v-model` with `input type=date` if your model stores dates as ISO strings (`yyyy-mm-dd`).
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q14: How to pass an argument to Vue.js filters? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Consider:
```js
filters:{
currency: function(value, arg1){
return arg1+value;
}
```
And usage:
```html
{{123 | currency('$') }}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q15: How to use Gulp with Vue.js? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: What's the equivalent of Angular Service in Vue.js? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: What is Vuex? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: Why we need Vue.js mixins? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: What is the best way to create a constant, that can be accessible from entire application in VueJs ? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: What is a proper way to communicate between sibling components in vuejs 2.0? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 20+ Agile Scrum Interview Questions for Software Developers in 2018
> Originally published on 👉 20+ Agile Scrum Interview Questions for Software Developers in 2018 | FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 22 Essential WCF Interview Questions That'll Make You Cry
> Originally published on 👉 22 Essential WCF Interview Questions That'll Make You Cry | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is WCF? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Windows Communication Foundation (WCF)** is a framework for building service-oriented applications. Using WCF, you can send data as asynchronous messages from one service endpoint to another. A service endpoint can be part of a continuously available service hosted by IIS, or it can be a service hosted in an application. An endpoint can be a client of a service that requests data from a service endpoint. The messages can be as simple as a single character or word sent as XML, or as complex as a stream of binary data.
**Source:** _docs.microsoft.com_
#### Q2: Could you name basic WCF service components? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Have a look at this mindmap to navigate yourself through WCF service components:

**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q3: What is a service contract in WCF? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **service contract** defines the operations which are exposed by the service to the outside world. A service contract is the interface of the WCF service and it tells the outside world what the service can do. It may have service-level settings, such as the name of the service and namespace for the service.
```csharp
[ServiceContract]
interface IMyContract {
[OperationContract]
string MyMethod();
}
class MyService: IMyContract {
public string MyMethod() {
return "Hello World";
}
}
```
**Source:** _dotnettricks.com_
#### Q4: Explain what is SOA? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**SOA** stands for **service-oriented architecture. Service Oriented Architecture is an architectural approach in software development where the application is organized as "Services". Services are a group of methods that contain the business logic to connect a DB or other services. For instance you go to a hotel and order food. Your order first goes to the counter and then it goes to the kitchen where the food is prepared and finally the waiter serves the food.
**Some important characteristics of Service Oriented Architecture**
* SOA services should be **independent** of other services. Altering a service should not affect the client calling the service.
* Services should be **self-contained. ** Services should be able to **define themselves** (in the Web Service Description Language (WSDL)). It should be able to tell the client what all of the operations it does, what are all the data types it uses and what kind of value it will return.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q5: What are the features and advantage of WCF? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Features of WCF**
Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) is a secure, reliable, and scalable messaging platform for the .NET Framework 3.0,
* Service Orientation
* Interoperability
* Multiple Message Patterns
* Service Metadata
* Data Contracts
* Security
* Multiple Transports and Encodings
* Reliable and Queued Messages
* Durable Messages
* Transactions
* AJAX and REST Support
* Extensibility
**Advantages of WCF**:
1. Service Oriented
2. Location Independent
3. Language Independent
4. Platform Independent
5. Support Multiple operation
6. WCF can maintain transaction like COM+ Does
7. It can maintain state
8. It can control concurrency
9. It can be hosted on IIS, WAS, Self hosting, Windows services.
**Source:** _docs.microsoft.com_
#### Q6: What is transport in WCF? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The WCF programming model separates endpoint operations (as expressed in a service contract) from the transport mechanism that connects two endpoints. This gives you the flexibility to decide how to expose your services to the network. The transport layer is at the lowest level of the channel stack. A transport sends or receives the serialized form of a message to or from another application. The main transports used in Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) are:
* HTTP,
* HTTPS,
* TCP
* named pipes.
**Source:** _weblogs.asp.net_
#### Q7: What is WCF Binding and how many of them do you know? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Bindings** specify how a Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) service endpoint communicates with other endpoints. At its most basic, a binding must specify the _transport_ (for example, HTTP or TCP) to use. You can also set other characteristics, such as security and transaction support, through bindings.
WCF provides nine built-in bindings:
* **BasicHttpBinding**: Basic web service communication. Exposes WCF services as legacy ASMX web services. Used for interoperability. No security by default.
* **WSHttpBinding**: Web services with WS-* support. Supports transactions and reliable messaging.
* **WSDualHttpBinding**: Web services with duplex contract and transaction support.
* **WSFederationHttpBinding**: Web services with federated security. Supports transactions.
* **MsmqIntegrationBinding**: Communication directly with MSMQ applications. Supports transactions.
* **NetMsmqBinding**: Communication between WCF applications by using queuing. Supports transactions.
* **NetNamedPipeBinding**: Communication between WCF applications on same computer. Supports duplex contracts and transactions.
* **NetPeerTcpBinding**: Communication between computers across peer-to-peer services. Supports duplex contracts.
* **NetTcpBinding**: Communication between WCF applications across computers. Supports duplex contracts and transactions.
**Source:** _weblogs.asp.net_
#### Q8: What are the Possible Ways of Hosting a WCF Service? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
For a **Windows Communication Foundation** service to host, we need at least a managed process, a `ServiceHost` instance and an `Endpoint` configured. Possible approaches for hosting a service are:
1. Hosting in a Managed Application/Self Hosting
1. Console Application
2. Windows Application
3. Windows Service
2. Hosting on Web Server
1. IIS 6.0 (ASP.NET Application supports only HTTP)
2. Windows Process Activation Service (WAS) i.e. IIS 7.0 supports HTTP, TCP, NamedPipes, MSMQ.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q9: What is Message Contract in WCF? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Sometimes complete control over the structure of a SOAP message is just as important as control over its contents (that defined by Data Contracts). This is especially true when interoperability is important or to specifically control security issues at the level of the message or message part. In these cases, you can create a _message contract_ that enables you to specify the structure of the precise SOAP message required.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q10: What is an Operation Contract in WCF? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An **operation contract** is defined within a service contract. It defines the parameters and return type of an operation. An operation contract can also defines operation-level settings, like as the transaction flow of the operation, the directions of the operation (one-way, two-way, or both ways), and fault contract of the operation.
```csharp
[ServiceContract]
interface IMyContract {
[FaultContract(typeof(MyFaultContract))]
[OperationContract]
string MyMethod();
}
```
**Source:** _dotnettricks.com_
#### Q11: Name some different types of contracts in WCF ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
WCF contract specifies the service and its operations. WCF has five types of contracts:
* service contract,
* operation contract,
* data contract,
* message contract
* fault contract.
**Source:** _dotnettricks.com_
#### Q12: Explain the difference between WCF vs ASP.NET Web API? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In the scenarios listed below you should go for WCF:
* If you need to send data on protocols like TCP, MSMQ or MIME
* If the consuming client just knows how to consume SOAP messages
WEB API is a framework for developing RESTful/HTTP services.
Consider:
|WCF|ASP.NET Web API|
|--- |--- |
|Enables building services that support multiple transport protocols (HTTP, TCP, UDP, and custom transports) and allows switching between them.|HTTP only. First-class programming model for HTTP. More suitable for access from various browsers, mobile devices etc enabling wide reach.|
|Enables building services that support multiple encodings (Text, MTOM, and Binary) of the same message type and allows switching between them.|Enables building Web APIs that support wide variety of media types including XML, JSON etc.|
|Supports building services with WS-* standards like Reliable Messaging, Transactions, Message Security.|Uses basic protocol and formats such as HTTP, WebSockets, SSL, JSON, and XML. There is no support for higher level protocols such as Reliable Messaging or Transactions.|
|Supports Request-Reply, One Way, and Duplex message exchange patterns.|HTTP is request/response but additional patterns can be supported through SignalR and WebSockets integration.|
|WCF SOAP services can be described in WSDL allowing automated tools to generate client proxies even for services with complex schemas.|There is a variety of ways to describe a Web API ranging from auto-generated HTML help page describing snippets to structured metadata for OData integrated APIs.|
|Ships with the .NET framework.|Ships with .NET framework but is open-source and is also available out-of-band as independent download.|
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q13: Why we need Streaming? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
When you have a large amount of data to transfer, the streaming transfer mode in WCF is a feasible alternative to the default behavior of buffering and processing messages in memory in their entirety.
In WCF any receiving message is delivered only once the entire message has been received. What I mean here is that first message is buffered at the receiving side and once it is fully received it gets delivered to the receiving end. The main problem with this approach is that the receiver end is unresponsive while the message is getting buffered. So default way of message handling in WCF is ok for small size messages but for the large size messages, this approach is not good. So to overcome this problem Streaming in WCF come into action.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q14: What is interoperability and how is it achieved with WCF services? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: When would you use Duplex WCF service? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: Will it make any difference if I change the operation contract of methods having no return value by [OperationContract(IsOneWay=true)]? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: Explain Binary vs MTOM vs Streaming in WCF? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: What is the difference between hosting WCF service on IIS, Windows Service and self-hosted app? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: Could we use WSHttpBinding with Request-CallBack (also called Duplex) exchange pattern? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: What is the main difference between Request-Response and Duplex in WCF Message Exchange Pattern? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: Should I use WCF or raw sockets? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: What replaces WCF in .Net Core? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 22 Important JavaScript/ES6/ES2015 Interview Questions
> Originally published on 👉 22 Important JavaScript/ES6/ES2015 Interview Questions | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: Could you explain the difference between ES5 and ES6 ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **ECMAScript 5 (ES5)**: The 5th edition of ECMAScript, standardized in 2009. This standard has been implemented fairly completely in all modern browsers
* **ECMAScript 6 (ES6)/ ECMAScript 2015 (ES2015)**: The 6th edition of ECMAScript, standardized in 2015. This standard has been partially implemented in most modern browsers.
Here are some key differences between ES5 and ES6:
* **Arrow functions** & **string interpolation**:
Consider:
```js
const greetings = (name) => {
return `hello ${name}`;
}
```
and even:
```js
const greetings = name => `hello ${name}`;
```
* **Const**.
Const works like a constant in other languages in many ways but there are some caveats. Const stands for ‘constant reference’ to a value. So with const, you can actually mutate the properties of an object being referenced by the variable. You just can’t change the reference itself.
```js
const NAMES = [];
NAMES.push("Jim");
console.log(NAMES.length === 1); // true
NAMES = ["Steve", "John"]; // error
```
* **Block-scoped variables**.
The new ES6 keyword `let` allows developers to scope variables at the block level.
`Let` doesn’t hoist in the same way `var` does.
* **Default parameter values**
Default parameters allow us to initialize functions with default values. A default is used when an argument is either omitted or undefined — meaning null is a valid value.
```js
// Basic syntax
function multiply (a, b = 2) {
return a * b;
}
multiply(5); // 10
```
* ** Class Definition and Inheritance**
ES6 introduces language support for classes (`class` keyword), constructors (`constructor` keyword), and the `extend` keyword for inheritance.
* **for-of operator**
The for...of statement creates a loop iterating over iterable objects.
* **Spread Operator**
For objects merging
```js
const obj1 = { a: 1, b: 2 }
const obj2 = { a: 2, c: 3, d: 4}
const obj3 = {...obj1, ...obj2}
```
* **Promises**
Promises provide a mechanism to handle the results and errors from asynchronous operations. You can accomplish the same thing with callbacks, but promises provide improved readability via method chaining and succinct error handling.
```js
const isGreater = (a, b) => {
return new Promise ((resolve, reject) => {
if(a > b) {
resolve(true)
} else {
reject(false)
}
})
}
isGreater(1, 2)
.then(result => {
console.log('greater')
})
.catch(result => {
console.log('smaller')
})
```
* **Modules exporting & importing**
Consider module exporting:
```js
const myModule = { x: 1, y: () => { console.log('This is ES5') }}
export default myModule;
```
and importing:
```js
import myModule from './myModule';
```
#### Q2: What is IIFEs (Immediately Invoked Function Expressions)? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It’s an Immediately-Invoked Function Expression, or IIFE for short. It executes immediately after it’s created:
```js
(function IIFE(){
console.log( "Hello!" );
})();
// "Hello!"
```
This pattern is often used when trying to avoid polluting the global namespace, because all the variables used inside the IIFE (like in any other normal function) are not visible outside its scope.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q3: When should I use Arrow functions in ES6? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
I'm now using the following rule of thumb for functions in ES6 and beyond:
* Use `function` in the global scope and for Object.prototype properties.
* Use `class` for object constructors.
* Use `=>` everywhere else.
Why use arrow functions almost everywhere?
* **Scope safety**: When arrow functions are used consistently, everything is guaranteed to use the same thisObject as the root. If even a single standard function callback is mixed in with a bunch of arrow functions there's a chance the scope will become messed up.
* **Compactness**: Arrow functions are easier to read and write. (This may seem opinionated so I will give a few examples further on).
* **Clarity**: When almost everything is an arrow function, any regular function immediately sticks out for defining the scope. A developer can always look up the next-higher function statement to see what the thisObject is.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q4: What is the motivation for bringing Symbols to ES6? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`Symbols` are a new, special kind of object that can be used as a unique property name in objects. Using `Symbol` instead of `string`'s allows different modules to create properties that don't conflict with one another. `Symbols` can also be made private, so that their properties can't be accessed by anyone who doesn't already have direct access to the `Symbol`.
`Symbols` are a new **primitive**. Just like the `number`, `string`, and `boolean` primitives, `Symbol` have a function which can be used to create them. Unlike the other primitives, `Symbols` do not have a literal syntax (e.g how `string` have `''`) - the only way to create them is with the `Symbol` constructor in the following way:
```js
let symbol = Symbol();
```
In reality, `Symbol`'s are just a slightly different way to attach properties to an object - you could easily provide the well-known `Symbols` as standard methods, just like `Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty` which appears in everything that inherits from `Object`.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q5: What are the benefits of using spread syntax in ES6 and how is it different from rest syntax? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ES6's spread syntax is very useful when coding in a functional paradigm as we can easily create copies of arrays or objects without resorting to `Object.create`, `slice`, or a library function. This language feature is used often in Redux and rx.js projects.
```js
function putDookieInAnyArray(arr) {
return [...arr, 'dookie'];
}
const result = putDookieInAnyArray(['I', 'really', "don't", 'like']); // ["I", "really", "don't", "like", "dookie"]
const person = {
name: 'Todd',
age: 29,
};
const copyOfTodd = { ...person };
```
ES6's rest syntax offers a shorthand for including an arbitrary number of arguments to be passed to a function. It is like an inverse of the spread syntax, taking data and stuffing it into an array rather than unpacking an array of data, and it works in function arguments, as well as in array and object destructuring assignments.
```js
function addFiveToABunchOfNumbers(...numbers) {
return numbers.map(x => x + 5);
}
const result = addFiveToABunchOfNumbers(4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10); // [9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]
const [a, b, ...rest] = [1, 2, 3, 4]; // a: 1, b: 2, rest: [3, 4]
const { e, f, ...others } = {
e: 1,
f: 2,
g: 3,
h: 4,
}; // e: 1, f: 2, others: { g: 3, h: 4 }
```
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q6: What are the differences between ES6 class and ES5 function constructors? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Let's first look at example of each:
```js
// ES5 Function Constructor
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// ES6 Class
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
```
For simple constructors, they look pretty similar.
The main difference in the constructor comes when using inheritance. If we want to create a `Student` class that subclasses `Person` and add a `studentId` field, this is what we have to do in addition to the above.
```js
// ES5 Function Constructor
function Student(name, studentId) {
// Call constructor of superclass to initialize superclass-derived members.
Person.call(this, name);
// Initialize subclass's own members.
this.studentId = studentId;
}
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Student.prototype.constructor = Student;
// ES6 Class
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, studentId) {
super(name);
this.studentId = studentId;
}
}
```
It's much more verbose to use inheritance in ES5 and the ES6 version is easier to understand and remember.
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q7: What's the difference between `.call` and `.apply`? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Both `.call` and `.apply` are used to invoke functions and the first parameter will be used as the value of `this` within the function. However, `.call` takes in comma-separated arguments as the next arguments while `.apply` takes in an array of arguments as the next argument. An easy way to remember this is C for `call` and comma-separated and A for `apply` and an array of arguments.
```js
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
console.log(add.call(null, 1, 2)); // 3
console.log(add.apply(null, [1, 2])); // 3
```
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q8: Why should we use ES6 classes? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Some reasons you might choose to use **Classes**:
* The syntax is simpler and less error-prone.
* It's **much** easier (and again, less error-prone) to set up inheritance hierarchies using the new syntax than with the old.
* `class` defends you from the common error of failing to use `new` with the constructor function (by having the constructor throw an exception if `this` isn't a valid object for the constructor).
* Calling the parent prototype's version of a method is much simpler with the new syntax than the old (`super.method()` instead of `ParentConstructor.prototype.method.call(this)` or `Object.getPrototypeOf(Object.getPrototypeOf(this)).method.call(this)`).
Consider:
```js
// **ES5**
var Person = function(first, last) {
if (!(this instanceof Person)) {
throw new Error("Person is a constructor function, use new with it");
}
this.first = first;
this.last = last;
};
Person.prototype.personMethod = function() {
return "Result from personMethod: this.first = " + this.first + ", this.last = " + this.last;
};
var Employee = function(first, last, position) {
if (!(this instanceof Employee)) {
throw new Error("Employee is a constructor function, use new with it");
}
Person.call(this, first, last);
this.position = position;
};
Employee.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Employee.prototype.constructor = Employee;
Employee.prototype.personMethod = function() {
var result = Person.prototype.personMethod.call(this);
return result + ", this.position = " + this.position;
};
Employee.prototype.employeeMethod = function() {
// ...
};
```
And the same with ES6 classes:
```js
// ***ES2015+**
class Person {
constructor(first, last) {
this.first = first;
this.last = last;
}
personMethod() {
// ...
}
}
class Employee extends Person {
constructor(first, last, position) {
super(first, last);
this.position = position;
}
employeeMethod() {
// ...
}
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q9: What is the preferred syntax for defining enums in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Since 1.8.5 it's possible to seal and freeze the object, so define the above as:
```js
var DaysEnum = Object.freeze({
"monday": 1,
"tuesday": 2,
"wednesday": 3,
...
})
```
or
```js
var DaysEnum = {
"monday": 1,
"tuesday": 2,
"wednesday": 3,
...
}
Object.freeze(DaysEnum)
```
and voila! JS enums.
However, this doesn't prevent you from assigning an undesired value to a variable, which is often the main goal of enums:
```js
let day = DaysEnum.tuesday
day = 298832342 // goes through without any errors
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q10: Explain the difference between Object.freeze() vs const ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`const` and `Object.freeze` are two completely different things.
* `const` applies to **bindings** ("variables"). It creates an immutable binding, i.e. you cannot assign a new value to the binding.
```js
const person = {
name: "Leonardo"
};
let animal = {
species: "snake"
};
person = animal; // ERROR "person" is read-only
```
* `Object.freeze` works on **values**, and more specifically, *object values*. It makes an object immutable, i.e. you cannot change its properties.
```js
let person = {
name: "Leonardo"
};
let animal = {
species: "snake"
};
Object.freeze(person);
person.name = "Lima"; //TypeError: Cannot assign to read only property 'name' of object
console.log(person);
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q11: What is generator in JS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Generators are functions which can be exited and later re-entered. Their context (variable bindings) will be saved across re-entrances. Generator functions are written using the `function*` syntax. When called initially, generator functions do not execute any of their code, instead returning a type of iterator called a Generator. When a value is consumed by calling the generator's `next` method, the Generator function executes until it encounters the `yield` keyword.
The function can be called as many times as desired and returns a new Generator each time, however each Generator may only be iterated once.
```js
function* makeRangeIterator(start = 0, end = Infinity, step = 1) {
let iterationCount = 0;
for (let i = start; i < end; i += step) {
iterationCount++;
yield i;
}
return iterationCount;
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q12: What is Hoisting in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: Explain the Prototype Design Pattern ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q14: What is the Temporal Dead Zone in ES6? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: When should you NOT use arrow functions in ES6? Name three or more cases. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: What are the actual uses of ES6 WeakMap? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: Explain why the following doesn't work as an IIFE. What needs to be changed to properly make it an IIFE? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```js
function foo(){ }();
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: Could you compare usage of Module Pattern vs Constructor/Prototype pattern? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: What's the difference between ES6 Map and WeakMap? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: Can you give an example of a curry function and why this syntax offers an advantage? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: How to "deep-freeze" object in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: Compare Async/Await and Generators usage to achive same functionality ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 22+ Angular 6 Interview Questions to Stand Out in 2018
> Originally published on 👉 22+ Angular 6 Interview Questions to Stand Out in 2018 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is difference between "declarations", "providers" and "import" in NgModule? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* `imports` makes the exported declarations of other modules available in the current module
* `declarations` are to make directives (including components and pipes) from the current module available to other directives in the current module. Selectors of directives, components or pipes are only matched against the HTML if they are declared or imported.
* `providers` are to make services and values known to DI. They are added to the root scope and they are injected to other services or directives that have them as dependency.
A special case for `providers` are lazy loaded modules that get their own child injector. `providers` of a lazy loaded module are only provided to this lazy loaded module by default (not the whole application as it is with other modules).
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q2: What is AOT? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The Angular Ahead-of-Time compiler pre-compiles application components and their templates during the build process.
Apps compiled with AOT launch faster for several reasons.
* Application components execute immediately, without client-side compilation.
* Templates are embedded as code within their components so there is no client-side request for template files.
* You don't download the Angular compiler, which is pretty big on its own.
* The compiler discards unused Angular directives that a tree-shaking tool can then exclude.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q3: Explain the difference between "Constructor" and "ngOnInit" ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* The `Constructor` is a default method of the class that is executed when the class is instantiated and ensures proper initialization of fields in the class and its subclasses.
* `ngOnInit` is a life cycle hook called by Angular to indicate that Angular is done creating the component. We have to import OnInit in order to use like this (actually implementing OnInit is not mandatory but considered good practice).
Mostly we use `ngOnInit` for all the initialization/declaration and avoid stuff to work in the constructor. The constructor should only be used to initialize class members but shouldn't do actual "work".
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q4: What's new in Angular 6 and why shall we upgrade to it? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Angular Elements** - Angular Elements is a project that lets you wrap your Angular components as Web Components and embed them in a non-Angular application.
* **New Rendering Engine: Ivy** - increases in speed and decreases in application size.
* **Tree-shakeable providers** - a new, recommended, way to register a provider, directly inside the @Injectable() decorator, using the new `providedIn` attribute
* **RxJS 6** - Angular 6 now uses RxJS 6 internally, and requires you to update your application also. RxJS released a library called rxjs-compat, that allows you to bump RxJS to version 6.0 even if you, or one of the libraries you’re using, is still using one of the “old” syntaxes.
* **ElementRef``** - in Angular 5.0 or older, is that the said ElementRef had its nativeElement property typed as any. In Angular 6.0, you can now type ElementRef more strictly.
* **Animations** - The polyfill web-animations-js is not necessary anymore for animations in Angular 6.0, except if you are using the AnimationBuilder.
* **i18n** - possibility to have “runtime i18n”, without having to build the application once per locale.
**Source:** _ninja-squad.com_
#### Q5: Why would you use renderer methods instead of using native element methods? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q6: What is Zone in Angular? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q7: Why would you use lazy loading modules in Angular app? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q8: What are the lifecycle hooks for components and directives? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q9: How would you insert an embedded view from a prepared TemplateRef? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q10: How to detect a route change in Angular? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q11: What does a just-in-time (JIT) compiler do (in general)? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q12: How do you create application to use scss? What changed for Angular 6? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: What is ngUpgrage? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q14: What is Reactive programming and how does it relate to Angular? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: Name some security best practices in Angular ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: Could I use jQuery with Angular? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: What is the Angular equivalent to an AngularJS "$watch"? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: Just-in-Time (JiT) vs Ahead-of-Time (AoT) compilation. Explain the difference. ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: Do you know how you can run angularJS and angular side by side? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: Could you provide some particular examples of using ngZone? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: Why angular uses url segment? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: When to use query parameters versus matrix parameters? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
* Query parameters: http://example.com/apples?order=random&color=blue
* Matrix parameters: http://example.com/apples;order=random;color=blue
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 23 Advanced JavaScript Interview Questions
> Originally published on 👉 23 Advanced JavaScript Interview Questions | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: Explain equality in JavaScript ⭐
**Answer:**
JavaScript has both strict and type–converting comparisons:
* **Strict comparison (e.g., ===)** checks for value equality without allowing *coercion*
* **Abstract comparison (e.g. ==)** checks for value equality with *coercion* allowed
```js
var a = "42";
var b = 42;
a == b; // true
a === b; // false
```
Some simple equalityrules:
* If either value (aka side) in a comparison could be the `true` or `false` value, avoid `==` and use `===`.
* If either value in a comparison could be of these specific values (`0`, `""`, or `[]` -- empty array), avoid `==` and use `===`.
* In all other cases, you're safe to use `==`. Not only is it safe, but in many cases it simplifies your code in a way that improves readability.
#### Q2: Provide some examples of non-bulean value coercion to a boolean one ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The question is when a non-boolean value is coerced to a boolean, does it become `true` or `false`, respectively?
The specific list of "falsy" values in JavaScript is as follows:
* `""` (empty string)
* `0`, `-0`, `NaN` (invalid number)
* `null`, `undefined`
* `false`
Any value that's not on this "falsy" list is "truthy." Here are some examples of those:
* `"hello"`
* `42`
* `true`
* `[ ]`, `[ 1, "2", 3 ]` (arrays)
* `{ }`, `{ a: 42 }` (objects)
* `function foo() { .. }` (functions)
#### Q3: What is IIFEs (Immediately Invoked Function Expressions)? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It’s an Immediately-Invoked Function Expression, or IIFE for short. It executes immediately after it’s created:
```js
(function IIFE(){
console.log( "Hello!" );
})();
// "Hello!"
```
This pattern is often used when trying to avoid polluting the global namespace, because all the variables used inside the IIFE (like in any other normal function) are not visible outside its scope.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q4: When should I use Arrow functions in ES6? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
I'm now using the following rule of thumb for functions in ES6 and beyond:
* Use `function` in the global scope and for Object.prototype properties.
* Use `class` for object constructors.
* Use `=>` everywhere else.
Why use arrow functions almost everywhere?
* **Scope safety**: When arrow functions are used consistently, everything is guaranteed to use the same thisObject as the root. If even a single standard function callback is mixed in with a bunch of arrow functions there's a chance the scope will become messed up.
* **Compactness**: Arrow functions are easier to read and write. (This may seem opinionated so I will give a few examples further on).
* **Clarity**: When almost everything is an arrow function, any regular function immediately sticks out for defining the scope. A developer can always look up the next-higher function statement to see what the thisObject is.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q5: What are the differences between ES6 class and ES5 function constructors? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Let's first look at example of each:
```js
// ES5 Function Constructor
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// ES6 Class
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
```
For simple constructors, they look pretty similar.
The main difference in the constructor comes when using inheritance. If we want to create a `Student` class that subclasses `Person` and add a `studentId` field, this is what we have to do in addition to the above.
```js
// ES5 Function Constructor
function Student(name, studentId) {
// Call constructor of superclass to initialize superclass-derived members.
Person.call(this, name);
// Initialize subclass's own members.
this.studentId = studentId;
}
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Student.prototype.constructor = Student;
// ES6 Class
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, studentId) {
super(name);
this.studentId = studentId;
}
}
```
It's much more verbose to use inheritance in ES5 and the ES6 version is easier to understand and remember.
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q6: Explain `Function.prototype.bind`. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Taken word-for-word from [MDN](https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_objects/Function/bind):
> The `bind()` method creates a new function that, when called, has its this keyword set to the provided value, with a given sequence of arguments preceding any provided when the new function is called.
In my experience, it is most useful for binding the value of `this` in methods of classes that you want to pass into other functions. This is frequently done in React components.
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q7: What's a typical use case for anonymous functions? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
They can be used in IIFEs to encapsulate some code within a local scope so that variables declared in it do not leak to the global scope.
```js
(function() {
// Some code here.
})();
```
As a callback that is used once and does not need to be used anywhere else. The code will seem more self-contained and readable when handlers are defined right inside the code calling them, rather than having to search elsewhere to find the function body.
```js
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('Hello world!');
}, 1000);
```
Arguments to functional programming constructs or Lodash (similar to callbacks).
```js
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const double = arr.map(function(el) {
return el * 2;
});
console.log(double); // [2, 4, 6]
```
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q8: Explain the difference between Object.freeze() vs const ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`const` and `Object.freeze` are two completely different things.
* `const` applies to **bindings** ("variables"). It creates an immutable binding, i.e. you cannot assign a new value to the binding.
```js
const person = {
name: "Leonardo"
};
let animal = {
species: "snake"
};
person = animal; // ERROR "person" is read-only
```
* `Object.freeze` works on **values**, and more specifically, *object values*. It makes an object immutable, i.e. you cannot change its properties.
```js
let person = {
name: "Leonardo"
};
let animal = {
species: "snake"
};
Object.freeze(person);
person.name = "Lima"; //TypeError: Cannot assign to read only property 'name' of object
console.log(person);
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q9: What is generator in JS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Generators are functions which can be exited and later re-entered. Their context (variable bindings) will be saved across re-entrances. Generator functions are written using the `function*` syntax. When called initially, generator functions do not execute any of their code, instead returning a type of iterator called a Generator. When a value is consumed by calling the generator's `next` method, the Generator function executes until it encounters the `yield` keyword.
The function can be called as many times as desired and returns a new Generator each time, however each Generator may only be iterated once.
```js
function* makeRangeIterator(start = 0, end = Infinity, step = 1) {
let iterationCount = 0;
for (let i = start; i < end; i += step) {
iterationCount++;
yield i;
}
return iterationCount;
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q10: When should we use generators in ES6? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
To put it simple, generator has two features:
* one can choose to jump out of a function and let outer code to determine when to jump back into the function.
* the control of asynchronous call can be done outside of your code
The most important feature in generators — we can get the next value in only when we really need it, not all the values at once. And in some situations it can be very convenient.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q11: Explain what is hoisting in Javascript ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q12: What will be the output of the following code? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```javascript
var output = (function(x) {
delete x;
return x;
})(0);
console.log(output);
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: What will be the output of the following code? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```javascript
var Employee = {
company: 'xyz'
}
var emp1 = Object.create(Employee);
delete emp1.company
console.log(emp1.company);
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q14: Explain the Prototype Design Pattern ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: What is the Temporal Dead Zone in ES6? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: Can you describe the main difference between a `.forEach` loop and a `.map()` loop and why you would pick one versus the other? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: What's the difference between a variable that is: `null`, `undefined` or undeclared? How would you go about checking for any of these states? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: Describe the Revealing Module Pattern design pattern ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: What's the difference between ES6 Map and WeakMap? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: Is JavaScript a pass-by-reference or pass-by-value language? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: How to "deep-freeze" object in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: In JavaScript, why is the “this” operator inconsistent? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: Compare Async/Await and Generators usage to achive same functionality ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 26 Top Angular 8 Interview Questions To Learn in 2019
> Originally published on 👉 26 Top Angular 8 Interview Questions To Learn in 2019 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: Explain the difference between `Promise` and `Observable` in Angular? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Promises**:
- return a single value
- not cancellable
- more readable code with try/catch and async/await
**Observables**:
- work with multiple values over time
- cancellable
- support map, filter, reduce and similar operators
- use Reactive Extensions (RxJS)
- an array whose items arrive asynchronously over time
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q2: Why should `ngOnInit` be used, if we already have a `constructor`? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* The `Constructor` is a default method of the class that is executed when the class is instantiated and ensures proper initialization of fields in the class and its subclasses.
* `ngOnInit` is a life cycle hook called by Angular2 to indicate that Angular is done creating the component.
Mostly we use `ngOnInit` for all the initialization/declaration and avoid stuff to work in the constructor. The constructor should only be used to initialize class members but shouldn't do actual "work". So you should use `constructor()` to setup Dependency Injection and not much else. ngOnInit() is better place to "start" - it's where/when components' bindings are resolved.
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q3: What is AOT? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The Angular Ahead-of-Time compiler pre-compiles application components and their templates during the build process.
Apps compiled with AOT launch faster for several reasons.
* Application components execute immediately, without client-side compilation.
* Templates are embedded as code within their components so there is no client-side request for template files.
* You don't download the Angular compiler, which is pretty big on its own.
* The compiler discards unused Angular directives that a tree-shaking tool can then exclude.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q4: What is the use of codelyzer? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
All enterprise applications follows a set of coding conventions and guidelines to maintain code in better way. **Codelyzer** is an open source tool to run and check whether the pre-defined coding guidelines has been followed or not. Codelyzer does only static code analysis for angular and typescript project.
Codelyzer runs on top of tslint and its coding conventions are usually defined in tslint.json file. Codelyzer can be run via angular cli or npm directly. Editors like Visual Studio Code and Atom also supports codelyzer just by doing a basic settings.
**Source:** _pankajagarwal.in_
#### Q5: What is the purpose of Wildcard route? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
If the URL doesn't match any predefined routes then it causes the router to throw an error and crash the app. In this case, you can use wildcard route. A wildcard route has a path consisting of two asterisks to match every URL.
For example, you can define PageNotFoundComponent for wildcard route as below
```javascript
{ path: '**', component: PageNotFoundComponent }
```
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q6: What are custom elements? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Custom elements (or Web Components) are a Web Platform feature which extends HTML by allowing you to define a tag whose content is created and controlled by JavaScript code. The browser maintains a `CustomElementRegistry` of defined custom elements, which maps an instantiable JavaScript class to an HTML tag. Currently this feature is supported by Chrome, Firefox, Opera, and Safari, and available in other browsers through polyfills.
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q7: What are the utility functions provided by RxJS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The RxJS library also provides below utility functions for creating and working with observables.
1. Converting existing code for async operations into observables
2. Iterating through the values in a stream
3. Mapping values to different types
4. Filtering streams
5. Composing multiple streams
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q8: What is subscribing? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An Observable instance begins publishing values only when someone subscribes to it. So you need to subscribe by calling the **subscribe()** method of the instance, passing an observer object to receive the notifications.
Let's take an example of creating and subscribing to a simple observable, with an observer that logs the received message to the console.
```javascript
Creates an observable sequence of 5 integers, starting from 1
const source = range(1, 5);
// Create observer object
const myObserver = {
next: x => console.log('Observer got a next value: ' + x),
error: err => console.error('Observer got an error: ' + err),
complete: () => console.log('Observer got a complete notification'),
};
// Execute with the observer object and Prints out each item
myObservable.subscribe(myObserver);
// => Observer got a next value: 1
// => Observer got a next value: 2
// => Observer got a next value: 3
// => Observer got a next value: 4
// => Observer got a next value: 5
// => Observer got a complete notification
```
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q9: What's new in Angular 8? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
This release is mostly about Ivy and the possibility to give it a try, but it also includes a few features and breaking changes, namely:
* **Differential loading** - with differential loading, two bundles are created when building for production: a bundle for modern browsers that support ES2015+ and a bundle for older browsers that only support the ES5 version of JavaScript
* **TypeScript 3.4** support
* **Ivy** - it is the new compiler/runtime of Angular. It will enable very cool features in the future, but it is currently focused on not breaking existing applications.
* **Bazel** support - it is a build tool developed and massively used by Google, as it can build pretty much any language.
* **Lazy-loading with import()** syntax
```js
// from
loadChildren: './admin/admin.module#AdminModule'
// to
loadChildren: () => import('./races/races.module').then(m => m.RacesModule)
```
* To help people migrating from AngularJS, a bunch of things have been added to the **location services** in Angular
* The **service worker registration** has a new option that allows to specify when the registration should take place.
* `@angular/http` has been removed from 8.0, after being replaced by `@angular/common/http` in 4.3 and officially deprecated in 5.0,
**Source:** _blog.ninja-squad.com_
#### Q10: Angular 8: What is Bazel? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Google open sourced the software responsible for building most of its projects under the name **Bazel**. Bazel is a powerful tool which can keep track of the dependencies between different packages and build targets.
Some of the features of Bazel are:
* It has a smart algorithm for determining the build dependencies - based on the dependency graph of a project, Bazel determines which targets it can build in parallel
* Bazel is independent of the tech stack. We can build anything we want with it using the same interface. For example, there are plugins for Java, Go, TypeScript, JavaScript, and more
**Source:** _blog.mgechev.com_
#### Q11: Angular 8: What is Angular Ivy? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A big part of Angular is its compiler: it takes all your HTML and generates the necessary JS code. This compiler (and the runtime) has been completely rewritten over the last year, and this is what Ivy is about. The last rewrite was done in Angular 4.0.
**Ivy** is a complete rewrite of the compiler (and runtime) in order to:
* reach better build times (with a more incremental compilation)
* reach better build sizes (with a generated code more compatible with tree-shaking)
* unlock new potential features (metaprogramming or higher order components, lazy loading of component instead of modules, a new change detection system not based on zone.js…)
**Source:** _blog.ninja-squad.com_
#### Q12: Angular 8: Explain Lazy Loading in Angular 8? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Lazy loading is one of the most useful concepts of Angular Routing and brings down the size of large files. This is done by lazily loading the files that are required _occasionally_.
Angular 8 comes up with support for **dynamic imports** in our router configuration. This means that we use the import statement for lazy loading the module and this will be understood by the IDEs, webpack, etc.
Angular 7:
```js
{path: ‘user’, loadChildren: ‘./users/user.module#UserModule’}
```
Angular 8:
```js
{path: ‘user’, loadChildren: () => import(‘./users/user.module’).then(m => m.UserModule)};
```
New with Angular 8, `loadChildren` expects a function that uses the dynamic import syntax to import your lazy-loaded module only when it’s needed. As you can see, the dynamic import is promise-based and gives you access to the module, where the module’s class can be called.
**Source:** _dev.to_
#### Q13: How to detect a route change in Angular? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q14: Are there any pros/cons (especially performance-wise) in using local storage to replace cookie functionality? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q15: What is Zone in Angular? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: What does a just-in-time (JIT) compiler do (in general)? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: What is ngUpgrage? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: What is incremental DOM? How is it different from virtual DOM? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: Angular 8: Why we should use Bazel for Angular builds? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: Explain the purpose of Service Workers in Angular ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: What is the Angular equivalent to an AngularJS "$watch"? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: Just-in-Time (JiT) vs Ahead-of-Time (AoT) compilation. Explain the difference. ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: Why did the Google team go with incremental DOM instead of virtual DOM? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: Why Incremental DOM is Tree Shakable? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: Angular 8: How does Ivy affect the (Re)build time? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: Angular 8: What are some changes in Location module? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 29 Essential Blockchain Interview Questions You Will Suck On
> Originally published on 👉 29 Essential Blockchain Interview Questions You Will Suck On | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is blockchain? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Blockchain** is a secure distributed ledger (data structure or database) that maintains a continuously growing list of ordered records, called “blocks”, that are linked using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the data. It is "an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way".
Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires consensus of the network majority.
**Source:** _en.wikipedia.org_
#### Q2: Explain the common structure of blockchains ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Blockchains are composed of three core parts:
* **Block**: A list of transactions recorded into a ledger over a given period. The size, period, and triggering event for blocks is different for every blockchain.
* **Chain**: A hash that links one block to another, mathematically “chaining” them together.
* **Network**: The network is composed of “full nodes.” Think of them as the computer running an algorithm that is securing the network. Each node contains a complete record of all the transactions that were ever recorded in that blockchain.
**Source:** _dummies.com_
#### Q3: What is the blockchain data structure? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Basically **the blockchain data structure** is explained as a back-linked record of blocks of transactions, which is ordered. It can be saved as a file or in a plain database. Each block can be recognized by a hash, created utilizing the SHA256 cryptographic hash algorithm on the header of the block. Each block mentions a former block, also identified as the parent block, in the “previous block hash” field, in the block header.
**Source:** _cryptoticker.io_
#### Q4: What is the Genesis Block? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **first block in any blockchain **is termed the **genesis block**. If you start at any block and follow the chain backwards chronologically, you will arrive at the genesis block. The genesis block is statically encoded within the client software, that it cannot be changed. Every node can identify the genesis block’s hash and structure, the fixed time of creation, and the single transactions within. Thus every node has a secure “root” from which is possible to build a trusted blockchain on.
**Source:** _linkedin.com_
#### Q5: What is the purpose of a blockchain node? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A blockchain exists out of blocks of data. These blocks of data are stored on nodes (compare it to small servers). **Nodes** can be any kind of device (mostly computers, laptops or even bigger servers). Nodes form the infrastructure of a blockchain.
All nodes on a blockchain are connected to each other and they constantly exchange the latest blockchain data with each other so all nodes stay up to date. They store, spread and preserve the blockchain data, so theoretically a blockchain exists on nodes.
A **full node** is basically a device (like a computer) that contains a full copy of the transaction history of the blockchain.
**Source:** _lisk.io_
#### Q6: What is proof-of-work? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **proof of work** is a piece of data which is difficult (costly, time-consuming) to produce but easy for others to verify and which satisfies certain requirements. Producing a proof of work can be a random process with low probability so that a lot of trial and error is required on average before a valid proof of work is generated. Difficulty is a measure of how difficult it is to find a hash below a given target.
**Source:** _en.bitcoin.it_
#### Q7: What is deterministic behavior? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
If A + B = C, then no matter what the circumstances, A+B will always be equal to C. That is called deterministic behavior.
Hash functions are deterministic, meaning A’s hash will always be H(A).
**Source:** _blockgeeks.com_
#### Q8: Why does Blockchain need coins or tokens? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
_Tokens/Coins are used as a medium of exchange between the states_. They are digital assets built in to perform a specific function within a blockchain.
When someone does a transaction, there is a _change of state_, and coins are moved from one address to another address. Apart from that, transactions contain some additional data; this data can be mutated through the change of state. For this reason, blockchains need coins or tokens to incentivize the participants to join their networks.
**Source:** _mindmajix.com_
#### Q9: What is Merkle Trees? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Merkle trees are a fundamental part of blockchain technology. A merkle tree is a structure that allows for efficient and secure verification of content in a large body of data.
A Merkle tree summarizes all the transactions in a block by producing a digital fingerprint of the entire set of transactions, thereby enabling a user to verify whether or not a transaction is included in a block.
Merkle trees are created by repeatedly hashing pairs of nodes until there is only one hash left (this hash is called the Root Hash, or the Merkle Root). They are constructed from the bottom up, from hashes of individual transactions (known as Transaction IDs). Hashing is usually conducted using the SHA-2 cryptographic hash function, though other functions can also be used.
**Source:** _hackernoon.com_
#### Q10: What are some advantages of using Merke Trees? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Using a Merkle tree can significantly reduce the amount of data that a trusted authority has to maintain for verification purposes. It separates the validation of the data from the data itself.
Merkle trees have three major benefits:
1. They provide a means to prove the integrity and validity of data
2. They require little memory or disk space as the proofs are computationally easy and fast
3. Their proofs and management only require tiny amounts of information to be transmitted across networks
The ability to prove that a log is complete and consistent is essential to blockchain technology and the general ledger concept. Merkle trees help verify that later versions of a log include everything from an earlier version and that all data is recorded and presented in chronological order.
**Source:** _hackernoon.com_
#### Q11: Explain what do nodes do? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
When a miner attempts to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain, it broadcasts the block to all the nodes on the network. Based on the block’s legitimacy (validity of signature and transactions), nodes can accept or reject the block. When a node accepts a new block of transactions, it saves and stores it on top of the rest of the blocks it already has stored. In short, here is what nodes do:
* Nodes **check** if a block of transactions is valid and **accept** or **reject** it.
* Nodes **save and store blocks of transactions** (storing blockchain transaction history).
* Nodes **broadcast and spread** this transaction history to other nodes that may need to synchronize with the blockchain (need to be updated on transaction history).
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q12: Why is the blockchain immutable? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Altering a single block requires a new signature for every other block that comes after it all the way to the end of the chain**. This is considered to be near impossible. Why?
Let’s say a corrupt miner has altered a block of transactions and is now trying to calculate new signatures for the subsequent blocks in order to have the rest of the network accept his change. The problem for him is, the rest of the network is also calculating new signatures for new blocks. The corrupt miner will have to calculate new signatures for these blocks too as they are being added to the end of the chain. After all, he needs to keep all of the blocks linked, including the new ones constantly being added. Unless the miner has more computational power than the rest of the network combined, he will never catch up with the rest of the network finding signatures.
Millions of users are mining on the blockchain, and therefore it can be assumed that a single bad actor or entity on the network will never have more computational power than the rest of the network combined, meaning the network will never accept any changes on the blockchain, making the blockchain immutable.
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q13: What is mining difficulty? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Mining difficulty** is the degree that determines how hard it is for miners in terms of hashing power (and thus also time) to find an eligible hash aka signature for their block (a block of transactions needs an eligible hash to be verified and added to the blockchain). On the Bitcoin blockchain, miners try to find an eligible hash by hashing random numbers.
A block of transactions will only be accepted by the rest of the network if it has a signature (hash) that meets certain requirements (in example of Bitcoin, the signature needs to start with a certain number of zeroes). In order to find this signature, miners are spending computational power (hashing power) to perform a set of pre-determined operations on random numbers untill they find a number that leads to an output number that meets the requirements.
Finding an output that starts with only one zero is much easier (generally more common) than finding an output number that starts with five consecutive zeroes (this is pretty rare so it would take much more time to find a number that leads to such output).
For example block 100 (back in 2009) only required a signature that started with eight consecutive zeroes, whereas the last recent block (block 542865) needed a signature that started with at least 18 consecutive zeroes.
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q14: Explain why there is a fixed supply of bitcoins? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There is a fixed supply of bitcoins. There will never be more than 21 million bitcoins. Bitcoins are created each time a user discovers a **new block**. The rate of block creation is adjusted every 2016 blocks to aim for a constant two week adjustment period (equivalent to 6 per hour).
The number of bitcoins generated per block is set to decrease geometrically, with a 50% reduction every 210,000 blocks, or approximately four years. The result is that the number of bitcoins in existence will not exceed slightly less than 21 million.
**Source:** _en.bitcoin.it_
#### Q15: What is DApp or Decentralised Application? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **decentralized application (DApp, dApp, Dapp, or dapp)** is a computer application that **runs on a distributed computing system**.
Decentralized applications don‘t necessarily need to run on top of a blockchain network. Tor, BitTorrent, Popcorn Time, BitMessage, are examples for decentralized applications that run on a P2P network, but not on a blockchain – which is a special kind of P2P network.
DApps have been mostly popularized by distributed ledger technologies (DLT), namely the Ethereum Blockchain, where DApps are often referred to as smart contracts. Its backend code runs on a decentralized peer-to-peer network, and all records of the applicationʼs operation are stored on a blockchain. In most cases, the entire code base is Open Source.
**Source:** _blockchainhub.net_
#### Q16: What is a trapdoor function, and why is it needed in blockchain development? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **trapdoor** function is a function that is easy to compute in one direction but difficult to compute in the opposite direction unless you have special information. Trapdoor functions are essential for public key encryption—that’s why they are commonly used in blockchain development to represent the ideas of addresses and private keys.
**Source:** _toptal.com_
#### Q17: Explain why a blockchain needs tokens to operate ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Coins/tokens** are used to implement _changes between states_. When somebody does a transaction, this is a change of state, and coins are moved from one address to another. Apart from that, transactions can contain additional data, and a change of state is used to mutate data—the only way to do this in an immutable-by-definition blockchain.
Technically, a blockchain doesn’t need coins for its essential operations, but without them, some other way needs to be introduced to manage states of the chain and to verify transactions.
**Source:** _toptal.com_
#### Q18: How do verifiers check if a block is valid? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Every full node on the network does block verification. When a new block is announced, every node that receives it does a list of checks. The two most important checks are of **proof of work** (if a block provides enough work to be included into chain) and of the **validity of all transactions** (each transaction must be valid).
**Source:** _toptal.com_
#### Q19: What is RSA algorithm? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman)** is an algorithm used by modern computers to encrypt and decrypt messages. It is an _asymmetric_ cryptographic algorithm. Asymmetric means that there are two different keys. This is also called public key cryptography, because one of the keys can be given to anyone. The other key must be kept private. The algorithm is based on the fact that finding the factors of a large composite number is difficult.
RSA involves a **public** key and **private** key. The public key can be known to everyone; it is used to encrypt messages. Messages encrypted using the public key can only be decrypted with the private key.
**Source:** _simple.wikipedia.org_
#### Q20: What is a smart contract? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A smart contract is a computer protocol intended to digitally facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract. Smart contracts allow the performance of credible transactions without third parties. These transactions are trackable and irreversible.
The aim of smart contracts is to provide security that is superior to traditional contract law and to reduce other transaction costs associated with contracting. Various cryptocurrencies have implemented types of smart contracts.
**Source:** _en.wikipedia.org_
#### Q21: What is a 51% attack? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: What is a stealth address? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: Explain what is target hash? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: What Is a Proof of Stake? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: What is the difference between PoW and PoS? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: What is off-chain transaction? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: Why is Git not considered a “block chain”? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: What are miners really solving? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
As with mining, what are miners really solving? I read they are solving hashes, but what does that really mean.
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: Is it possible to brute force bitcoin address creation in order to steal money? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 30 Best MongoDB Interview Questions and Answers (2018 Update)
> Originally published on 👉 30 Best MongoDB Interview Questions and Answers (2018 Update) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: Explain what is MongoDB? ⭐
**Answer:**
MongoDB is an open-source document database that provides high performance, high availability, and automatic scaling.
It's Key Features are:
* Document Oriented and NoSQL database.
* Supports Aggregation
* Uses BSON format
* Sharding (Helps in Horizontal Scalability)
* Supports Ad Hoc Queries
* Schema Less
* Capped Collection
* Indexing (Any field in MongoDB can be indexed)
* MongoDB Replica Set (Provides high availability)
* Supports Multiple Storage Engines
**Source:** _mongodb.com_
#### Q2: What Is Replication In MongoDB? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Replication** is the process of synchronizing data across multiple servers. Replication provides redundancy and increases data availability. With multiple copies of data on different database servers, replication protects a database from the loss of a single server. Replication also allows you to recover from hardware failure and service interruptions.
**Source:** _interviewbubble.com_
#### Q3: How is data stored in MongoDB? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Data in MongoDB is stored in BSON documents – JSON-style data structures. Documents contain one or more fields, and each field contains a value of a specific data type, including arrays, binary data and sub-documents. Documents that tend to share a similar structure are organized as collections. It may be helpful to think of documents as analogous to rows in a relational database, fields as similar to columns, and collections as similar to tables.
The advantages of using documents are:
* Documents (i.e. objects) correspond to native data types in many programming languages.
* Embedded documents and arrays reduce need for expensive joins.
* Dynamic schema supports fluent polymorphism.
**Source:** _mongodb.com_
#### Q4: What are Indexes in MongoDB? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Indexes support the efficient execution of queries in MongoDB. Without indexes, MongoDB must perform a collection scan, i.e. scan every document in a collection, to select those documents that match the query statement. If an appropriate index exists for a query, MongoDB can use the index to limit the number of documents it must inspect.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q5: Can you create an index on an array field in MongoDB? If yes, what happens in this case? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Yes. An array field can be indexed in MongoDB. In this case, MongoDB would index each value of the array so you can query for individual items:
```js
> db.col1.save({'colors': ['red','blue']})
> db.col1.ensureIndex({'colors':1})
> db.col1.find({'colors': 'red'})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("4ccc78f97cf9bdc2a2e54ee9"), "colors" : [ "red", "blue" ] }
> db.col1.find({'colors': 'blue'})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("4ccc78f97cf9bdc2a2e54ee9"), "colors" : [ "red", "blue" ] }
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q6: What is Aggregation in MongoDB? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Aggregations* operations process data records and return computed results. Aggregation operations group values from multiple documents together, and can perform a variety of operations on the grouped data to return a single result. MongoDB provides three ways to perform aggregation:
* the aggregation pipeline,
* the map-reduce function,
* and single purpose aggregation methods and commands.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q7: How to query MongoDB with %like%? ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
I want to query something as SQL's like query:
```sql
select *
from users
where name like '%m%'
```
How to do the same in MongoDB?
**Answer:**
```js
db.users.find({name: /a/}) //like '%a%'
db.users.find({name: /^pa/}) //like 'pa%'
db.users.find({name: /ro$/}) //like '%ro'
```
Or using Mongoose:
```js
db.users.find({'name': {'$regex': 'sometext'}})
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q8: How do I perform the SQL JOIN equivalent in MongoDB? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Mongo is not a relational database, and the devs are being careful to recommend specific use cases for $lookup, but at least as of 3.2 doing join is now possible with MongoDB. The new $lookup operator added to the aggregation pipeline is essentially identical to a left outer join:
```js
{
$lookup:
{
from: ,
localField: ,
foreignField: ,
as:
}
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q9: What is the difference b/w MongoDB and CouchDB? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
MongoDB and CouchDB both are the great example of open source NoSQL database. Both are document oriented databases. Although both stores data but there is a lot of difference between them in terms of implementation of their data models, interfaces, object storage and replication methods etc.
**Source:** _medium.com/@hub4tech_
#### Q10: What are NoSQL databases? What are the different types of NoSQL databases? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A NoSQL database provides a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data that is modeled in means other than the tabular relations used in relational databases (like SQL, Oracle, etc.).
Types of NoSQL databases:
* Document Oriented
* Key Value
* Graph
* Column Oriented
**Source:** _interviewbubble.com_
#### Q11: Explain the structure of ObjectID in MongoDB ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**ObjectIds** are small, likely unique, fast to generate, and ordered. ObjectId values consist of 12 bytes, where the first four bytes are a timestamp that reflect the ObjectId’s creation. Specifically:
* a 4-byte value representing the seconds since the Unix epoch,
* a 5-byte random value, and
* a 3-byte counter, starting with a random value.
In MongoDB, each document stored in a collection requires a unique _id field that acts as a primary key. If an inserted document omits the _id field, the MongoDB driver automatically generates an ObjectId for the _id field.
**Source:** _mongodb.com_
#### Q12: What is a covered query in MongoDB? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A covered query is the one in which:
* fields used in the query are part of an index used in the query, and
* the fields returned in the results are in the same index
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q13: Find objects between two dates MongoDB ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
```js
db.CollectionName.find({"whenCreated": {
'$gte': ISODate("2018-03-06T13:10:40.294Z"),
'$lt': ISODate("2018-05-06T13:10:40.294Z")
}});
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q14: What is oplog? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The *oplog* (operations log) is a special capped collection that keeps a rolling record of all operations that modify the data stored in your databases. MongoDB applies database operations on the primary and then records the operations on the primary’s oplog. The secondary members then copy and apply these operations in an asynchronous process.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q15: Does MongoDB support ACID transaction management and locking functionalities? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ACID stands that any update is:
* **Atomic**: it either fully completes or it does not
* **Consistent**: no reader will see a "partially applied" update
* **Isolated**: no reader will see a "dirty" read
* **Durable**: (with the appropriate write concern)
Historically MongoDB does not support default multi-document ACID transactions (multiple-document updates that can be rolled back and are ACID-compliant). However, MongoDB provides atomic operation on a single document. MongoDB 4.0 **will add support for multi-document transactions**, making it the only database to combine the speed, flexibility, and power of the document model with ACID data integrity guarantees.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q16: What is Sharding in MongoDB? Explain. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Sharding* is a method for storing data across multiple machines. MongoDB uses sharding to support deployments with very large data sets and high throughput operations.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q17: Should I normalize my data before storing it in MongoDB? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It depends from your goals. Normalization will provide an _update efficient data representation_. Denormalization will make data _reading efficient_.
In general, use embedded data models (denormalization) when:
* you have “contains” relationships between entities.
* you have one-to-many relationships between entities. In these relationships the “many” or child documents always appear with or are viewed in the context of the “one” or parent documents.
In general, use normalized data models:
* when embedding would result in duplication of data but would not provide sufficient read performance advantages to outweigh the implications of the duplication.
* to represent more complex many-to-many relationships.
* to model large hierarchical data sets.
Also normalizing your data like you would with a relational database is usually not a good idea in MongoDB. Normalization in relational databases is only feasible under the premise that JOINs between tables are relatively cheap. The $lookup aggregation operator provides some limited JOIN functionality, but it doesn't work with sharded collections. So joins often need to be emulated by the application through multiple subsequent database queries, which is very slow (see question MongoDB and JOINs for more information).
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q18: How does MongoDB provide concurrency? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: What are Primary and Secondary Replica sets? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: How does Journaling work in MongoDB? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: When to Redis or MongoDB? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: MongoDB relationships. What to use - embed or reference? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
I want to design a question structure with some comments, but I don't know which relationship to use for comments: embed or reference? Explain me pros and cons of both solutions?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: Is MongoDB schema-less? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: How does MongoDB ensure high availability? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: How to check if a field contains a substring? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: What are alternatives to MongoDB? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: How to find document with array that contains a specific value? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
You have this schema:
```js
person = {
name : String,
favoriteFoods : Array
}
```
where the `favoriteFoods` array is populated with strings. How can I find all persons that have `sushi` as their favorite food using MongoDB?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: Is it possible to update MongoDB field using value of another field? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
In SQL we will use:
```sql
UPDATE Person SET Name = FirstName + ' ' + LastName
```
Is it possible with MongoDB?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: Explain what is horizontal scalability? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: What are the differences between MongoDB and MySQL? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 30 Docker Interview Questions and Answers in 2019
> Originally published on 👉 30 Docker Interview Questions and Answers in 2019 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is the need for DevOps? ⭐
**Answer:**
Nowadays instead of releasing big sets of features, companies are trying to see if small features can be transported to their customers through a series of release trains. This has many advantages like quick feedback from customers, better quality of software etc. which in turn leads to high customer satisfaction. To achieve this, companies are required to:
1. Increase deployment frequency
2. Lower failure rate of new releases
3. Shortened lead time between fixes
4. Faster mean time to recovery in the event of new release crashing
DevOps fulfills all these requirements and helps in achieving seamless software delivery.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q2: What are the advantages of DevOps? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Technical benefits:
* Continuous software delivery
* Less complex problems to fix
* Faster resolution of problems
Business benefits:
* Faster delivery of features
* More stable operating environments
* More time available to add value (rather than fix/maintain)
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q3: What is the function of CI (Continuous Integration) server? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
CI server function is to continuously integrate all changes being made and committed to repository by different developers and check for compile errors. It needs to build code several times a day, preferably after every commit so it can detect which commit made the breakage if the breakage happens.
**Source:** _linoxide.com_
#### Q4: What is Docker? ⭐
**Answer:**
* Docker is a containerization platform which packages your application and all its dependencies together in the form of containers so as to ensure that your application works seamlessly in any environment be it development or test or production.
* Docker containers, wrap a piece of software in a complete filesystem that contains everything needed to run: code, runtime, system tools, system libraries etc. anything that can be installed on a server.
* This guarantees that the software will always run the same, regardless of its environment.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q5: How to build envrionment-agnostic systems with Docker? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are three main features helping to achieve that:
* Volumes
* Environment variable injection
* Read-only file systems
**Source:** _rafalgolarz.com_
#### Q6: What is the difference between the `COPY` and `ADD` commands in a Dockerfile? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Although `ADD` and `COPY` are functionally similar, generally speaking, `COPY` is preferred.
That’s because it’s more transparent than ADD. COPY only supports the basic copying of local files into the container, while ADD has some features (like local-only tar extraction and remote URL support) that are not immediately obvious. Consequently, the best use for ADD is local tar file auto-extraction into the image, as in ADD rootfs.tar.xz /.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q7: What is Docker image? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Docker image** is the source of Docker container. In other words, Docker images are used to create containers. Images are created with the build command, and they’ll produce a container when started with run. Images are stored in a Docker registry such as ` registry.hub.docker.com` because they can become quite large, images are designed to be composed of layers of other images, allowing a minimal amount of data to be sent when transferring images over the network.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q8: What is Docker container? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Docker containers** include the application and all of its dependencies, but share the kernel with other containers, running as isolated processes in user space on the host operating system. Docker containers are not tied to any specific infrastructure: they run on any computer, on any infrastructure, and in any cloud.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q9: What is Docker hub? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Docker hub** is a cloud-based registry service which allows you to link to code repositories, build your images and test them, stores manually pushed images, and links to Docker cloud so you can deploy images to your hosts. It provides a centralized resource for container image discovery, distribution and change management, user and team collaboration, and workflow automation throughout the development pipeline.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q10: What are the various states that a Docker container can be in at any given point in time? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are four states that a Docker container can be in, at any given point in time. Those states are as given as follows:
* Running
* Paused
* Restarting
* Exited
**Source:** _mindmajix.com_
#### Q11: Is there a way to identify the status of a Docker container? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
We can identify the status of a Docker container by running the command
```sh
docker ps –a
```
which will in turn list down all the available docker containers with its corresponding statuses on the host. From there we can easily identify the container of interest to check its status correspondingly.
**Source:** _mindmajix.com_
#### Q12: What are the most common instructions in Dockerfile? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Some of the common instructions in Dockerfile are as follows:
* **FROM**: We use FROM to set the base image for subsequent instructions. In every valid Dockerfile, FROM is the first instruction.
* **LABEL**: We use LABEL to organize our images as per project, module, licensing etc. We can also use LABEL to help in automation.
In LABEL we specify a key value pair that can be later used for programmatically handling the Dockerfile.
* **RUN**: We use RUN command to execute any instructions in a new layer on top of the current image. With each RUN command we add something on top of the image and use it in subsequent steps in Dockerfile.
* **CMD**: We use CMD command to provide default values of an executing container. In a Dockerfile, if we include multiple CMD commands, then only the last instruction is used.
**Source:** _knowledgepowerhouse.com_
#### Q13: What type of applications - Stateless or Stateful are more suitable for Docker Container? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It is preferable to create Stateless application for Docker Container. We can create a container out of our application and take out the configurable state parameters from application. Now we can run same container in Production as well as QA environments with different parameters. This helps in reusing the same Image in different scenarios. Also a stateless application is much easier to scale with Docker Containers than a stateful application.
**Source:** _mindmajix.com_
#### Q14: Explain basic Docker usage workflow ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
1. Everything starts with the **Dockerfile**. The Dockerfile is the source code of the Image.
2. Once the Dockerfile is created, you build it to create the **image** of the container. The image is just the "compiled version" of the "source code" which is the Dockerfile.
3. Once you have the image of the container, you should redistribute it using the **registry**. The registry is like a git repository -- you can push and pull images.
4. Next, you can use the image to run **containers**. A running container is very similar, in many aspects, to a virtual machine (but without the hypervisor).
```sh
+------------+ docker build +--------------+ docker run -dt +-----------+ docker exec -it +------+
| Dockerfile | --------------> | Image | ---------------> | Container | -----------------> | Bash |
+------------+ +--------------+ +-----------+ +------+
^
| docker pull
|
+--------------+
| Registry |
+--------------+
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q15: What is the difference between Docker Image and Layer? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
- **Image**: A Docker image is built up from a series of **read-only** layers
- **Layer**: Each layer represents an instruction in the image’s Dockerfile.
The below Dockerfile contains four commands, each of which creates a layer.
```sh
FROM ubuntu:15.04
COPY . /app
RUN make /app
CMD python /app/app.py
```
Importantly, each layer is only a set of differences from the layer before it.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q16: What is virtualisation? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In its conceived form, **virtualisation** was considered a method of logically dividing mainframes to allow multiple applications to run simultaneously. However, the scenario drastically changed when companies and open source communities were able to provide a method of handling the privileged instructions in one way or another and allow for multiple operating systems to be run simultaneously on a single x86 based system.
The net effect is that virtualization allows you to run two completely different OS on same hardware. Each guest OS goes through all the process of bootstrapping, loading kernel etc. You can have very tight security, for example, guest OS can't get full access to host OS or other guests and mess things up.
The virtualization method can be categorized based on how it mimics hardware to a guest operating system and emulates guest operating environment. Primarily, there are three types of virtualization:
* Emulation
* Paravirtualization
* Container-based virtualization
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q17: What is Hypervisor? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **hypervisor** handles creating the virtual environment on which the guest virtual machines operate. It supervises the guest systems and makes sure that resources are allocated to the guests as necessary. The hypervisor sits in between the physical machine and virtual machines and provides virtualization services to the virtual machines. To realize it, it intercepts the guest operating system operations on the virtual machines and emulates the operation on the host machine's operating system.
The rapid development of virtualization technologies, primarily in cloud, has driven the use of virtualization further by allowing multiple virtual servers to be created on a single physical server with the help of hypervisors, such as Xen, VMware Player, KVM, etc., and incorporation of hardware support in commodity processors, such as Intel VT and AMD-V.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q18: What is Docker Swarm? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Docker Swarm** is native clustering for Docker. It turns a pool of Docker hosts into a single, virtual Docker host. Docker Swarm serves the standard Docker API, any tool that already communicates with a Docker daemon can use Swarm to transparently scale to multiple hosts.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q19: How will you monitor Docker in production? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Docker provides tools like docker stats and docker events to monitor Docker in production. We can get reports on important statistics with these commands.
* **Docker stats**: When we call docker stats with a container id, we get the CPU, memory usage etc of a container. It is similar to top command in Linux.
* **Docker events**: Docker events are a command to see the stream of activities that are going on in Docker daemon.
Some of the common Docker events are: attach, commit, die, detach, rename, destroy etc. We can also use various options to limit or filter the events that we are interested in.
**Source:** _knowledgepowerhouse.com_
#### Q20: What is an orphant volume and how to remove it? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: What is Paravirtualization? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: How is Docker different from a virtual machine? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: Can you explain dockerfile ONBUILD instruction? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: Is it good practice to run stateful applications on Docker? What are the scenarios where Docker best fits in? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: Can you run Docker containers natively on Windows? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: How does Docker run containers in non-Linux systems? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: How containers works at low level? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: Name some limitations of containers vs VM ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: How to use Docker with multiple environments? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: Why Docker compose does not wait for a container to be ready before moving on to start next service in dependency order? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 32 jQuery Interview Questions You'll Simply Fail On
> Originally published on 👉 32 jQuery Interview Questions You'll Simply Fail On | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is jQuery? ⭐
**Answer:**
**jQuery** is **fast, lightweight and feature-rich** client side JavaScript Library/Framework which helps in to traverse HTML DOM, make animations, add Ajax interaction, manipulate the page content, change the style and provide cool UI effect. It is one of the most popular client side library and as per a survey it runs on every second website.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q2: Why do we use jQuery? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Due to following advantages.
* Easy to use and learn.
* Easily expandable.
* Cross-browser support (IE 6.0+, FF 1.5+, Safari 2.0+, Opera 9.0+)
* Easy to use for DOM manipulation and traversal.
* Large pool of built in methods.
* AJAX Capabilities.
* Methods for changing or applying CSS, creating animations.
* Event detection and handling.
* Tons of plug-ins for all kind of needs.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q3: How JavaScript and jQuery are different? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
JavaScript is a language While jQuery is a library built in the JavaScript language that helps to use the JavaScript language.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q4: Is jQuery a W3C standard? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
No. jQuery is not a W3C standard.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q5: What does dollar sign ($) means in jQuery? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Dollar Sign is nothing but it's an alias for JQuery. Take a look at below jQuery code.
```js
$(document).ready(function(){
});
```
Over here $ sign can be replaced with "jQuery" keyword.
```js
jQuery(document).ready(function(){
});
```
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q6: Can we have multiple document.ready() function on the same page? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**YES**. We can have any number of document.ready() function on the same page.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q7: What is jQuery.noConflict? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
As other client side libraries like MooTools, Prototype can be used with jQuery and they also use `$()` as their global function and to define variables. This situation creates conflict as `$()` is used by jQuery and other library as their global function. To overcome from such situations, jQuery has introduced `jQuery.noConflict()`.
```js
jQuery.noConflict();
// Use jQuery via jQuery(...)
jQuery(document).ready(function(){
jQuery("div").hide();
});
```
You can also use your own specific character in the place of `$` sign in jQuery.
```js
var $j = jQuery.noConflict();
// Use jQuery via jQuery(...)
$j(document).ready(function(){
$j("div").hide();
});
```
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q8: What is the difference between .js and .min.js? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
jQuery library comes in 2 different versions Development and Production/Deployment. The deployment version is also known as _minified_ version. So .min.js is basically the minified version of jQuery library file. Both the files are same as far as functionality is concerned. but .min.js is quite small in size so it loads quickly and saves bandwidth.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q9: How do you select element by ID in jQuery? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
To select element use ID selector. We need to prefix the id with "#" (hash symbol). For example, to select element with ID "txtName", then syntax would be,
```js
$('#txtName')
```
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q10: What does $("div.parent") will select? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
All the div element with parent class.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q11: What is the use of jquery .each() function? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The `$.each()` function is used to iterate over a jQuery object. The `$.each()` function can be used to iterate over any collection, whether it is an object or an array.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q12: Is there any difference between body onload() and document.ready() function? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`document.ready()` function is different from body `onload()` function for several reasons:
1. We can have more than one `document.ready()` function in a page where we can have only one body `onload` function.
2. `document.ready()` function is called as soon as DOM is loaded where `body.onload()` function is called when everything gets loaded on the page that includes DOM, images and all associated resources of the page.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q13: What are the fastest/slowest selectors in jQuery? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ID and element selectors are the _fastest_ selectors in jQuery. Class selectors are the _slow_ compared to ID and element.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q14: Which is fast document.getElementByID('txtName') or $('#txtName').? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Native JavaScipt is always fast. jQuery method to select txtName "`$('#txtName')`" will internally makes a call to `document.getElementByID('txtName')`. As jQuery is written on top of JavaScript and it internally uses JavaScript only so JavaScript is always fast.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q15: Difference between $(this) and 'this' in jQuery? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`this` and `$(this)` refers to the same element. The only difference is the way they are used. 'this' is used in traditional sense, when 'this' is wrapped in `$()` then it becomes a jQuery object and you are able to use the power of jQuery.
```js
$(document).ready(function(){
$('#spnValue').mouseover(function(){
alert($(this).text());
});
});
```
In below example, this is an object but since it is not wrapped in `$()`, we can't use jQuery method and use the native JavaScript to get the value of span element.
```js
$(document).ready(function(){
$('#spnValue').mouseover(function(){
alert(this.innerText);
});
});
```
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q16: What is the difference between eq() and get() methods in jQuery? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* `eq()` returns the element as a jQuery object. This method constructs a new jQuery object from one element within that set and returns it. That means that you can use jQuery functions on it.
* `get()` return a DOM element. The method retrieve the DOM elements matched by the jQuery object. But as it is a DOM element and it is not a jQuery-wrapped object. So jQuery functions can't be used.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q17: What is wrong with this code line "$('#myid\\.3').text('blah blah!!!');" ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The problem with above statement is that the selectors is having meta characters and to use any of the meta-characters ( such as !"#$%&'()\*+,./:;<=>?@\[\\\]^\`{|}~ ) as a literal part of a name, it must be escaped with with two backslashes: \\\\. For example, an element with id="foo.bar", can use the selector $("#foo\\\\.bar").
So the correct syntax is:
```js
$('#myid\\\\.3').text('blah blah!!!');
```
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q18: How to create clone of any object using jQuery? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
jQuery provides `clone()` method which performs a deep copy of the set of matched elements, meaning that it copies the matched elements as well as all of their descendant elements and text nodes.
```js
$(document).ready(function(){
$('#btnClone').click(function(){
$('#dvText').clone().appendTo('body');
return false;
});
});
```
The default implementation of the `clone()` method doesn't copy events unless you tell the `clone()` method to copy the events. The `clone()` method takes a parameter, if you pass true then it will copy the events as well.
```js
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#btnClone").bind('click', function(){
$('#dvClickme').clone(true).appendTo('body');
});
```
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q19: What is difference between prop and attr? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`attr()`: Get the value of an attribute for the first element in the set of matched elements. Whereas, `.prop()`: (Introduced in jQuery 1.6) Get the value of a property for the first element in the set of matched elements.
Attributes carry additional information about an HTML element and come in name="value" pairs. Where Property is a representation of an attribute in the HTML DOM tree. once the browser parse your HTML code ,corresponding DOM node will be created which is an object thus having properties.
`attr()` gives you the value of element as it was defines in the html on page load. It is always recommended to use `prop()` to get values of elements which is modified via javascript/jquery , as it gives you the original value of an element's current state. Find out more [here](http://techbrij.com/jquery-attr-vs-prop-difference).
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q20: What are various methods to make ajax request in jQuery? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Using below jQuery methods, you can make ajax calls.
* `load()` : Load a piece of html into a container DOM
* `$.getJSON()`: Load JSON with GET method.
* `$.getScript()`: Load a JavaScript file.
* `$.get()`: Use to make a GET call and play extensively with the response.
* `$.post()`: Use to make a POST call and don't want to load the response to some container DOM.
* `$.ajax()`: Use this to do something on XHR failures, or to specify ajax options (e.g. cache: true) on the fly.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q21: What is the difference between $('div') and $('
') in jQuery? ⭐⭐⭐⭐**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: What is the difference between event.PreventDefault and "return false"? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: How do you attach a event to element which should be executed only once? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: In what situation you would use multiple version of jQuery and how would you include them? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: Is there any advantage of using $.ajax() for ajax call against $.get() or $.post()? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: What are deferred and promise object in jQuery? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: How can I get jQuery to perform a synchronous, rather than asynchronous, Ajax request? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: What are the differences between JavaScript's window.onload and jQuery's $(document).ready() method? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: Is there any significant difference between event.preventDefault() vs. return false to stop event propagation? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: Is it possible to hold or delay document.ready execution for sometime? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: Is it possible to get value of multiple CSS properties in single statement? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: How can I implement my own $(document).ready functionality without using jQuery? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 33 Frequently Asked Node.js Interview Questions (2020 Update)
> Originally published on 👉 33 Frequently Asked Node.js Interview Questions (2020 Update) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Node.js? ⭐
**Answer:**
Node.js is a web application framework built on Google Chrome's JavaScript Engine (V8 Engine).
Node.js comes with runtime environment on which a Javascript based script can be interpreted and executed (It is analogus to JVM to JAVA byte code). This runtime allows to execute a JavaScript code on any machine outside a browser. Because of this runtime of Node.js, JavaScript is now can be executed on server as well.
*Node.js = Runtime Environment + JavaScript Library*
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q2: What do you mean by Asynchronous API? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
All APIs of Node.js library are aynchronous that is non-blocking. It essentially means a Node.js based server never waits for a API to return data. Server moves to next API after calling it and a notification mechanism of Events of Node.js helps server to get response from the previous API call.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q3: What are the benefits of using Node.js? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Following are main benefits of using Node.js
* **Aynchronous and Event Driven** - All APIs of Node.js library are aynchronous that is non-blocking. It essentially means a Node.js based server never waits for a API to return data. Server moves to next API after calling it and a notification mechanism of Events of Node.js helps server to get response from the previous API call.
* **Very Fast** - Being built on Google Chrome's V8 JavaScript Engine, Node.js library is very fast in code execution.
* **Single Threaded but highly Scalable** - Node.js uses a single threaded model with event looping. Event mechanism helps server to respond in a non-bloking ways and makes server highly scalable as opposed to traditional servers which create limited threads to handle requests. Node.js uses a single threaded program and same program can services much larger number of requests than traditional server like Apache HTTP Server.
* **No Buffering** \- Node.js applications never buffer any data. These applications simply output the data in chunks.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q4: What are the key features of Node.js? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Let’s look at some of the key features of Node.js.
* **Asynchronous event driven IO helps concurrent request handling –** All APIs of Node.js are asynchronous. This feature means that if a Node receives a request for some Input/Output operation, it will execute that operation in the background and continue with the processing of other requests. Thus it will not wait for the response from the previous requests.
* **Fast in Code execution –** Node.js uses the V8 JavaScript Runtime engine, the one which is used by Google Chrome. Node has a wrapper over the JavaScript engine which makes the runtime engine much faster and hence processing of requests within Node.js also become faster.
* **Single Threaded but Highly Scalable –** Node.js uses a single thread model for event looping. The response from these events may or may not reach the server immediately. However, this does not block other operations. Thus making Node.js highly scalable. Traditional servers create limited threads to handle requests while Node.js creates a single thread that provides service to much larger numbers of such requests.
* **Node.js library uses JavaScript –** This is another important aspect of Node.js from the developer’s point of view. The majority of developers are already well-versed in JavaScript. Hence, development in Node.js becomes easier for a developer who knows JavaScript.
* **There is an Active and vibrant community for the Node.js framework –** The active community always keeps the framework updated with the latest trends in the web development.
* **No Buffering –** Node.js applications never buffer any data. They simply output the data in chunks.
**Source:** _techbeamers.com_
#### Q5: What is libuv? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**libuv** is a C library that is used to abstract non-blocking I/O operations to a consistent interface across all supported platforms. It provides mechanisms to handle file system, DNS, network, child processes, pipes, signal handling, polling and streaming. It also includes a thread pool for offloading work for some things that can't be done asynchronously at the operating system level.
**Source:** _nodejs.org_
#### Q6: What is a blocking code? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
If application has to wait for some I/O operation in order to complete its execution any further then the code responsible for waiting is known as blocking code.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q7: What is difference between synchronous and asynchronous method of fs module? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Every method in `fs` module has synchronous as well as asynchronous form. Asynchronous methods takes a last parameter as completion function callback and first parameter of the callback function is error. It is preferred to use asynchronous method instead of synchronous method as former never block the program execution where the latter one does.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q8: What is Chaining in Node? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Chanining** is a mechanism to connect output of one stream to another stream and create a chain of multiple stream operations. It is normally used with piping operations.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q9: What's the event loop? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**The event loop** is what allows Node.js to perform non-blocking I/O operations — despite the fact that JavaScript is single-threaded — by offloading operations to the system kernel whenever possible.

Every I/O requires a callback - once they are done they are pushed onto the event loop for execution. Since most modern kernels are multi-threaded, they can handle multiple operations executing in the background. When one of these operations completes, the kernel tells Node.js so that the appropriate callback may be added to the poll queue to eventually be executed.
**Source:** _blog.risingstack.com_
#### Q10: When should we use Node.js? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Node.js** is well suited for applications that have a lot of concurrent connections and each _request only needs very few CPU cycles_, because the event loop (with all the other clients) is blocked during execution of a function. I believe Node.js is best suited for real-time applications: online games, collaboration tools, chat rooms, or anything where what one user (or robot? or sensor?) does with the application needs to be seen by other users immediately, without a page refresh.
**Source:** _techbeamers.com_
#### Q11: How does Node.js handle child threads? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Node.js, in its essence, is a single thread process. It does not expose child threads and thread management methods to the developer. Technically, Node.js does spawn child threads for certain tasks such as asynchronous I/O, but these run behind the scenes and do not execute any application JavaScript code, nor block the main event loop.
If threading support is desired in a Node.js application, there are tools available to enable it, such as the ChildProcess module.
**Source:** _lazyquestion.com_
#### Q12: What is the preferred method of resolving unhandled exceptions in Node.js? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Unhandled exceptions in Node.js can be caught at the `Process` level by attaching a handler for `uncaughtException` event.
```js
process.on('uncaughtException', function(err) {
console.log('Caught exception: ' + err);
});
```
However, `uncaughtException` is a very crude mechanism for exception handling and may be removed from Node.js in the future. An exception that has bubbled all the way up to the `Process` level means that your application, and Node.js may be in an undefined state, and the only sensible approach would be to restart everything.
The preferred way is to add another layer between your application and the Node.js process which is called the [domain](http://nodejs.org/api/domain.html).
Domains provide a way to handle multiple different I/O operations as a single group. So, by having your application, or part of it, running in a separate domain, you can safely handle exceptions at the domain level, before they reach the `Process` level.
**Source:** _lazyquestion.com_
#### Q13: How to use Buffer in Node.js? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Buffer is used to process binary data, such as pictures, mp3, database files, etc. Buffer supports a variety of encoding and decoding, binary string conversion.
**Source:** _github.com/jimuyouyou_
#### Q14: Rewrite promise-based Node.js applications to Async/Await ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Rewrite this code to Async/Await:
```js
function asyncTask() {
return functionA()
.then((valueA) => functionB(valueA))
.then((valueB) => functionC(valueB))
.then((valueC) => functionD(valueC))
.catch((err) => logger.error(err))
}
```
**Answer:**
```js
async function asyncTask() {
try {
const valueA = await functionA()
const valueB = await functionB(valueA)
const valueC = await functionC(valueB)
return await functionD(valueC)
} catch (err) {
logger.error(err)
}
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q15: Are you familiar with differences between Node.js nodules and ES6 nodules? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The modules used in Node.js follow a module specification known as the **CommonJS** specification. The recent updates to the JavaScript programming language, in the form of ES6, specify changes to the language, adding things like new class syntax and a module system. This module system is different from Node.js modules. To import ES6 module, we'd use the ES6 `import` functionality.
Now ES6 modules are incompatible with Node.js modules. This has to do with the way modules are loaded differently between the two formats. If you use a compiler like Babel, you can mix and match module formats.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q16: Name some of the events fired by streams. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: What's a stub? Name a use case. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: Is Node.js entirely based on a single-thread? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: When to not use Node.js? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: What are the timing features of Node.js? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: How would you handle errors for async code in Node.js? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: How do you convert an existing callback API to promises? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
How to convert this callback code to Promise? Provide some examples.
```js
function divisionAPI (number, divider, successCallback, errorCallback) {
if (divider == 0) {
return errorCallback( new Error("Division by zero") )
}
successCallback( number / divider )
}
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: Can Node.js work without V8? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: Is it possible to use "Class" in Node.js? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: Can Node.js use other engines than V8? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: What is the difference between process.nextTick() and setImmediate() ? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: Explain what is Reactor Pattern in Node.js? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: Why should you separate Express 'app' and 'server'? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: How many threads does Node actually create? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: How V8 compiles JavaScript code? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: What is V8 Templates? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: Why Node.js devs tend to lean towards the Module Requiring vs Dependency Injection? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: What will happen when that code will be executed? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
What will happen when that code will be executed?
```js
var EventEmitter = require('events');
var crazy = new EventEmitter();
crazy.on('event1', function () {
console.log('event1 fired!');
process.nextTick(function () {
crazy.emit('event2');
});
});
crazy.on('event2', function () {
console.log('event2 fired!');
process.nextTick(function () {
crazy.emit('event3');
});
});
crazy.on('event3', function () {
console.log('event3 fired!');
process.nextTick(function () {
crazy.emit('event1');
});
});
crazy.emit('event1');
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 35 LINQ Interview Questions and Answers in 2019
> Originally published on 👉 35 LINQ Interview Questions and Answers in 2019 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is LINQ? ⭐
**Answer:**
**LINQ** stands for Language INtegrated Query. LINQ allows us to write queries over local collection objects and remote data sources like SQL, XML documents etc. We can write LINQ query on any collection class which implements the `IEnumerable` interface.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q2: What are the types of LINQ? ⭐
**Answer:**
* LINQ to Objects
* LINQ to XML
* LINQ to Dataset
* LINQ to SQL
* LINQ to Entities
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q3: Explain what is LINQ? Why is it required? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Language Integrated Query** or **LINQ** is the collection of standard query operators which provides query facilities into.NET framework language like C#, VB.NET. LINQ is required as it bridges the gap between the world of data and the world of objects.
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q4: List out the three main components of LINQ? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Three main components of LINQ are
* Standard Query Operators
* Language Extensions
* LINQ Providers
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q5: What is Anonymous function? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An Anonymous function is a special function which does not have any name. We just define their parameters and define the code into the curly braces.
Consider:
```csharp
delegate int func(int a, int b);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
func f1 = delegate(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
};
Console.WriteLine(f1(1, 2));
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q6: What are Anonymous Types? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Anonymous types are types that are generated by compiler at run time. When we create a anonymous type we do not specify a name. We just write properties names and their values. Compiler at runtime create these properties and assign values to them.
```csharp
var k = new { FirstProperty = "value1", SecondProperty = "value2" };
Console.WriteLine(k.FirstProperty);
```
Anonymous class is useful in LINQ queries to save our intermediate results.
There are some restrictions on Anonymous types as well:
* Anonymous types can not implement interfaces.
* Anonymous types can not specify any methods.
* We can not define static members.
* All defined properties must be initialized.
* We can only define public fields.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q7: What are Extension Methods? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Extension methods** are static functions of a static class. These methods can be invoked just like instance method syntax. These methods are useful when we can not want to modify the class. Consider:
```csharp
public static class StringMethods
{
public static bool IsStartWithLetterM(this string s)
{
return s.StartsWith("m");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string value = "malslfds";
Console.WriteLine(value.IsStartWithLetterM()); //print true;
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q8: Explain what is “LINQ to Objects”? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
When LINQ queries any `IEnumerable()` collection or IEnumerable directly without the use of an intermediate LINQ provider or API such as LINQ to SQL or LINQ to XML is referred as **LINQ to Objects**.
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q9: Explain what is the purpose of LINQ providers in LINQ? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
LINQ providers are set of classes that take an LINQ query which generates method that executes an equivalent query against a particular data source.
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q10: Mention what is the role of DataContext classes in LINQ? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**DataContext** class acts as a bridge between SQL Server database and the LINQ to SQL. For accessing the database and also for changing the data in the database, it contains connections string and the functions. Essentially a DataContext class performs the following three tasks:
* Create connection to database.
* It submits and retrieves object to database.
* Converts objects to SQL queries and vice versa.
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q11: In LINQ how will you find the index of the element using where() with Lambda Expressions? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In order to find the index of the element use the overloaded version of `where()` with the lambda expression:
```csharp
where(( i, ix ) => i == ix);
```
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q12: Explain how LINQ is useful than Stored Procedures? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Debugging:** It is difficult to debug a stored procedure but as LINQ is part of.NET, visual studio debugger can be used to debug the queries
* **Deployment:** For stored procedure, additional script should be provided but with LINQ everything gets compiled into single DLL hence deployment becomes easy
* **Type Safety:** LINQ is type safe, so queries errors are type checked at compile time
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q13: Explain why SELECT clause comes after FROM clause in LINQ? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
With other programming language and C#, LINQ is used, it requires all the variables to be declared first. “FROM” clause of LINQ query defines the range or conditions to select records. So, FROM clause must appear before SELECT in LINQ.
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q14: Could you compare Entity Framework vs LINQ to SQL vs ADO.NET with stored procedures? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Stored procedures:**
(++)
- Great flexibility
- Full control over SQL
- The highest performance available
(--)
- Requires knowledge of SQL
- Stored procedures are out of source control (harder to test)
- Substantial amount of "repeating yourself" while specifying the same table and field names. The high chance of breaking the application after renaming a DB entity and missing some references to it somewhere.
- Slow development
**ORM (EF, L2SQL, ADO.NET):**
(++)
- Rapid development
- Data access code now under source control
- You're isolated from changes in DB. If that happens you only need to update your model/mappings in one place.
(--)
- Performance may be worse
- No or little control over SQL the ORM produces (could be inefficient or worse buggy). Might need to intervene and replace it with custom stored procedures. That will render your code messy (some LINQ in code, some SQL in code and/or in the DB out of source control).
- As any abstraction can produce "high-level" developers having no idea how it works under the hood
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q15: When trying to decide between using the Entity Framework and LINQ to SQL as an ORM, what's the difference? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **LINQ to SQL** only supports 1 to 1 mapping of database tables, views, sprocs and functions available in Microsoft SQL Server. It's a great API to use for quick data access construction to relatively well designed SQL Server databases. LINQ2SQL was first released with C# 3.0 and .Net Framework 3.5.
* **LINQ to Entities** (ADO.Net Entity Framework) is an ORM (Object Relational Mapper) API which allows for a broad definition of object domain models and their relationships to many different ADO.Net data providers. As such, you can mix and match a number of different database vendors, application servers or protocols to design an aggregated mash-up of objects which are constructed from a variety of tables, sources, services, etc. ADO.Net Framework was released with the .Net Framework 3.5 SP1.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q16: Using LINQ to remove elements from a List ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Given that `authorsList` is of type `List`, how can I delete the `Author` elements that are equalling to `Bob`?
**Answer:**
Consider:
```csharp
authorsList.RemoveAll(x => x.FirstName == "Bob");
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q17: What is the difference between First() and Take(1)? ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider:
```csharp
var result = List.Where(x => x == "foo").First();
var result = List.Where(x => x == "foo").Take(1);
```
**Answer:**
The difference between `First()` and `Take()` is that `First()` returns the element itself, while `Take()` returns a sequence of elements that contains exactly one element. (If you pass 1 as the parameter).
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q18: When to use First() and when to use FirstOrDefault() with LINQ? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Use `First()` when you know or expect the sequence to have at least one element. In other words, when it is an exceptional occurrence that the sequence is empty.
* Use `FirstOrDefault()` when you know that you will need to check whether there was an element or not. In other words, when it is legal for the sequence to be empty. You should not rely on exception handling for the check. (It is bad practice and might hurt performance).
`First()` will throw an exception if there's no row to be returned, while `FirstOrDefault()` will return the default value (NULL for all reference types) instead.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q19: Explain how standard query operators useful in LINQ? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A set of extension methods forming a query pattern is known as LINQ Standard Query Operators. As building blocks of LINQ query expressions, these operators offer a range of query capabilities like filtering, sorting, projection, aggregation, etc.
LINQ standard query operators can be categorized into the following ones on the basis of their functionality.
* Filtering Operators (Where, OfType)
* Join Operators (Join, GroupJoin)
* Projection Operations (Select, SelectMany)
* Sorting Operators (OrderBy, ThenBy, Reverse, ...)
* Grouping Operators (GroupBy, ToLookup)
* Conversions (Cast, ToArray, ToList, ...)
* Concatenation (Concat)
* Aggregation (Aggregate, Average, Count, Max, ...)
* Quantifier Operations (All, Any, Contains)
* Partition Operations (Skip, SkipWhile, Take, ...)
* Generation Operations (DefaultIfEmpty, Empty, Range, Repeat)
* Set Operations (Distinct, Except, ...)
* Equality (SequenceEqual)
* Element Operators (ElementAt, First, Last, ...)
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q20: What is Expression Trees and how they used in LINQ? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An **Expression Tree** is a data structure that contains Expressions, which is basically code. So it is a tree structure that represents a calculation you may make in code. These pieces of code can then be executed by "running" the expression tree over a set of data.
In LINQ, expression trees are used to represent structured queries that target sources of data that implement `IQueryable`. For example, the LINQ provider implements the `IQueryable` interface for querying relational data stores. The C# compiler compiles queries that target such data sources into code that builds an expression tree at runtime. The query provider can then traverse the expression tree data structure and translate it into a query language appropriate for the data source.
**Source:** _docs.microsoft.com_
#### Q21: Could you explian what is the exact deference between deferred execution and Lazy evaluation in C#? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In practice, they mean essentially the same thing. However, it's preferable to use the term deferred.
* Lazy means "don't do the work until you absolutely have to."
* Deferred means "don't compute the result until the caller actually uses it."
When the caller decides to use the result of an evaluation (i.e. start iterating through an `IEnumerable`), that is precisely the point at which the "work" needs to be done (such as issuing a query to the database).
The term _deferred_ is more specific/descriptive as to what's actually going on. When I say that I am lazy, it means that I avoid doing unnecessary work; it's ambiguous as to what that really implies. However, when I say that execution/evaluation is deferred, it essentially means that I am not giving you the real result at all, but rather a ticket you can use to claim the result. I defer actually going out and getting that result until you claim it.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q22: Explain what are LINQ compiled queries? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There may be scenario where we need to execute a particular query many times and repeatedly. LINQ allows us to make this task very easy by enabling us to create a query and make it compiled always. Benefits of Compiled Queries:
* Query does need to compiled each time so execution of the query is fast.
* Query is compiled once and can be used any number of times.
* Query does need to be recompiled even if the parameter of the query is being changed.
Consider:
```csharp
static class MyCompliedQueries {
public static Func > CompliedQueryForPerson =
CompiledQuery.Compile((DataClasses1DataContext context) = >from c in context.Persons select c);
}
```
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q23: Get the indexes of top n items where item value = true ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
I have a `List`. I need to get the indexes of top n items where item `value = true`.
```csharp
10011001000
TopTrueIndexes(3) = The first 3 indexes where bits are true are 0, 3, 4
TopTrueIndexes(4) = The first 4 indexes where bits are true are 0, 3, 4, 7
```
**Answer:**
Assuming you have some easily-identifiable condition, you can do something like this, which will work for any `IEnumerable`:
```csharp
var query = source.Select((value, index) => new { value, index })
.Where(x => x.value => Condition(value))
.Select(x => x.index)
.Take(n);
```
The important bits are that you use the overload of `Select` to get index/value pairs before the Where, and then another Select to get just the indexes after the Where... and use Take to only get the first n results.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q24: Define what is Let clause? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In a query expression, it is sometimes useful to store the result of a sub-expression in order to use it in subsequent clauses. You can do this with the `let` keyword, which creates a new range variable and initializes it with the result of the expression you supply.
Consider:
```csharp
var names = new string[] { "Dog", "Cat", "Giraffe", "Monkey", "Tortoise" };
var result =
from animalName in names
let nameLength = animalName.Length
where nameLength > 3
orderby nameLength
select animalName;
```
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q25: Explain what is the difference between Skip() and SkipWhile() extension method? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Skip()** **:** It will take an integer argument and from the given `IEnumerable` it skips the top `n` numbers
* **SkipWhile ():** It will continue to skip the elements as far as the input condition is `true`. It will return all remaining elements if the condition is `false`.
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q26: Explain what is lambda expressions in LINQ? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Lambda expression** is referred as a unique function use to form delegates or expression tree types, where right side is the output and left side is the input to the method. For writing LINQ queries particularly, Lambda expression is used.
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q27: Name some advantages of LINQ over Stored Procedures ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: What are the benefits of a Deferred Execution in LINQ? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: When should I use a CompiledQuery? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: What is an equivalent to the "let" keyword in chained LINQ extension method calls? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: Can you provide a concise distinction between anonymous method and lambda expressions? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: Name some disadvantages of LINQ over sprocs ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: What is the difference between Select and SelectMany? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q34: What is the difference between returning IQueryable vs. IEnumerable? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
What is the difference between returning `IQueryable` vs. `IEnumerable`?
```csharp
IQueryable < Customer > custs = from c in db.Customers
where c.City == ""
select c;
IEnumerable < Customer > custs = from c in db.Customers
where c.City == ""
select c;
```
Will both be deferred execution and when should one be preferred over the other?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q35: Why use .AsEnumerable() rather than casting to IEnumerable? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 35 Microservices Interview Questions You Most Likely Can't Answer
> Originally published on 👉 35 Microservices Interview Questions You Most Likely Can't Answer | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is meant by Continuous Integration? ⭐
**Answer:**
*Continuous Integration (CI)* is a development practice that requires developers to integrate code into a shared repository several times a day. Each check-in is then verified by an automated build, allowing teams to detect problems early.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q2: What does Containerization mean? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Containerisation* is a type of *virtualization* strategy that emerged as an alternative to traditional hypervisor-based virtualization.
In containerization, the operating system is shared by the different containers rather than cloned for each virtual machine. For example Docker provides a container virtualization platform that serves as a good alternative to hypervisor-based arrangements.
**Source:** _linoxide.com_
#### Q3: Explain Blue-Green Deployment Technique ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Blue-green deployment** is a technique that reduces downtime and risk by running two identical production environments called Blue and Green. At any time, only one of the environments is live, with the live environment serving all production traffic. For this example, Blue is currently live and Green is idle.
As you prepare a new version of your software, deployment and the final stage of testing takes place in the environment that is not live: in this example, Green. Once you have deployed and fully tested the software in Green, you switch the router so all incoming requests now go to Green instead of Blue. Green is now live, and Blue is idle.
This technique can eliminate downtime due to application deployment. In addition, blue-green deployment reduces risk: if something unexpected happens with your new version on Green, you can immediately roll back to the last version by switching back to Blue.
**Source:** _cloudfoundry.org_
#### Q4: What's the difference between a blue/green deployment and a rolling deployment? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* In **Blue Green Deployment**, you have TWO complete environments.
One is Blue environment which is running and the Green environment to which you want to upgrade. Once you swap the environment from blue to green, the traffic is directed to your new green environment. You can delete or save your old blue environment for backup until the green environment is stable.
* In **Rolling Deployment**, you have only ONE complete environment. The code is deployed in the subset of instances of the same environment and moves to another subset after completion.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q5: What are the differences between continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Developers practicing **continuous integration** merge their changes back to the main branch as often as possible. By doing so, you avoid the integration hell that usually happens when people wait for release day to merge their changes into the release branch.
* **Continuous delivery** is an extension of continuous integration to make sure that you can release new changes to your customers quickly in a sustainable way. This means that on top of having automated your testing, you also have automated your release process and you can deploy your application at any point of time by clicking on a button.
* **Continuous deployment** goes one step further than continuous delivery. With this practice, every change that passes all stages of your production pipeline is released to your customers. There's no human intervention, and only a failed test will prevent a new change to be deployed to production.
**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q6: What do you know about serverless model? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Serverless** refers to a model where the existence of servers is hidden from developers. It means you no longer have to deal with capacity, deployments, scaling and fault tolerance and OS. It will essentially reducing maintenance efforts and allow developers to quickly focus on developing codes.
Examples are:
* Amazon AWS Lambda
* Azure Functions
**Source:** _linoxide.com_
#### Q7: How is container different from a virtual machine? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q8: What is Canary Releasing? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q9: What is Docker? ⭐
**Answer:**
* Docker is a containerization platform which packages your application and all its dependencies together in the form of containers so as to ensure that your application works seamlessly in any environment be it development or test or production.
* Docker containers, wrap a piece of software in a complete filesystem that contains everything needed to run: code, runtime, system tools, system libraries etc. anything that can be installed on a server.
* This guarantees that the software will always run the same, regardless of its environment.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q10: How virtualization works at low level? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q11: What is Paravirtualization? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q12: Define Microservice Architecture ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Microservices**, aka **_Microservice Architecture_**, is an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of small autonomous services, modeled around a **business domain.**
**Source:** _lambdatest.com_
#### Q13: What are the features of Microservices? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Decoupling** – Services within a system are largely decoupled. So the application as a whole can be easily built, altered, and scaled
* **Componentization** – Microservices are treated as independent components that can be easily replaced and upgraded
* **Business Capabilities** – Microservices are very simple and focus on a single capability
* **Autonomy** – Developers and teams can work independently of each other, thus increasing speed
* **Continous** **Delivery** – Allows frequent releases of software, through systematic automation of software creation, testing, and approval
* **Responsibility** – Microservices do not focus on applications as projects. Instead, they treat applications as products for which they are responsible
* **Decentralized Governance** – The focus is on using the right tool for the right job. That means there is no standardized pattern or any technology pattern. Developers have the freedom to choose the best useful tools to solve their problems
* **Agility** – Microservices support agile development. Any new feature can be quickly developed and discarded again
**Source:** _lambdatest.com_
#### Q14: How does Microservice Architecture work? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Clients** – Different users from various devices send requests.
* **Identity Providers** – Authenticates user or clients identities and issues security tokens.
* **API Gateway** – Handles client requests.
* **Static Content** – Houses all the content of the system.
* **Management** – Balances services on nodes and identifies failures.
* **Service Discovery** – A guide to find the route of communication between microservices.
* **Content Delivery Networks** – Distributed network of proxy servers and their data centers.
* **Remote Service** – Enables the remote access information that resides on a network of IT devices.

**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q15: What is the difference between Monolithic, SOA and Microservices Architecture? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Monolithic Architecture** is similar to a big container wherein all the software components of an application are assembled together and tightly packaged.
* A **Service-Oriented Architecture** is a collection of services which communicate with each other. The communication can involve either simple data passing or it could involve two or more services coordinating some activity.
* **Microservice Architecture** is an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of small autonomous services, modeled around a business domain.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q16: What are main differences between Microservices and Monolithic Architecture? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Microservices**
* Service Startup is fast
* Microservices are loosely coupled architecture.
* Changes done in a single data model does not affect other Microservices.
* Microservices focuses on products, not projects
**Monolithic Architecture**
* Service startup takes time
* Monolithic architecture is mostly tightly coupled.
* Any changes in the data model affect the entire database
* Monolithic put emphasize over the whole project
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q17: What are the standard patterns of orchestrating microservices? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
As we start to model more and more complex logic, we have to deal with the problem of managing business processes that stretch across the boundary of individual services.
* With **orchestration**, we rely on a central brain to guide and drive the process, much like the conductor in an orchestra. The orchestration style corresponds more to the SOA idea of orchestration/task services. For example we could wrap the business flow in its own service. Where the proxy orchestrates the interaction between the microservices like shown in the below picture.
* With **choreography**, we inform each part of the system of its job, and let it work out the details, like dancers all find‐ ing their way and reacting to others around them in a ballet. The choreography style corresponds to the dumb pipes and smart endpoints mentioned by Martin Fowler's. That approach is also called the **domain approach** and is using domain events, where each service publish events regarding what have happened and other services can subscribe to those events.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q18: What are smart endpoints and dumb pipes? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Smart endpoints** just meaning actual business rules and any other validations happens behind those endpoints which are not visible to anyone to the consumers of those endpoints think of it as a place where actual Magic happens.
* **Dumb pipelines** means any communication means where no further actions e.g validations are taken place, it simply carries the data across that particular channel and it may also be replaceable if need be. The infrastructure chosen is typically dumb (dumb as in acts as a message router only). It just means that routing is the only function the pipes should be doing.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q19: Whether do you find GraphQL the right fit for designing microservice architecture? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
_GraphQL and microservices are a perfect fit_, because GraphQL hides the fact that you have a microservice architecture from the clients. From a backend perspective, you want to split everything into microservices, but from a frontend perspective, you would like all your data to come from a single API. Using GraphQL is the best way I know of that lets you do both. It lets you split up your backend into microservices, while still providing a single API to all your application, and allowing joins across data from different services.

**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q20: What is Idempotence? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: What are the pros and cons of Microservice Architecture? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: What do you understand by Contract Testing? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: What is the role of an architect in Microservices architecture? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: Explain what is the API Gateway pattern ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: Mention some benefits and drawbacks of an API Gateway ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: What is Materialized View pattern and when will you use it? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: What Did The Law Stated By Melvin Conway Implied? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: Name the main differences between SOA and Microservices? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: What is the difference between cohesion and coupling? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: What is a Consumer-Driven Contract (CDC)? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: What are Reactive Extensions in Microservices? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: What is the most accepted transaction strategy for microservices ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: Why would one use sagas over 2PC and vice versa? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q34: Provide an example of "smart pipes" and "dumb endpoint" ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q35: How would you implement SSO for Microservice Architecture? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 35 Top Angular 7 Interview Questions To Crack in 2019
> Originally published on 👉 35 Top Angular 7 Interview Questions To Crack in 2019 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What are pipes? Give me an example. ⭐
**Answer:**
A **pipe** takes in data as input and transforms it to a desired output. You can chain pipes together in potentially useful combinations. You can write your own custom pipes. Angular comes with a stock of pipes such as `DatePipe`, `UpperCasePipe`, `LowerCasePipe`, `CurrencyPipe`, and `PercentPipe`.
Consider:
```html
The hero's birthday is {{ birthday | date }}
```
In this page, you'll use pipes to transform a component's birthday property into a human-friendly date.
**Source:** _angular.io_
#### Q2: What is the minimum definition of a component? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The absolute minimal configuration for a `@Component` in Angular is a template. Both template properties are set to optional because you have to define either `template` or `templateUrl`.
When you don't define them, you will get an exception like this:
```sh
No template specified for component 'ComponentName'
```
A selector property is not required, as you can also use your components in a route.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q3: What's the difference between an Angular component and module? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Components* control views (html). They also communicate with other components and services to bring functionality to your app.
*Modules* consist of one or more components. They do not control any html. Your modules declare which components can be used by components belonging to other modules, which classes will be injected by the dependency injector and which component gets bootstrapped. Modules allow you to manage your components to bring modularity to your app.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q4: How can I select an element in a component template? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
You can get a handle to the DOM element via ElementRef by injecting it into your component's constructor:
```js
constructor(myElement: ElementRef) { ... }
```
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q5: What is an observer? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Observer is an interface for a consumer of push-based notifications delivered by an Observable. It has below structure,
```javascript
interface Observer {
closed?: boolean;
next: (value: T) => void;
error: (err: any) => void;
complete: () => void;
}
```
A handler that implements the Observer interface for receiving observable notifications will be passed as a parameter for observable as below,
```javascript
myObservable.subscribe(myObserver);
```
**Note:** If you don't supply a handler for a notification type, the observer ignores notifications of that type.
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q6: What is an observable? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An Observable is a unique Object similar to a Promise that can help manage async code. Observables are not part of the JavaScript language so we need to rely on a popular Observable library called RxJS.
The observables are created using new keyword. Let see the simple example of observable,
```javascript
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
const observable = new Observable(observer => {
setTimeout(() => {
observer.next('Hello from a Observable!');
}, 2000);
});`
```
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q7: What is TestBed? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **Angular Test Bed (ATB)** is a higher level *Angular Only* testing framework that allows us to easily test behaviours that depend on the Angular Framework.
We still write our tests in Jasmine and run using Karma but we now have a slightly easier way to create components, handle injection, test asynchronous behaviour and interact with our application.
The TestBed creates a dynamically-constructed Angular test module that emulates an Angular `@NgModule`.
**Source:** _angular.io_
#### Q8: What is Redux and how does it relate to an Angular app? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Redux** is a way to manage application state and improve maintainability of asynchronicity in your application by providing a single source of truth for the application state, and a unidirectional flow of data change in the application. `ngrx/store` is one implementation of Redux principles.
**Source:** _github.com/WebPredict_
#### Q9: What are the Core Dependencies of Angular 7? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are two types of core dependencies, RxJS and TypeScript.
* **RxJS 6.3** - RxJS version 6.3 is used by Angular 7. It has no changes in the version from Angular 6
* **TypeScript 3.1** - TypeScript version 3.1 is used by Angular 7. It is the upgrade from the version 2.9 of Angular 6.
**Source:** _onlineinterviewquestions.com_
#### Q10: Why Incremental DOM Has Low Memory Footprint? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Virtual DOM creates a whole tree from scratch every time you rerender.
Incremental DOM, on the other hand, doesn’t need any memory to rerender the view if it doesn’t change the DOM. We only have to allocate the memory when the DOM nodes are added or removed. And the size of the allocation is proportional to the size of the DOM change.
**Source:** _blog.nrwl.io_
#### Q11: What are the ways to control AOT compilation? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
You can control your app compilation in two ways
1. By providing template compiler options in the `tsconfig.json` file
2. By configuring Angular metadata with decorators
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q12: What is activated route? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**ActivatedRoute** contains the information about a route associated with a component loaded in an outlet. It can also be used to traverse the router state tree. The ActivatedRoute will be injected as a router service to access the information. In the below example, you can access route path and parameters,
```js
@Component({
...
})
class MyComponent {
constructor(route: ActivatedRoute) {
const id: Observable < string > = route.params.pipe(map(p => p.id));
const url: Observable < string > = route.url.pipe(map(segments => segments.join('')));
// route.data includes both `data` and `resolve`
const user = route.data.pipe(map(d => d.user));
}
}
```
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q13: What is router outlet? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **RouterOutlet** is a directive from the router library and it acts as a placeholder that marks the spot in the template where the router should display the components for that outlet. Router outlet is used as a component,
```html
```
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q14: What are the utility functions provided by RxJS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The RxJS library also provides below utility functions for creating and working with observables.
1. Converting existing code for async operations into observables
2. Iterating through the values in a stream
3. Mapping values to different types
4. Filtering streams
5. Composing multiple streams
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q15: What is multicasting? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Multi-casting** is the practice of broadcasting to a list of multiple subscribers in a single execution. Let's demonstrate the multi-casting feature,
```javascript
var source = Rx.Observable.from([1, 2, 3]);
var subject = new Rx.Subject();
var multicasted = source.multicast(subject);
// These are, under the hood, `subject.subscribe({...})`:
multicasted.subscribe({
next: (v) => console.log('observerA: ' + v)
});
multicasted.subscribe({
next: (v) => console.log('observerB: ' + v)
});
// This is, under the hood, `s
```
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q16: What is subscribing? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An Observable instance begins publishing values only when someone subscribes to it. So you need to subscribe by calling the **subscribe()** method of the instance, passing an observer object to receive the notifications.
Let's take an example of creating and subscribing to a simple observable, with an observer that logs the received message to the console.
```javascript
Creates an observable sequence of 5 integers, starting from 1
const source = range(1, 5);
// Create observer object
const myObserver = {
next: x => console.log('Observer got a next value: ' + x),
error: err => console.error('Observer got an error: ' + err),
complete: () => console.log('Observer got a complete notification'),
};
// Execute with the observer object and Prints out each item
myObservable.subscribe(myObserver);
// => Observer got a next value: 1
// => Observer got a next value: 2
// => Observer got a next value: 3
// => Observer got a next value: 4
// => Observer got a next value: 5
// => Observer got a complete notification
```
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q17: How to set headers for every request in Angular? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: Why would you use renderer methods instead of using native element methods? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: What is Zone in Angular? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: What does a just-in-time (JIT) compiler do (in general)? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: What is ngUpgrage? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: Why would you use lazy loading modules in Angular app? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: What is Ivy Renderer? Is it supported by Angular 7? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: What is incremental DOM? How is it different from virtual DOM? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: What are the advantages with AOT? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: Do I need to bootstrap custom elements? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: What is the difference between pure and impure pipe? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: What is the difference between BehaviorSubject vs Observable? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: What is the Angular equivalent to an AngularJS "$watch"? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: Name some differences between SystemJS vs WebPack? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: Just-in-Time (JiT) vs Ahead-of-Time (AoT) compilation. Explain the difference. ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: Why angular uses url segment? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: Why did the Google team go with incremental DOM instead of virtual DOM? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q34: Why Incremental DOM is Tree Shakable? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q35: What's new in Angular 7? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 37 ASP.NET Interview Questions You Must Know
> Originally published on 👉 37 ASP.NET Interview Questions You Must Know | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is ViewData? ⭐
**Answer:**
Viewdata contains the key, value pairs as dictionary and this is derived from class — “ViewDataDictionary“. In action method we are setting the value for viewdata and in view the value will be fetched by typecasting.
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q2: What is ASP.Net? ⭐
**Answer:**
It is a framework developed by Microsoft on which we can develop new generation web sites using web forms(aspx), MVC, HTML, Javascript, CSS etc. Its successor of Microsoft Active Server Pages(ASP). Currently there is ASP.NET 4.0, which is used to develop web sites. There are various page extensions provided by Microsoft that are being used for web site development. Eg: aspx, asmx, ascx, ashx, cs, vb, html, XML etc.
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q3: What is ASP.NET Core? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ASP.NET Core is a brand new cross-platform web framework built with .NET Core framework. It is not an update to existing ASP.NET framework. It is a complete rewrite of the ASP.NET framework. It works with both .NET Core and .NET Framework.
Main characterestics of ASP.NET Core:
* DI Container which is quite simple and built-in. You can extend it with other popular DI containers
* Built-in and extensible structured logging. You can redirect output to as many sources as you want (file, Azure, AWS, console)
* Extensible strongly typed configuration, which can also be used to reload at run-time
* Kestrel – new, cross-platform and super fast web server which can stand alone without IIS, Nginx or Apache
* New, fully async pipeline. It is easily configured via middleware
* ASP.NET All meta package which improves development speed, and enables you to reference all Microsoft packages for ASP.NET Core and it will deploy only those that are being used by your code
* There is no _web.config_. We now use _appsettings.json_ file in combination with other sources of configuration (command line args, environment variables, etc.)
* There is no _Global._asax – We have _Startup.cs_ which is used to set up Middleware and services for DI Container.
**Source:** _talkingdotnet.com_
#### Q4: Can ASP.NET Core work with the .NET framework? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Yes. This might surprise many, but ASP.NET Core works with .NET framework and this is officially supported by Microsoft.
ASP.NET Core works with:
* .NET Core framework
* .NET framework
**Source:** _talkingdotnet.com_
#### Q5: Explain startup process in ASP.NET Core? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Everything starts from Program.cs
```csharp
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BuildWebHost(args).Run();
}
public static IWebHost BuildWebHost(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseStartup()
.Build();
```
CreateDefaultBuilder extension method will create a default configuration which will look first into `appsettings.json` files then will look for Environment variables and at the end, it will use command line arguments.
This part will also set up default logger sources (debug and console) and load the settings for logging from appsettings.json.
After the `CreateDefaultBuilder` finishes, then `Startup` class is executed. First, the constructor code is executed. After that, services are added to DI container via `AddServices` method that lives in Startup class. After that, an order of middleware that will handle every incoming request is set up.
**Source:** _codingblast.com_
#### Q6: What is the difference between ASP.NET and ASP.NET MVC? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ASP.NET, at its most basic level, provides a means for you to provide general HTML markup combined with server side "controls" within the event-driven programming model that can be leveraged with VB, C#, and so on. You define the page(s) of a site, drop in the controls, and provide the programmatic plumbing to make it all work.
ASP.NET MVC is an application framework based on the Model-View-Controller architectural pattern. This is what might be considered a "canned" framework for a specific way of implementing a web site, with a page acting as the "controller" and dispatching requests to the appropriate pages in the application. The idea is to "partition" the various elements of the application, eg business rules, presentation rules, and so on.
Think of the former as the "blank slate" for implementing a site architecture you've designed more or less from the ground up. MVC provides a mechanism for designing a site around a pre-determined "pattern" of application access, if that makes sense. There's more technical detail to it than that, to be sure, but that's the nickel tour for the purposes of the question.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q7: What is a postback? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **postback** originates from the client browser. Usually one of the controls on the page will be manipulated by the user (a button clicked or dropdown changed, etc), and this control will initiate a postback. The state of this control, plus all other controls on the page (known as the View State) is Posted Back to the web server.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q8: What is ViewState? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**View State** is the method to preserve the Value of the Page and Controls between round trips. It is a Page-Level State Management technique. View State is turned on by default and normally serializes the data in every control on the page regardless of whether it is actually used during a post-back.
A web application is stateless. That means that a new instance of a page is created every time when we make a request to the server to get the page and after the round trip our page has been lost immediately
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q9: What exactly is an application pool? What is its purpose? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Application pools** allow you to isolate your applications from one another, even if they are running on the same server. This way, if there is an error in one app, it won't take down other applications.
Additionally, applications pools allow you to separate different apps which require different levels of security.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q10: Explain Middleware in ASP.NET Core? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Middleware is actually sequential series of delegates (piece of code), that can either short-circuit or pass on the HTTP request to next delegate. These are known as middleware, a concept well known to people who worked with Node.js.
Piece of your middleware can do one of the following:
* Handle an incoming HTTP request by generating an HTTP response (maybe your authentication or authorization middleware will stop the request early and immediately create response)
* Process the incoming request, change it and pass it to the next middleware in the pipeline
* Process the outgoing response, change it and pass it on to next middleware in the pipeline or directly to the ASP.NET Core web server
**Source:** _talkingdotnet.com_
#### Q11: What are the different types of caching? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ASP.NET has 3 kinds of caching :
1. Output Caching,
2. Fragment Caching,
3. Data Caching.
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q12: How long the items in ViewState exists? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
They exist for the life of the current page.
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q13: In which event of page cycle is the ViewState available? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
After the Init() and before the Page_Load().
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q14: What are the sub types of ActionResult? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ActionResult is used to represent the action method result. Below are the subtypes of ActionResult:
* ViewResult
* PartialViewResult
* RedirectToRouteResult
* RedirectResult
* JavascriptResult
* JSONResult
* FileResult
* HTTPStatusCodeResult
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q15: What is the difference between Server.Transfer and Response.Redirect? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In Server.Transfer page processing transfers from one page to the other page without making a round-trip back to the client's browser. This provides a faster response with a little less overhead on the server. The clients url history list or current url Server does not update in case of Server.Transfer.
Response.Redirect is used to redirect the user's browser to another page or site. It performs trip back to the client where the client's browser is redirected to the new page. The user's browser history list is updated to reflect the new address.
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q16: How can we prevent browser from caching an ASPX page? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
We can SetNoStore on HttpCachePolicy object exposed by the Response object's Cache property:
```csharp
Response.Cache.SetNoStore();
Response.Write(DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString ());
```
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q17: What are the event handlers that we can have in Global.asax file? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Application Events:** Application_Start , Application_End, Application_AcquireRequestState, Application_AuthenticateRequest, Application_AuthorizeRequest, Application_BeginRequest, Application_Disposed, Application_EndRequest, Application_Error, Application_PostRequestHandlerExecute, Application_PreRequestHandlerExecute,Application_PreSendRequestContent, Application_PreSendRequestHeaders, Application_ReleaseRequestState, Application_ResolveRequestCache, Application_UpdateRequestCache
* **Session Events:** Session_Start,Session_End
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q18: In which event are the controls fully loaded? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Page load** event.
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q19: What is ViewState? How is it encoded? Is it encrypted? Who uses ViewState? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**View state** is a kind of hash map (or at least you can think of it that way) that ASP.NET uses to store all the temporary information about a page - like what options are currently chosen in each select box, what values are there in each text box, which panel are open, etc. You can also use it to store any arbitrary information.
The entire map is serialized and encoded and kept in a _hidden variable_ (__VIEWSTATE form field) that's posted back to the server whenever you take any action on the page that requires a server round trip. This is how you can access the values on the controls from the server code. If you change any value in the server code, that change is made in the view state and sent back to the browser.
Just be careful about how much information you store in the view state, though... it can quickly become bloated and slow to transfer each time to the server and back.
It's not encrypted at all. Just base encoded, which easily reversible.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q20: What exactly is the difference between .NET Core and ASP.NET Core? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**.NET Core** is a runtime. It can execute applications that are built for it.
**ASP.NET Core** is a collection of libraries that form a Framework for building web applications. ASP.NET Core libraries can be used on both .NET Core and the "Full .NET Framework" (what has shipped with windows for many years).
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q21: What are the different Session state management options available in ASP.NET? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: What is the difference between web config and machine config? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: List the major built-in objects in ASP.NET? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: What are the different types of cookies in ASP.NET? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: What is Katana? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: How to choose between ASP.NET 4.x and ASP.NET Core? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: What is an HttpHandler in ASP.NET? Why and how is it used? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: What is the difference between and ? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: What is HttpModule in ASP.Net? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: Name some ASP.NET WebForms disadvantages over MVC? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: What exactly is OWIN and what problems does it solve? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: Are static class instances unique to a request or a server in ASP.NET? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
On an ASP.NET website, are static classes unique to each web request, or are they instantiated whenever needed and GCed whenever the GC decides to disposed of them?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: What are the Advantages of Using ASP.NET Web API? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Using ASP.NET Web API has a number of advantages, but core of the advantages are:
* It works the HTTP way using standard HTTP verbs like `GET`, `POST`, `PUT`, `DELETE`, etc. for all CRUD operations
* Complete support for routing
* Response generated in JSON or XML format using `MediaTypeFormatter`
* It has the ability to be hosted in IIS as well as self-host outside of IIS
* Supports Model binding and Validation
* Support for OData
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q34: Compare WCF vs ASP.NET Web API? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Windows Communication Foundation** is designed to exchange standard SOAP-based messages using variety of transport protocols like HTTP, TCP, NamedPipes or MSMQ, etc.
* On the other hand, **ASP.NET API** is a framework for building non-SOAP based services over HTTP only.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q35: What's the difference between REST & RESTful? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Representational state transfer (REST) is a style of software architecture. As described in a dissertation by Roy Fielding, REST is an "architectural style" that basically exploits the existing technology and protocols of the Web.
* RESTful is typically used to refer to web services implementing such an architecture.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q36: What's the difference between OpenID and OAuth? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q37: Explain the difference between WCF, Web API, WCF REST and Web Service? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 39 Advanced React Interview Questions You Must Clarify (2020 Update)
> Originally published on 👉 39 Advanced React Interview Questions You Must Clarify (2020 Update) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is virtual DOM? ⭐
**Answer:**
**The virtual DOM (VDOM)** is an in-memory representation of Real DOM. The representation of a UI is kept in memory and synced with the “real” DOM. It’s a step that happens between the render function being called and the displaying of elements on the screen. This entire process is called reconciliation.
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q2: What are the differences between a class component and functional component? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
- **Class components** allows you to use additional features such as local state and lifecycle hooks. Also, to enable your component to have direct access to your store and thus holds state.
- When your component just receives props and renders them to the page, this is a **stateless component**, for which a pure function can be used. These are also called dumb components or presentational components.
**Source:** _github.com/Pau1fitz_
#### Q3: What are refs used for in React? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Refs* are an escape hatch which allow you to get direct access to a DOM element or an instance of a component. In order to use them you add a ref attribute to your component whose value is a callback function which will receive the underlying DOM element or the mounted instance of the component as its first argument.
```js
class UnControlledForm extends Component {
handleSubmit = () => {
console.log("Input Value: ", this.input.value)
}
render () {
return (
this.input = input} />
Submit
)
}
}
```
Above notice that our input field has a ref attribute whose value is a function. That function receives the actual DOM element of input which we then put on the instance in order to have access to it inside of the handleSubmit function.
It’s often misconstrued that you need to use a class component in order to use refs, but refs can also be used with functional components by leveraging closures in JavaScript.
```js
function CustomForm ({handleSubmit}) {
let inputElement
return (
handleSubmit(inputElement.value)}>
inputElement = input} />
Submit
)
}
```
**Source:** _github.com/Pau1fitz_
#### Q4: Describe how events are handled in React. ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In order to solve cross browser compatibility issues, your event handlers in React will be passed instances of SyntheticEvent, which is React’s cross-browser wrapper around the browser’s native event. These synthetic events have the same interface as native events you’re used to, except they work identically across all browsers.
What’s mildly interesting is that React doesn’t actually attach events to the child nodes themselves. React will listen to all events at the top level using a single event listener. This is good for performance and it also means that React doesn’t need to worry about keeping track of event listeners when updating the DOM.
**Source:** _tylermcginnis.com_
#### Q5: What is the difference between state and props? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Both **props** and **state** are plain JavaScript objects. While both of them hold information that influences the output of render, they are different in their functionality with respect to component. i.e,
* Props get passed to the component similar to function parameters
* state is managed within the component similar to variables declared within a function.
**Source:** _https://github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q6: How to create refs? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Refs** are created using `React.createRef()` method and attached to React elements via the ref attribute. In order to use refs throughout the component, just assign the ref to the instance property with in constructor.
```js
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.myRef = React.createRef();
}
render() {
return
}
}
```
And:
```js
class UserForm extends Component {
handleSubmit = () => {
console.log("Input Value is: ", this.input.value)
}
render () {
return (
this.input = input} /> // Access DOM input in handle submit
Submit
)
}
}
```
We can also use it in functional components with the help of closures.
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q7: What are Higher-Order components? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A higher-order component **(HOC)** is a function that takes a component and returns a new component. Basically, it’s a pattern that is derived from React’s compositional nature
We call them as **“pure’ components”** because they can accept any dynamically provided child component but they won’t modify or copy any behavior from their input components.
```js
const EnhancedComponent = higherOrderComponent(WrappedComponent);
```
HOC can be used for many use cases as below,
1. Code reuse, logic and bootstrap abstraction
2. Render High jacking
3. State abstraction and manipulation
4. Props manipulation
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q8: What is the purpose of using super constructor with props argument? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A child class constructor cannot make use of **this** reference until `super()` method has been called. The same applies for ES6 sub-classes as well. The main reason of passing props parameter to super() call is to access this.props in your child constructors.
**Passing props:**
```js
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log(this.props); // Prints { name: 'sudheer',age: 30 }
}
}
```
**Not passing props:**
```js
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super();
console.log(this.props); // Prints undefined
// But Props parameter is still available
console.log(props); // Prints { name: 'sudheer',age: 30 }
}
render() {
// No difference outside constructor
console.log(this.props) // Prints { name: 'sudheer',age: 30 }
}
}
```
The above code snippets reveals that this.props behavior is different only with in the constructor. It would be same outside the constructor.
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q9: What are controlled components? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In HTML, form elements such as ``, ``, and `` typically maintain their own state and update it based on user input. When a user submits a form the values from the aforementioned elements are sent with the form. With React it works differently. The component containing the form will keep track of the value of the input in it's state and will re-render the component each time the callback function e.g. `onChange` is fired as the state will be updated. An input form element whose value is controlled by React in this way is called a **controlled component**.
**Source:** _github.com/Pau1fitz_
#### Q10: What is equivalent of the following using React.createElement? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Question**:
```js
const element = (
Hello, world!
);
```
What is equivalent of the following using `React.createElement`?
**Answer**:
```js
const element = React.createElement(
'h1',
{className: 'greeting'},
'Hello, world!'
);
```
**Source:** _github.com/Pau1fitz_
#### Q11: What can you tell me about JSX? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
When Facebook first released React to the world, they also introduced a new dialect of JavaScript called JSX that embeds raw HTML templates inside JavaScript code. JSX code by itself cannot be read by the browser; it must be transpiled into traditional JavaScript using tools like Babel and webpack. While many developers understandably have initial knee-jerk reactions against it, JSX (in tandem with ES2015) has become the defacto method of defining React components.
```js
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
let props = this.props;
return (
);
}
}
```
**Source:** _codementor.io_
#### Q12: Given the code defined above, can you identify two problems? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Take a look at the code below:
```js
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
// set the default internal state
this.state = {
clicks: 0
};
}
componentDidMount() {
this.refs.myComponentDiv.addEventListener('click', this.clickHandler);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.refs.myComponentDiv.removeEventListener('click', this.clickHandler);
}
clickHandler() {
this.setState({
clicks: this.clicks + 1
});
}
render() {
let children = this.props.children;
return (
My Component ({this.state.clicks} clicks})
{this.props.headerText}
{children}
);
}
}
```
Given the code defined above, can you identify two problems?
**Answer:**
1. The constructor does not pass its props to the super class. It should include the following line:
```js
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// ...
}
```
2. The event listener (when assigned via `addEventListener()`) is not properly scoped because [ES2015 doesn’t provide autobinding](https://facebook.github.io/react/docs/reusable-components.html#no-autobinding). Therefore the developer can re-assign `clickHandler` in the constructor to include the correct binding to this:
```js
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.clickHandler = this.clickHandler.bind(this);
// ...
}
```
**Source:** _codementor.io_
#### Q13: Why should not we update the state directly? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
If you try to update state directly then it won’t re-render the component.
```js
//Wrong
This.state.message =”Hello world”;
```
Instead use `setState()` method. It schedules an update to a component’s state object. When state changes, the component responds by re-rendering
```js
//Correct
This.setState({message: ‘Hello World’});
```
**Note:** The only place you can assign the state is constructor.
**Source:** _https://github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q14: What are the different phases of ReactJS component lifecycle? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are four different phases of React component’s lifecycle:
1. **Initialization:** In this phase react component prepares setting up the initial state and default props.
2. **Mounting:** The react component is ready to mount in the browser DOM. This phase covers **componentWillMount** and **componentDidMount** lifecycle methods.
3. **Updating:** In this phase, the component get updated in two ways, sending the new props and updating the state. This phase covers **shouldComponentUpdate, componentWillUpdate and componentDidUpdate** lifecycle methods.
4. **Unmounting:** In this last phase, the component is not needed and get unmounted from the browser DOM. This phase include **componentWillUnmount** lifecycle method.

**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q15: What are the lifecycle methods of ReactJS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
- **componentWillMount:** Executed before rendering and is used for App level configuration in your root component.
- **componentDidMount:** Executed after first rendering and here all AJAX requests, DOM or state updates, and set up eventListeners should occur.
- **componentWillReceiveProps:** Executed when particular prop updates to trigger state transitions.
- **shouldComponentUpdate:** Determines if the component will be updated or not. By default it returns true. If you are sure that the component doesn't need to render after state or props are updated, you can return false value. It is a great place to improve performance as it allows you to prevent a rerender if component receives new prop.
- **componentWillUpdate:** Executed before re-rendering the component when there are pros & state changes confirmed by shouldComponentUpdate which returns true.
- **componentDidUpdate:** Mostly it is used to update the DOM in response to prop or state changes.
- **componentWillUnmount:** It will be used to cancel any outgoing network requests, or remove all event listeners associated with the component.
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q16: What do these three dots (...) in React do? ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
What does the ... do in this React (using JSX) code and what is it called?
```html
```
would be the same as:
```html
```
Spread notation is handy not only for that use case, but for creating a new object with most (or all) of the properties of an existing object — which comes up a lot when you're updating state, since you can't modify state directly:
```js
this.setState(prevState => {
return {foo: {...prevState.foo, a: "updated"}};
});
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q17: What are advantages of using React Hooks? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Primarily, hooks in general enable the extraction and reuse of stateful logic that is common across multiple components without the burden of higher order components or render props. Hooks allow to easily manipulate the state of our functional component without needing to convert them into class components.
Hooks don’t work inside classes (because they let you use React without classes). By using them, we can totally avoid using lifecycle methods, such as `componentDidMount`, `componentDidUpdate`, `componentWillUnmount`. Instead, we will use built-in hooks like `useEffect` .
**Source:** _hackernoon.com_
#### Q18: What are React Hooks? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Hooks** are a new addition in React 16.8. They let you use state and other React features without writing a class. With Hooks, you can extract stateful logic from a component so it can be tested independently and reused. Hooks allow you to reuse stateful logic without changing your component hierarchy. This makes it easy to share Hooks among many components or with the community.
**Source:** _reactjs.org_
#### Q19: What is useState() in React? ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Explain what is the use of `useState(0)` there:
```js
...
const [count, setCounter] = useState(0);
const [moreStuff, setMoreStuff] = useState(...);
...
const setCount = () => {
setCounter(count + 1);
setMoreStuff(...);
...
};
```
**Answer:**
`useState` is one of build-in react hooks. `useState(0)` returns a tuple where the first parameter count is the current state of the counter and setCounter is the method that will allow us to update the counter's state.
We can use the `setCounter` method to update the state of count anywhere - In this case we are using it inside of the setCount function where we can do more things; the idea with hooks is that we are able to keep our code more functional and avoid class based components if not desired/needed.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q20: What is StrictMode in React? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
React's StrictMode is sort of a helper component that will help you write better react components, you can wrap a set of components with `` and it'll basically:
* Verify that the components inside are following some of the recommended practices and warn you if not in the console.
* Verify the deprecated methods are not being used, and if they're used strict mode will warn you in the console.
* Help you prevent some side effects by identifying potential risks.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q21: Why do class methods need to be bound to a class instance? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In JavaScript, the value of `this` changes depending on the current context. Within React class component methods, developers normally expect this to refer to the current instance of a component, so it is necessary to _bind_ these methods to the instance. Normally this is done in the constructor—for example:
```js
class SubmitButton extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
isFormSubmitted: false
};
this.handleSubmit = this.handleSubmit.bind(this);
}
handleSubmit() {
this.setState({
isFormSubmitted: true
});
}
render() {
return (
Submit
)
}
}
```
**Source:** _toptal.com_
#### Q22: What is prop drilling and how can you avoid it? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
When building a React application, there is often the need for a deeply nested component to use data provided by another component that is much higher in the hierarchy. The simplest approach is to simply pass a prop from each component to the next in the hierarchy from the source component to the deeply nested component. This is called **prop drilling**.
The primary disadvantage of prop drilling is that components that should not otherwise be aware of the data become unnecessarily complicated and are harder to maintain.
To avoid prop drilling, a common approach is to use React context. This allows a `Provider` component that supplies data to be defined, and allows nested components to consume context data via either a `Consumer` component or a `useContext` hook.
**Source:** _toptal.com_
#### Q23: Describe Flux vs MVC? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: What is the difference between a controlled component and an uncontrolled component? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: What is wrong with this code? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: What is the React context? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: What is React Fiber? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: How to apply validation on Props in ReactJS? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: What is the difference between ReactJS and Angular? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: What is the difference between using constructor vs getInitialState in React? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: When is it important to pass props to super(), and why? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: How to conditionally add attributes to React components? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Is there a way to only add attributes to a React component if a certain condition is met?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: Do Hooks replace render props and higher-order components? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q34: How would you go about investigating slow React application rendering? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q35: When would you use StrictMode component in React? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q36: What is a pure function? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q37: How does React renderer work exactly when we call setState? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q38: What is the key architectural difference between a JavaScript library such as React and a JavaScript framework such as Angular? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q39: How to avoid the need for binding in React? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 40 Advanced OOP Interview Questions and Answers [2019 Update]
> Originally published on 👉 40 Advanced OOP Interview Questions and Answers [2019 Update] | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is inheritance? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Inheritance** allows us to define a class in terms of another class, which makes it easier to create and maintain an application. This also provides an opportunity to reuse the code functionality and speeds up implementation time.
When creating a class, instead of writing completely new data members and member functions, the programmer can designate that the new class should inherit the members of an existing class. This existing class is called the base class, and the new class is referred to as the derived class.
The idea of inheritance implements the IS-A relationship. For example, mammal IS A animal, dog IS-A mammal hence dog IS-A animal as well, and so on.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q2: What is object-oriented programming (OOP)? ⭐
**Answer:**
OOP is a technique to develop logical modules, such as classes that contain properties, methods, fields, and events. An object is created in the program to represent a class. Therefore, an object encapsulates all the features, such as data and behavior that are associated to a class. OOP allows developers to develop modular programs and assemble them as software. Objects are used to access data and behaviors of different software modules, such as classes, namespaces, and sharable assemblies. .NET Framework supports only OOP languages, such as Visual Basic .NET, Visual C#, and Visual C++.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q3: What is encapsulation? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Encapsulation** is defined _as the process of enclosing one or more items within a physical or logical package_. Encapsulation, in object oriented programming methodology, prevents access to implementation details.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q4: What is polymorphism? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The word polymorphism means having many forms. In object-oriented programming paradigm, polymorphism is often expressed as _one interface, multiple functions_.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q5: What is the difference between procedural and object-oriented programming? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Procedural programming is based upon the modular approach in which the larger programs are broken into procedures. Each procedure is a set of instructions that are executed one after another. On the other hand, OOP is based upon objects. An object consists of various elements, such as methods and variables.
Access modifiers are not used in procedural programming, which implies that the entire data can be accessed freely anywhere in the program. In OOP, you can specify the scope of a particular data by using access modifiers - _public_, _private_, _internal_, _protected_, and _protected_ internal.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q6: Explain the concept of constructor? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Constructor** is a special method of a class, which is called automatically when the instance of a class is created. It is created with the same name as the class and initializes all class members, whenever you access the class. The main features of a constructor are as follows:
* Constructors do not have any return type.
* Constructors can be overloaded.
* It is not mandatory to declare a constructor; it is invoked automatically by .NET Framework.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q7: Why is the virtual keyword used in code? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The `virtual` keyword is used while defining a class to specify that the methods and the properties of that class can be overridden in derived classes.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q8: What is the difference between a class and a structure? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Class**:
* A class is a reference type.
* While instantiating a class, CLR allocates memory for its instance in heap.
* Classes support inheritance.
* Variables of a class can be assigned as null.
* Class can contain constructor/destructor.
**Structure**:
* A structure is a value type.
* In structure, memory is allocated on stack.
* Structures do not support inheritance.
* Structure members cannot have null values.
* Structure does not require constructor/destructor and members can be initialiazed automatically.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q9: What is the relationship between a class and an object? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A class acts as a blue-print that defines the properties, states, and behaviors that are common to a number of objects. An object is an instance of the class. For example, you have a class called _Vehicle_ and _Car_ is the object of that class. You can create any number of objects for the class named _Vehicle_, such as _Van_, _Truck_, and _Auto_.
The _new_ operator is used to create an object of a class. When an object of a class is instantiated, the system allocates memory for every data member that is present in the class.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q10: When should I use a struct instead of a class? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Do not define a structure unless the type has all of the following characteristics:
* It logically represents a single value, similar to primitive types (integer, double, and so on).
* It has an instance size smaller than 16 bytes.
* It is immutable.
* It will not have to be boxed frequently.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q11: What is polymorphism, what is it for, and how is it used? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Polymorphism describes a pattern in object oriented programming in which classes have different functionality while sharing a common interface.
The beauty of polymorphism is that the code working with the different classes does not need to know which class it is using since they’re all used the same way. A real world analogy for polymorphism is a button. Everyone knows how to use a button: you simply apply pressure to it. What a button “does,” however, depends on what it is connected to and the context in which it is used — but the result does not affect how it is used. If your boss tells you to press a button, you already have all the information needed to perform the task.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q12: What do you mean by data encapsulation? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Data encapsulation** is a concept of binding data and code in single unit called object and hiding all the implementation details of a class from the user. It prevents unauthorized access of data and restricts the user to use the necessary data only.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q13: What are abstract classes? What are the distinct characteristics of an abstract class? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An abstract class is a class that cannot be instantiated and is always used as a base class.
The following are the characteristics of an abstract class:
* You cannot instantiate an abstract class directly. This implies that you cannot create an object of the abstract class; it must be inherited.
* You can have abstract as well as non-abstract members in an abstract class.
* You must declare at least one abstract method in the abstract class.
* An abstract class is always public.
* An abstract class is declared using the _abstract_ keyword.
The basic purpose of an abstract class is to provide a common definition of the base class that multiple derived classes can share.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q14: What are similarities between a class and a structure? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The following are some of the similarities between a class and a structure:
* Access specifiers, such as _public_, _private_, and _protected_, are identically used in structures and classes to restrict the access of their data and methods outside their body.
* The access level for class members and struct members, including nested classes and structs, is private by default. Private nested types are not accessible from outside the containing type.
* Both can have constructors, methods, properties, fields, constants, enumerations, events, and event handlers.
* Both structures and classes can implement interfaces to use multiple-inheritance in code.
* Both structures and classes can have constructors with parameter.
* Both structures and classes can have delegates and events.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q15: How can you prevent a class from overriding in C#? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
You can prevent a class from overriding in C# by using the `sealed` keyword.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q16: How is method overriding different from method overloading? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Overriding** involves the creation of two or more methods with the same name and same signature in different classes (one of them should be parent class and other should be child).
* **Overloading** is a concept of using a method at different places with same name and different signatures within the same class.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q17: Can you specify the accessibility modifier for methods inside the interface? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
All the methods inside an interface are always `public`, by default. You cannot specify any other access modifier for them.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q18: Is it possible for a class to inherit the constructor of its base class? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
No, a class cannot inherit the constructor of its base class.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q19: What is the difference between cohesion and coupling? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: What's the advantage of using getters and setters - that only get and set - instead of simply using public fields for those variables? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: What exactly is the difference between an interface and abstract class? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: What is Coupling in OOP? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: What is Cohesion in OOP? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: Explain the concept of destructor? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: Differentiate between an abstract class and an interface. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: What is a static constructor? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: Explain different types of inheritance. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: Does .NET support multiple inheritance? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: Can you declare an overridden method to be static if the original method is not static? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: Why Doesn't C# Allow Static Methods to Implement an Interface? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: What is the difference between a mixin and inheritance? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: In terms that an OOP programmer would understand (without any functional programming background), what is a monad? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: What is LSP (Liskov Substitution Principle) and what are some examples of its use (good and bad)? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q34: Could you elaborate Polymorphism vs Overriding vs Overloading? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q35: What does it mean to “program to an interface”? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q36: Can you provide a simple explanation of methods vs. functions in OOP context? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q37: Why prefer composition over inheritance? What trade-offs are there for each approach? When should you choose inheritance over composition? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q38: What is the difference between association, aggregation and composition? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q39: Can you declare a private class in a namespace? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q40: You have defined a destructor in a class that you have developed by using the C# programming language, but the destructor never executed. Why did the destructor not execute? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 40 Common ADO.NET Interview Questions to Know in 2019
> Originally published on 👉 40 Common ADO.NET Interview Questions to Know in 2019 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is ADO.NET? ⭐
**Answer:**
**ADO** stands for Active Data Object and ADO.NET is a set of .NET libraries for ADO.
NET is a collection of managed libraries used by .NET applications for data source communication using a driver or provider:
* Enterprise applications handle a large amount of data. This data is primarily stored in relational databases, such as Oracle, SQL Server, and Access and so on. These databases use Structured Query Language (SQL) for retrieval of data.
* To access enterprise data from a .NET application, an interface was needed. This interface acts as a bridge between an RDBMS system and a .NET application. ADO.NET is such an interface that is created to connect .NET applications to RDBMS systems.
* In the .NET framework, Microsoft introduced a new version of Active X Data Objects (ADO) called ADO.NET. Any .NET application, either Windows based or web based, can interact with the database using a rich set of classes of the ADO.NET library. Data can be accessed from any database using connected or disconnected architecture.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q2: What do you understand by DataRelation class? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **DataRelation** is a class of disconnected architecture in the .NET framework. It is found in the System.Data namespace. It represents a relationship between database tables and correlates tables on the basis of matching column.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q3: Describe when you would use the DataView in ADO.NET? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **DataView** enables you to create different views of the data stored in a DataTable, a capability that is often used in data binding applications. Using a DataView, you can expose the data in a table with different sort orders, and you can filter the data by row state or based on a filter expression. A DataView provides a dynamic view of data whose content, ordering, and membership reflect changes to the underlying DataTable as they occur. This is different from the Select method of the DataTable, which returns a DataRow array from a table per particular filter and/or sort order and whose content reflects changes to the underlying table, but whose membership and ordering remain static. The dynamic capabilities of the DataView make it ideal for data-binding applications.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q4: What is the SqlCommandBuilder? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**CommandBuilder** helps you to generate update, delete, and insert commands on a single database table for a data adapter. Similar to other objects, each data provider has a command builder class. The OleDbCommandBuilder, SqlCommonBuilder, and OdbcCommandBuilder classes represent the CommonBuilder object in the OleDb, Sql, and ODBC data providers.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q5: What is the basic difference between ADO.NET and Entity Framework? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ADO.NET Entity Framework is an ORM (object-relational mapping) which creates a higher abstract object model over ADO.NET components. ADO.NET is a layer closer to the database (datatables, datasets and etc...). The main and the only benefit of EF is it auto-generates code for the Model (middle layer), Data Access Layer, and mapping code, thus reducing a lot of development time. Consider the following example:
**ADO.NET**:
```csharp
DataTable table = adoDs.Tables[0];
for (int j = 0; j < table.Rows.Count; j++)
{
DataRow row = table.Rows[j];
// Get the values of the fields
string CustomerName =
(string)row["Customername"];
string CustomerCode =
(string)row["CustomerCode"];
}
```
**EF**:
```csharp
foreach (Customer objCust in obj.Customers)
{}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q6: What is SqlCommand Object? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **SqlCommand** carries the SQL statement that needs to be executed on the database. SqlCommand carries the command in the CommandText property and this property will be used when the SqlCommand calls any of its execute methods.
* The Command Object uses the connection object to execute SQL queries.
* The queries can be in the form of Inline text, Stored Procedures or direct Table access.
* An important feature of Command object is that it can be used to execute queries and Stored Procedures with Parameters.
* If a select query is issued, the result set it returns is usually stored in either a DataSet or a DataReader object.
The three important methods exposed by the SqlCommand object is shown below:
* ExecuteScalar
* ExecuteNonQuery
* ExecuteReader
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q7: What is Connection Pooling in ADO.NET? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ADO.NET uses a technique called **connection pooling**, which minimizes the cost of repeatedly opening and closing connections. Connection pooling reuses existing active connections with the same connection string instead of creating new connections when a request is made to the database. It involves the use of a connection manager that is responsible for maintaining a list, or pool, of available connections for a given connection string. Several pools exist if different connection strings ask for connection pooling.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q8: How can you define the DataSet structure? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **DataSet** object falls in disconnected components series. The `DataSet` consists of a collection of tables, rows, columns and relationships.
`DataSet` contains a collection of `DataTables` and the `DataTable` contains a collection of `DataRows`, `DataRelations`, and `DataColumns`. A `DataTable` maps to a table in the database.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q9: What are the ADO.NET components? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ADO.NET components categorized in three modes:
* disconnected,
* common or shared and
* the .NET data providers.
The disconnected components build the basic ADO.NET architecture. You can use these components (or classes) with or without data providers. For example, you can use a `DataTable` object with or without providers and shared or common components are the base classes for data providers. Shared or common components are the base classes for data providers and shared by all data providers. The data provider components are specifically designed to work with different kinds of data sources. For example, ODBC data providers work with ODBC data sources and OleDb data providers work with OLE-DB data sources.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q10: What is exactly meaning of disconnected and connected approach in ADO.NET? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In short:
* **Disconnected** = Make Connection , Fetch Data , Close Connection
* **Connected** = Make Connection , Keep Connection alive , Close Connection when close is called.
The ADO.net architecture, in which connection must be kept open till the end to retrieve and access data from database is called as _connected architecture_. Connected architecture is built on the these types - `connection`, `command`, `datareader`
The ADO.net architecture, in which connection will be kept open only till the data retrieved from database, and later can be accessed even when connection to database is closed is called as _disconnected architecture_. Disconnected architecture of ADO.net is built on these types - `connection`, `dataadapter`, `commandbuilder` and `dataset` and `dataview`.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q11: Mention what is the difference between ADO.NET and classic ADO? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* In NET, we have data-set while ADO we have record-set
* In record-set we can only have one table and to insert more than one table you have to do inner join. While the dataset in ADO.NET can have multiple tables
* In NET, all data persist in XML while in classic ADO the data persists in binary format also
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q12: Could you explain me some of the main differences between Connection-oriented access and connectionless access in ADO.NET? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Connection Oriented means** : connection is exist throw out your process.
Example : using DataReader in Ado.Net you can get data as connection oriented database connection type.
* **Connection Less means** : Your connection is not available throw out your whole process.
Example: using DataAdapter in Ado.Net you can get data as connection less database connection type.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q13: What is the difference between Integrated Security = True and Integrated Security = SSPI? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
To connect to the database server is recommended to use Windows Authentication, commonly known as _integrated security_. To specify the Windows authentication, you can use any of the following two key-value pairs with the data provider. NET Framework for SQL Server:
```sh
Integrated Security = true;
Integrated Security = SSPI;
```
However, only the second works with the data provider *.NET Framework OleDb*. If you set `Integrated Security = true` for ConnectionString an exception is thrown.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q14: What is Unit Of Work? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Unit of Work** is referred to as a single transaction that involves multiple operations of insert/update/delete and so on kinds. To say it in simple words, it means that for a specific user action (say registration on a website), all the transactions like insert/update/delete and so on are done in one single transaction, rather than doing multiple database transactions.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q15: How could you control connection pooling behavior? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
You can manage connection pools using certain keywords in your connection string. The important ones include the following:
* ConnectionTimeout -- this is used to specify the wait period (in seconds) when a new database connection is requested for. The default value is 15.
* MinPoolSize -- this represents the minimum number of connections in the pool.
* MaxPoolSize -- this represents the maximum number of connections in the pool. The default value is 100.
* Pooling -- this controls if connection pooling is turned on or off and can have a value of true of false. When this is set to true, the requested connection is retrieved from the appropriate connection pool.
**Source:** _infoworld.com_
#### Q16: What are the differences between using SqlDataAdapter vs SqlDataReader for getting data from a DB? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**SqlDataReader**:
* Holds the connection open until you are finished (don't forget to close it or use using).
* Can typically only be iterated over once
* Is not as useful for updating back to the database
On the other hand, it:
* Only has one record in memory at a time rather than an entire result set (this can be huge)
* Is about as fast as you can get for that one iteration
* Allows you start processing results sooner (once the first record is available)
**SqlDataAdapter/DataSet**:
* Lets you close the connection as soon it's done loading data, and may even close it for you automatically
* All of the results are available in memory
* You can iterate over it as many times as you need, or even look up a specific record by index
* Has some built-in faculties for updating back to the database
At the cost of:
* _Much_ higher memory use
* You wait until all the data is loaded before using any of it
So really it depends on what you're doing, but I tend to prefer a DataReader until I need something that's only supported by a dataset. SqlDataReader is perfect for the common data access case of binding to a read-only grid.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q17: What is the difference between DataView, DataTable and DataSet? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* A **DataTable** is a collection of DataRows whose DataColumns satisfy a particular schema and may be subject to certain Constraints. As such, it is normally used as an 'in memory' representation of the rows, columns and constraints of a relational database table.
* A **DataSet** is a collection of DataTables and DataRelations between them. As such, it can be used to represent all the tables within a relational database file and the parent/child relationships between them.
* A **DataView** is a customized view of a DataTable for sorting, filtering, searching, editing, and navigation. It corresponds to a view (i.e. a virtual table produced by a query) in a relational database.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q18: What is the difference between ExecuteScalar, ExecuteReader and ExecuteNonQuery? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* `ExecuteScalar` is typically used when your query returns a single value. If it returns more, then the result is the first column of the first row. An example might be `SELECT @@IDENTITY AS 'Identity'`.
* `ExecuteReader` is used for any result set with multiple rows/columns (e.g., `SELECT col1, col2 from sometable`).
* `ExecuteNonQuery` is typically used for SQL statements without results (e.g., UPDATE, INSERT, etc.).
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q19: What is the difference between OLE DB and ODBC data sources? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: What is the difference between ADODB, OLEDB and ADO.NET? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: How could you monitor connection pooling behavior? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: Can you explain the difference between a DataReader, a DataAdapter, a Dataset, and a DataView? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: Where should I use disconnected architecture approach? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: Where should I use connected architecture approach? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: Is there anything faster than SqlDataReader in .NET? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: Is it necessary to manually close and dispose of SqlDataReader? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: What's better: DataSet or DataReader? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: Could you explain some benefits of Repository Pattern? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: Name types of transactions in ADO.NET ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: Name some problems that could occur with connection pooling ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: What are the advantages of using Stored Procedures? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Stored procedure can reduced network traffic and latency, boosting application performance.
* Stored procedure execution plans can be reused, staying cached in SQL Server's memory, reducing server overhead.
* Stored procedures help promote code reuse.
* Stored procedures can encapsulate logic. You can change stored procedure code without affecting clients.
* Stored procedures provide better security to your data.
**Source:** _github.com/dhaval1406_
#### Q32: What is Denormalization? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It is the process of improving the performance of the database by _adding_ redundant data.
**Source:** _github.com/dhaval1406_
#### Q33: Define ACID Properties ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Atomicity**: It ensures all-or-none rule for database modifications.
* **Consistency**: Data values are consistent across the database.
* **Isolation**: Two transactions are said to be independent of one another.
* **Durability**: Data is not lost even at the time of server failure.
**Source:** _github.com/chetansomani_
#### Q34: How do I UPDATE from a SELECT in SQL Server? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
```sql
UPDATE
Table_A
SET
Table_A.col1 = Table_B.col1,
Table_A.col2 = Table_B.col2
FROM
Some_Table AS Table_A
INNER JOIN Other_Table AS Table_B
ON Table_A.id = Table_B.id
WHERE
Table_A.col3 = 'cool'
```
or using `MERGE`:
```sql
MERGE INTO YourTable T
USING other_table S
ON T.id = S.id
AND S.tsql = 'cool'
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE
SET col1 = S.col1,
col2 = S.col2;
```
**Source:** _github.com/chetansomani_
#### Q35: Discuss INNER JOIN ON vs WHERE clause ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
You can do:
```sql
SELECT
table1.this, table2.that, table2.somethingelse
FROM
table1, table2
WHERE
table1.foreignkey = table2.primarykey
AND (some other conditions)
```
Or else:
```sql
SELECT
table1.this, table2.that, table2.somethingelse
FROM
table1 INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.foreignkey = table2.primarykey
WHERE
(some other conditions)
```
What syntax would you choose and why?
**Answer:**
`INNER JOIN` is ANSI syntax which you should use. INNER JOIN helps human readability, and that's a top priority. It can also be easily replaced with an OUTER JOIN whenever a need arises.
Implicit joins (with multiple `FROM` tables) become much much more confusing, hard to read, and hard to maintain once you need to start adding more tables to your query.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q36: How to generate row number in SQL Without ROWNUM ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q37: How does truncate and delete operation effect Identity? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q38: What is Optimistic Locking and Pessimistic locking? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q39: How does database indexing work? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q40: What are some other types of indexes? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 42 Advanced Java Interview Questions For Senior Developers
> Originally published on 👉 42 Advanced Java Interview Questions For Senior Developers | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is the difference between an Interface and an Abstract class? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Java provides and supports the creation both of **abstract** classes and **interfaces**. Both implementations share some common characteristics, but they differ in the following features:
* All methods in an interface are implicitly abstract. On the other hand, an abstract class may contain both abstract and non-abstract methods.
* A class may implement a number of Interfaces, but can extend only one abstract class.
* In order for a class to implement an interface, it must implement all its declared methods. However, a class may not implement all declared methods of an abstract class. Though, in this case, the sub-class must also be declared as abstract.
* Abstract classes can implement interfaces without even providing the implementation of interface methods.
* Variables declared in a Java interface is by default final. An abstract class may contain non-final variables.
* Members of a Java interface are public by default. A member of an abstract class can either be private, protected or public.
* An interface is absolutely abstract and cannot be instantiated. An abstract class also cannot be instantiated, but can be invoked if it contains a main method.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q2: What differences exist between HashMap and Hashtable? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are several differences between `HashMap` and `Hashtable` in Java:
1. `Hashtable` is synchronized, whereas `HashMap` is not. This makes `HashMap` better for non-threaded applications, as unsynchronized Objects typically perform better than synchronized ones.
2. `Hashtable` does not allow `null` keys or values. `HashMap` allows one `null` key and any number of `null` values.
3. One of HashMap's subclasses is `LinkedHashMap`, so in the event that you'd want predictable iteration order (which is insertion order by default), you could easily swap out the `HashMap` for a `LinkedHashMap`. This wouldn't be as easy if you were using `Hashtable`.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q3: What is the difference between Exception and Error in java? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* An **Error** "indicates serious problems that a reasonable application should not try to catch."
* An **Exception** "indicates conditions that a reasonable application might want to catch."
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q4: How does Garbage Collection prevent a Java application from going out of memory? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It doesn’t! Garbage Collection simply cleans up unused memory when an object goes out of scope and is no longer needed. However an application could create a huge number of large objects that causes an `OutOfMemoryError`.
**Source:** _codementor.io_
#### Q5: What is reflection and why is it useful? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The name **reflection** is used to describe code which is able to inspect other code in the same system (or itself) and to make modifications at runtime.
For example, say you have an object of an unknown type in Java, and you would like to call a 'doSomething' method on it if one exists. Java's static typing system isn't really designed to support this unless the object conforms to a known interface, but using reflection, your code can look at the object and find out if it has a method called 'doSomething' and then call it if you want to.
```java
Method method = foo.getClass().getMethod("doSomething", null);
method.invoke(foo, null);
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q6: What is Function Overriding and Overloading in Java? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Method **overloading** in Java occurs when two or more methods in the same class have the exact same name, but different parameters.
```java
class Dog{
public void bark(){
System.out.println("woof ");
}
//overloading method
public void bark(int num){
for(int i=0; iFullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: What is the difference between Serial and Throughput Garbage collector? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: Given two double values d1, d2, what is the most reliable way to test their equality? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: Explain Marshalling and demarshalling. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: Why is char[] preferred over String for passwords? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Why does `String` pose a threat to security when it comes to passwords? It feels inconvenient to use `char[]`?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: When to use LinkedList over ArrayList in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: What is Double Brace initialization in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: Is it possible to call one constructor from another in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Is it possible to call a constructor from another (within the same class, not from a subclass)? If yes how?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: Does Java support default parameter values? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: Explain a use case for the Builder Design Pattern ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: Is null check needed before calling instanceof? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Will
```java
null instanceof SomeClass
```
return `false` or throw a `NullPointerException`?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: What exactly is marker interface in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q34: What does 'synchronized' mean? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q35: Why ArrayList are preferable in many more use-cases than LinkedList? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q36: What's wrong with Double Brace initialization in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q37: Provide some examples when a finally block won't be executed in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q38: Explain what will the code return ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider:
```java
try { return true; } finally { return false; }
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q39: What is an efficient way to implement a singleton pattern in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q40: What's the difference between SoftReference and WeakReference in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q41: Why isn’t String‘s .length() accurate? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q42: Compare volatile vs static variables in Java ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 45 Important PHP Interview Questions That May Land You a Job
> Originally published on 👉 45 Important PHP Interview Questions That May Land You a Job | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is the difference between == and ===? ⭐
**Answer:**
* The operator `==` casts between two different types if they are different
* The `===` operator performs a '_typesafe comparison_'
That means that it will only return true if both operands have the same type and the same value.
```php
1 === 1: true
1 == 1: true
1 === "1": false // 1 is an integer, "1" is a string
1 == "1": true // "1" gets casted to an integer, which is 1
"foo" === "foo": true // both operands are strings and have the same value
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q2: How can you pass a variable by reference? ⭐
**Answer:**
To be able to pass a variable by **reference**, we use an _ampersand_ in front of it, as follows:
```php
$var1 = &$var2
```
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q3: What does $GLOBALS mean? ⭐
**Answer:**
`$GLOBALS` is associative array including references to all variables which are currently defined in the global scope of the script.
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q4: What is the use of ini_set()? ⭐
**Answer:**
PHP allows the user to modify some of its settings mentioned in php.ini using ini_set(). This function requires two string arguments. First one is the name of the setting to be modified and the second one is the new value to be assigned to it.
Given line of code will enable the display_error setting for the script if it’s disabled.
`ini_set('display_errors', '1');`
We need to put the above statement, at the top of the script so that, the setting remains enabled till the end. Also, the values set via ini_set() are applicable, only to the current script. Thereafter, PHP will start using the original values from php.ini.
**Source:** _github.com/Bootsity_
#### Q5: When should I use require vs. include? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The `require()` function is identical to `include()`, except that it handles errors differently. If an error occurs, the `include()` function generates a warning, but the script will continue execution. The `require()` generates a fatal error, and the script will stop.
My suggestion is to just use `require_once` 99.9% of the time.
Using `require` or `include` instead implies that your code is not **reusable** elsewhere, i.e. that the scripts you're pulling in actually execute code instead of making available a class or some function libraries.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q6: What is stdClass in PHP? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`stdClass` is just a generic 'empty' class that's used when casting other types to objects. `stdClass` is **not** the base class for objects in PHP. This can be demonstrated fairly easily:
```js
class Foo{}
$foo = new Foo();
echo ($foo instanceof stdClass)?'Y':'N'; // outputs 'N'
```
It is useful for anonymous objects, dynamic properties, etc.
An easy way to consider the `StdClass` is as an alternative to associative array. See this example below that shows how `json_decode()` allows to get an StdClass instance or an associative array.
Also but not shown in this example, `SoapClient::__soapCall` returns an `StdClass` instance.
```js
//Example with StdClass
$json = '{ "foo": "bar", "number": 42 }';
$stdInstance = json_decode($json);
echo $stdInstance - > foo.PHP_EOL; //"bar"
echo $stdInstance - > number.PHP_EOL; //42
//Example with associative array
$array = json_decode($json, true);
echo $array['foo'].PHP_EOL; //"bar"
echo $array['number'].PHP_EOL; //42
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q7: What are the differences between die() and exit() functions in PHP? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There's no difference - they are the same. The only advantage of choosing `die()` over `exit()`, might be the time you spare on typing an extra letter.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q8: What are the main differences between const vs define ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The fundamental difference between `const` vs `define` is that `const` defines constants at compile time, whereas `define` defines them at run time.
```php
const FOO = 'BAR';
define('FOO', 'BAR');
// but
if (...) {
const FOO = 'BAR'; // Invalid
}
if (...) {
define('FOO', 'BAR'); // Valid
}
```
Also until PHP 5.3, `const` could not be used in the global scope. You could only use this from within a class. This should be used when you want to set some kind of constant option or setting that pertains to that class. Or maybe you want to create some kind of enum. An example of good `const` usage is to get rid of magic numbers.
`Define` can be used for the same purpose, but it can only be used in the global scope. It should only be used for global settings that affect the entire application.
Unless you need any type of conditional or expressional definition, use `consts` instead of `define() `- simply for the sake of readability!
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q9: What's the difference between isset() and array_key_exists()? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* `array_key_exists` will tell you if a key exists in an array and complains when `$a` does not exist.
* `isset` will only return `true` if the key/variable exists **and is not `null`**. `isset` doesn't complain when `$a` does not exist.
Consider:
```js
$a = array('key1' => 'Foo Bar', 'key2' => null);
isset($a['key1']); // true
array_key_exists('key1', $a); // true
isset($a['key2']); // false
array_key_exists('key2', $a); // true
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q10: What is the difference between var_dump() and print_r()? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* The `var_dump` function displays structured information about variables/expressions including its **type** and **value**. Arrays are explored recursively with values indented to show structure. It also shows which array values and object properties are references.
* The `print_r()` displays information about a variable in a way that's readable by humans. array values will be presented in a format that shows keys and elements. Similar notation is used for objects.
Consider:
```php
$obj = (object) array('qualitypoint', 'technologies', 'India');
```
`var_dump($obj) `will display below output in the screen:
```
object(stdClass)#1 (3) {
[0]=> string(12) "qualitypoint"
[1]=> string(12) "technologies"
[2]=> string(5) "India"
}
```
And, `print_r($obj)` will display below output in the screen.
```
stdClass Object (
[0] => qualitypoint
[1] => technologies
[2] => India
)
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q11: Explain what the different PHP errors are ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* A `notice` is a non-critical error saying something went wrong in execution, something minor like an undefined variable.
* A `warning` is given when a more critical error like if an include() command went to retrieve a non-existent file. In both this and the error above, the script would continue.
* A `fatal error` would terminate the code. Failure to satisfy a require() would generate this type of error, for example.
**Source:** _pangara.com_
#### Q12: How can you enable error reporting in PHP? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Check if “`display_errors`” is equal “on” in the php.ini or declare “`ini_set('display_errors', 1)`” in your script.
Then, include “`error_reporting(E_ALL)`” in your code to display all types of error messages during the script execution.
**Source:** _codementor.io_
#### Q13: Declare some function with default parameter ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Consider:
```php
function showMessage($hello = false){
echo ($hello) ? 'hello' : 'bye';
}
```
**Source:** _codementor.io_
#### Q14: Is multiple inheritance supported in PHP? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
PHP supports only single inheritance; it means that a class can be extended from only one single class using the keyword 'extended'.
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q15: In PHP, objects are they passed by value or by reference? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In PHP, objects passed by **value**.
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q16: What is the differences between $a != $b and $a !== $b? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`!=` means _inequality_ (TRUE if $a is not equal to $b) and `!==` means _non-identity_ (TRUE if $a is not identical to $b).
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q17: What is PDO in PHP? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**PDO** stands for PHP Data Object.
It is a set of PHP extensions that provide a core PDO class and database, specific drivers. It provides a vendor-neutral, lightweight, data-access abstraction layer. Thus, no matter what database we use, the function to issue queries and fetch data will be same. It focuses on data access abstraction rather than database abstraction.
**Source:** _github.com/Bootsity_
#### Q18: Explain how we handle exceptions in PHP? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
When an exception is thrown, code following the statement will not be executed, and PHP will attempt to find the first matching catch block. If an exception is not caught, a PHP Fatal Error will be issued with an "Uncaught Exception".
An exception can be thrown, and caught within PHP.
To handle exceptions, code may be surrounded in a `try` block.
Each try must have at least one corresponding `catch` block. Multiple catch blocks can be used to catch different classes of exceptions.
Exceptions can be thrown (or re-thrown) within a catch block.
Consider:
```php
try {
print "this is our try block n";
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception $e) {
print "something went wrong, caught yah! n";
} finally {
print "this part is always executed n";
}
```
**Source:** _github.com/Bootsity_
#### Q19: Differentiate between echo and print() ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`echo` and `print` are more or less the same. They are both used to output data to the screen.
The differences are:
- echo has no return value while print has a return value of 1 so it can be used in expressions.
- echo can take multiple parameters (although such usage is rare) while print can take one argument.
- echo is faster than print.
**Source:** _github.com/Bootsity_
#### Q20: When should I use require_once vs. require? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The `require_once()` statement is identical to `require()` except PHP will check if the file has already been included, and if so, not include (require) it again.
My suggestion is to just use `require_once` 99.9% of the time.
Using `require` or `include` instead implies that your code is not **reusable** elsewhere, i.e. that the scripts you're pulling in actually execute code instead of making available a class or some function libraries.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q21: Check if PHP array is associative ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Consider:
```php
function has_string_keys(array $array) {
return count(array_filter(array_keys($array), 'is_string')) > 0;
}
```
If there is at least one string key, `$array` will be regarded as an _associative array_.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q22: How do I pass variables and data from PHP to JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are actually several approaches to do this:
* Use AJAX to get the data you need from the server.
Consider **get-data.php**:
```php
echo json_encode(42);
```
Consider **index.html:**
```js
function reqListener () {
console.log(this.responseText);
}
var oReq = new XMLHttpRequest(); // New request object
oReq.onload = function() {
// This is where you handle what to do with the response.
// The actual data is found on this.responseText
alert(this.responseText); // Will alert: 42
};
oReq.open("get", "get-data.php", true);
// ^ Don't block the rest of the execution.
// Don't wait until the request finishes to
// continue.
oReq.send();
```
* Echo the data into the page somewhere, and use JavaScript to get the information from the DOM.
```php
var div = document.getElementById("dom-target");
var myData = div.textContent;
```
* Echo the data directly to JavaScript.
```php
var data = <?php echo json_encode("42", JSON_HEX_TAG); ?>; // Don't forget the extra semicolon!
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q23: Is there a function to make a copy of a PHP array to another? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In PHP arrays are assigned by copy, while objects are assigned by reference so PHP will copy the array by default. References in PHP have to be explicit:
```php
$a = array(1,2);
$b = $a; // $b will be a different array
$c = &$a; // $c will be a reference to $a
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q24: What will be returned by this code? ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider the code:
```php
$a = new stdClass();
$a->foo = "bar";
$b = clone $a;
var_dump($a === $b);
```
What will be echoed to the console?
**Answer:**
Two instances of the same class with equivalent members do NOT match the `===` operator. So the answer is:
```php
bool(false)
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q25: What will be returned by this code? Explain the result. ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider the code. What will be returned as a result?
```php
$something = 0;
echo ('password123' == $something) ? 'true' : 'false';
```
**Answer:**
The answer is `true`. You should never use `==` for string comparison. Even if you are comparing strings to strings, PHP will implicitly cast them to floats and do a numerical comparison if they appear numerical. `===` is OK.
For example
```php
'1e3' == '1000' // true
```
also returns true.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q26: What exactly is the the difference between array_map, array_walk and array_filter? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* `array_walk` takes an array and a function F and modifies it by replacing every element x with F(x).
* `array_map` does the exact same thing **except** that instead of modifying in-place it will return a new array with the transformed elements.
* `array_filter` with function F, instead of transforming the elements, will remove any elements for which F(x) **is not true**
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q27: Explain the difference between exec() vs system() vs passthru()? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* `exec()` is for calling a system command, and perhaps dealing with the output yourself.
* `system()` is for executing a system command and immediately displaying the output - presumably text.
* `passthru()` is for executing a system command which you wish the raw return from - presumably something binary.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q28: How would you create a Singleton class using PHP? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
```php
/**
* Singleton class
*
*/
final class UserFactory {
/**
* Call this method to get singleton
*
* @return UserFactory
*/
public static
function Instance() {
static $inst = null;
if ($inst === null) {
$inst = new UserFactory();
}
return $inst;
}
/**
* Private ctor so nobody else can instantiate it
*
*/
private
function __construct() {
}
}
```
To use:
```php
$fact = UserFactory::Instance();
$fact2 = UserFactory::Instance();
```
But:
```php
$fact = new UserFactory()
```
Throws an error.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q29: What is the difference between PDO's query() vs execute()? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* `query` runs a standard SQL statement and requires you to properly escape all data to avoid SQL Injections and other issues.
* `execute` runs a prepared statement which allows you to bind parameters to avoid the need to escape or quote the parameters. execute will also perform better if you are repeating a query multiple times.
Best practice is to stick with prepared statements and execute for increased _security_. Aside from the escaping on the client-side that it provides, a _prepared statement is compiled_ on the server-side once, and then can be passed different parameters at each execution.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q30: What is use of Null Coalesce Operator? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Null coalescing operator returns its first operand if it exists and is not NULL. Otherwise it returns its second operand.
Example:
```php
$name = $firstName ?? $username ?? $placeholder ?? "Guest";
```
**Source:** _github.com/Bootsity_
#### Q31: Differentiate between exception and error ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
- Recovering from `Error` is not possible. The only solution to errors is to terminate the execution. Where as you can recover from `Exception` by using either try-catch blocks or throwing exception back to caller.
- You will not be able to handle the `Errors` using try-catch blocks. Even if you handle them using try-catch blocks, your application will not recover if they happen. On the other hand, `Exceptions` can be handled using try-catch blocks and can make program flow normal if they happen.
- `Exceptions` are related to application where as `Errors` are related to environment in which application is running.
**Source:** _github.com/Bootsity_
#### Q32: What are the exception class functions? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are following functions which can be used from `Exception` class.
* `getMessage()` − message of exception
* `getCode()` − code of exception
* `getFile()` − source filename
* `getLine()` − source line
* `getTrace()` − n array of the `backtrace()`
* `getTraceAsString()` − formated string of trace
* `Exception::__toString` gives the string representation of the exception.
**Source:** _github.com/Bootsity_
#### Q33: Differentiate between parameterised and non parameterised functions ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
- **Non parameterised functions** don't take any parameter at the time of calling.
- **Parameterised functions** take one or more arguments while calling. These are used at run time of the program when output depends on dynamic values given at run time
There are two ways to access the parameterised function:
1. _call by value_: (here we pass the value directly )
2. _call by reference_: (here we pass the address location where the value is stored)
**Source:** _github.com/Bootsity_
#### Q34: Explain function call by reference ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In case of call by reference, actual value is modified if it is modified inside the function. In such case, we need to use `&` symbol with formal arguments. The `&` represents reference of the variable.
Example:
```php
function adder(&$str2) {
$str2 .= 'Call By Reference';
}
$str = 'This is ';
adder($str);
echo $str;
```
Output:
```sh
This is Call By Reference
```
**Source:** _github.com/Bootsity_
#### Q35: Why do we use extract()? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The `extract()` function imports variables into the local symbol table from an array.
This function uses array keys as variable names and values as variable values. For each element it will create a variable in the current symbol table.
This function returns the number of variables extracted on success.
Example:
```php
$a = "Original";
$my_array = array("a" => "Cat","b" => "Dog", "c" => "Horse");
extract($my_array);
echo "\$a = $a; \$b = $b; \$c = $c";
```
Output:
```sh
$a = Cat; $b = Dog; $c = Horse
```
**Source:** _github.com/Bootsity_
#### Q36: explain what is a closure in PHP and why does it use the “use” identifier? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider this code:
```php
public function getTotal($tax)
{
$total = 0.00;
$callback =
function ($quantity, $product) use ($tax, &$total)
{
$pricePerItem = constant(__CLASS__ . "::PRICE_" .
strtoupper($product));
$total += ($pricePerItem * $quantity) * ($tax + 1.0);
};
array_walk($this->products, $callback);
return round($total, 2);
}
```
Could you explain why use it?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q37: What exactly are late static bindings in PHP? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q38: How to measure execution times of PHP scripts? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
I want to know how many milliseconds a PHP while-loop takes to execute. Could you help me?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q39: What is the best method to merge two PHP objects? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```php
//We have this:
$objectA->a;
$objectA->b;
$objectB->c;
$objectB->d;
//We want the easiest way to get:
$objectC->a;
$objectC->b;
$objectC->c;
$objectC->d;
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q40: Compare mysqli or PDO - what are the pros and cons? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q41: What is use of Spaceship Operator? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q42: Does PHP have threading? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q43: Is PHP single or multi threaded? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q44: Provide some ways to mimic multiple constructors in PHP ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
It's known you can't put two __construct functions with unique argument signatures in a PHP class but I'd like to do something like this:
```php
class Student
{
protected $id;
protected $name;
// etc.
public function __construct($id){
$this->id = $id;
// other members are still uninitialised
}
public function __construct($row_from_database){
$this->id = $row_from_database->id;
$this->name = $row_from_database->name;
// etc.
}
}
```
What is the best way to achieve this in PHP?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q45: How could we implement method overloading in PHP? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 5 Salary Negotiation Rules for Software Developers
> Originally published on 👉 5 Salary Negotiation Rules for Software Developers | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: career test ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
test
**Answer:**
test
## [[⬆]](#toc) 50 Common Front End Developer Interview Questions [2019 Edition]
> Originally published on 👉 50 Common Front End Developer Interview Questions [2019 Edition] | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: Explain the CSS “box model” and the layout components that it consists of ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The CSS box model is a rectangular layout paradigm for HTML elements that consists of the following:
* **Content** - The content of the box, where text and images appear
* **Padding** - A transparent area surrounding the content (i.e., the amount of space between the border and the content)
* **Border** - A border surrounding the padding (if any) and content
* **Margin** - A transparent area surrounding the border (i.e., the amount of space between the border and any neighboring elements)
**Source:** _toptal.com_
#### Q2: What is a CSS rule? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Web browsers apply **CSS rules** to a document to affect how they are displayed. A CSS rule is formed from:
* A **set of properties**, which have values set to update how the HTML content is displayed,
* A **selector**, which selects the element(s) you want to apply the updated property values to.
A set of CSS rules contained within a stylesheet determines how a webpage should look.
**Source:** _developer.mozilla.org_
#### Q3: What is Sass? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Sass** or **Syntactically Awesome StyleSheets** is a *CSS* preprocessor that adds power and elegance to the basic language. It allows you to use variables, nested rules, mixins, inline imports, and more, all with a fully CSS-compatible syntax. Sass helps keep large stylesheets well-organized, and get small stylesheets up and running quickly.
A *CSS preprocessor* is a scripting language that extends CSS by allowing developers to write code in one language and then compile it into CSS.
**Source:** _sass-lang.com_
#### Q4: What is a Mixin and how to use on? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **Mixin** is a block of code that lets us group CSS declarations we may reuse throughout our site.
To define mixin:
```css
@mixin grid($flex: true /*default argument*/) {
@if $flex {
@include flex;
} @else {
display: block;
}
}
```
To use a Mixin, we simply use `@include` followed by the name of the Mixin and a semi-colon.
```css
/*scss*/
.row {
@include grid(true);
}
/*css*/
.row {
display: -webkit-flex;
display: flex;
}
```
**Source:** _scotch.io_
#### Q5: What’s the difference between “resetting” and “normalizing” CSS? Which would you choose, and why? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Resetting** — is meant to strip all default browser styling on elements. For e.g. `margins`, `paddings`, `font-sizes` of all elements are reset to be the same. You will have to redeclare styling for common typographic elements.
* **Normalizing** — preserves useful default styles rather than “unstyling” everything. It also corrects bugs for common browser dependencies.
It's a good idea to choose resetting when you have very a customized or unconventional site design such that I need to do a lot of my own styling do not need any default styling to be preserved.
**Source:** _codeburst.io_
#### Q6: What is a Grid System in CSS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A grid system is a structure that allows for content to be stacked both vertically and horizontally in a consistent and easily manageable fashion. Grid systems include two key components: rows and columns.
Some Grid Systems:
* Simple Grid
* Pure
* Flexbox Grid
* Bootstrap
* Foundation
**Source:** _sitepoint.com_
#### Q7: Explain meta tags in HTML ⭐
**Answer:**
- **Meta tags** always go inside **head tag** of the HTML page
- **Meta tags** is always passed as name/value pairs
- **Meta tags** are not displayed on the page but intended for the browser
- **Meta tags** can contain information about **character encoding**, **description**, **title** of the document etc,
**Example**:
```html
Home Page
```
**Source:** _github.com/FuelFrontend_
#### Q8: What is the difference between span and div? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* `div` is a block element
* `span` is inline element
For bonus points, you could point out that it’s illegal to place a block element inside an inline element, and that while `div` can have a `p` tag, and a `p` tag can have a `span`, it is not possible for `span` to have a `div` or `p` tag inside.
**Source:** _thatjsdude.com_
#### Q9: What are `defer` and `async` attributes on a `` tag? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
If neither attribute is present, the script is downloaded and executed synchronously, and will halt parsing of the document until it has finished executing (default behavior). Scripts are downloaded and executed in the order
they are encountered.
The `defer` attribute downloads the script while the document is still parsing but waits until the document has finished parsing before executing it, equivalent to executing inside a `DOMContentLoaded` event listener. `defer` scripts will execute in order.
The `async` attribute downloads the script during parsing the document but will pause the parser to execute the script before it has fully finished parsing. `async` scripts will not necessarily execute in order.
Note: both attributes must only be used if the script has a `src` attribute (i.e. not an inline script).
```html
<script src="myscript.js">
```
**Source:** _growingwiththeweb.com_
#### Q10: What's new in HTML 5? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
HTML 5 adds a lot of new features to the HTML specification
**New Doctype**
Still using that pesky, impossible-to-memorize XHTML doctype?
```html
```
If so, why? Switch to the new HTML5 doctype. You'll live longer -- as Douglas Quaid might say.
```html
```
**New Structure**
- `` - to define sections of pages
- `` - defines the header of a page
- `` - defines the footer of a page
- `` - defines the navigation on a page
- `` - defines the article or primary content on a page
- `` - defines extra content like a sidebar on a page
- `` - defines images that annotate an article
**New Inline Elements**
These inline elements define some basic concepts and keep them semantically marked up, mostly to do with time:
- `` - to indicate content that is marked in some fashion
- `
**New Form Types**
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
**New Elements**
There are a few exciting new elements in HTML 5:
- `` - an element to give you a drawing space in JavaScript on your Web pages. It can let you add images or graphs to tool tips or just create dynamic graphs on your Web pages, built on the fly.
- `` - add video to your Web pages with this simple tag.
- `` - add sound to your Web pages with this simple tag.
**No More Types for Scripts and Links**
You possibly still add the `type` attribute to your `link` and `script` tags.
```html
```
This is no longer necessary. It's implied that both of these tags refer to stylesheets and scripts, respectively. As such, we can remove the `type` attribute all together.
```html
```
**Make your content editable**
The new browsers have a nifty new attribute that can be applied to elements, called `contenteditable`. As the name implies, this allows the user to edit any of the text contained within the element, including its children. There are a variety of uses for something like this, including an app as simple as a to-do list, which also takes advantage of local storage.
```html
To-Do List
- Break mechanical cab driver.
- Drive to abandoned factory
- Watch video of self
```
**Attributes**
- `require` to mention the form field is required
- `autofocus` puts the cursor on the input field
**Source:** _github.com/FuelFrontend_
#### Q11: What is Coercion in JavaScript?
**Answer:**
In JavaScript conversion between different two build-in types called `coercion`. Coercion comes in two forms in JavaScript: *explicit* and *implicit*.
Here's an example of explicit coercion:
```js
var a = "42";
var b = Number( a );
a; // "42"
b; // 42 -- the number!
```
And here's an example of implicit coercion:
```js
var a = "42";
var b = a * 1; // "42" implicitly coerced to 42 here
a; // "42"
b; // 42 -- the number!
```
#### Q12: What is Scope in JavaScript? ⭐
**Answer:**
In JavaScript, each function gets its own *scope*. Scope is basically a collection of variables as well as the rules for how those variables are accessed by name. Only code inside that function can access that function's scoped variables.
A variable name has to be unique within the same scope. A scope can be nested inside another scope. If one scope is nested inside another, code inside the innermost scope can access variables from either scope.
#### Q13: What is strict mode? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Strict Mode* is a new feature in ECMAScript 5 that allows you to place a program, or a function, in a "strict" operating context. This strict context prevents certain actions from being taken and throws more exceptions.
```js
// Non-strict code...
(function(){
"use strict";
// Define your library strictly...
})();
// Non-strict code...
```
#### Q14: What is IIFEs (Immediately Invoked Function Expressions)? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It’s an Immediately-Invoked Function Expression, or IIFE for short. It executes immediately after it’s created:
```js
(function IIFE(){
console.log( "Hello!" );
})();
// "Hello!"
```
This pattern is often used when trying to avoid polluting the global namespace, because all the variables used inside the IIFE (like in any other normal function) are not visible outside its scope.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q15: What is “closure” in javascript? Provide an example? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: Explain the Prototype Design Pattern ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q17: Compare SQL databases and MongoDB at a high level. ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
SQL databases store data in form of tables, rows, columns and records. This data is stored in a pre-defined data model which is not very much flexible for today's real-world highly growing applications. MongoDB in contrast uses a flexible structure which can be easily modified and extended.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q18: What is Node.js? ⭐
**Answer:**
Node.js is a web application framework built on Google Chrome's JavaScript Engine (V8 Engine).
Node.js comes with runtime environment on which a Javascript based script can be interpreted and executed (It is analogus to JVM to JAVA byte code). This runtime allows to execute a JavaScript code on any machine outside a browser. Because of this runtime of Node.js, JavaScript is now can be executed on server as well.
*Node.js = Runtime Environment + JavaScript Library*
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q19: What is npm? ⭐
**Answer:**
`npm` stands for Node Package Manager. npm provides following two main functionalities:
* Online repositories for node.js packages/modules which are searchable on [search.nodejs.org](http://search.nodejs.org)
* Command line utility to install packages, do version management and dependency management of Node.js packages.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q20: If Node.js is single threaded then how it handles concurrency? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Node provides a single thread to programmers so that code can be written easily and without bottleneck. Node internally uses multiple POSIX threads for various I/O operations such as File, DNS, Network calls etc.
When Node gets I/O request it creates or uses a thread to perform that I/O operation and once the operation is done, it pushes the result to the event queue. On each such event, event loop runs and checks the queue and if the execution stack of Node is empty then it adds the queue result to execution stack.
This is how Node manages concurrency.
**Source:** _codeforgeek.com_
#### Q21: What is Callback Hell? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The asynchronous function requires callbacks as a return parameter. When multiple asynchronous functions are chained together then callback hell situation comes up.
**Source:** _codeforgeek.com_
#### Q22: How can you avoid callback hells? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
To do so you have more options:
* **modularization**: break callbacks into independent functions
* use _Promises_
* use `yield` with _Generators_ and/or _Promises_
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q23: How would you scale Node application? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: What is encapsulation? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Encapsulation** is defined _as the process of enclosing one or more items within a physical or logical package_. Encapsulation, in object oriented programming methodology, prevents access to implementation details.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q25: What is polymorphism? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The word polymorphism means having many forms. In object-oriented programming paradigm, polymorphism is often expressed as _one interface, multiple functions_.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q26: What is ReactJS? ⭐
**Answer:**
ReactJS is an **open-source frontend JavaScript library** which is used for building user interfaces especifically for single page applications. It is used for handling view layer for web and mobile apps. React was created by Jordan Walke, a software engineer working for Facebook. ReactJS was first deployed on Facebook’s newsfeed in 2011 and on Instagram.com in 2012.
**Source:** _https://github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q27: What is the point of Redux? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Application state management that is easy to reason about, maintain and manage in an asynchronous web application environment.
**Source:** _github.com/WebPredict_
#### Q28: What is Flux? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Unidrectional application flow paradigm popular a few years back in React; mostly superceded by Redux these days.
**Source:** _github.com/WebPredict_
#### Q29: What are advantages of REST web services? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Some of the advantages of REST web services are:
* Learning curve is easy since it works on HTTP protocol
* Supports multiple technologies for data transfer such as text, xml, json, image etc.
* No contract defined between server and client, so loosely coupled implementation.
* REST is a lightweight protocol
* REST methods can be tested easily over browser.
**Source:** _journaldev.com_
#### Q30: Mention what is the difference between PUT and POST? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*PUT* puts a file or resource at a particular URI and exactly at that URI. If there is already a file or resource at that URI, PUT changes that file or resource. If there is no resource or file there, PUT makes one
*POST* sends data to a particular URI and expects the resource at that URI to deal with the request. The web server at this point can decide what to do with the data in the context of specified resource
*PUT is idempotent* meaning, invoking it any number of times will not have an impact on resources.
However, *POST is not idempotent*, meaning if you invoke POST multiple times it keeps creating more resources
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q31: Name some best practices for better RESTful API design ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: What is meant by the KISS principle? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**KISS**, a backronym for "keep it simple, stupid", is a design principle noted by the U.S. Navy in 1960. The KISS principle states that most systems work best if they are kept simple rather than made complicated; therefore simplicity should be a key goal in design, and that unnecessary complexity should be avoided.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q33: What Is Load Balancing? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Load balancing** is simple technique for distributing workloads across multiple machines or clusters. The most common and simple load balancing algorithm is Round Robin. In this type of load balancing the request is divided in circular order ensuring all machines get equal number of requests and no single machine is overloaded or underloaded.
**The Purpose of load balancing is to**
* Optimize resource usage (avoid overload and under-load of any machines)
* Achieve Maximum Throughput
* Minimize response time
**Most common load balancing techniques in web based applications are**
1. Round robin
2. Session affinity or sticky session
3. IP Address affinity
**Source:** _fromdev.com_
#### Q34: What does SOLID stand for? What are its principles? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**S.O.L.I.D** is an acronym for the first five object-oriented design (OOD) principles by Robert C. Martin.
* **S** - *Single-responsiblity principle*. A class should have one and only one reason to change, meaning that a class should have only one job.
* **O** - *Open-closed principle*. Objects or entities should be open for extension, but closed for modification.
* **L** - *Liskov substitution principle*. Let q(x) be a property provable about objects of x of type T. Then q(y) should be provable for objects y of type S where S is a subtype of T.
* **I** - *Interface segregation principle*. A client should never be forced to implement an interface that it doesn't use or clients shouldn't be forced to depend on methods they do not use.
* **D** - *Dependency Inversion Principle*. Entities must depend on abstractions not on concretions. It states that the high level module must not depend on the low level module, but they should depend on abstractions.
**Source:** _scotch.io_
#### Q35: Are you familiar with The Twelve-Factor App principles? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q36: Name some basic design elements ⭐
**Answer:**
The elements of design are:
* **LINE** – The linear marks made with a pen or brush or the edge created when two shapes meet.
* **SHAPE** – A shape is a self contained defined area of geometric (squares and circles), or organic (free formed shapes or natural shapes). A positive shape automatically creates a negative shape.
* **DIRECTION** – All lines have direction – Horizontal, Vertical or Oblique. Horizontal suggests calmness, stability and tranquillity. Vertical gives a feeling of balance, formality and alertness. Oblique suggests movement and action
* **SIZE** – Size is simply the relationship of the area occupied by one shape to that of another.
* **TEXTURE** – Texture is the surface quality of a shape – rough, smooth, soft hard glossy etc.
* **COLOUR** – Colour is light reflected off objects. Color has three main characteristics: hue or its name (red, green, blue, etc.), value (how light or dark it is), and intensity (how bright or dull it is).

**Source:** _j6design.com.au_
#### Q37: What is User Centered Design? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**User-centered design** is an iterative design process in which designers focus on the users and their needs in each phase of the design process. UCD calls for involving users throughout the design process via a variety of research and design techniques so as to create highly usable and accessible products for them.
User-centered design demands that designers employ a mixture of *investigative* (e.g., surveys and interviews) and *generative* (e.g., brainstorming) methods and tools to develop an understanding of user needs.
**Source:** _interaction-design.org_
#### Q38: Name fundamental principles of design ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The fundamental principles of design are:
* **BALANCE** — Balance in design is similar to balance in physics. A large shape close to the center can be balanced by a small shape close to the edge. Balance provides stability and structure to a design. It’s the weight distributed in the design by the placement of your elements.
* **PROXIMITY** — Proximity creates a relationship between elements. It provides a focal point. Proximity doesn’t mean that elements have to be placed together, it means they should be visually connected in some way.
* **ALIGNMENT** — Allows us to create order and organization. Aligning elements allows them to create a visual connection with each other.
* **REPETITION** — Repetition strengthens a design by tying together individual elements. It helps to create association and consistency. Repetition can create rhythm (a feeling of organized movement).
* **CONTRAST** — Contrast is the juxtaposition of opposing elements (opposite colors on the color wheel, or value light/dark, or direction — horizontal/vertical). Contrast allows us to emphasize or highlight key elements in your design.
* **SPACE** — Space in art refers to the distance or area between, around, above, below, or within elements. Both positive and negative space are important factors to be considered in every design.
**Source:** _uxplanet.org_
#### Q39: What is SQL injection? ⭐
**Answer:**
Injection attacks stem from a lack of strict separation between program instructions (i.e., code) and user-provided (or external) input. This allows an attacker to inject malicious code into a data snippet.
*SQL injection* is one of the most common types of injection attack. To carry it out, an attacker provides malicious SQL statements through the application.
How to prevent:
* **Prepared statements with parameterized queries**
* **Stored procedures**
* **Input validation** - blacklist validation and whitelist validation
* **Principle of least privilege** - Application accounts shouldn’t assign DBA or admin type access onto the database server. This ensures that if an application is compromised, an attacker won’t have the rights to the database through the compromised application.
**Source:** _https://www.synopsys.com_
#### Q40: What is Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is an attack that occurs when an attacker uses a web application to send malicious code, generally in the form of a browser side script, to a different end user.
The page provided by the server when someone requests it is unaltered. Instead, an XSS attack exploits a weakness in a page that include a variable submitted in a request to show up in raw form in the response. The page is only reflecting back what was submitted in that request.
**Source:** _synopsys.com_
#### Q41: What is Content Security Policy? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Content Security Policy (CSP)** is an HTTP header that allows site operators fine-grained control over where resources on their site can be loaded from. The use of this header is the best method to prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities. Due to the difficulty in retrofitting CSP into existing websites, CSP is mandatory for all new websites and is strongly recommended for all existing high-risk sites.
The primary benefit of CSP comes from disabling the use of unsafe inline JavaScript. Inline JavaScript – either reflected or stored – means that improperly escaped user-inputs can generate code that is interpreted by the web browser as JavaScript. By using CSP to disable inline JavaScript, you can effectively eliminate almost all XSS attacks against your site.
**Source:** _infosec.mozilla.org_
#### Q42: What is ClickJacking? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**ClickJacking** is an attack that fools users into thinking they are clicking on one thing when they are actually clicking on another. The attack is possible thanks to HTML frames (iframes).
Its other name, user interface (UI) redressing, better describes what is going on. Users think they are using a web page’s normal UI, but in fact there is a hidden UI in control; in other words, the UI has been redressed. When users click something they think is safe, the hidden UI performs a different action.
**Source:** _synopsys.com_
#### Q43: What is webpack? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Webpack** is a build tool that puts all of your assets, including Javascript, images, fonts, and CSS, in a dependency graph. Webpack lets you use `require()` in your source code to point to local files, like images, and decide how they're processed in your final Javascript bundle, like replacing the path with a URL pointing to a CDN.
**Source:** _blog.andrewray.me_
#### Q44: Why and when should I Use Webpack? ⭐
**Answer:**
If you're building a complex Front End application with many **non-code static assets** such as CSS, images, fonts, etc, then yes, Webpack will give you great benefits.
If your application is fairly small, and you don't have many static assets and you only need to build one Javascript file to serve to the client, then Webpack might be more overhead than you need.
**Source:** _blog.andrewray.me_
#### Q45: Why do we use jQuery? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Due to following advantages.
* Easy to use and learn.
* Easily expandable.
* Cross-browser support (IE 6.0+, FF 1.5+, Safari 2.0+, Opera 9.0+)
* Easy to use for DOM manipulation and traversal.
* Large pool of built in methods.
* AJAX Capabilities.
* Methods for changing or applying CSS, creating animations.
* Event detection and handling.
* Tons of plug-ins for all kind of needs.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q46: How JavaScript and jQuery are different? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
JavaScript is a language While jQuery is a library built in the JavaScript language that helps to use the JavaScript language.
**Source:** _codeproject.com_
#### Q47: When would you use AngularJS vs jQuery? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **jQuery** - is a library used for DOM Manipulations - Has nothing to do with models - don't have two-way binding feature - becomes complex and difficult to maintain when size of project increases - Sometimes you have to write more code to achieve the same functionality as in Angular
* **Angular** - is a MVVM Framework - Used for creating SPA (Single Page Applications) - Has key features like routing, directives, two way data binding, models, dependency injection, unit tests etc - is modular - Maintainable, when project size increases - is Fast and many more.
Basically jQuery is a single tool (solves one specific problem: dom manipulation) where AngularJS is a whole toolbox with all kind of tools for different problems (routing, modelbindings, dom manipulation, etc.). Actually jqLite (subset of jQuery) is part of the AngularJS and you use it to solve the dom-manipulation thing.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
## [[⬆]](#toc) 50 Common Web Developer Interview Questions [2020 Updated]
> Originally published on 👉 50 Common Web Developer Interview Questions [2020 Updated] | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Sprint Planning? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The work to be performed in the Sprint is planned at the **Sprint Planning**. This plan is created by the collaborative work of the entire Scrum Team.
Sprint Planning answers the following:
* What can be delivered in the Increment resulting from the upcoming Sprint?
* How will the work needed to deliver the Increment be achieved?
The Sprint Goal is an objective set for the Sprint that can be met through the implementation of Product Backlog.
**Source:** _scrum.org_
#### Q2: What is test driven development? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Test driven development (TDD)** is also known as test-driven design. In this method, developer first writes an automated test case which describes new function or improvement and then creates small codes to pass that test, and later re-factors the new code to meet the acceptable standards.
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q3: What is blockchain? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Blockchain** is a secure distributed ledger (data structure or database) that maintains a continuously growing list of ordered records, called “blocks”, that are linked using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the data. It is "an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way".
Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires consensus of the network majority.
**Source:** _en.wikipedia.org_
#### Q4: What is DOM (Document Object Model) and how is it linked to CSS? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The *Document Object Model (DOM)* is a cross-platform and language-independent *application programming interface* that treats an HTML, XHTML, or XML document as a tree structure wherein each node is an object representing a part of the document.
With the Document Object Model, programmers can create and build documents, navigate their structure, and add, modify, or delete elements and content. The DOM specifies interfaces which may be used to manage XML or HTML documents.
When a browser displays a document, it must combine the document's content with its style information. The browser converts HTML and CSS into the DOM (Document Object Model). The DOM represents the document in the computer's memory. It combines the document's content with its style.
**Source:** _en.wikipedia.org_
#### Q5: What is CSS selectors? Name some. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A CSS selector is the part of a CSS rule set that actually selects the content you want to style.
Consider some types of CSS selectors:
* **Universal selector**: `*`
* **Element type selector**: `ul`, `td`
* **ID Selector**: `#id`
* **Class selector**: `.box`
* **Descendant combinator**: `#id .box`. The .box element doesn’t have to be an immediate child of #id.
* **Child combinator**: `#id > .box`. Unlike the descendant combinator, there can’t be another element wrapping .box
* **General Sibling Combinator**: `~`
* **Adjacent Sibling Combinator**: `+`. The difference from general sibling combinaltor is that the targeted element must be an immediate sibling, not just a general sibling.
* **Attribute Selector**: `input[type="text"]`
* **Pseudo-class**: `a:hover`. A pseudo-class uses a colon character to identify a pseudo-state that an element might be in.
* **Pseudo-element**: `.container::before`. This selector inserts an imaginary element into the page, inside the targeted element, before its contents.
**Source:** _sitepoint.com_
#### Q6: How is responsive design different from adaptive design? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Both *responsive* and *adaptive* design attempt to optimize the user experience across different devices, adjusting for different viewport sizes, resolutions, usage contexts, control mechanisms, and so on.
**Responsive design** works on the principle of flexibility — a single fluid website that can look good on any device. Responsive websites use *media queries*, *flexible grids*, and *responsive images* to create a user experience that flexes and changes based on a multitude of factors. Like a single ball growing or shrinking to fit through several different hoops.
**Adaptive design** is more like the modern definition of progressive enhancement. Instead of one flexible design, adaptive design detects the device and other features, and then provides the appropriate feature and layout based on a *predefined set of viewport sizes* and other characteristics. The site detects the type of device used, and delivers the pre-set layout for that device. Instead of a single ball going through several different-sized hoops, you’d have several different balls to use depending on the hoop size.
**Source:** _codeburst.io_
#### Q7: What is Design Patterns and why anyone should use them? ⭐
**Answer:**
Design patterns are a well-described solution to the most commonly encountered problems which occur during software development.
Design pattern represents the best practices evolved over a period of time by experienced software developers. They promote reusability which leads to a more robust and maintainable code.
**Source:** _www.educba.com_
#### Q8: What is Adapter Pattern? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Adapter pattern* works as a bridge between two incompatible interfaces. This pattern involves a single class which is responsible to join functionalities of independent or incompatible interfaces (adaptees).

A real life example could be a case of card reader which acts as an adapter between memory card and a laptop. You plugin the memory card into card reader and card reader into the laptop so that memory card can be read via laptop.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q9: What is meant by Continuous Integration? ⭐
**Answer:**
*Continuous Integration (CI)* is a development practice that requires developers to integrate code into a shared repository several times a day. Each check-in is then verified by an automated build, allowing teams to detect problems early.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q10: What does Containerization mean? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Containerisation* is a type of *virtualization* strategy that emerged as an alternative to traditional hypervisor-based virtualization.
In containerization, the operating system is shared by the different containers rather than cloned for each virtual machine. For example Docker provides a container virtualization platform that serves as a good alternative to hypervisor-based arrangements.
**Source:** _linoxide.com_
#### Q11: What is the purpose of the alt attribute on images? ⭐
**Answer:**
The `alt` attribute provides alternative information for an image if a user cannot view it. The `alt` attribute should be used to describe any images except those which only serve a decorative purposes, in which case it should be left empty.
**Source:** _developer.mozilla.org_
#### Q12: What is the difference between span and div? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* `div` is a block element
* `span` is inline element
For bonus points, you could point out that it’s illegal to place a block element inside an inline element, and that while `div` can have a `p` tag, and a `p` tag can have a `span`, it is not possible for `span` to have a `div` or `p` tag inside.
**Source:** _thatjsdude.com_
#### Q13: Explain almost standard, full standard and quirks mode ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are now three modes used by the layout engines in web browsers: quirks mode, almost standards mode, and full standards mode.
* In **quirks mode**, layout emulates nonstandard behavior in Navigator 4 and Internet Explorer 5. This is essential in order to support websites that were built before the widespread adoption of web standards.
* In **full standards mode**, the behavior is (hopefully) the behavior described by the HTML and CSS specifications.
* In **almost standards mode**, there are only a very small number of quirks implemented.
For HTML documents, browsers use a `DOCTYPE` in the beginning of the document to decide whether to handle it in quirks mode or standards mode.
**Source:** _developer.mozilla.org_
#### Q14: What is HTML5 Web Storage? Explain `localStorage` and `sessionStorage`. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
With HTML5, web pages can store data locally within the user’s browser.
The data is stored in name/value pairs, and a web page can only access data stored by itself.
**Differences between `localStorage` and `sessionStorage` regarding lifetime:**
* Data stored through `localStorage` is permanent: it does not expire and remains stored on the user’s computer until a web app deletes it or the user asks the browser to delete it.
* `sessionStorage` has the same lifetime as the top-level window or browser tab in which the data got stored. When the tab is permanently closed, any data stored through `sessionStorage` is deleted.
**Differences between `localStorage` and `sessionStorage` regarding storage scope:**
Both forms of storage are scoped to the document origin so that documents with different origins will never share the stored objects.
* `sessionStorage` is also scoped on a per-window basis. Two browser tabs with documents from the same origin have separate `sessionStorage` data.
* Unlike in `localStorage`, the same scripts from the same origin can't access each other's `sessionStorage` when opened in different tabs.
**Source:** _w3schools.com_
#### Q15: What is progressive rendering? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q16: What is Coercion in JavaScript?
**Answer:**
In JavaScript conversion between different two build-in types called `coercion`. Coercion comes in two forms in JavaScript: *explicit* and *implicit*.
Here's an example of explicit coercion:
```js
var a = "42";
var b = Number( a );
a; // "42"
b; // 42 -- the number!
```
And here's an example of implicit coercion:
```js
var a = "42";
var b = a * 1; // "42" implicitly coerced to 42 here
a; // "42"
b; // 42 -- the number!
```
#### Q17: What is Scope in JavaScript? ⭐
**Answer:**
In JavaScript, each function gets its own *scope*. Scope is basically a collection of variables as well as the rules for how those variables are accessed by name. Only code inside that function can access that function's scoped variables.
A variable name has to be unique within the same scope. A scope can be nested inside another scope. If one scope is nested inside another, code inside the innermost scope can access variables from either scope.
#### Q18: Explain equality in JavaScript ⭐
**Answer:**
JavaScript has both strict and type–converting comparisons:
* **Strict comparison (e.g., ===)** checks for value equality without allowing *coercion*
* **Abstract comparison (e.g. ==)** checks for value equality with *coercion* allowed
```js
var a = "42";
var b = 42;
a == b; // true
a === b; // false
```
Some simple equalityrules:
* If either value (aka side) in a comparison could be the `true` or `false` value, avoid `==` and use `===`.
* If either value in a comparison could be of these specific values (`0`, `""`, or `[]` -- empty array), avoid `==` and use `===`.
* In all other cases, you're safe to use `==`. Not only is it safe, but in many cases it simplifies your code in a way that improves readability.
#### Q19: Explain Null and Undefined in JavaScript ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
JavaScript (and by extension TypeScript) has two bottom types: `null` and `undefined`. They are *intended* to mean different things:
* Something hasn't been initialized : `undefined`.
* Something is currently unavailable: `null`.
#### Q20: Implement enqueue and dequeue using only two stacks ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Enqueue* means to add an element, *dequeue* to remove an element.
```js
var inputStack = []; // First stack
var outputStack = []; // Second stack
// For enqueue, just push the item into the first stack
function enqueue(stackInput, item) {
return stackInput.push(item);
}
function dequeue(stackInput, stackOutput) {
// Reverse the stack such that the first element of the output stack is the
// last element of the input stack. After that, pop the top of the output to
// get the first element that was ever pushed into the input stack
if (stackOutput.length <= 0) {
while(stackInput.length > 0) {
var elementToOutput = stackInput.pop();
stackOutput.push(elementToOutput);
}
}
return stackOutput.pop();
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q21: What does "use strict" do? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The `use strict` literal is entered at the top of a JavaScript program or at the top of a function and it helps you write safer JavaScript code by throwing an error if a global variable is created by mistake. For example, the following program will throw an error:
```js
function doSomething(val) {
"use strict";
x = val + 10;
}`
```
It will throw an error because `x` was not defined and it is being set to some value in the global scope, which isn't allowed with `use strict` The small change below fixes the error being thrown:
```js
function doSomething(val) {
"use strict";
var x = val + 10;
}
```
**Source:** _coderbyte.com_
#### Q22: How to compare two objects in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Two non-primitive values, like objects (including function and array) held by reference, so both `==` and `===` comparisons will simply check whether the references match, not anything about the underlying values.
For example, `arrays` are by default coerced to strings by simply joining all the values with commas (`,`) in between. So two arrays with the same contents would not be `==` equal:
```js
var a = [1,2,3];
var b = [1,2,3];
var c = "1,2,3";
a == c; // true
b == c; // true
a == b; // false
```
For *deep object comparison* use external libs like `deep-equal` or implement your own recursive equality algorithm.
#### Q23: Could you explain the difference between ES5 and ES6 ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **ECMAScript 5 (ES5)**: The 5th edition of ECMAScript, standardized in 2009. This standard has been implemented fairly completely in all modern browsers
* **ECMAScript 6 (ES6)/ ECMAScript 2015 (ES2015)**: The 6th edition of ECMAScript, standardized in 2015. This standard has been partially implemented in most modern browsers.
Here are some key differences between ES5 and ES6:
* **Arrow functions** & **string interpolation**:
Consider:
```js
const greetings = (name) => {
return `hello ${name}`;
}
```
and even:
```js
const greetings = name => `hello ${name}`;
```
* **Const**.
Const works like a constant in other languages in many ways but there are some caveats. Const stands for ‘constant reference’ to a value. So with const, you can actually mutate the properties of an object being referenced by the variable. You just can’t change the reference itself.
```js
const NAMES = [];
NAMES.push("Jim");
console.log(NAMES.length === 1); // true
NAMES = ["Steve", "John"]; // error
```
* **Block-scoped variables**.
The new ES6 keyword `let` allows developers to scope variables at the block level.
`Let` doesn’t hoist in the same way `var` does.
* **Default parameter values**
Default parameters allow us to initialize functions with default values. A default is used when an argument is either omitted or undefined — meaning null is a valid value.
```js
// Basic syntax
function multiply (a, b = 2) {
return a * b;
}
multiply(5); // 10
```
* ** Class Definition and Inheritance**
ES6 introduces language support for classes (`class` keyword), constructors (`constructor` keyword), and the `extend` keyword for inheritance.
* **for-of operator**
The for...of statement creates a loop iterating over iterable objects.
* **Spread Operator**
For objects merging
```js
const obj1 = { a: 1, b: 2 }
const obj2 = { a: 2, c: 3, d: 4}
const obj3 = {...obj1, ...obj2}
```
* **Promises**
Promises provide a mechanism to handle the results and errors from asynchronous operations. You can accomplish the same thing with callbacks, but promises provide improved readability via method chaining and succinct error handling.
```js
const isGreater = (a, b) => {
return new Promise ((resolve, reject) => {
if(a > b) {
resolve(true)
} else {
reject(false)
}
})
}
isGreater(1, 2)
.then(result => {
console.log('greater')
})
.catch(result => {
console.log('smaller')
})
```
* **Modules exporting & importing**
Consider module exporting:
```js
const myModule = { x: 1, y: () => { console.log('This is ES5') }}
export default myModule;
```
and importing:
```js
import myModule from './myModule';
```
#### Q24: Given two strings, return true if they are anagrams of one another ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
For example: `Mary` is an anagram of `Army`
**Answer:**
```js
var firstWord = "Mary";
var secondWord = "Army";
isAnagram(firstWord, secondWord); // true
function isAnagram(first, second) {
// For case insensitivity, change both words to lowercase.
var a = first.toLowerCase();
var b = second.toLowerCase();
// Sort the strings, and join the resulting array to a string. Compare the results
a = a.split("").sort().join("");
b = b.split("").sort().join("");
return a === b;
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q25: What is IIFEs (Immediately Invoked Function Expressions)? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It’s an Immediately-Invoked Function Expression, or IIFE for short. It executes immediately after it’s created:
```js
(function IIFE(){
console.log( "Hello!" );
})();
// "Hello!"
```
This pattern is often used when trying to avoid polluting the global namespace, because all the variables used inside the IIFE (like in any other normal function) are not visible outside its scope.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q26: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using "use strict"? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
'use strict' is a statement used to enable strict mode to entire scripts or individual functions. Strict mode is a way to opt into a restricted variant of JavaScript.
Advantages:
* Makes it impossible to accidentally create global variables.
* Makes assignments which would otherwise silently fail to throw an exception.
* Makes attempts to delete undeletable properties throw (where before the attempt would simply have no effect).
* Requires that function parameter names be unique.
* `this` is undefined in the global context.
* It catches some common coding bloopers, throwing exceptions.
* It disables features that are confusing or poorly thought out.
Disadvantages:
* Many missing features that some developers might be used to.
* No more access to `function.caller` and `function.arguments`.
* Concatenation of scripts written in different strict modes might cause issues.
Overall, I think the benefits outweigh the disadvantages, and I never had to rely on the features that strict mode blocks. I would recommend using strict mode.
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q27: Explain the difference between Object.freeze() vs const ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`const` and `Object.freeze` are two completely different things.
* `const` applies to **bindings** ("variables"). It creates an immutable binding, i.e. you cannot assign a new value to the binding.
```js
const person = {
name: "Leonardo"
};
let animal = {
species: "snake"
};
person = animal; // ERROR "person" is read-only
```
* `Object.freeze` works on **values**, and more specifically, *object values*. It makes an object immutable, i.e. you cannot change its properties.
```js
let person = {
name: "Leonardo"
};
let animal = {
species: "snake"
};
Object.freeze(person);
person.name = "Lima"; //TypeError: Cannot assign to read only property 'name' of object
console.log(person);
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q28: What is Hoisting in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: How does the “this” keyword work? Provide some code examples. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: Write a recursive function that performs a binary search ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: What is “closure” in javascript? Provide an example? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: Explain difference between: `function Person(){}`, `var person = Person()`, and `var person = new Person()`? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: What are the features of Microservices? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Decoupling** – Services within a system are largely decoupled. So the application as a whole can be easily built, altered, and scaled
* **Componentization** – Microservices are treated as independent components that can be easily replaced and upgraded
* **Business Capabilities** – Microservices are very simple and focus on a single capability
* **Autonomy** – Developers and teams can work independently of each other, thus increasing speed
* **Continous** **Delivery** – Allows frequent releases of software, through systematic automation of software creation, testing, and approval
* **Responsibility** – Microservices do not focus on applications as projects. Instead, they treat applications as products for which they are responsible
* **Decentralized Governance** – The focus is on using the right tool for the right job. That means there is no standardized pattern or any technology pattern. Developers have the freedom to choose the best useful tools to solve their problems
* **Agility** – Microservices support agile development. Any new feature can be quickly developed and discarded again
**Source:** _lambdatest.com_
#### Q34: What is npm? ⭐
**Answer:**
`npm` stands for Node Package Manager. npm provides following two main functionalities:
* Online repositories for node.js packages/modules which are searchable on [search.nodejs.org](http://search.nodejs.org)
* Command line utility to install packages, do version management and dependency management of Node.js packages.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q35: What is the difference between procedural and object-oriented programming? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Procedural programming is based upon the modular approach in which the larger programs are broken into procedures. Each procedure is a set of instructions that are executed one after another. On the other hand, OOP is based upon objects. An object consists of various elements, such as methods and variables.
Access modifiers are not used in procedural programming, which implies that the entire data can be accessed freely anywhere in the program. In OOP, you can specify the scope of a particular data by using access modifiers - _public_, _private_, _internal_, _protected_, and _protected_ internal.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q36: State the features of an interface. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An interface is a template that contains only the signature of methods. The signature of a method consists of the numbers of parameters, the type of parameter (value, reference, or output), and the order of parameters. An interface has no implementation on its own because it contains only the definition of methods without any method body. An interface is defined using the _interface_ keyword. Moreover, you cannot instantiate an interface. The various features of an interface are as follows:
* An interface is used to implement multiple inheritance in code. This feature of an interface is quite different from that of abstract classes because a class cannot derive the features of more than one class but can easily implement multiple interfaces.
* It defines a specific set of methods and their arguments.
* Variables in interface must be declared as _public_, _static_, and _final_ while methods must be _public_ and _abstract_.
* A class implementing an interface must implement all of its methods.
* An interface can derive from more than one interface.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q37: What is the difference between cohesion and coupling? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q38: What does it mean to “program to an interface”? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q39: What is Reactive Programming? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Reactive programming is programming with asynchronous data streams.** Event buses or your typical click events are really an asynchronous event stream, on which you can observe and do some side effects. Reactive is that idea on steroids. You are able to create data streams of anything, not just from click and hover events. Streams are cheap and ubiquitous, anything can be a stream: variables, user inputs, properties, caches, data structures, etc. For example, imagine your Twitter feed would be a data stream in the same fashion that click events are. You can listen to that stream and react accordingly.
**Source:** _github.com_
#### Q40: What are different HTTP Methods supported in Restful Web Services? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Restful web services supported HTTP methods are:
* GET,
* POST,
* PUT,
* DELETE and
* HEAD.
**Source:** _journaldev.com_
#### Q41: How would you choose between SOAP and REST web services? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Web Services work on client-server model and when it comes to choose between SOAP and REST, it all depends on project requirements. Let’s look at some of the conditions affecting our choice:
* Do you know your web service clients beforehand? If Yes, then you can define a contract before implementation and SOAP seems better choice. But if you don’t then REST seems better choice because you can provide sample request/response and test cases easily for client applications to use later on.
* How much time you have? For quick implementation REST is the best choice. You can create web service easily, test it through browser/curl and get ready for your clients.
What kind of data format are supported? If only XML then you can go with SOAP but if you think about supporting JSON also in future then go with REST.
**Source:** _journaldev.com_
#### Q42: What are the best practices for caching? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Always keep static contents like images, css, JavaScript cacheable, with expiration date of 2 to 3 days. Never keep expiry date too high.
Dynamic contents should be cached for few hours only.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q43: What should be the purpose of OPTIONS method of RESTful web services? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q44: What are the DRY and DIE principles? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In software engineering, **Don't Repeat Yourself (DRY)** or **Duplication is Evil (DIE)** is a principle of software development.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q45: What is GOD class and why should we avoid it? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q46: What is CORS and how to enable one? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A request for a resource (like an image or a font) outside of the origin is known as a *cross-origin request*. CORS (cross-origin resource sharing) manages cross-origin requests. CORS allows servers to specify who (i.e., which origins) can access the assets on the server, among many other things.
**Access-Control-Allow-Origin** is an HTTP header that defines which foreign origins are allowed to access the content of pages on your domain via scripts using methods such as XMLHttpRequest.
For example, if your server provides both a website and an API intended for XMLHttpRequest access on a remote websites, only the API resources should return the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header. Failure to do so will allow foreign origins to read the contents of any page on your origin.
```sh
# Allow any site to read the contents of this JavaScript library, so that subresource integrity works
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
```
**Source:** _infosec.mozilla.org_
#### Q47: What is Cross Site Scripting (XSS)? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
By using **Cross Site Scripting (XSS)** technique, users executed malicious scripts (also called payloads) unintentionally by clicking on untrusted links and hence, these scripts pass cookies information to attackers.
**Source:** _allabouttesting.org_
#### Q48: How can I prevent XSS? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
XSS can be prevented by sanitizing user input to the application. Always allowed those elements as input which is absolutely essential for that field.
**Source:** _allabouttesting.org_
#### Q49: What is webpack? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Webpack** is a build tool that puts all of your assets, including Javascript, images, fonts, and CSS, in a dependency graph. Webpack lets you use `require()` in your source code to point to local files, like images, and decide how they're processed in your final Javascript bundle, like replacing the path with a URL pointing to a CDN.
**Source:** _blog.andrewray.me_
#### Q50: Describe tree shaking mechanism in webpack ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 50 Junior Web Developer Interview Questions. The Ultimate 2018 Guide.
> Originally published on 👉 50 Junior Web Developer Interview Questions. The Ultimate 2018 Guide. | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: Explain what is Bootstrap? ⭐
**Answer:**
Bootstrap is CSS/Javascript framework for building the rich web applications with
minimal effort. This framework emphasis more on building mobile web
applications.
**Source:** _medium.com/@alisonbenhar_
#### Q2: Explain the three main ways to apply CSS styles to a web page ⭐
**Answer:**
Using the inline style attribute on an element
```html
```
Using a `` block in the `<head>` section of your HTML
```html
<head>
<title>CSS Refresher</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: sans-serif;
font-size: 1.2em;
}
```
Loading an external CSS file using the `` tag
```html
CSS Refresher
```
**Source:** _goskills.com_
#### Q3: What is CSS? ⭐
**Answer:**
**CSS** stands for **Cascading Style Sheets**. CSS is used to define styles for your web pages, including the design, layout and variations in display for different devices and screen sizes.
CSS was intended to allow web professionals to separate the content and structure of a website's code from the visual design.
**Source:** _w3schools.com_
#### Q4: Explain the CSS “box model” and the layout components that it consists of ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The CSS box model is a rectangular layout paradigm for HTML elements that consists of the following:
* **Content** - The content of the box, where text and images appear
* **Padding** - A transparent area surrounding the content (i.e., the amount of space between the border and the content)
* **Border** - A border surrounding the padding (if any) and content
* **Margin** - A transparent area surrounding the border (i.e., the amount of space between the border and any neighboring elements)
**Source:** _toptal.com_
#### Q5: Describe floats and how they work ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Float* is a CSS positioning property. Floated elements remain a part of the flow of the web page. This is distinctly different than page elements that use absolute positioning. Absolutely positioned page elements are removed from the flow of the webpage.
```css
#sidebar {
float: right; // left right none inherit
}
```
The CSS clear property can be used to be positioned below `left`/`right`/`both` floated elements.
**Source:** _css-tricks.com_
#### Q6: Have you played around with the new CSS Flexbox or Grid specs? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Yes. Flexbox is mainly meant for 1-dimensional layouts while Grid is meant for 2-dimensional layouts.
Flexbox solves many common problems in CSS, such as vertical centering of elements within a container, sticky footer, etc. Bootstrap and Bulma are based on Flexbox, and it is probably the recommended way to create layouts these days. Have tried Flexbox before but ran into some browser incompatibility issues (Safari) in using `flex-grow`, and I had to rewrite my code using `inline-blocks` and math to calculate the widths in percentages, it wasn't a nice experience.
Grid is by far the most intuitive approach for creating grid-based layouts (it better be!) but browser support is not wide at the moment.
**Source:** _codeburst.io_
#### Q7: What existing CSS frameworks have you used locally, or in production? How would you change/improve them? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Bootstrap** - Slow release cycle. Bootstrap 4 has been in alpha for almost 2 years. Add a spinner button component, as it is widely used.
* **Semantic UI** - Source code structure makes theme customization extremely hard to understand. Its unconventional theming system is a pain to customize. Hardcoded config path within the vendor library. Not well-designed for overriding variables unlike in Bootstrap.
* **Bulma** - A lot of non-semantic and superfluous classes and markup required. Not backward compatible. Upgrading versions breaks the app in subtle manners.
**Source:** _codeburst.io_
#### Q8: What is DOM (Document Object Model) and how is it linked to CSS? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The *Document Object Model (DOM)* is a cross-platform and language-independent *application programming interface* that treats an HTML, XHTML, or XML document as a tree structure wherein each node is an object representing a part of the document.
With the Document Object Model, programmers can create and build documents, navigate their structure, and add, modify, or delete elements and content. The DOM specifies interfaces which may be used to manage XML or HTML documents.
When a browser displays a document, it must combine the document's content with its style information. The browser converts HTML and CSS into the DOM (Document Object Model). The DOM represents the document in the computer's memory. It combines the document's content with its style.
**Source:** _en.wikipedia.org_
#### Q9: What is CSS preprocessor and why to user one? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A **CSS preprocessor** is a program that lets you generate CSS from the preprocessor's own unique syntax. There are many CSS preprocessors to choose from, however most CSS preprocessors will add some features that don't exist in pure CSS, such as mixin, nesting selector, inheritance selector, and so on. These features make the CSS structure more readable and easier to maintain.
Here are a few of the most popular CSS preprocessors:
* SASS (SCSS)
* LESS
* Stylus
* PostCSS
**Source:** _developer.mozilla.org_
#### Q10: How to create a zebra striped table with CSS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
To create a zebra-striped table, use the `nth-child()` selector and add a background-color to all even (or odd) table rows:
```css
tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #f2f2f2
}
```
**Source:** _w3schools.com_
#### Q11: What is a Grid System in CSS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A grid system is a structure that allows for content to be stacked both vertically and horizontally in a consistent and easily manageable fashion. Grid systems include two key components: rows and columns.
Some Grid Systems:
* Simple Grid
* Pure
* Flexbox Grid
* Bootstrap
* Foundation
**Source:** _sitepoint.com_
#### Q12: What is Singleton pattern? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Singleton pattern** comes under *creational* patterns category and introduces a single class which is responsible to create an object while making sure that only single object gets created. This class provides a way to access its only object which can be accessed directly without need to instantiate the object of the class.

**Source:** _refactoring.guru_
#### Q13: What is Dependency Injection? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Dependency injection* makes it easy to create loosely coupled components, which typically means that components consume functionality defined by interfaces without having any first-hand knowledge of which implementation classes are being used.
*Dependency injection* makes it easier to change the behavior of an application by changing the components that implement the interfaces that define application features. It also results in components that are easier to isolate for unit testing.
**Source:** _Pro ASP.NET Core MVC 2_
#### Q14: What is Observer pattern? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Observer pattern** (also known as *Publish-Subscribe Pattern*) is used when there is one-to-many relationship between objects such as if one object is modified, its dependent objects are to be notified automatically. Observer pattern falls under _behavioral_ pattern category.
An object with a one-to-many relationship with other objects who are interested in its state is called the _subject_ or _publisher_. The _observers_ are notified whenever the state of the _subject_ changes and can act accordingly. The _subject_ can have any number of dependent _observers_ which it notifies, and any number of _observers_ can subscribe to the _subject_ to receive such notifications.
Observer pattern uses two actor classes:
* The Observer (os Subscriber) abstract class provides an `update()` method which will be called by the subject to notify it of the subject’s state change.
* The Subject (or Publisher) class is also an abstract class and defines four primary methods: `attach()`, `detach()`, `setState()`, and `notify()`

**Source:** _sitepoint.com_
#### Q15: What is meant by Continuous Integration? ⭐
**Answer:**
*Continuous Integration (CI)* is a development practice that requires developers to integrate code into a shared repository several times a day. Each check-in is then verified by an automated build, allowing teams to detect problems early.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q16: What do you know about serverless model? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Serverless** refers to a model where the existence of servers is hidden from developers. It means you no longer have to deal with capacity, deployments, scaling and fault tolerance and OS. It will essentially reducing maintenance efforts and allow developers to quickly focus on developing codes.
Examples are:
* Amazon AWS Lambda
* Azure Functions
**Source:** _linoxide.com_
#### Q17: What is Git? ⭐
**Answer:**
Git is a Distributed Version Control system (DVCS). It can track changes to a file and allows you to revert back to any particular change.
Its distributed architecture provides many advantages over other Version Control Systems (VCS) like SVN one major advantage is that it does not rely on a central server to store all the versions of a project’s files.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q18: How does the Centralized Workflow work? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **Centralized Workflow** uses a central repository to serve as the single point-of-entry for all changes to the project. The default development branch is called master and all changes are committed into this branch.
Developers start by cloning the central repository. In their own local copies of the project, they edit files and commit changes. These new commits are stored locally.
To publish changes to the official project, developers *push* their local master branch to the central repository. Before the developer can publish their feature, they need to *fetch* the updated central commits and rebase their changes on top of them.
Compared to other workflows, the Centralized Workflow has no defined pull request or forking patterns.
**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q19: You need to update your local repos. What git commands will you use? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It’s a two steps process. First you fetch the changes from a remote named origin:
```sh
git fetch origin
```
Then you merge a branch master to local:
```sh
git merge origin/master
```
Or simply:
```sh
git pull origin master
```
If origin is a default remote and ‘master’ is default branch, you can drop it eg. `git pull`.
**Source:** _samwize.com_
#### Q20: Could you explain the Gitflow workflow? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Gitflow workflow employs two parallel *long-running* branches to record the history of the project, `master` and `develop`:
* **Master** - is always ready to be released on LIVE, with everything fully tested and approved (production-ready).
* **Hotfix** - Maintenance or “hotfix” branches are used to quickly patch production releases. Hotfix branches are a lot like release branches and feature branches except they're based on `master` instead of `develop`.
* **Develop** - is the branch to which all feature branches are merged and where all tests are performed. Only when everything’s been thoroughly checked and fixed it can be merged to the `master`.
* **Feature** - Each new feature should reside in its own branch, which can be pushed to the `develop` branch as their parent one.

**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q21: Explain meta tags in HTML ⭐
**Answer:**
- **Meta tags** always go inside **head tag** of the HTML page
- **Meta tags** is always passed as name/value pairs
- **Meta tags** are not displayed on the page but intended for the browser
- **Meta tags** can contain information about **character encoding**, **description**, **title** of the document etc,
**Example**:
```html
Home Page
```
**Source:** _github.com/FuelFrontend_
#### Q22: Write a HTML table tag sequence that outputs the following ⭐
**Answer:**
Write a HTML table tag sequence that outputs the following:
```
50 pcs 100 500
10 pcs 5 50
```
**Answer:**
```html
50 pcs
100
500
10 pcs
5
50
```
**Source:** _toptal.com_
#### Q23: What is the difference between span and div? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* `div` is a block element
* `span` is inline element
For bonus points, you could point out that it’s illegal to place a block element inside an inline element, and that while `div` can have a `p` tag, and a `p` tag can have a `span`, it is not possible for `span` to have a `div` or `p` tag inside.
**Source:** _thatjsdude.com_
#### Q24: How Can I Get Indexed Better by Search Engines? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It is possible to get indexed better by placing the following two statements in the `` part of your documents:
```html
```
Both may contain up to 1022 characters. If a keyword is used more than 7 times, the keywords tag will be ignored altogether. Also, you cannot put markup (other than entities) in the description or keywords list.
**Source:** _freejavaguide.com_
#### Q25: Explain the difference between cookies, session and local storage ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Cookies**
- **Limited** storage space **4096 bytes / ~4 kb**
- Only allow to store data as **strings**
- Stored data is sent back to server on every **HTTP request** such as HTML, CSS, Images etc,
- Can store only **20 cookies per domain**
- In total **300** cookies are allowed on a site
- Setting **HTTP only** flag will **prevent accessing cookies** via javascript
- Can set **expiration** duration for auto deletion (can be set either from server or client)
**Example**:
```js
// Set with expiration & path
document.cookie = "name=Gokul; expires=Thu, 18 Dec 2016 12:00:00 UTC; path=/;";
// Get
document.cookie;
// Delete by setting empty value and same path
document.cookie = "name=; expires=Thu, 18 Dec 2016 12:00:00 UTC; path=/;";
```
**Session Storage**
- Storage space is **5 mb / ~5120 kb**
- Storage space may **vary a little** based on the browser
- Only allow to store data as **strings**
- Data is available per **window or tab**
- Once window or tab is closed stored data is **deleted**
- Data will be **only available on same origin**
**Example**:
```js
// Set
sessionStorage.setItem("name", "gokul");
// Get
sessionStorage.getItem("name"); // gokul
// Delete
sessionStorage.removeItem("name");
// Delete All
sessionStorage.clear();
```
**Local Storage**
- Storage space is **5 mb / ~5120 kb**
- Storage space may **vary a little** based on the browser
- Only allow to store data as **strings**
- Data will be **only available on same origin**
- Data is **persistant** (untill explicitly deleted)
- API is similar to session storage
**Example**:
```js
// Set
localStorage.setItem("name", "gokul");
// Get
localStorage.getItem("name"); // gokul
// Delete
localStorage.removeItem("name");
// Delete All
localStorage.clear();
```
**Source:** _github.com/FuelFrontend_
#### Q26: What's new in HTML 5? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
HTML 5 adds a lot of new features to the HTML specification
**New Doctype**
Still using that pesky, impossible-to-memorize XHTML doctype?
```html
```
If so, why? Switch to the new HTML5 doctype. You'll live longer -- as Douglas Quaid might say.
```html
```
**New Structure**
- `` - to define sections of pages
- `` - defines the header of a page
- `` - defines the footer of a page
- `` - defines the navigation on a page
- `` - defines the article or primary content on a page
- `` - defines extra content like a sidebar on a page
- `` - defines images that annotate an article
**New Inline Elements**
These inline elements define some basic concepts and keep them semantically marked up, mostly to do with time:
- `` - to indicate content that is marked in some fashion
- `
**New Form Types**
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
- ``
**New Elements**
There are a few exciting new elements in HTML 5:
- `` - an element to give you a drawing space in JavaScript on your Web pages. It can let you add images or graphs to tool tips or just create dynamic graphs on your Web pages, built on the fly.
- `` - add video to your Web pages with this simple tag.
- `` - add sound to your Web pages with this simple tag.
**No More Types for Scripts and Links**
You possibly still add the `type` attribute to your `link` and `script` tags.
```html
```
This is no longer necessary. It's implied that both of these tags refer to stylesheets and scripts, respectively. As such, we can remove the `type` attribute all together.
```html
```
**Make your content editable**
The new browsers have a nifty new attribute that can be applied to elements, called `contenteditable`. As the name implies, this allows the user to edit any of the text contained within the element, including its children. There are a variety of uses for something like this, including an app as simple as a to-do list, which also takes advantage of local storage.
```html
To-Do List
- Break mechanical cab driver.
- Drive to abandoned factory
- Watch video of self
```
**Attributes**
- `require` to mention the form field is required
- `autofocus` puts the cursor on the input field
**Source:** _github.com/FuelFrontend_
#### Q27: What is the purpose of cache busting and how can you achieve it? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Browsers have a cache to temporarily store files on websites so they don't need to be re-downloaded again when switching between pages or reloading the same page. The server is set up to send headers that tell the browser to store the file for a given amount of time. This greatly increases website speed and preserves bandwidth.
However, it can cause problems when the website has been changed by developers because the user's cache still references old files. This can either leave them with old functionality or break a website if the cached CSS and JavaScript files are referencing elements that no longer exist, have moved or have been renamed.
Cache busting is the process of forcing the browser to download the new files. This is done by naming the file something different to the old file.
A common technique to force the browser to re-download the file is to append a query string to the end of the file.
* `src="js/script.js"` => `src="js/script.js?v=2"`
The browser considers it a different file but prevents the need to change the file name.
**Source:** _css-tricks.com_
#### Q28: Explain equality in JavaScript ⭐
**Answer:**
JavaScript has both strict and type–converting comparisons:
* **Strict comparison (e.g., ===)** checks for value equality without allowing *coercion*
* **Abstract comparison (e.g. ==)** checks for value equality with *coercion* allowed
```js
var a = "42";
var b = 42;
a == b; // true
a === b; // false
```
Some simple equalityrules:
* If either value (aka side) in a comparison could be the `true` or `false` value, avoid `==` and use `===`.
* If either value in a comparison could be of these specific values (`0`, `""`, or `[]` -- empty array), avoid `==` and use `===`.
* In all other cases, you're safe to use `==`. Not only is it safe, but in many cases it simplifies your code in a way that improves readability.
#### Q29: What is Scope in JavaScript? ⭐
**Answer:**
In JavaScript, each function gets its own *scope*. Scope is basically a collection of variables as well as the rules for how those variables are accessed by name. Only code inside that function can access that function's scoped variables.
A variable name has to be unique within the same scope. A scope can be nested inside another scope. If one scope is nested inside another, code inside the innermost scope can access variables from either scope.
#### Q30: Explain event bubbling and how one may prevent it ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Event bubbling** is the concept in which an event triggers at the deepest possible element, and triggers on parent elements in nesting order. As a result, when clicking on a child element one may exhibit the handler of the parent activating.
One way to prevent event bubbling is using `event.stopPropagation()` or `event.cancelBubble` on IE < 9.
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q31: Given a string, reverse each word in the sentence ⭐⭐
**Details:**
For example `Welcome to this Javascript Guide!` should be become `emocleW ot siht tpircsavaJ !ediuG`
**Answer:**
```js
var string = "Welcome to this Javascript Guide!";
// Output becomes !ediuG tpircsavaJ siht ot emocleW
var reverseEntireSentence = reverseBySeparator(string, "");
// Output becomes emocleW ot siht tpircsavaJ !ediuG
var reverseEachWord = reverseBySeparator(reverseEntireSentence, " ");
function reverseBySeparator(string, separator) {
return string.split(separator).reverse().join(separator);
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q32: What does "use strict" do? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The `use strict` literal is entered at the top of a JavaScript program or at the top of a function and it helps you write safer JavaScript code by throwing an error if a global variable is created by mistake. For example, the following program will throw an error:
```js
function doSomething(val) {
"use strict";
x = val + 10;
}`
```
It will throw an error because `x` was not defined and it is being set to some value in the global scope, which isn't allowed with `use strict` The small change below fixes the error being thrown:
```js
function doSomething(val) {
"use strict";
var x = val + 10;
}
```
**Source:** _coderbyte.com_
#### Q33: What is a Polyfill? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A polyfill is essentially the specific code (or plugin) that would allow you to have some specific functionality that you expect in current or “modern” browsers to also work in other browsers that do not have the support for that functionality built in.
* Polyfills are not part of the HTML5 standard
* Polyfilling is not limited to Javascript
**Source:** _programmerinterview.com_
#### Q34: Explain Null and Undefined in JavaScript ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
JavaScript (and by extension TypeScript) has two bottom types: `null` and `undefined`. They are *intended* to mean different things:
* Something hasn't been initialized : `undefined`.
* Something is currently unavailable: `null`.
#### Q35: What will be the output of the following code? ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```js
var y = 1;
if (function f() {}) {
y += typeof f;
}
console.log(y);
```
**Answer:**
Above code would give output `1undefined`. If condition statement evaluate using `eval` so `eval(function f() {})` which return `function f() {}` which is true so inside if statement code execute. `typeof f` return undefined because if statement code execute at run time, so statement inside `if` condition evaluated at run time.
```js
var k = 1;
if (1) {
eval(function foo() {});
k += typeof foo;
}
console.log(k);
```
Above code will also output `1undefined`.
```js
var k = 1;
if (1) {
function foo() {};
k += typeof foo;
}
console.log(k); // output 1function
```
**Source:** _github.com/ganqqwerty_
#### Q36: How to compare two objects in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Two non-primitive values, like objects (including function and array) held by reference, so both `==` and `===` comparisons will simply check whether the references match, not anything about the underlying values.
For example, `arrays` are by default coerced to strings by simply joining all the values with commas (`,`) in between. So two arrays with the same contents would not be `==` equal:
```js
var a = [1,2,3];
var b = [1,2,3];
var c = "1,2,3";
a == c; // true
b == c; // true
a == b; // false
```
For *deep object comparison* use external libs like `deep-equal` or implement your own recursive equality algorithm.
#### Q37: Given two strings, return true if they are anagrams of one another ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
For example: `Mary` is an anagram of `Army`
**Answer:**
```js
var firstWord = "Mary";
var secondWord = "Army";
isAnagram(firstWord, secondWord); // true
function isAnagram(first, second) {
// For case insensitivity, change both words to lowercase.
var a = first.toLowerCase();
var b = second.toLowerCase();
// Sort the strings, and join the resulting array to a string. Compare the results
a = a.split("").sort().join("");
b = b.split("").sort().join("");
return a === b;
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q38: Explain the difference between "undefined" and "not defined" in JavaScript ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In JavaScript if you try to use a variable that doesn't exist and has not been declared, then JavaScript will throw an error `var name is not defined` and the script will stop execute thereafter. But If you use `typeof undeclared_variable` then it will return `undefined`.
Before starting further discussion let's understand the difference between declaration and definition.
`var x` is a declaration because you are not defining what value it holds yet, but you are declaring its existence and the need of memory allocation.
```javascript
var x; // declaring x
console.log(x); //output: undefined
```
`var x = 1` is both declaration and definition (also we can say we are doing initialisation), Here declaration and assignment of value happen inline for variable x, In JavaScript every variable declaration and function declaration brings to the top of its current scope in which it's declared then assignment happen in order this term is called `hoisting`.
A variable that is declared but not define and when we try to access it, It will result `undefined`.
```javascript
var x; // Declaration
if(typeof x === 'undefined') // Will return true
```
> A variable that neither declared nor defined when we try to reference such variable then It result `not defined`.
```javascript
console.log(y); // Output: ReferenceError: y is not defined
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q39: Describe closure concept in JavaScript as best as you could ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Consider:
```js
function makeAdder(x) {
// parameter `x` is an inner variable
// inner function `add()` uses `x`, so
// it has a "closure" over `x`
function add(y) {
return y + x;
};
return add;
}
```
Reference to inner `add` function returned is able to remember what `x` value was passed to makeAdder function call.
```js
var plusOne = makeAdder( 1 ); // x is 1, plusOne has a reference to add(y)
var plusTen = makeAdder( 10 ); // x is 10
plusOne(3); // 1 (x) + 3 (y) = 4
plusTen(13); // 10 (x) + 13 (y) = 23
```
In C and most other common languages, after a function returns, all the local variables are no longer accessible because the stack-frame is destroyed.
In JavaScript, if you declare a function within another function, then the local variables can remain accessible after returning from the function you called.
A closure is a stack frame which is allocated when a function starts its execution, and not freed after the function returns (as if a 'stack frame' were allocated on the heap rather than the stack!). In JavaScript, you can think of a function reference variable as having both a pointer to a function as well as a hidden pointer to a closure.
**Source:** _https://stackoverflow.com/questions/111102/how-do-javascript-closures-work_
#### Q40: What is npm? ⭐
**Answer:**
`npm` stands for Node Package Manager. npm provides following two main functionalities:
* Online repositories for node.js packages/modules which are searchable on [search.nodejs.org](http://search.nodejs.org)
* Command line utility to install packages, do version management and dependency management of Node.js packages.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q41: What is Node.js? ⭐
**Answer:**
Node.js is a web application framework built on Google Chrome's JavaScript Engine (V8 Engine).
Node.js comes with runtime environment on which a Javascript based script can be interpreted and executed (It is analogus to JVM to JAVA byte code). This runtime allows to execute a JavaScript code on any machine outside a browser. Because of this runtime of Node.js, JavaScript is now can be executed on server as well.
*Node.js = Runtime Environment + JavaScript Library*
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q42: What is global installation of dependencies? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Globally installed packages/dependencies are stored in ****/npm directory. Such dependencies can be used in CLI (Command Line Interface) function of any node.js but can not be imported using require() in Node application directly. To install a Node project globally use -g flag.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q43: What is Sass? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Sass** or **Syntactically Awesome StyleSheets** is a *CSS* preprocessor that adds power and elegance to the basic language. It allows you to use variables, nested rules, mixins, inline imports, and more, all with a fully CSS-compatible syntax. Sass helps keep large stylesheets well-organized, and get small stylesheets up and running quickly.
A *CSS preprocessor* is a scripting language that extends CSS by allowing developers to write code in one language and then compile it into CSS.
**Source:** _sass-lang.com_
#### Q44: Describe what User Interface (UI) Design does mean for you? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**User Interface (UI) design** is the design of software or websites with the focus on the user’s experience and interaction. The goal of user interface design is to make the user’s interaction as simple and efficient as possible. Good user interface design puts emphasis on *goals* and *completing tasks*, and good UI design never draws more attention to itself than enforcing user goals.
**Source:** _uxplanet.org_
#### Q45: What is SQL injection? ⭐
**Answer:**
Injection attacks stem from a lack of strict separation between program instructions (i.e., code) and user-provided (or external) input. This allows an attacker to inject malicious code into a data snippet.
*SQL injection* is one of the most common types of injection attack. To carry it out, an attacker provides malicious SQL statements through the application.
How to prevent:
* **Prepared statements with parameterized queries**
* **Stored procedures**
* **Input validation** - blacklist validation and whitelist validation
* **Principle of least privilege** - Application accounts shouldn’t assign DBA or admin type access onto the database server. This ensures that if an application is compromised, an attacker won’t have the rights to the database through the compromised application.
**Source:** _https://www.synopsys.com_
#### Q46: What is impersonation? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Impersonation is an act of pretending to be another person. For IT Systems impersonation means that some specific users (usually Admins) could get an access to other user's data.
#### Q47: What is Cross Site Scripting (XSS)? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
By using **Cross Site Scripting (XSS)** technique, users executed malicious scripts (also called payloads) unintentionally by clicking on untrusted links and hence, these scripts pass cookies information to attackers.
**Source:** _allabouttesting.org_
#### Q48: What is ClickJacking? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**ClickJacking** is an attack that fools users into thinking they are clicking on one thing when they are actually clicking on another. The attack is possible thanks to HTML frames (iframes).
Its other name, user interface (UI) redressing, better describes what is going on. Users think they are using a web page’s normal UI, but in fact there is a hidden UI in control; in other words, the UI has been redressed. When users click something they think is safe, the hidden UI performs a different action.
**Source:** _synopsys.com_
## [[⬆]](#toc) 50 Senior Java Developer Interview Questions To Ask in 2020
> Originally published on 👉 50 Senior Java Developer Interview Questions To Ask in 2020 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Builder pattern? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Builder pattern* builds a complex object using simple objects and using a step by step approach. This builder is independent of other objects.
*The Director* class is optional and is used to make sure that the building steps are executed in the *right order* with the right data by the right builder. It's about validation and delegation.
Builder/Director pattern's steps invocations could be semantically presented by *method chaining* or so called *Fluent Interface* syntax.
```js
Pizza pizza = new Pizza.Builder()
.cheese(true)
.pepperoni(true)
.bacon(true)
.build();
```
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q2: What is Adapter Pattern? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Adapter pattern* works as a bridge between two incompatible interfaces. This pattern involves a single class which is responsible to join functionalities of independent or incompatible interfaces (adaptees).

A real life example could be a case of card reader which acts as an adapter between memory card and a laptop. You plugin the memory card into card reader and card reader into the laptop so that memory card can be read via laptop.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q3: What is Facade pattern? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Facade pattern** hides the complexities of the system and provides an interface to the client using which the client can access the system. This type of design pattern comes under *structural pattern* as this pattern adds an interface to existing system to hide its complexities.

This pattern involves a single class which provides simplified methods required by client and delegates calls to methods of existing system classes.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q4: What is the function of CI (Continuous Integration) server? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
CI server function is to continuously integrate all changes being made and committed to repository by different developers and check for compile errors. It needs to build code several times a day, preferably after every commit so it can detect which commit made the breakage if the breakage happens.
**Source:** _linoxide.com_
#### Q5: What are the differences between continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Developers practicing **continuous integration** merge their changes back to the main branch as often as possible. By doing so, you avoid the integration hell that usually happens when people wait for release day to merge their changes into the release branch.
* **Continuous delivery** is an extension of continuous integration to make sure that you can release new changes to your customers quickly in a sustainable way. This means that on top of having automated your testing, you also have automated your release process and you can deploy your application at any point of time by clicking on a button.
* **Continuous deployment** goes one step further than continuous delivery. With this practice, every change that passes all stages of your production pipeline is released to your customers. There's no human intervention, and only a failed test will prevent a new change to be deployed to production.
**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q6: What is JVM? Why is Java called the “Platform Independent Programming Language”? ⭐
**Answer:**
A Java virtual machine (JVM) is a process virtual machine that can execute Java bytecode. Each Java source file is compiled into a bytecode file, which is executed by the JVM. Java was designed to allow application programs to be built that could be run on any platform, without having to be rewritten or recompiled by the programmer for each separate platform. A Java virtual machine makes this possible, because it is aware of the specific instruction lengths and other particularities of the underlying hardware platform.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q7: What is the Difference between JDK and JRE? ⭐
**Answer:**
* **The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) **is basically the Java Virtual Machine (**JVM**) where your Java programs are being executed. It also includes browser plugins for applet execution.
* **The Java Development Kit (JDK)** is the full featured Software Development Kit for Java, including the JRE, the compilers and tools (like JavaDoc, and Java Debugger), in order for a user to develop, compile and execute Java applications.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q8: What does System.gc() and Runtime.gc() methods do? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
These methods can be used as a hint to the JVM, in order to start a garbage collection. However, this it is up to the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) to start the garbage collection immediately or later in time.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q9: What is JDBC? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
JDBC is an abstraction layer that allows users to choose between databases. [JDBC enables developers to write database applications in Java](http://www.javacodegeeks.com/2014/03/java-8-friday-java-8-will-revolutionize-database-access.html), without having to concern themselves with the underlying details of a particular database.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q10: What is reflection and why is it useful? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The name **reflection** is used to describe code which is able to inspect other code in the same system (or itself) and to make modifications at runtime.
For example, say you have an object of an unknown type in Java, and you would like to call a 'doSomething' method on it if one exists. Java's static typing system isn't really designed to support this unless the object conforms to a known interface, but using reflection, your code can look at the object and find out if it has a method called 'doSomething' and then call it if you want to.
```java
Method method = foo.getClass().getMethod("doSomething", null);
method.invoke(foo, null);
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q11: What is difference between fail-fast and fail-safe? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The [Iterator's](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/Iterator.html) fail-safe property works with the clone of the underlying collection and thus, it is not affected by any modification in the collection. All the collection classes in java.util package are fail-fast, while the collection classes in java.util.concurrent are fail-safe. Fail-fast iterators throw a [ConcurrentModificationException](http://examples.javacodegeeks.com/java-basics/exceptions/java-util-concurrentmodificationexception-how-to-handle-concurrent-modification-exception/), while fail-safe iterator never throws such an exception.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q12: What is structure of Java Heap? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The JVM has a heap that is the runtime data area from which memory for all class instances and arrays is allocated. It is created at the JVM start-up. Heap memory for objects is reclaimed by an automatic memory management system which is known as a garbage collector. Heap memory consists of live and dead objects. Live objects are accessible by the application and will not be a subject of garbage collection. Dead objects are those which will never be accessible by the application, but have not been collected by the garbage collector yet. Such objects occupy the heap memory space until they are eventually collected by the garbage collector.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q13: Which Swing methods are thread-safe? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are only three thread-safe methods:
* repaint,
* revalidate,
* invalidate.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q14: Is Java “pass-by-reference” or “pass-by-value”? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Java is always **pass-by-value**. Unfortunately, when we pass the value of an object, we are passing the _reference_ to it. There is no such thing as "pass-by-reference" in Java. This is confusing to beginners.
The key to understanding this is that something like
```java
Dog myDog;
```
is not a Dog; it's actually a `pointer` to a Dog.
So when you have
```java
Dog myDog = new Dog("Rover");
foo(myDog);
```
you're essentially passing the address of the created `Dog` object to the `foo` method.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q15: How do I read/convert an InputStream into a String in Java? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A nice way to do this is using Apache commons `IOUtils` to copy the `InputStream` into a `StringWriter` like:
```java
tringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
IOUtils.copy(inputStream, writer, encoding);
String theString = writer.toString();
```
or
```java
// NB: does not close inputStream, you'll have to use try-with-resources for that
String theString = IOUtils.toString(inputStream, encoding);
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q16: What is a JavaBean exactly? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Basically, a "Bean" follows the standart:
* is a **serializable** object (that is, it implements `java.io.Serializable`, and does so correctly), that
* has "properties" whose getters and setters are just methods with certain names (like, say, getFoo() is the getter for the "Foo" property), and
* has a public 0-arg constructor (so it can be created at will and configured by setting its properties).
There is no syntactic difference between a JavaBean and another class - a class is a JavaBean if it follows the standards.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q17: Can == be used on enum? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Yes**: enums have tight instance controls that allows you to use == to compare instances. Here's the guarantee provided by the language specification.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q18: What are the differences between == and equals? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
As a reminder, it needs to be said that generally, `==` is NOT a viable alternative to `equals`. When it is, however (such as with enum), there are two important differences to consider:
1. `==` never throws `NullPointerException`
```java
enum Color { BLACK, WHITE };
Color nothing = null;
if (nothing == Color.BLACK); // runs fine
if (nothing.equals(Color.BLACK)); // throws NullPointerEx
```
2. `==` is subject to type compatibility check at compile time
```java
enum Color { BLACK, WHITE };
enum Chiral { LEFT, RIGHT };
if (Color.BLACK.equals(Chiral.LEFT)); // compiles fine
if (Color.BLACK == Chiral.LEFT); // DOESN'T COMPILE!!! Incompatible types!
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q19: Is there anything like static class in java? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Java has **no way** of making a top-level class static but you can simulate a static class like this:
* Declare your class final - Prevents extension of the class since extending a static class makes no sense
* Make the constructor private - Prevents instantiation by client code as it makes no sense to instantiate a static class
* Make all the members and functions of the class static - Since the class cannot be instantiated no instance methods can be called or instance fields accessed
* Note that the compiler will not prevent you from declaring an instance (non-static) member. The issue will only show up if you attempt to call the instance member
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q20: What do the ... dots in the method parameters mean? ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
What do the 3 dots in the following method mean?
```java
public void myMethod(String... strings){
// method body
}
```
**Answer:**
That feature is called varargs, and it's a feature introduced in Java 5. It means that function can receive multiple `String` arguments:
```java
myMethod("foo", "bar");
myMethod("foo", "bar", "baz");
myMethod(new String[]{"foo", "var", "baz"}); // you can eve
```
Then, you can use the `String` var as an array:
```java
public void myMethod(String... strings){
for(String whatever : strings){
// do what ever you want
}
// the code above is is equivalent to
for( int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++){
// classical for. In this case you use strings[i]
}
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q21: What is the JIT? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **JIT** is the JVM’s mechanism by which it can optimize code at runtime.
JIT means **Just In Time**. It is a central feature of any JVM. Among other optimizations, it can perform code inlining, lock coarsening or lock eliding, escape analysis etc.
The main benefit of the JIT is on the programmer’s side: code should be written so that it just works; if the code can be optimized at runtime, more often than not, the JIT will find a way.
**Source:** _codementor.io_
#### Q22: What is the volatile keyword useful for? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`volatile` has semantics for memory visibility. Basically, the value of a volatile field becomes visible to all readers (other threads in particular) after a write operation completes on it. Without volatile, readers could see some non-updated value.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q23: Compare the sleep() and wait() methods in Java ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* `sleep()` is a blocking operation that keeps a hold on the monitor / lock of the shared object for the specified number of milliseconds.
* `wait()`, on the other hand, simply pauses the thread until either (a) the specified number of milliseconds have elapsed or (b) it receives a desired notification from another thread (whichever is first), without keeping a hold on the monitor/lock of the shared object.
`sleep()` is most commonly used for polling, or to check for certain results, at a regular interval. `wait()` is generally used in multithreaded applications, in conjunction with `notify() / notifyAll()`, to achieve synchronization and avoid race conditions.
**Source:** _toptal.com_
#### Q24: What is the difference between Serial and Throughput Garbage collector? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q25: What is RMI? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: Why is Spring MVC better than Servlets / JSP ? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: Why is char[] preferred over String for passwords? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Why does `String` pose a threat to security when it comes to passwords? It feels inconvenient to use `char[]`?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: What is Double Brace initialization in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: Explain a use case for the Builder Design Pattern ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: Is null check needed before calling instanceof? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Will
```java
null instanceof SomeClass
```
return `false` or throw a `NullPointerException`?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: What does 'synchronized' mean? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: What's wrong with Double Brace initialization in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: Provide some examples when a finally block won't be executed in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q34: Explain what will the code return ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider:
```java
try { return true; } finally { return false; }
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q35: What is an efficient way to implement a singleton pattern in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q36: What's the difference between SoftReference and WeakReference in Java? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q37: Compare volatile vs static variables in Java ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q38: What are the pros and cons of Microservice Architecture? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q39: What is Materialized View pattern and when will you use it? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q40: What is the relationship between a class and an object? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A class acts as a blue-print that defines the properties, states, and behaviors that are common to a number of objects. An object is an instance of the class. For example, you have a class called _Vehicle_ and _Car_ is the object of that class. You can create any number of objects for the class named _Vehicle_, such as _Van_, _Truck_, and _Auto_.
The _new_ operator is used to create an object of a class. When an object of a class is instantiated, the system allocates memory for every data member that is present in the class.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q41: State the features of an interface. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An interface is a template that contains only the signature of methods. The signature of a method consists of the numbers of parameters, the type of parameter (value, reference, or output), and the order of parameters. An interface has no implementation on its own because it contains only the definition of methods without any method body. An interface is defined using the _interface_ keyword. Moreover, you cannot instantiate an interface. The various features of an interface are as follows:
* An interface is used to implement multiple inheritance in code. This feature of an interface is quite different from that of abstract classes because a class cannot derive the features of more than one class but can easily implement multiple interfaces.
* It defines a specific set of methods and their arguments.
* Variables in interface must be declared as _public_, _static_, and _final_ while methods must be _public_ and _abstract_.
* A class implementing an interface must implement all of its methods.
* An interface can derive from more than one interface.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q42: What is Coupling in OOP? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q43: What is Spring? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Spring** is an open source development framework for enterprise Java. The core features of the Spring Framework can be used in developing any Java application, but there are extensions for building web applications on top of the Java EE platform. Spring framework targets to make J2EE development easier to use and promote good programming practice by enabling a POJO-based (Plain Old Java Object) programming model.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q44: What are benefits of using Spring? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Following is the list of few of the great benefits of using Spring Framework:
* **Lightweight** − Spring is lightweight when it comes to size and transparency. The basic version of spring framework is around 2MB.
* **Inversion of control (IOC)** − Loose coupling is achieved in spring using the technique Inversion of Control. The objects give their dependencies instead of creating or looking for dependent objects.
* **Aspect oriented (AOP)** − Spring supports Aspect oriented programming and enables cohesive development by separating application business logic from system services.
* **Container** − Spring contains and manages the life cycle and configuration of application objects.
* **MVC Framework** − Spring's web framework is a well-designed web MVC framework, which provides a great alternative to web frameworks such as Struts or other over-engineered or less popular web frameworks.
* **Transaction Management** − Spring provides a consistent transaction management interface that can scale down to a local transaction (using a single database, for example) and scale up to global transactions (using JTA, for example).
* **Exception Handling** − Spring provides a convenient API to translate technology-specific exceptions (thrown by JDBC, Hibernate, or JDO, for example) into consistent, unchecked exceptions.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q45: What are Spring beans? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The objects that form the backbone of your application and that are managed by the Spring IoC container are called **beans**. A bean is an object that is instantiated, assembled, and otherwise managed by a Spring IoC container. These beans are created with the configuration metadata that you supply to the container, for example, in the form of XML `` definitions.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q46: What is Application Context? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
On the surface, an application context is the same as a bean factory. Both load bean definitions, wire beans together, and dispense beans upon request. But it also provides:
* A means for resolving text messages, including support for internationalization
* A generic way to load file resources
* Events to beans that are registered as listeners
**Source:** _developersbook.com_
#### Q47: What is Spring IoC container? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The Spring IoC creates the objects, wire them together, configure them, and manage their complete lifecycle from creation till destruction. The Spring container uses dependency injection (DI) to manage the components that make up an application.
There are two types of IoC containers in Spring:
* **Bean Factory container** − This is the simplest container providing basic support for DI .The BeanFactory is usually preferred where the resources are limited like mobile devices or applet based applications
* **Spring ApplicationContext Container** − This container adds more enterprise-specific functionality such as the ability to resolve textual messages from a properties file and the ability to publish application events to interested event listeners.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q48: What is Controller in Spring MVC framework? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Controllers** provide access to the application behavior that you typically define through a service interface. Controllers interpret user input and transform it into a model that is represented to the user by the view. Spring implements a controller in a very abstract way, which enables you to create a wide variety of controllers.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q49: Does Spring Bean provide thread safety? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The default scope of Spring bean is singleton, so there will be only one instance per context. That means that all the having a class level variable that any thread can update will lead to inconsistent data. Hence in default mode spring beans are not thread-safe.
However, we can change spring bean scope to request, prototype or session to achieve thread-safety at the cost of performance. It’s a design decision and based on the project requirements.
**Source:** _journaldev.com_
#### Q50: What is the difference between concern and cross-cutting concern in Spring AOP? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 6 Web Security Interview Questions for Full Stack Developers
> Originally published on 👉 6 Web Security Interview Questions for Full Stack Developers | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: How to mitigate the SQL Injection risks? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
To mitigate SQL injection:
* **Prepared Statements with Parameterized Queries:** Always ensure that your SQL interpreter always able to differentiate between code and data. Never use dynamic queries which fail to find the difference between code and data. Instead, use static SQL query and then pass in the external input as a parameter to query. Use of Prepared Statements (with Parameterized Queries) force developer to first define all the SQL code, and then pass in each parameter to the query later.
* **Use of Stored Procedures:** Stored Procedure is like a function in C where database administrator call it whenever he/she need it. It is not completely mitigated SQL injection but definitely helps in reducing risks of SQL injection by avoiding dynamic SQL generation inside.
* **White List Input Validation:** Always use white list input validation and allow only preapproved input by the developer. Never use blacklist approach as it is less secure than whitelist approach.
* **Escaping All User Supplied Input**
* **Enforcing Least Privilege**
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q2: What is Cross Site Scripting (XSS)? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
By using **Cross Site Scripting (XSS)** technique, users executed malicious scripts (also called payloads) unintentionally by clicking on untrusted links and hence, these scripts pass cookies information to attackers.
**Source:** _allabouttesting.org_
#### Q3: What is ClickJacking? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**ClickJacking** is an attack that fools users into thinking they are clicking on one thing when they are actually clicking on another. The attack is possible thanks to HTML frames (iframes).
Its other name, user interface (UI) redressing, better describes what is going on. Users think they are using a web page’s normal UI, but in fact there is a hidden UI in control; in other words, the UI has been redressed. When users click something they think is safe, the hidden UI performs a different action.
**Source:** _synopsys.com_
#### Q4: List the attributes of Security Testing ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Security testing** is to be carried out to make sure that whether the system prevents the unauthorized user to access the resource and data. Security Testing needs to cover the seven attributes of Security Testing:
* **Authentication** - Authentication is a process of identifying the person before accessing the system. It allows user to access the system information only if authentication check got passed.
* **Authorization** - Once the Authentication passed the Authorization comes in the picture to limit the user as per the permission set for the user.
* **Confidentiality** - Confidentiality is to be carried out to check if unauthorized user and less privileged users are not able to access the information. It is to check that the protection of information and resources from the users other than the authorized and authenticated.
* **Availability** - The availability of system is to check the system is available for authorized users whenever they want to use except for the maintenance window & upgrade for security patches.
* **Integrity** - Integrity is to make sure that the information received is not altered during the transit & check if correct information presented to user is as per the user groups, privileges & restrictions.
* **Non-repudiation** - Nonrepudiation is the assurance that someone cannot deny something. For security testing it is tracking who is accessing the systems and which of the requests were denied along with additional details like the Timestamp and the IP address from where the requests came from.
* **Resilience** - Resilience is to check the system is resistance to bear the attacks, this can be implemented using encryption, use OTP (One Time Password), two layer authentication or RSA key token.
**Source:** _softwaretestingclass.com_
#### Q5: What are the types of XSS? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q6: What is HSTS? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 60 Java and Spring Interview Questions You Must Know
> Originally published on 👉 60 Java and Spring Interview Questions You Must Know | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Circular Queue and why will you use one? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Circular Queue** is a *linear data structure* in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position to make a circle. It is also called *Ring Buffer*. Circular queue avoids the *wastage of space* in a regular queue implementation using arrays.
**Source:** _programiz.com_
#### Q2: What does “program to interfaces, not implementations” mean? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Coding against interface* means, the client code always holds an Interface object which is supplied by a *factory*.
Any instance returned by the factory would be of type Interface which any factory candidate class must have implemented. This way the client program is not worried about implementation and the interface signature determines what all operations can be done.
This approach can be used to change the behavior of a program at run-time. It also helps you to write far better programs from the maintenance point of view.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q3: What is Observer pattern? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Observer pattern** (also known as *Publish-Subscribe Pattern*) is used when there is one-to-many relationship between objects such as if one object is modified, its dependent objects are to be notified automatically. Observer pattern falls under _behavioral_ pattern category.
An object with a one-to-many relationship with other objects who are interested in its state is called the _subject_ or _publisher_. The _observers_ are notified whenever the state of the _subject_ changes and can act accordingly. The _subject_ can have any number of dependent _observers_ which it notifies, and any number of _observers_ can subscribe to the _subject_ to receive such notifications.
Observer pattern uses two actor classes:
* The Observer (os Subscriber) abstract class provides an `update()` method which will be called by the subject to notify it of the subject’s state change.
* The Subject (or Publisher) class is also an abstract class and defines four primary methods: `attach()`, `detach()`, `setState()`, and `notify()`

**Source:** _sitepoint.com_
#### Q4: What's the difference between the Dependency Injection and Service Locator patterns? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q5: What is the Difference between JDK and JRE? ⭐
**Answer:**
* **The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) **is basically the Java Virtual Machine (**JVM**) where your Java programs are being executed. It also includes browser plugins for applet execution.
* **The Java Development Kit (JDK)** is the full featured Software Development Kit for Java, including the JRE, the compilers and tools (like JavaDoc, and Java Debugger), in order for a user to develop, compile and execute Java applications.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q6: What is the difference between an Applet and a Java Application? ⭐
**Answer:**
* Applets are executed within a Java enabled browser, but a
* Java application is a standalone Java program that can be executed outside of a browser.
However, they both require the existence of a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Furthermore, a Java application requires a main method with a specific signature, in order to start its execution. Java applets don’t need such a method to start their execution. Finally, Java applets typically use a restrictive security policy, while Java applications usually use more relaxed security policies.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q7: What is a JSP Page? ⭐
**Answer:**
A **Java Server Page (JSP)** is a text document that contains two types of text:
* static data and
* JSP elements.
Static data can be expressed in any text-based format, such as HTML or XML. JSP is a technology that mixes static content with dynamically-generated content.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q8: What is a Servlet? ⭐
**Answer:**
The servlet is a Java programming language class used to process client requests and generate dynamic web content. Servlets are mostly used to process or store data submitted by an HTML form, provide dynamic content and manage state information that does not exist in the stateless HTTP protocol.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q9: What are pass by reference and pass by value? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* When an object is **passed by value**, this means that a copy of the object is passed. Thus, even if changes are made to that object, it doesn’t affect the original value.
* When an object is **passed by reference**, this means that the actual object is not passed, rather a reference of the object is passed. Thus, any changes made by the external method, are also reflected in all places.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q10: What are the basic interfaces of Java Collections Framework? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Java Collections Framework** provides a well designed set of interfaces and classes that support operations on a collections of objects. The most basic interfaces that reside in the Java Collections Framework are:
* **Collection**, which represents a group of objects known as its elements.
* **Set**, which is a collection that cannot contain duplicate elements.
* **List**, which is an ordered collection and can contain duplicate elements.
* **Map**, which is an object that maps keys to values and cannot contain duplicate keys.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q11: What differences exist between HashMap and Hashtable? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are several differences between `HashMap` and `Hashtable` in Java:
1. `Hashtable` is synchronized, whereas `HashMap` is not. This makes `HashMap` better for non-threaded applications, as unsynchronized Objects typically perform better than synchronized ones.
2. `Hashtable` does not allow `null` keys or values. `HashMap` allows one `null` key and any number of `null` values.
3. One of HashMap's subclasses is `LinkedHashMap`, so in the event that you'd want predictable iteration order (which is insertion order by default), you could easily swap out the `HashMap` for a `LinkedHashMap`. This wouldn't be as easy if you were using `Hashtable`.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q12: What does System.gc() and Runtime.gc() methods do? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
These methods can be used as a hint to the JVM, in order to start a garbage collection. However, this it is up to the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) to start the garbage collection immediately or later in time.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q13: What is the difference between Exception and Error in java? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* An **Error** "indicates serious problems that a reasonable application should not try to catch."
* An **Exception** "indicates conditions that a reasonable application might want to catch."
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q14: What is an Java Applet? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A Java Applet is program that can be included in a HTML page and be executed in a java enabled client browser. Applets are used for creating dynamic and interactive web applications.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q15: What is JDBC? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
JDBC is an abstraction layer that allows users to choose between databases. [JDBC enables developers to write database applications in Java](http://www.javacodegeeks.com/2014/03/java-8-friday-java-8-will-revolutionize-database-access.html), without having to concern themselves with the underlying details of a particular database.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q16: How are the JSP requests handled? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
On the arrival of a JSP request, the browser first requests a page with a .jsp extension. Then, the Web server reads the request and using the JSP compiler, the Web server converts the JSP page into a servlet class. Notice that the JSP file is compiled only on the first request of the page, or if the JSP file has changed.The generated servlet class is invoked, in order to handle the browser’s request. Once the execution of the request is over, the servlet sends a response back to the client. See [how to get Request parameters in a JSP](http://examples.javacodegeeks.com/enterprise-java/jsp/get-request-parameter-in-jsp-page/).
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q17: What are Decalarations? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Declarations are similar to variable declarations in Java. Declarations are used to declare variables for subsequent use in expressions or scriptlets. To add a declaration, you must use the sequences to enclose your declarations.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q18: Can you access non static variable in static context? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A static variable in Java belongs to its class and its value remains the same for all its instances. A static variable is initialized when the class is loaded by the JVM. If your code tries to access a non-static variable, without any instance, the compiler will complain, because those variables are not created yet and they are not associated with any instance.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q19: Does Java support multiple inheritance? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
No, Java does not support multiple inheritance. Each class is able to extend only on one class, but is able to implement more than one interfaces.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q20: Explain different ways of creating a thread. Which one would you prefer and why? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are three ways that can be used in order for a [Thread](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/Thread.html) to be created:
* A class may extend the [Thread](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/Thread.html) class.
* A class may implement the [Runnable](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/Runnable.html) interface.
* An application can use the [Executor](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/Executor.html) framework, in order to create a thread pool.
The [Runnable](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/Runnable.html) interface is preferred, as it does not require an object to inherit the [Thread](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/Thread.html) class. In case your application design requires multiple inheritance, only interfaces can help you. Also, the thread pool is very efficient and can be implemented and used very easily.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q21: What’s a deadlock? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A condition that occurs when [two processes are waiting for each other to complete](http://www.javacodegeeks.com/2013/01/java-deadlock-example-how-to-analyze-deadlock-situation.html), before proceeding. The result is that both processes wait endlessly.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q22: What is difference between fail-fast and fail-safe? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The [Iterator's](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/Iterator.html) fail-safe property works with the clone of the underlying collection and thus, it is not affected by any modification in the collection. All the collection classes in java.util package are fail-fast, while the collection classes in java.util.concurrent are fail-safe. Fail-fast iterators throw a [ConcurrentModificationException](http://examples.javacodegeeks.com/java-basics/exceptions/java-util-concurrentmodificationexception-how-to-handle-concurrent-modification-exception/), while fail-safe iterator never throws such an exception.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q23: What is Java Priority Queue? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The [PriorityQueue](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/PriorityQueue.html) is an unbounded queue, based on a priority heap and its elements are ordered in their natural order. At the time of its creation, we can provide a Comparator that is responsible for ordering the elements of the [PriorityQueue](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/PriorityQueue.html). A [PriorityQueue](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/PriorityQueue.html) doesn’t allow null values, those objects that doesn’t provide natural ordering, or those objects that don’t have any comparator associated with them. Finally, the Java [PriorityQueue](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/PriorityQueue.html) is not thread-safe and it requires O(log(n)) time for its enqueing and dequeing operations.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q24: When is the finalize() called? What is the purpose of finalization? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The finalize method is called by the garbage collector, just before releasing the object’s memory. It is normally advised to release resources held by the object inside the finalize method.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q25: What is structure of Java Heap? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The JVM has a heap that is the runtime data area from which memory for all class instances and arrays is allocated. It is created at the JVM start-up. Heap memory for objects is reclaimed by an automatic memory management system which is known as a garbage collector. Heap memory consists of live and dead objects. Live objects are accessible by the application and will not be a subject of garbage collection. Dead objects are those which will never be accessible by the application, but have not been collected by the garbage collector yet. Such objects occupy the heap memory space until they are eventually collected by the garbage collector.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q26: What are the restrictions imposed on Java applets? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Mostly due to security reasons, the following restrictions are imposed on Java applets:
* An applet cannot load libraries or define native methods.
* An applet cannot ordinarily read or write files on the execution host.
* An applet cannot read certain system properties.
* An applet cannot make network connections except to the host that it came from.
* An applet cannot start any program on the host that’s executing it.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q27: What are Scriptlets? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In Java Server Pages (JSP) technology, a scriptlet is a piece of Java-code embedded in a JSP page. The scriptlet is everything inside the tags. Between these tags, a user can add any valid scriplet.
**Source:** _github.com/snowdream_
#### Q28: What is the difference between a synchronized method and a synchronized block? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: How do you ensure that N threads can access N resources without deadlock? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: What is Perm Gen space in Heap? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: What is RMI? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: What are the layers of RMI Architecture? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: State the features of an interface. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An interface is a template that contains only the signature of methods. The signature of a method consists of the numbers of parameters, the type of parameter (value, reference, or output), and the order of parameters. An interface has no implementation on its own because it contains only the definition of methods without any method body. An interface is defined using the _interface_ keyword. Moreover, you cannot instantiate an interface. The various features of an interface are as follows:
* An interface is used to implement multiple inheritance in code. This feature of an interface is quite different from that of abstract classes because a class cannot derive the features of more than one class but can easily implement multiple interfaces.
* It defines a specific set of methods and their arguments.
* Variables in interface must be declared as _public_, _static_, and _final_ while methods must be _public_ and _abstract_.
* A class implementing an interface must implement all of its methods.
* An interface can derive from more than one interface.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q34: Explain different types of inheritance. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q35: What is the difference between association, aggregation and composition? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q36: What does SOLID stand for? What are its principles? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**S.O.L.I.D** is an acronym for the first five object-oriented design (OOD) principles by Robert C. Martin.
* **S** - *Single-responsiblity principle*. A class should have one and only one reason to change, meaning that a class should have only one job.
* **O** - *Open-closed principle*. Objects or entities should be open for extension, but closed for modification.
* **L** - *Liskov substitution principle*. Let q(x) be a property provable about objects of x of type T. Then q(y) should be provable for objects y of type S where S is a subtype of T.
* **I** - *Interface segregation principle*. A client should never be forced to implement an interface that it doesn't use or clients shouldn't be forced to depend on methods they do not use.
* **D** - *Dependency Inversion Principle*. Entities must depend on abstractions not on concretions. It states that the high level module must not depend on the low level module, but they should depend on abstractions.
**Source:** _scotch.io_
#### Q37: What are the DRY and DIE principles? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In software engineering, **Don't Repeat Yourself (DRY)** or **Duplication is Evil (DIE)** is a principle of software development.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q38: Is it better to return NULL or empty values from functions/methods where the return value is not present? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Returning `null` is usually the best idea if you intend to indicate that no data is available.
An empty object implies data has been returned, whereas returning `null` clearly indicates that nothing has been returned.
Additionally, returning a `null` will result in a null exception if you attempt to access members in the object, which can be useful for highlighting buggy code - attempting to access a member of nothing makes no sense. Accessing members of an empty object will not fail meaning bugs can go undiscovered.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q39: What is GOD class and why should we avoid it? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q40: What are benefits of using Spring? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Following is the list of few of the great benefits of using Spring Framework:
* **Lightweight** − Spring is lightweight when it comes to size and transparency. The basic version of spring framework is around 2MB.
* **Inversion of control (IOC)** − Loose coupling is achieved in spring using the technique Inversion of Control. The objects give their dependencies instead of creating or looking for dependent objects.
* **Aspect oriented (AOP)** − Spring supports Aspect oriented programming and enables cohesive development by separating application business logic from system services.
* **Container** − Spring contains and manages the life cycle and configuration of application objects.
* **MVC Framework** − Spring's web framework is a well-designed web MVC framework, which provides a great alternative to web frameworks such as Struts or other over-engineered or less popular web frameworks.
* **Transaction Management** − Spring provides a consistent transaction management interface that can scale down to a local transaction (using a single database, for example) and scale up to global transactions (using JTA, for example).
* **Exception Handling** − Spring provides a convenient API to translate technology-specific exceptions (thrown by JDBC, Hibernate, or JDO, for example) into consistent, unchecked exceptions.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q41: What are Spring beans? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The objects that form the backbone of your application and that are managed by the Spring IoC container are called **beans**. A bean is an object that is instantiated, assembled, and otherwise managed by a Spring IoC container. These beans are created with the configuration metadata that you supply to the container, for example, in the form of XML `` definitions.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q42: What are ORM's Spring supports? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Spring supports the following ORM's:
* Hibernate
* iBatis
* JPA (Java Persistence API)
* TopLink
* JDO (Java Data Objects)
* OJB
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q43: What is Spring Security? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Spring Security** is a separate module of the Spring framework that focuses on providing authentication and authorization methods in Java applications. It also takes care of most of the common security vulnerabilities such as CSRF attacks.
To use Spring Security in web applications, you can get started with a simple annotation: _@EnableWebSecurity_.
**Source:** _developersbook.com_
#### Q44: Explain Bean lifecycle in Spring framework ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Following is sequence of a bean lifecycle in Spring:
* **Instantiate** − First the spring container finds the bean's definition from the XML file and instantiates the bean..
* **Populate properties** − Using the dependency injection, spring populates all of the properties as specified in the bean definition.
* **Set Bean Name** − If the bean implements BeanNameAware interface, spring passes the bean's id to setBeanName() method.
* **Set Bean factory** − If Bean implements BeanFactoryAware interface, spring passes the beanfactory to setBeanFactory() method.
* **Pre Initialization** − Also called postprocess of bean. If there are any bean BeanPostProcessors associated with the bean, Spring calls postProcesserBeforeInitialization() method.
* **Initialize beans** − If the bean implements IntializingBean,its afterPropertySet() method is called. If the bean has init method declaration, the specified initialization method is called.
* **Post Initialization** − If there are any BeanPostProcessors associated with the bean, their postProcessAfterInitialization() methods will be called.
* **Ready to use** − Now the bean is ready to use by the application.
* **Destroy** − If the bean implements DisposableBean , it will call the destroy() method .
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q45: What is Controller in Spring MVC framework? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Controllers** provide access to the application behavior that you typically define through a service interface. Controllers interpret user input and transform it into a model that is represented to the user by the view. Spring implements a controller in a very abstract way, which enables you to create a wide variety of controllers.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q46: What is Aspect? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An **Aspect** is a module which has a set of APIs providing _cross-cutting_ requirements. For example, a logging module would be called AOP aspect for logging. An application can have any number of aspects depending on the requirement. In Spring AOP, aspects are implemented using regular classes (the schema-based approach) or regular classes annotated with the @Aspect annotation (`@AspectJ` style).
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q47: What is the typical Bean life cycle in Spring Bean Factory Container? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Bean life cycle in Spring Bean Factory Container is as follows:
* The spring container finds the beans definition from the XML file and instantiates the bean.
* Using the dependency injection, spring populates all of the properties as specified in the bean definition
* If the bean implements the BeanNameAware interface, the factory calls `setBeanName()` passing the beans ID.
* If the bean implements the BeanFactoryAware interface, the factory calls `setBeanFactory()`, passing an instance of itself.
* If there are any BeanPostProcessors associated with the bean, their post- `ProcessBeforeInitialization()` methods will be called.
* If an init-method is specified for the bean, it will be called.
* Finally, if there are any BeanPostProcessors associated with the bean, their `postProcessAfterInitialization()` methods will be called.
**Source:** _developersbook.com_
#### Q48: How to handle exceptions in Spring MVC Framework? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Spring MVC Framework provides the following ways to help us achieving robust exception handling.
1. **Controller Based** – We can define exception handler methods in our controller classes. All we need is to annotate these methods with @ExceptionHandler annotation.
2. **Global Exception Handler** – Exception Handling is a cross-cutting concern and Spring provides @ControllerAdvice annotation that we can use with any class to define our global exception handler.
3. **HandlerExceptionResolver implementation** – For generic exceptions, most of the times we serve static pages. Spring Framework provides `HandlerExceptionResolver` interface that we can implement to create global exception handler. The reason behind this additional way to define global exception handler is that Spring framework also provides default implementation classes that we can define in our spring bean configuration file to get spring framework exception handling benefits.
**Source:** _journaldev.com_
#### Q49: What is Spring IoC Container? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Inversion of Control** (IoC) is the mechanism to achieve loose-coupling between Objects dependencies. To achieve loose coupling and dynamic binding of the objects at runtime, the objects define their dependencies that are being injected by other assembler objects. Spring IoC container is the program that injects dependencies into an object and makes it ready for our use.
Spring Framework IoC container classes are part of `org.springframework.beans` and `org.springframework.context` packages and provides us different ways to decouple the object dependencies.
Some of the useful ApplicationContext implementations that we use are;
* `AnnotationConfigApplicationContext`: For standalone java applications using annotations based configuration.
* `ClassPathXmlApplicationContext`: For standalone java applications using XML based configuration.
* `FileSystemXmlApplicationContext`: Similar to ClassPathXmlApplicationContext except that the xml configuration file can be loaded from anywhere in the file system.
* `AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext` and `XmlWebApplicationContext` for web applications.
**Source:** _journaldev.com_
#### Q50: Is the DispatcherServlet instantiated via an application context? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
No, the `DispatcherServlet` is instantiated by Servlet containers like Tomcat or Jetty. You must define the `DispatcherServlet` into the web.xml file as shown below.
You can see that load-on-startup tag is 1, which means `DispatcherServlet` is instantiated when you deploy the Spring MVC application to Tomcat or any other Servlet container. During instantiation, it looks for a file servlet-name-context.xml and then initializes beans defined in this file.
**Source:** _dzone.com_
#### Q51: What is the purpose of the session scope? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The purpose of the **session scope** is to create an instance of the bean for an HTTP Session. This means the same bean can serve multiple requests if it is scoped in session. You can define the scope of a Spring bean using scope attribute or the `@Scope` annotation in a Spring MVC application.
**Source:** _dzone.com_
#### Q52: What bean scopes does Spring support? Explain them. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q53: What is Weaving? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q54: What is the difference between concern and cross-cutting concern in Spring AOP? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q55: What are some benefits of using Spring Transactions? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q56: What is Aspect-Oriented Programming? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q57: What is Spring WebFlux? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q58: Compare @Component (v2.5) versus @Bean (v 3.0) ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Would it have been possible to re-use the @Component annotation instead of introducing @Bean annotation?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q59: What are some of the best practices for Spring Framework? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q60: How does autowiring work in Spring? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 70 C# Interview Questions You Must Know [2019 Update]
> Originally published on 👉 70 C# Interview Questions You Must Know [2019 Update] | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is the .NET Framework? ⭐
**Answer:**
The .NET is a Framework, which is a collection of classes of reusable libraries given by Microsoft to be used in other .NET applications and to develop, build and deploy many types of applications on the Windows platform including the following:
* Console Applications
* Windows Forms Applications
* Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) Applications
* Web Applications
* Web Services
* Windows Services
* Services-oriented applications using Windows Communications Foundation (WCF)
* Workflow-enabled applications using Windows Workflow Foundation(WF)
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q2: What is .NET Standard? ⭐
**Answer:**
The **.NET Standard** is a formal specification of .NET APIs that are intended to be available on all .NET implementations.
**Source:** _docs.microsoft.com_
#### Q3: What is a .NET application domain? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It is an isolation layer provided by the .NET runtime. As such, App domains live with in a process (1 process can have many app domains) and have their own virtual address space.
App domains are useful because:
* They are less expensive than full processes
* They are multithreaded
* You can stop one without killing everything in the process
* Segregation of resources/config/etc
* Each app domain runs on its own security level
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q4: When should we use .NET Core and .NET Standard Class Library project types? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Use a **.NET Standard** library when you want to increase the number of apps that will be compatible with your library, and you are okay with a decrease in the .NET API surface area your library can access.
* Use a **.NET Core** library when you want to increase the .NET API surface area your library can access, and you are okay with allowing only .NET Core apps to be compatible with your library.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q5: How to choose the target version of .NET Standard library? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q6: What is an Object? ⭐
**Answer:**
According to MSDN, "_a class or struct definition is like a blueprint that specifies what the type can do. An object is basically a block of memory that has been allocated and configured according to the blueprint. A program may create many objects of the same class. Objects are also called instances, and they can be stored in either a named variable or in an array or collection. Client code is the code that uses these variables to call the methods and access the public properties of the object. In an object-oriented language such as C#, a typical program consists of multiple objects interacting dynamically"._
Objects helps us to access the member of a class or struct either they can be fields, methods or properties, by using the dot.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q7: What is Managed or Unmanaged Code? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Managed Code** - The code, which is developed in .NET framework is known as managed code. This code is directly executed by CLR with the help of managed code execution. Any language that is written in .NET Framework is managed code.
* **Unmanaged Code** - The code, which is developed outside .NET framework is known as unmanaged code. Applications that do not run under the control of the CLR are said to be unmanaged, and certain languages such as C++ can be used to write such applications, which, for example, access low - level functions of the operating system. Background compatibility with the code of VB, ASP and COM are examples of unmanaged code.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q8: What is Boxing and Unboxing? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Boxing and Unboxing both are used for type conversion but have some difference:
* **Boxing** - Boxing is the process of converting a value type data type to the object or to any interface data type which is implemented by this value type. When the CLR boxes a value means when CLR is converting a value type to Object Type, it wraps the value inside a System.Object and stores it on the heap area in application domain.
* **Unboxing** - Unboxing is also a process which is used to extract the value type from the object or any implemented interface type. Boxing may be done implicitly, but unboxing have to be explicit by code.
The concept of boxing and unboxing underlines the C# unified view of the type system in which a value of any type can be treated as an object.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q9: What are generics in C#? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Generics** allow you to delay the specification of the data type of programming elements in a class or a method, until it is actually used in the program. In other words, generics allow you to write a class or method that can work with any data type.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q10: What is Serialization? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Serialization** means saving the state of your object to secondary memory, such as a file.
1. Binary serialization (Save your object data into binary format).
2. Soap Serialization (Save your object data into binary format; mainly used in network related communication).
3. XmlSerialization (Save your object data into an XML file).
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q11: Why can't you specify the accessibility modifier for methods inside the interface? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In an interface, we have virtual methods that do not have method definition. All the methods are there to be overridden in the derived class. That's why they all are public.
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q12: What is an Abstract Class? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An **Abstract class** is a class which is denoted by abstract keyword and can be used only as a Base class. An Abstract class should always be inherited. An instance of the class itself cannot be created. If we do not want any program to create an object of a class, then such classes can be made abstract.
Any method in the abstract class does not have implementations in the same class. But they must be implemented in the child class.
**Source:** _softwaretestinghelp.com_
#### Q13: In how many ways you can pass parameters to a method? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are three ways that parameters can be passed to a method:
* **Value parameters** − This method copies the actual value of an argument into the formal parameter of the function. In this case, changes made to the parameter inside the function have no effect on the argument.
* **Reference parameters** − This method copies the reference to the memory location of an argument into the formal parameter. This means that changes made to the parameter affect the argument.
* **Output parameters** − This method helps in returning more than one value.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q14: What are reference types in C#? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **reference types** do not contain the actual data stored in a variable, but they contain a reference to the variables.
In other words, they refer to a memory location. Using multiple variables, the reference types can refer to a memory location. If the data in the memory location is changed by one of the variables, the other variable automatically reflects this change in value. Example of built-in reference types are: object, dynamic, and string.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q15: What are nullable types in C#? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
C# provides a special data types, the **nullable types**, to which you can assign normal range of values as well as null values.
For example, you can store any value from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 or null in a `Nullable` variable. Similarly, you can assign true, false, or null in a `Nullable` variable.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q16: Why to use “finally” block in C#? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Finally** block will be executed irrespective of exception. So while executing the code in try block when exception is occurred, control is returned to catch block and at last `finally` block will be executed. So closing connection to database / releasing the file handlers can be kept in `finally` block.
**Source:** _a4academics.com_
#### Q17: What is the difference between Interface and Abstract Class? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are some differences between **Abstract Class** and **Interface** which are listed below:
* A class can implement any number of interfaces but a subclass can at most use only one abstract class.
* An abstract class can have non-abstract methods (concrete methods) while in case of interface all the methods has to be abstract.
* An abstract class can declare or use any variables while an interface is not allowed to do so.
* In an abstract class all data member or functions are private by default while in interface all are public, we can't change them manually.
* In an abstract class we need to use abstract keyword to declare abstract methods while in an interface we don't need to use that.
* An abstract class can't be used for multiple inheritance while interface can be used as multiple inheritance.
* An abstract class use constructor while in an interface we don't have any type of constructor.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q18: What is the difference between overloading and overriding? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Overloading** is when you have multiple methods in the same scope, with the same name but different signatures.
```csharp
//Overloading
public class test
{
public void getStuff(int id)
{}
public void getStuff(string name)
{}
}
```
* **Overriding** is a principle that allows you to change the functionality of a method in a child class.
```csharp
//Overriding
public class test
{
public virtual void getStuff(int id)
{
//Get stuff default location
}
}
public class test2 : test
{
public override void getStuff(int id)
{
//base.getStuff(id);
//or - Get stuff new location
}
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q19: What is Virtual Method in C#? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A virtual method is a method that can be redefined in derived classes. A virtual method has an implementation in a base class as well as derived class. When a virtual method is invoked, the run-time type of the object is checked for an overriding member.
1. By default, methods are non-virtual. We can't override a non-virtual method.
2. We can't use the virtual modifier with the static, abstract, private or override modifiers.
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q20: Explain Anonymous type in C# ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Anonymous types** allow us to create a new type without defining them. This is way to defining read only properties into a single object without having to define type explicitly. Here Type is generating by the compiler and it is accessible only for the current block of code. The type of properties is also inferred by the compiler.
Consider:
```csharp
var anonymousData = new
{
ForeName = "Jignesh",
SurName = "Trivedi"
};
Console.WriteLine("First Name : " + anonymousData.ForeName);
```
**Source:** _c-sharpcorner.com_
#### Q21: What is difference between constants and readonly? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Constant variables are declared and initialized at compile time. The value can't be changed afterwards. Readonly is used only when we want to assign the value at run time.
**Source:** _guru99.com_
#### Q22: What is the difference between Virtual method and Abstract method? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* A **Virtual method** must always have a default implementation. However, it can be overridden in the derived class, though not mandatory. It can be overridden using _override_ keyword.
* An **Abstract method** does not have an implementation. It resides in the abstract class. It is mandatory that the derived class implements the abstract method. An _override_ keyword is not necessary here though it can be used.
**Source:** _softwaretestinghelp.com_
#### Q23: What is the difference between dynamic type variables and object type variables? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Dynamic types are similar to object types except that type checking for object type variables takes place at compile time, whereas that for the dynamic type variables takes place at run time.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q24: What is the use of Null Coalescing Operator (??) in C#? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **??** operator is called the **null-coalescing operator** and is used to define a default value for nullable value types or reference types. It returns the left-hand operand if the operand is not null; otherwise, it returns the right operand.
```csharp
string name = null;
string myname = name ?? "Laxmi";
Console.WriteLine(myname);
```
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q25: What is the output of the program below? Explain your answer. ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider:
```csharp
delegate void Printer();
static void Main()
{
List printers = new List();
int i=0;
for(; i < 10; i++)
{
printers.Add(delegate { Console.WriteLine(i); });
}
foreach (var printer in printers)
{
printer();
}
}
```
**Answer:**
This program will output the number 10 ten times.
Here’s why: The delegate is added in the for loop and “reference” (or perhaps “pointer” would be a better choice of words) to `i` is stored, rather than the value itself. Therefore, after we exit the loop, the variable `i` has been set to 10, so by the time each delegate is invoked, the value passed to all of them is 10.
**Source:** _toptal.com_
#### Q26: What is marshalling and why do we need it? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q27: What is the Constructor Chaining in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q28: What is an Object Pool in .Net? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q29: What are the differences between a multidimensional array and an array of arrays in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
What are the differences between multidimensional arrays `double[,]` and array-of-arrays `double[][]` in C#?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q30: What are the different ways a method can be overloaded? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: Can you create a function in C# which can accept varying number of arguments? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q32: Is operator overloading supported in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q33: What is the use of conditional preprocessor directive in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q34: Can we have only “try” block without “catch” block in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q35: What are the uses of delegates in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q36: Can Multiple Inheritance implemented in C# ? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q37: What is the output of the program below? Explain your answer. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider:
```csharp
class Program {
private static string result;
static void Main() {
SaySomething();
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
static async Task SaySomething() {
await Task.Delay(5);
result = "Hello world!";
return “Something”;
}
}
```
Also, would the answer change if we were to replace `await Task.Delay(5);` with `Thread.Sleep(5)`? Why or why not?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q38: What is the "yield" keyword used for in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Consider:
```csharp
IEnumerable FilteredList()
{
foreach( object item in FullList )
{
if( IsItemInPartialList( item )
yield return item;
}
}
```
Could you explain what does the `yield` keyword do there?
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q39: Explain what is short-circuit evaluation in C# ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q40: What is deep or shallow copy concept in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q41: What is multicast delegate in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q42: List some different ways for equality check in .Net ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q43: What is a preprocessor directives in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q44: Calculate the circumference of the circle ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Given an instance circle of the following class:
```csharp
public sealed class Circle {
private double radius;
public double Calculate(Func op) {
return op(radius);
}
}
write code to calculate the circumference of the circle, without modifying the `Circle` class itself.
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q45: What is the difference between lambdas and delegates? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q46: Could you explain the difference between Func vs. Action vs. Predicate? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q47: Can you add extension methods to an existing static class? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q48: Implement the "Where" method in C# ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q49: Explain what is weak reference in C#? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q50: What is Anonymous function? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An Anonymous function is a special function which does not have any name. We just define their parameters and define the code into the curly braces.
Consider:
```csharp
delegate int func(int a, int b);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
func f1 = delegate(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
};
Console.WriteLine(f1(1, 2));
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q51: Mention what is the role of DataContext classes in LINQ? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**DataContext** class acts as a bridge between SQL Server database and the LINQ to SQL. For accessing the database and also for changing the data in the database, it contains connections string and the functions. Essentially a DataContext class performs the following three tasks:
* Create connection to database.
* It submits and retrieves object to database.
* Converts objects to SQL queries and vice versa.
**Source:** _career.guru99.com_
#### Q52: Using LINQ to remove elements from a List ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
Given that `authorsList` is of type `List`, how can I delete the `Author` elements that are equalling to `Bob`?
**Answer:**
Consider:
```csharp
authorsList.RemoveAll(x => x.FirstName == "Bob");
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q53: What is Expression Trees and how they used in LINQ? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
An **Expression Tree** is a data structure that contains Expressions, which is basically code. So it is a tree structure that represents a calculation you may make in code. These pieces of code can then be executed by "running" the expression tree over a set of data.
In LINQ, expression trees are used to represent structured queries that target sources of data that implement `IQueryable`. For example, the LINQ provider implements the `IQueryable` interface for querying relational data stores. The C# compiler compiles queries that target such data sources into code that builds an expression tree at runtime. The query provider can then traverse the expression tree data structure and translate it into a query language appropriate for the data source.
**Source:** _docs.microsoft.com_
#### Q54: Get the indexes of top n items where item value = true ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
I have a `List`. I need to get the indexes of top n items where item `value = true`.
```csharp
10011001000
TopTrueIndexes(3) = The first 3 indexes where bits are true are 0, 3, 4
TopTrueIndexes(4) = The first 4 indexes where bits are true are 0, 3, 4, 7
```
**Answer:**
Assuming you have some easily-identifiable condition, you can do something like this, which will work for any `IEnumerable`:
```csharp
var query = source.Select((value, index) => new { value, index })
.Where(x => x.value => Condition(value))
.Select(x => x.index)
.Take(n);
```
The important bits are that you use the overload of `Select` to get index/value pairs before the Where, and then another Select to get just the indexes after the Where... and use Take to only get the first n results.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q55: Name some advantages of LINQ over Stored Procedures ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q56: When should I use a CompiledQuery? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q57: Name some disadvantages of LINQ over sprocs ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q58: A structure in C# can implement one or more interfaces. Is it true or false? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Yes, it is true. Like classes, in C#, structures can implement one or more interfaces.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q59: Can you allow a class to be inherited, but prevent a method from being overridden in C#? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Yes. Just declare the class `public` and make the method `sealed`.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q60: How can you prevent a class from overriding in C#? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
You can prevent a class from overriding in C# by using the `sealed` keyword.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q61: Can you specify the accessibility modifier for methods inside the interface? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
All the methods inside an interface are always `public`, by default. You cannot specify any other access modifier for them.
**Source:** _indiabix.com_
#### Q62: What is Coupling in OOP? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q63: What is Cohesion in OOP? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q64: Explain the concept of destructor? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q65: Explain different types of inheritance. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q66: Why Doesn't C# Allow Static Methods to Implement an Interface? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q67: What is LSP (Liskov Substitution Principle) and what are some examples of its use (good and bad)? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q68: Why prefer composition over inheritance? What trade-offs are there for each approach? When should you choose inheritance over composition? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q69: Can you declare a private class in a namespace? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q70: You have defined a destructor in a class that you have developed by using the C# programming language, but the destructor never executed. Why did the destructor not execute? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 75+ JavaScript Interview Questions [ES6/ES2015 Update] in 2019
> Originally published on 👉 75+ JavaScript Interview Questions [ES6/ES2015 Update] in 2019 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Coercion in JavaScript?
**Answer:**
In JavaScript conversion between different two build-in types called `coercion`. Coercion comes in two forms in JavaScript: *explicit* and *implicit*.
Here's an example of explicit coercion:
```js
var a = "42";
var b = Number( a );
a; // "42"
b; // 42 -- the number!
```
And here's an example of implicit coercion:
```js
var a = "42";
var b = a * 1; // "42" implicitly coerced to 42 here
a; // "42"
b; // 42 -- the number!
```
#### Q2: What is Scope in JavaScript? ⭐
**Answer:**
In JavaScript, each function gets its own *scope*. Scope is basically a collection of variables as well as the rules for how those variables are accessed by name. Only code inside that function can access that function's scoped variables.
A variable name has to be unique within the same scope. A scope can be nested inside another scope. If one scope is nested inside another, code inside the innermost scope can access variables from either scope.
#### Q3: Explain equality in JavaScript ⭐
**Answer:**
JavaScript has both strict and type–converting comparisons:
* **Strict comparison (e.g., ===)** checks for value equality without allowing *coercion*
* **Abstract comparison (e.g. ==)** checks for value equality with *coercion* allowed
```js
var a = "42";
var b = 42;
a == b; // true
a === b; // false
```
Some simple equalityrules:
* If either value (aka side) in a comparison could be the `true` or `false` value, avoid `==` and use `===`.
* If either value in a comparison could be of these specific values (`0`, `""`, or `[]` -- empty array), avoid `==` and use `===`.
* In all other cases, you're safe to use `==`. Not only is it safe, but in many cases it simplifies your code in a way that improves readability.
#### Q4: What is typeof operator? ⭐
**Answer:**
JavaScript provides a `typeof` operator that can examine a value and tell you what type it is:
```js
var a;
typeof a; // "undefined"
a = "hello world";
typeof a; // "string"
a = 42;
typeof a; // "number"
a = true;
typeof a; // "boolean"
a = null;
typeof a; // "object" -- weird, bug
a = undefined;
typeof a; // "undefined"
a = { b: "c" };
typeof a; // "object"
```
#### Q5: What is the object type? ⭐
**Answer:**
The object type refers to a compound value where you can set properties (named locations) that each hold their own values of any type.
```js
var obj = {
a: "hello world", // property
b: 42,
c: true
};
obj.a; // "hello world", accessed with doted notation
obj.b; // 42
obj.c; // true
obj["a"]; // "hello world", accessed with bracket notation
obj["b"]; // 42
obj["c"]; // true
```
Bracket notation is also useful if you want to access a property/key but the name is stored in another variable, such as:
```js
var obj = {
a: "hello world",
b: 42
};
var b = "a";
obj[b]; // "hello world"
obj["b"]; // 42
```
#### Q6: Explain arrays in JavaScript ⭐
**Answer:**
An `array` is an object that holds values (of any type) not particularly in named properties/keys, but rather in numerically indexed positions:
```js
var arr = [
"hello world",
42,
true
];
arr[0]; // "hello world"
arr[1]; // 42
arr[2]; // true
arr.length; // 3
typeof arr; // "object"
```
#### Q7: Explain Values and Types in JavaScript ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
JavaScript has typed values, not typed variables. The following built-in types are available:
* `string`
* `number`
* `boolean`
* `null` and `undefined`
* `object`
* `symbol` (new to ES6)
#### Q8: Explain Null and Undefined in JavaScript ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
JavaScript (and by extension TypeScript) has two bottom types: `null` and `undefined`. They are *intended* to mean different things:
* Something hasn't been initialized : `undefined`.
* Something is currently unavailable: `null`.
#### Q9: What is a Polyfill? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A polyfill is essentially the specific code (or plugin) that would allow you to have some specific functionality that you expect in current or “modern” browsers to also work in other browsers that do not have the support for that functionality built in.
* Polyfills are not part of the HTML5 standard
* Polyfilling is not limited to Javascript
**Source:** _programmerinterview.com_
#### Q10: What is let keyword in JavaScript? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In addition to creating declarations for variables at the function level, ES6 lets you declare variables to belong to individual blocks (pairs of { .. }), using the `let` keyword.
**Source:** _github.com/getify_
#### Q11: Being told that an unsorted array contains (n - 1) of n consecutive numbers (where the bounds are defined), find the missing number in O(n) time ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
```js
// The output of the function should be 8
var arrayOfIntegers = [2, 5, 1, 4, 9, 6, 3, 7];
var upperBound = 9;
var lowerBound = 1;
findMissingNumber(arrayOfIntegers, upperBound, lowerBound); // 8
function findMissingNumber(arrayOfIntegers, upperBound, lowerBound) {
// Iterate through array to find the sum of the numbers
var sumOfIntegers = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < arrayOfIntegers.length; i++) {
sumOfIntegers += arrayOfIntegers[i];
}
// Find theoretical sum of the consecutive numbers using a variation of Gauss Sum.
// Formula: [(N * (N + 1)) / 2] - [(M * (M - 1)) / 2];
// N is the upper bound and M is the lower bound
upperLimitSum = (upperBound * (upperBound + 1)) / 2;
lowerLimitSum = (lowerBound * (lowerBound - 1)) / 2;
theoreticalSum = upperLimitSum - lowerLimitSum;
return theoreticalSum - sumOfIntegers;
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q12: Remove duplicates of an array and return an array of only unique elements ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
```js
// ES6 Implementation
var array = [1, 2, 3, 5, 1, 5, 9, 1, 2, 8];
Array.from(new Set(array)); // [1, 2, 3, 5, 9, 8]
// ES5 Implementation
var array = [1, 2, 3, 5, 1, 5, 9, 1, 2, 8];
uniqueArray(array); // [1, 2, 3, 5, 9, 8]
function uniqueArray(array) {
var hashmap = {};
var unique = [];
for(var i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
// If key returns undefined (unique), it is evaluated as false.
if(!hashmap.hasOwnProperty(array[i])) {
hashmap[array[i]] = 1;
unique.push(array[i]);
}
}
return unique;
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q13: Given a string, reverse each word in the sentence ⭐⭐
**Details:**
For example `Welcome to this Javascript Guide!` should be become `emocleW ot siht tpircsavaJ !ediuG`
**Answer:**
```js
var string = "Welcome to this Javascript Guide!";
// Output becomes !ediuG tpircsavaJ siht ot emocleW
var reverseEntireSentence = reverseBySeparator(string, "");
// Output becomes emocleW ot siht tpircsavaJ !ediuG
var reverseEachWord = reverseBySeparator(reverseEntireSentence, " ");
function reverseBySeparator(string, separator) {
return string.split(separator).reverse().join(separator);
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q14: Implement enqueue and dequeue using only two stacks ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Enqueue* means to add an element, *dequeue* to remove an element.
```js
var inputStack = []; // First stack
var outputStack = []; // Second stack
// For enqueue, just push the item into the first stack
function enqueue(stackInput, item) {
return stackInput.push(item);
}
function dequeue(stackInput, stackOutput) {
// Reverse the stack such that the first element of the output stack is the
// last element of the input stack. After that, pop the top of the output to
// get the first element that was ever pushed into the input stack
if (stackOutput.length <= 0) {
while(stackInput.length > 0) {
var elementToOutput = stackInput.pop();
stackOutput.push(elementToOutput);
}
}
return stackOutput.pop();
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q15: Explain event bubbling and how one may prevent it ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Event bubbling** is the concept in which an event triggers at the deepest possible element, and triggers on parent elements in nesting order. As a result, when clicking on a child element one may exhibit the handler of the parent activating.
One way to prevent event bubbling is using `event.stopPropagation()` or `event.cancelBubble` on IE < 9.
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q16: How to check if an object is an array or not? Provide some code. ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
> The best way to find whether an object is instance of a particular class or not using `toString` method from `Object.prototype`
```javascript
var arrayList = [1 , 2, 3];
```
One of the best use cases of type checking of an object is when we do method overloading in JavaScript. For understanding this let say we have a method called `greet` which take one single string and also a list of string, so making our `greet` method workable in both situation we need to know what kind of parameter is being passed, is it single value or list of value?
```javascript
function greet(param) {
if() {
// here have to check whether param is array or not
}
else {
}
}
```
However, in above implementation it might not necessary to check type for array, we can check for single value string and put array logic code in else block, let see below code for the same.
```javascript
function greet(param) {
if(typeof param === 'string') {
}
else {
// If param is of type array then this block of code would execute
}
}
```
Now it's fine we can go with above two implementations, but when we have a situation like a parameter can be `single value`, `array`, and `object` type then we will be in trouble.
Coming back to checking type of object, As we mentioned that we can use `Object.prototype.toString`
```javascript
if(Object.prototype.toString.call(arrayList) === '[object Array]') {
console.log('Array!');
}
```
If you are using `jQuery` then you can also used jQuery `isArray` method:
```javascript
if($.isArray(arrayList)) {
console.log('Array');
} else {
console.log('Not an array');
}
```
FYI jQuery uses `Object.prototype.toString.call` internally to check whether an object is an array or not.
In modern browser, you can also use:
```javascript
Array.isArray(arrayList);
```
`Array.isArray` is supported by Chrome 5, Firefox 4.0, IE 9, Opera 10.5 and Safari 5
**Source:** _github.com/ganqqwerty_
#### Q17: Write a function that would allow you to do this. ⭐⭐
**Details:**
```js
var addSix = createBase(6);
addSix(10); // returns 16
addSix(21); // returns 27
```
**Answer:**
You can create a closure to keep the value passed to the function `createBase` even after the inner function is returned. The inner function that is being returned is created within an outer function, making it a closure, and it has access to the variables within the outer function, in this case the variable `baseNumber`.
```js
function createBase(baseNumber) {
return function(N) {
// we are referencing baseNumber here even though it was declared
// outside of this function. Closures allow us to do this in JavaScript
return baseNumber + N;
}
}
var addSix = createBase(6);
addSix(10);
addSix(21);
```
**Source:** _coderbyte.com_
#### Q18: How would you check if a number is an integer? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A very simply way to check if a number is a decimal or integer is to see if there is a remainder left when you divide by 1.
```js
function isInt(num) {
return num % 1 === 0;
}
console.log(isInt(4)); // true
console.log(isInt(12.2)); // false
console.log(isInt(0.3)); // false
```
**Source:** _coderbyte.com_
#### Q19: What does "use strict" do? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The `use strict` literal is entered at the top of a JavaScript program or at the top of a function and it helps you write safer JavaScript code by throwing an error if a global variable is created by mistake. For example, the following program will throw an error:
```js
function doSomething(val) {
"use strict";
x = val + 10;
}`
```
It will throw an error because `x` was not defined and it is being set to some value in the global scope, which isn't allowed with `use strict` The small change below fixes the error being thrown:
```js
function doSomething(val) {
"use strict";
var x = val + 10;
}
```
**Source:** _coderbyte.com_
#### Q20: Explain what a callback function is and provide a simple example. ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A `callback` function is a function that is passed to another function as an argument and is executed after some operation has been completed. Below is an example of a simple callback function that logs to the console *after* some operations have been completed.
```js
function modifyArray(arr, callback) {
// do something to arr here
arr.push(100);
// then execute the callback function that was passed
callback();
}
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
modifyArray(arr, function() {
console.log("array has been modified", arr);
});
```
**Source:** _coderbyte.com_
#### Q21: What are some of the advantages/disadvantages of writing JavaScript code in a language that compiles to JavaScript? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Some examples of languages that compile to JavaScript include CoffeeScript, Elm, ClojureScript, PureScript, and TypeScript.
Advantages:
* Fixes some of the longstanding problems in JavaScript and discourages JavaScript anti-patterns.
* Enables you to write shorter code, by providing some syntactic sugar on top of JavaScript, which I think ES5 lacks, but ES2015 is awesome.
* Static types are awesome (in the case of TypeScript) for large projects that need to be maintained over time.
Disadvantages:
* Require a build/compile process as browsers only run JavaScript and your code will need to be compiled into JavaScript before being served to browsers.
* Debugging can be a pain if your source maps do not map nicely to your pre-compiled source.
* Most developers are not familiar with these languages and will need to learn it. There's a ramp up cost involved for your team if you use it for your projects.
* Smaller community (depends on the language), which means resources, tutorials, libraries, and tooling would be harder to find.
* IDE/editor support might be lacking.
* These languages will always be behind the latest JavaScript standard.
* Developers should be cognizant of what their code is being compiled to — because that is what would actually be running, and that is what matters in the end.
Practically, ES2015 has vastly improved JavaScript and made it much nicer to write. I don't really see the need for CoffeeScript these days.
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q22: Why would you use something like the `load` event? Does this event have disadvantages? Do you know any alternatives, and why would you use those? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The `load` event fires at the end of the document loading process. At this point, all of the objects in the document are in the DOM, and all the images, scripts, links and sub-frames have finished loading.
The DOM event `DOMContentLoaded` will fire after the DOM for the page has been constructed, but do not wait for other resources to finish loading. This is preferred in certain cases when you do not need the full page to be loaded before initializing.
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q23: Make this work ⭐⭐
**Details:**
```js
duplicate([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]); // [1,2,3,4,5,1,2,3,4,5]
```
**Answer:**
```js
function duplicate(arr) {
return arr.concat(arr);
}
duplicate([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]); // [1,2,3,4,5,1,2,3,4,5]
```
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q24: Explain the same-origin policy with regards to JavaScript. ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The same-origin policy prevents JavaScript from making requests across domain boundaries. An origin is defined as a combination of URI scheme, hostname, and port number. This policy prevents a malicious script on one page from obtaining access to sensitive data on another web page through that page's Document Object Model.
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q25: What is the difference between `==` and `===`? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`==` is the abstract equality operator while `===` is the strict equality operator. The `==` operator will compare for equality after doing any necessary type conversions. The `===` operator will not do type conversion, so if two values are not the same type `===` will simply return `false`. When using `==`, funky things can happen, such as:
```js
1 == '1'; // true
1 == [1]; // true
1 == true; // true
0 == ''; // true
0 == '0'; // true
0 == false; // true
```
My advice is never to use the `==` operator, except for convenience when comparing against `null` or `undefined`, where `a == null` will return `true` if `a` is `null` or `undefined`.
```js
var a = null;
console.log(a == null); // true
console.log(a == undefined); // true
```
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q26: Is there anyway to force using strict mode in Node.js? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
you can place
```js
"use strict";
```
at the top of your file in **node >= 0.10.7**, but if you want your whole app to run in strict (**including external modules**) you can do this
```sh
node --use_strict
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q27: How to compare two objects in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Two non-primitive values, like objects (including function and array) held by reference, so both `==` and `===` comparisons will simply check whether the references match, not anything about the underlying values.
For example, `arrays` are by default coerced to strings by simply joining all the values with commas (`,`) in between. So two arrays with the same contents would not be `==` equal:
```js
var a = [1,2,3];
var b = [1,2,3];
var c = "1,2,3";
a == c; // true
b == c; // true
a == b; // false
```
For *deep object comparison* use external libs like `deep-equal` or implement your own recursive equality algorithm.
#### Q28: What is the difference between anonymous and named functions? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Consider:
```js
var foo = function() { // anonymous function assigned to variable foo
// ..
};
var x = function bar(){ // named function (bar) assigned to variable x
// ..
};
foo(); // actual function execution
x();
```
#### Q29: What is the difference between a shim and a polyfill? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* A **shim** is any piece of code that performs interception of an API call and provides a layer of abstraction. It isn't necessarily restricted to a web application or HTML5/CSS3.
* A **polyfill** is a type of shim that retrofits legacy browsers with modern HTML5/CSS3 features usually using Javascript or Flash.
A shim is a library that brings a new API to an older environment, using only the means of that environment. Thus, a polyfill is a shim for a browser API.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com/_
#### Q30: Could you explain the difference between ES5 and ES6 ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **ECMAScript 5 (ES5)**: The 5th edition of ECMAScript, standardized in 2009. This standard has been implemented fairly completely in all modern browsers
* **ECMAScript 6 (ES6)/ ECMAScript 2015 (ES2015)**: The 6th edition of ECMAScript, standardized in 2015. This standard has been partially implemented in most modern browsers.
Here are some key differences between ES5 and ES6:
* **Arrow functions** & **string interpolation**:
Consider:
```js
const greetings = (name) => {
return `hello ${name}`;
}
```
and even:
```js
const greetings = name => `hello ${name}`;
```
* **Const**.
Const works like a constant in other languages in many ways but there are some caveats. Const stands for ‘constant reference’ to a value. So with const, you can actually mutate the properties of an object being referenced by the variable. You just can’t change the reference itself.
```js
const NAMES = [];
NAMES.push("Jim");
console.log(NAMES.length === 1); // true
NAMES = ["Steve", "John"]; // error
```
* **Block-scoped variables**.
The new ES6 keyword `let` allows developers to scope variables at the block level.
`Let` doesn’t hoist in the same way `var` does.
* **Default parameter values**
Default parameters allow us to initialize functions with default values. A default is used when an argument is either omitted or undefined — meaning null is a valid value.
```js
// Basic syntax
function multiply (a, b = 2) {
return a * b;
}
multiply(5); // 10
```
* ** Class Definition and Inheritance**
ES6 introduces language support for classes (`class` keyword), constructors (`constructor` keyword), and the `extend` keyword for inheritance.
* **for-of operator**
The for...of statement creates a loop iterating over iterable objects.
* **Spread Operator**
For objects merging
```js
const obj1 = { a: 1, b: 2 }
const obj2 = { a: 2, c: 3, d: 4}
const obj3 = {...obj1, ...obj2}
```
* **Promises**
Promises provide a mechanism to handle the results and errors from asynchronous operations. You can accomplish the same thing with callbacks, but promises provide improved readability via method chaining and succinct error handling.
```js
const isGreater = (a, b) => {
return new Promise ((resolve, reject) => {
if(a > b) {
resolve(true)
} else {
reject(false)
}
})
}
isGreater(1, 2)
.then(result => {
console.log('greater')
})
.catch(result => {
console.log('smaller')
})
```
* **Modules exporting & importing**
Consider module exporting:
```js
const myModule = { x: 1, y: () => { console.log('This is ES5') }}
export default myModule;
```
and importing:
```js
import myModule from './myModule';
```
#### Q31: Given an array of integers, find the largest difference between two elements such that the element of lesser value must come before the greater element ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
```js
var array = [7, 8, 4, 9, 9, 15, 3, 1, 10];
// [7, 8, 4, 9, 9, 15, 3, 1, 10] would return `11` based on the difference between `4` and `15`
// Notice: It is not `14` from the difference between `15` and `1` because 15 comes before 1.
findLargestDifference(array);
function findLargestDifference(array) {
// If there is only one element, there is no difference
if (array.length <= 1) return -1;
// currentMin will keep track of the current lowest
var currentMin = array[0];
var currentMaxDifference = 0;
// We will iterate through the array and keep track of the current max difference
// If we find a greater max difference, we will set the current max difference to that variable
// Keep track of the current min as we iterate through the array, since we know the greatest
// difference is yield from `largest value in future` - `smallest value before it`
for (var i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] > currentMin && (array[i] - currentMin > currentMaxDifference)) {
currentMaxDifference = array[i] - currentMin;
} else if (array[i] <= currentMin) {
currentMin = array[i];
}
}
// If negative or 0, there is no largest difference
if (currentMaxDifference <= 0) return -1;
return currentMaxDifference;
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q32: Find the intersection of two arrays. An intersection would be the common elements that exists within both arrays. In this case, these elements should be unique! ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
```js
var firstArray = [2, 2, 4, 1];
var secondArray = [1, 2, 0, 2];
intersection(firstArray, secondArray); // [2, 1]
function intersection(firstArray, secondArray) {
// The logic here is to create a hashmap with the elements of the firstArray as the keys.
// After that, you can use the hashmap's O(1) look up time to check if the element exists in the hash
// If it does exist, add that element to the new array.
var hashmap = {};
var intersectionArray = [];
firstArray.forEach(function(element) {
hashmap[element] = 1;
});
// Since we only want to push unique elements in our case... we can implement a counter to keep track of what we already added
secondArray.forEach(function(element) {
if (hashmap[element] === 1) {
intersectionArray.push(element);
hashmap[element]++;
}
});
return intersectionArray;
// Time complexity O(n), Space complexity O(n)
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q33: Given two strings, return true if they are anagrams of one another ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
For example: `Mary` is an anagram of `Army`
**Answer:**
```js
var firstWord = "Mary";
var secondWord = "Army";
isAnagram(firstWord, secondWord); // true
function isAnagram(first, second) {
// For case insensitivity, change both words to lowercase.
var a = first.toLowerCase();
var b = second.toLowerCase();
// Sort the strings, and join the resulting array to a string. Compare the results
a = a.split("").sort().join("");
b = b.split("").sort().join("");
return a === b;
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q34: Explain the difference between "undefined" and "not defined" in JavaScript ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In JavaScript if you try to use a variable that doesn't exist and has not been declared, then JavaScript will throw an error `var name is not defined` and the script will stop execute thereafter. But If you use `typeof undeclared_variable` then it will return `undefined`.
Before starting further discussion let's understand the difference between declaration and definition.
`var x` is a declaration because you are not defining what value it holds yet, but you are declaring its existence and the need of memory allocation.
```javascript
var x; // declaring x
console.log(x); //output: undefined
```
`var x = 1` is both declaration and definition (also we can say we are doing initialisation), Here declaration and assignment of value happen inline for variable x, In JavaScript every variable declaration and function declaration brings to the top of its current scope in which it's declared then assignment happen in order this term is called `hoisting`.
A variable that is declared but not define and when we try to access it, It will result `undefined`.
```javascript
var x; // Declaration
if(typeof x === 'undefined') // Will return true
```
> A variable that neither declared nor defined when we try to reference such variable then It result `not defined`.
```javascript
console.log(y); // Output: ReferenceError: y is not defined
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q35: What is the drawback of creating true private in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
One of the drawback of creating a true private method in JavaScript is that they are very memory inefficient because a new copy of the method would be created for each instance.
```javascript
var Employee = function (name, company, salary) {
this.name = name || ""; //Public attribute default value is null
this.company = company || ""; //Public attribute default value is null
this.salary = salary || 5000; //Public attribute default value is null
// Private method
var increaseSalary = function () {
this.salary = this.salary + 1000;
};
// Public method
this.dispalyIncreasedSalary = function() {
increaseSalary();
console.log(this.salary);
};
};
// Create Employee class object
var emp1 = new Employee("John","Pluto",3000);
// Create Employee class object
var emp2 = new Employee("Merry","Pluto",2000);
// Create Employee class object
var emp3 = new Employee("Ren","Pluto",2500);
```
Here each instance variable `emp1`, `emp2`, `emp3` has own copy of increaseSalary private method.
So as recommendation don't go for a private method unless it's necessary.
**Source:** _github.com/ganqqwerty_
#### Q36: What will be the output of the following code? ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```javascript
var x = 1;
var output = (function() {
delete x;
return x;
})();
console.log(output);
```
**Answer:**
Above code will output `1` as output. `delete` operator is used to delete property from object. Here `x` is not an object it's **global variable** of type `number`.
**Source:** _github.com/ganqqwerty_
#### Q37: What is IIFEs (Immediately Invoked Function Expressions)? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It’s an Immediately-Invoked Function Expression, or IIFE for short. It executes immediately after it’s created:
```js
(function IIFE(){
console.log( "Hello!" );
})();
// "Hello!"
```
This pattern is often used when trying to avoid polluting the global namespace, because all the variables used inside the IIFE (like in any other normal function) are not visible outside its scope.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q38: Write a function that would allow you to do this ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```js
multiply(5)(6);
```
**Answer:**
You can create a *closure* to keep the value of a even after the inner function is returned. The inner function that is being returned is created within an outer function, making it a closure, and it has access to the variables within the outer function, in this case the variable `a`.
```js
function multiply(a) {
return function(b) {
return a * b;
}
}
multiply(5)(6);
```
**Source:** _coderbyte.com_
#### Q39: What's the difference between using “let” and “var” to declare a variable in ES6? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The difference is _scoping_. `var` is scoped to the nearest function block and `let` is scoped to the nearest enclosing block, which can be smaller than a function block. Both are global if outside any block. Also, variables declared with `let` are not accessible before they are declared in their enclosing block. This will throw a `ReferenceError` exception.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q40: What are the benefits of using spread syntax in ES6 and how is it different from rest syntax? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
ES6's spread syntax is very useful when coding in a functional paradigm as we can easily create copies of arrays or objects without resorting to `Object.create`, `slice`, or a library function. This language feature is used often in Redux and rx.js projects.
```js
function putDookieInAnyArray(arr) {
return [...arr, 'dookie'];
}
const result = putDookieInAnyArray(['I', 'really', "don't", 'like']); // ["I", "really", "don't", "like", "dookie"]
const person = {
name: 'Todd',
age: 29,
};
const copyOfTodd = { ...person };
```
ES6's rest syntax offers a shorthand for including an arbitrary number of arguments to be passed to a function. It is like an inverse of the spread syntax, taking data and stuffing it into an array rather than unpacking an array of data, and it works in function arguments, as well as in array and object destructuring assignments.
```js
function addFiveToABunchOfNumbers(...numbers) {
return numbers.map(x => x + 5);
}
const result = addFiveToABunchOfNumbers(4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10); // [9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]
const [a, b, ...rest] = [1, 2, 3, 4]; // a: 1, b: 2, rest: [3, 4]
const { e, f, ...others } = {
e: 1,
f: 2,
g: 3,
h: 4,
}; // e: 1, f: 2, others: { g: 3, h: 4 }
```
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q41: What is 'Currying'? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Currying is when you break down a function that takes multiple arguments into a series of functions that take part of the arguments. Here's an example in JavaScript:
```js
function add (a, b) {
return a + b;
}
add(3, 4); // returns 7
```
This is a function that takes two arguments, a and b, and returns their sum. We will now curry this function:
```js
function add (a) {
return function (b) {
return a + b;
}
}
```
In an algebra of functions, dealing with functions that take multiple arguments (or equivalent one argument that's an N-tuple) is somewhat inelegant. So how do you deal with something you'd naturally express as, say, f(x,y)? Well, you take that as equivalent to f(x)(y) -- f(x), call it g, is a function, and you apply that function to y. In other words, you only have functions that take one argument -- but some of those functions return other functions (which ALSO take one argument).
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q42: What are the differences between ES6 class and ES5 function constructors? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Let's first look at example of each:
```js
// ES5 Function Constructor
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// ES6 Class
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
```
For simple constructors, they look pretty similar.
The main difference in the constructor comes when using inheritance. If we want to create a `Student` class that subclasses `Person` and add a `studentId` field, this is what we have to do in addition to the above.
```js
// ES5 Function Constructor
function Student(name, studentId) {
// Call constructor of superclass to initialize superclass-derived members.
Person.call(this, name);
// Initialize subclass's own members.
this.studentId = studentId;
}
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Student.prototype.constructor = Student;
// ES6 Class
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, studentId) {
super(name);
this.studentId = studentId;
}
}
```
It's much more verbose to use inheritance in ES5 and the ES6 version is easier to understand and remember.
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q43: Explain the differences on the usage of `foo` between `function foo() {}` and `var foo = function() {}` ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The former is a _function declaration_ while the latter is a _function expression_. The key difference is that function declarations have its body hoisted but the bodies of function expressions are not (they have the same hoisting behavior as variables). If you try to invoke a function expression before it is defined, you will get an `Uncaught TypeError: XXX is not a function` error.
**Function Declaration**
```js
foo(); // 'FOOOOO'
function foo() {
console.log('FOOOOO');
}
```
**Function Expression**
```js
foo(); // Uncaught TypeError: foo is not a function
var foo = function() {
console.log('FOOOOO');
};
```
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q44: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using "use strict"? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
'use strict' is a statement used to enable strict mode to entire scripts or individual functions. Strict mode is a way to opt into a restricted variant of JavaScript.
Advantages:
* Makes it impossible to accidentally create global variables.
* Makes assignments which would otherwise silently fail to throw an exception.
* Makes attempts to delete undeletable properties throw (where before the attempt would simply have no effect).
* Requires that function parameter names be unique.
* `this` is undefined in the global context.
* It catches some common coding bloopers, throwing exceptions.
* It disables features that are confusing or poorly thought out.
Disadvantages:
* Many missing features that some developers might be used to.
* No more access to `function.caller` and `function.arguments`.
* Concatenation of scripts written in different strict modes might cause issues.
Overall, I think the benefits outweigh the disadvantages, and I never had to rely on the features that strict mode blocks. I would recommend using strict mode.
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q45: Explain `Function.prototype.bind`. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Taken word-for-word from [MDN](https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_objects/Function/bind):
> The `bind()` method creates a new function that, when called, has its this keyword set to the provided value, with a given sequence of arguments preceding any provided when the new function is called.
In my experience, it is most useful for binding the value of `this` in methods of classes that you want to pass into other functions. This is frequently done in React components.
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q46: What's the difference between `.call` and `.apply`? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Both `.call` and `.apply` are used to invoke functions and the first parameter will be used as the value of `this` within the function. However, `.call` takes in comma-separated arguments as the next arguments while `.apply` takes in an array of arguments as the next argument. An easy way to remember this is C for `call` and comma-separated and A for `apply` and an array of arguments.
```js
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
console.log(add.call(null, 1, 2)); // 3
console.log(add.apply(null, [1, 2])); // 3
```
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q47: What's a typical use case for anonymous functions? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
They can be used in IIFEs to encapsulate some code within a local scope so that variables declared in it do not leak to the global scope.
```js
(function() {
// Some code here.
})();
```
As a callback that is used once and does not need to be used anywhere else. The code will seem more self-contained and readable when handlers are defined right inside the code calling them, rather than having to search elsewhere to find the function body.
```js
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('Hello world!');
}, 1000);
```
Arguments to functional programming constructs or Lodash (similar to callbacks).
```js
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const double = arr.map(function(el) {
return el * 2;
});
console.log(double); // [2, 4, 6]
```
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q48: What do you think of AMD vs CommonJS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Both are ways to implement a module system, which was not natively present in JavaScript until ES2015 came along. CommonJS is synchronous while AMD (Asynchronous Module Definition) is obviously asynchronous. CommonJS is designed with server-side development in mind while AMD, with its support for asynchronous loading of modules, is more intended for browsers.
I find AMD syntax to be quite verbose and CommonJS is closer to the style you would write import statements in other languages. Most of the time, I find AMD unnecessary, because if you served all your JavaScript into one concatenated bundle file, you wouldn't benefit from the async loading properties. Also, CommonJS syntax is closer to Node style of writing modules and there is less context-switching overhead when switching between client side and server side JavaScript development.
I'm glad that with ES2015 modules, that has support for both synchronous and asynchronous loading, we can finally just stick to one approach. Although it hasn't been fully rolled out in browsers and in Node, we can always use transpilers to convert our code.
**Source:** _github.com/yangshun_
#### Q49: Why should we use ES6 classes? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Some reasons you might choose to use **Classes**:
* The syntax is simpler and less error-prone.
* It's **much** easier (and again, less error-prone) to set up inheritance hierarchies using the new syntax than with the old.
* `class` defends you from the common error of failing to use `new` with the constructor function (by having the constructor throw an exception if `this` isn't a valid object for the constructor).
* Calling the parent prototype's version of a method is much simpler with the new syntax than the old (`super.method()` instead of `ParentConstructor.prototype.method.call(this)` or `Object.getPrototypeOf(Object.getPrototypeOf(this)).method.call(this)`).
Consider:
```js
// **ES5**
var Person = function(first, last) {
if (!(this instanceof Person)) {
throw new Error("Person is a constructor function, use new with it");
}
this.first = first;
this.last = last;
};
Person.prototype.personMethod = function() {
return "Result from personMethod: this.first = " + this.first + ", this.last = " + this.last;
};
var Employee = function(first, last, position) {
if (!(this instanceof Employee)) {
throw new Error("Employee is a constructor function, use new with it");
}
Person.call(this, first, last);
this.position = position;
};
Employee.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Employee.prototype.constructor = Employee;
Employee.prototype.personMethod = function() {
var result = Person.prototype.personMethod.call(this);
return result + ", this.position = " + this.position;
};
Employee.prototype.employeeMethod = function() {
// ...
};
```
And the same with ES6 classes:
```js
// ***ES2015+**
class Person {
constructor(first, last) {
this.first = first;
this.last = last;
}
personMethod() {
// ...
}
}
class Employee extends Person {
constructor(first, last, position) {
super(first, last);
this.position = position;
}
employeeMethod() {
// ...
}
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q50: Explain the difference between Object.freeze() vs const ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
`const` and `Object.freeze` are two completely different things.
* `const` applies to **bindings** ("variables"). It creates an immutable binding, i.e. you cannot assign a new value to the binding.
```js
const person = {
name: "Leonardo"
};
let animal = {
species: "snake"
};
person = animal; // ERROR "person" is read-only
```
* `Object.freeze` works on **values**, and more specifically, *object values*. It makes an object immutable, i.e. you cannot change its properties.
```js
let person = {
name: "Leonardo"
};
let animal = {
species: "snake"
};
Object.freeze(person);
person.name = "Lima"; //TypeError: Cannot assign to read only property 'name' of object
console.log(person);
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q51: What is generator in JS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Generators are functions which can be exited and later re-entered. Their context (variable bindings) will be saved across re-entrances. Generator functions are written using the `function*` syntax. When called initially, generator functions do not execute any of their code, instead returning a type of iterator called a Generator. When a value is consumed by calling the generator's `next` method, the Generator function executes until it encounters the `yield` keyword.
The function can be called as many times as desired and returns a new Generator each time, however each Generator may only be iterated once.
```js
function* makeRangeIterator(start = 0, end = Infinity, step = 1) {
let iterationCount = 0;
for (let i = start; i < end; i += step) {
iterationCount++;
yield i;
}
return iterationCount;
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q52: When should we use generators in ES6? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
To put it simple, generator has two features:
* one can choose to jump out of a function and let outer code to determine when to jump back into the function.
* the control of asynchronous call can be done outside of your code
The most important feature in generators — we can get the next value in only when we really need it, not all the values at once. And in some situations it can be very convenient.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q53: What is Hoisting in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q54: How does the “this” keyword work? Provide some code examples. ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q55: What does the term "Transpiling" stand for? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q56: Check if a given string is a isomorphic ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q57: Write a recursive function that performs a binary search ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q58: Given an integer, determine if it is a power of 2. If so, return that number, else return -1 ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q59: What is “closure” in javascript? Provide an example? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q60: What will be the output of the following code? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```javascript
var Employee = {
company: 'xyz'
}
var emp1 = Object.create(Employee);
delete emp1.company
console.log(emp1.company);
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q61: Explain the Prototype Design Pattern ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q62: How would you add your own method to the Array object so the following code would work? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```js
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
var avg = arr.average();
console.log(avg);
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q63: What will the following code output? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```js
0.1 + 0.2 === 0.3
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q64: How would you create a private variable in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q65: What are the actual uses of ES6 WeakMap? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q66: Can you give an example for destructuring an object or an array in ES6? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q67: Explain difference between: `function Person(){}`, `var person = Person()`, and `var person = new Person()`? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q68: What's the difference between a variable that is: `null`, `undefined` or undeclared? How would you go about checking for any of these states? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q69: Explain why the following doesn't work as an IIFE. What needs to be changed to properly make it an IIFE? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```js
function foo(){ }();
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q70: Describe the Revealing Module Pattern design pattern ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q71: Can you give an example of a curry function and why this syntax offers an advantage? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q72: How to "deep-freeze" object in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q73: What is the difference between the await keyword and the yield keyword? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q74: Is it possible to reset an ECMAScript 6 generator to its initial state? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q75: Compare Async/Await and Generators usage to achive same functionality ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 8 Common Full Stack Interview Questions To Brush Up (2018 Edition)
> Originally published on 👉 8 Common Full Stack Interview Questions To Brush Up (2018 Edition) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Inversion of Control? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Inversion of control* is a broad term but for a software developer it's most commonly described as a pattern used for decoupling components and layers in the system.
For example, say your application has a text editor component and you want to provide spell checking. Your standard code would look something like this:
```js
public class TextEditor {
private SpellChecker checker;
public TextEditor() {
this.checker = new SpellChecker();
}
}
```
What we've done here creates a dependency between the TextEditor and the SpellChecker. In an IoC scenario we would instead do something like this:
```js
public class TextEditor {
private IocSpellChecker checker;
public TextEditor(IocSpellChecker checker) {
this.checker = checker;
}
}
```
You have *inverted control* by handing the responsibility of instantiating the spell checker from the TextEditor class to the caller.
```js
SpellChecker sc = new SpellChecker; // dependency
TextEditor textEditor = new TextEditor(sc);
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q2: What is Bridge pattern? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Bridge pattern** is used when we need to decouple an abstraction from its implementation so that the two can vary independently. This type of design pattern comes under *structural* pattern as this pattern decouples implementation class and abstract class by providing a bridge structure between them.
The bridge pattern is useful when both the class and what it does vary often. The class itself can be thought of as the abstraction and what the class can do as the implementation. The bridge pattern can also be thought of as two layers of abstraction.
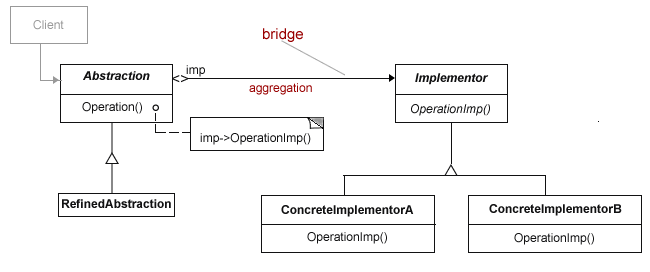
This pattern involves an interface which acts as a bridge which makes the functionality of concrete classes independent from interface implementer classes. Both types of classes can be altered structurally without affecting each other.
The example of bridge pattern implementation is when:
```sh
----Shape---
/ \
Rectangle Circle
/ \ / \
BlueRectangle RedRectangle BlueCircle RedCircle
```
refactored to:
```sh
----Shape--- Color
/ \ / \
Rectangle(Color) Circle(Color) Blue Red
```
or in general when:
```sh
A
/ \
Aa Ab
/ \ / \
Aa1 Aa2 Ab1 Ab2
```
refactored to:
```sh
A N
/ \ / \
Aa(N) Ab(N) 1 2
```
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q3: What are the success factors for Continuous Integration? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Maintain a code repository
* Automate the build
* Make the build self-testing
* Everyone commits to the baseline every day
* Every commit (to baseline) should be built
* Keep the build fast
* Test in a clone of the production environment
* Make it easy to get the latest deliverables
* Everyone can see the results of the latest build
* Automate deployment
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q4: Explain a use case for Docker ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Docker a low overhead way to run virtual machines on your local box or in the cloud. Although they're not strictly distinct machines, nor do they need to boot an OS, they give you many of those benefits.
* Docker can encapsulate legacy applications, allowing you to deploy them to servers that might not otherwise be easy to setup with older packages & software versions.
* Docker can be used to build test boxes, during your deploy process to facilitate continuous integration testing.
* Docker can be used to provision boxes in the cloud, and with swarm you can orchestrate clusters too.
**Source:** _dev.to_
#### Q5: Can you explain what “git reset” does in plain english? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q6: Explain the main difference between REST and GraphQL ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The main and most important difference between REST and GraphQL is that *GraphQL is not dealing with dedicated resources, instead everything is regarded as a graph and therefore is connected and can be queried to app exact needs*.
**Source:** _medium.com/codingthesmartway-com-blog_
#### Q7: Explain prototype inheritance in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q8: What is Event Loop? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Node.js is a single threaded application but it support concurrency via concept of event and callbacks. As every API of Node js are asynchronous and being a single thread, it uses async function calls to maintain the concurrency. Node uses observer pattern. Node thread keeps an event loop and whenever any task get completed, it fires the corresponding event which signals the event listener function to get executed.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
## [[⬆]](#toc) 8 DevOps Interview Questions and Answers in 2018
> Originally published on 👉 8 DevOps Interview Questions and Answers in 2018 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: Explain what is DevOps ? ⭐
**Answer:**
**DevOps** is a newly emerging term in IT field, which is nothing but a practice that emphasizes the collaboration and communication of both software developers and other information-technology (IT) professionals. It focuses on delivering software product faster and lowering the failure rate of releases.
**Source:** _quora.com_
#### Q2: How is DevOps different from Agile/SDLC? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Agile software development methodology focuses on the development of software.
* DevOps on the other hand is responsible for development as well as deployment of the software in the safest and most reliable way possible.
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q3: What does Containerization mean? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Containerisation* is a type of *virtualization* strategy that emerged as an alternative to traditional hypervisor-based virtualization.
In containerization, the operating system is shared by the different containers rather than cloned for each virtual machine. For example Docker provides a container virtualization platform that serves as a good alternative to hypervisor-based arrangements.
**Source:** _linoxide.com_
#### Q4: What is the difference between resource allocation and resource provisioning? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Resource allocation is the process of reservation that demarcates a quantity of a resource for a tenant's use.
* Resource provision is the process of activation of a bundle of the allocated quantity to bear the tenant's workload.
Immediately after allocation, all the quantity of a resource is available. Provision removes a quantity of a resource from the available set. De-provision returns a quantity of a resource to the available set.
At any time:
```
Allocated quantity = Available quantity + Provisioned quantity
```
**Source:** _dev.to_
#### Q5: Classify Cloud Platforms by category ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Cloud Computing software can be classified as:
* **Software as a Service or SaaS** - is peace of software that runs over network on remote server and has only user interface exposed to users, usually in web browser. For example salesforce.com.
* **Infrastructure as a Service or IaaS** - is a cloud environment that exposes VM to user to use as entire OS or container where you could install anything you would install on your server. Example for this would be OpenStack, AWS, Eucalyptus.
* **Platform as a Service or PaaS** - allows users to deploy their own application on the preinstalled platform, usually framework of application server and suite of developer tools. Examples for this would be Heroku.
**Source:** _linoxide.com_
#### Q6: How is container different from a virtual machine? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q7: Are you familiar with The Twelve-Factor App principles? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 8 GraphQL Interview Questions To Know (in 2018)
> Originally published on 👉 8 GraphQL Interview Questions To Know (in 2018) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is GraphQL? ⭐
**Answer:**
GraphQL is a query language created by [Facebook](http://facebook.github.io/) in 2012 which provides a **common interface between the client and the server for data fetching and manipulations**.
The client asks for various data from the GraphQL server via queries. The response format is described in the query and defined by the client instead of the server: they are called **client‐specified queries**.
The structure of the data is not hardcoded as in traditional REST APIs - this makes retrieving data from the server more efficient for the client.
**Source:** _howtographql.com_
#### Q2: How to do Error Handling? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A successful GraphQL query is supposed to return a JSON object with a root field called `"data"`. If the request fails or partially fails (e.g. because the user requesting the data doesn’t have the right access permissions), a second root field called `"errors"` is added to the response:
```js
{
"data": { ... },
"errors": [ ... ]
}
```
**Source:** _howtographql.com_
#### Q3: What is GraphQL schema? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Every GraphQL server has two core parts that determine how it works: a schema and resolve functions.
The *schema* is a model of the data that can be fetched through the GraphQL server. It defines what queries clients are allowed to make, what types of data can be fetched from the server, and what the relationships between these types are.
Consider:
```css
type Author {
id: Int
name: String
posts: [Post]
}
type Post {
id: Int
title: String
text: String
author: Author
}
type Query {
getAuthor(id: Int): Author
getPostsByTitle(titleContains: String): [Post]
}
schema {
query: Query
}
```
**Source:** _dev-blog.apollodata.com_
#### Q4: How to do Authentication and Authorization? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Authentication and authorization are often confused. _Authentication_ describes the process of claiming an _identity_. That’s what you do when you log in to a service with a username and password, you authenticate yourself. _Authorization_ on the other hand describes _permission rules_ that specify the access rights of individual users and user groups to certain parts of the system.
Authentication in GraphQL can be implemented with common patterns such as [OAuth](https://oauth.net/).
To implement authorization, it is [recommended](http://graphql.org/learn/authorization/) to delegate any data access logic to the business logic layer and not handle it directly in the GraphQL implementation.
**Source:** _howtographql.com_
#### Q5: How to do Server-side Caching? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
One common concern with GraphQL, especially when comparing it to REST, are the difficulties to maintain server-side cache. With REST, it’s easy to cache the data for each endpoint, since it’s sure that the _structure_ of the data will not change.
With GraphQL on the other hand, it’s not clear what a client will request next, so putting a caching layer right behind the API doesn’t make a lot of sense.
Server-side caching still is a challenge with GraphQL.
**Source:** _howtographql.com_
#### Q6: List the key concepts of the GraphQL query language ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Key concepts of the GraphQL** query language are:
* Hierarchical
* Product‐centric
* Strong‐typing
* Client‐specified queries
* Introspective
**Source:** _blog.risingstack.com_
#### Q7: Explain the main difference between REST and GraphQL ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The main and most important difference between REST and GraphQL is that *GraphQL is not dealing with dedicated resources, instead everything is regarded as a graph and therefore is connected and can be queried to app exact needs*.
**Source:** _medium.com/codingthesmartway-com-blog_
#### Q8: Are there any disadvantages to GraphQL? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 8 Performance Testing Interview Questions & Answers in 2018
> Originally published on 👉 8 Performance Testing Interview Questions & Answers in 2018 | FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 8 Steps to Increase Your Dev Resume Response Rate by 90%
> Originally published on 👉 8 Steps to Increase Your Dev Resume Response Rate by 90% | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: career test ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
test
**Answer:**
test
## [[⬆]](#toc) 9 Basic webpack Interview Questions And Answers in 2019
> Originally published on 👉 9 Basic webpack Interview Questions And Answers in 2019 | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is webpack? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Webpack** is a build tool that puts all of your assets, including Javascript, images, fonts, and CSS, in a dependency graph. Webpack lets you use `require()` in your source code to point to local files, like images, and decide how they're processed in your final Javascript bundle, like replacing the path with a URL pointing to a CDN.
**Source:** _blog.andrewray.me_
#### Q2: Name some benefits of using webpack ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Webpack and static assets in a dependency graph offers many benefits. Here's a few:
* **Dead asset elimination.** This is killer, especially for CSS rules. You only build the images and CSS into your `dist/` folder that your application actually needs.
* **Easier code splitting.** For example, because you know that your file `Homepage.js` only requires specific CSS files, Webpack could easily build a `homepage.css` file to greatly reduce initial file size.
* **You control how assets are processed.** If an image is below a certain size, you could [base64 encode it](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WindowBase64/Base64_encoding_and_decoding) directly into your Javascript for fewer HTTP requests. If a JSON file is too big, you can load it from a URL. You can `require('./style.less')` and it's automaticaly parsed by Less into vanilla CSS.
* **Stable production deploys.** You can't accidentally deploy code with images missing, or outdated styles.
* Webpack will slow you down at the start, but give you **great speed benefits** when used correctly. You get hot page reloading. True CSS management. CDN cache busting because Webpack automatically changes file names to hashes of the file contents, etc.
Webpack is the main build tool adopted by the React community.
**Source:** _blog.andrewray.me_
#### Q3: Name some plugins you think are very important and helpful ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **CommonsChunkPlugin** - creates a separate file (known as a chunk), consisting of common modules shared between multiple entry points.
* **DefinePlugin** - allows you to create global constants which can be configured at compile time.
* **HtmlWebpackPlugin** - simplifies creation of HTML files to serve your webpack bundles.
* **ExtractTextWebpackPlugin** - Extract text from a bundle, or bundles, into a separate file.
* **CompressionWebpackPlugin** - Prepare compressed versions of assets to serve them with Content-Encoding.
**Source:** _webpack.js.org_
#### Q4: Webpack gives us a dependency graph. What does that mean? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Any time one file depends on another, webpack treats this as a *dependency*. This allows webpack to take non-code assets, such as images or web fonts, and also provide them as dependencies for your application.
Webpack lets you use require() on local "static assets":
```js
```
When webpack processes your application, it starts from a list of modules defined on the command line or in its config file. Starting from these entry points, webpack recursively builds a dependency graph that includes every module your application needs, then packages all of those modules into a small number of bundles - often, just one - to be loaded by the browser.
The `require('logo.png')` source code never actually gets executed in the browser (nor in Node.js). Webpack builds a new Javascript file, replacing `require()` calls with valid Javascript code, such as URLs. The bundled file is what's executed by Node or the browser.
**Source:** _blog.andrewray.me_
#### Q5: List some pitfalls of Webpack ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q6: Explain me the difference between NPM vs. Bower vs. Browserify vs. Gulp vs. Grunt vs. Webpack? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q7: What's the difference between webpack loaders and plugins? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q8: Explain this code ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```javascript
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'common',
filename: 'common.js',
chunks: ['home', 'dashboard']
})
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q9: Describe tree shaking mechanism in webpack ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 9 Expert Design Patterns Interview Questions To Know (in 2018)
> Originally published on 👉 9 Expert Design Patterns Interview Questions To Know (in 2018) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Design Patterns and why anyone should use them? ⭐
**Answer:**
Design patterns are a well-described solution to the most commonly encountered problems which occur during software development.
Design pattern represents the best practices evolved over a period of time by experienced software developers. They promote reusability which leads to a more robust and maintainable code.
**Source:** _www.educba.com_
#### Q2: What is Filter pattern? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Filter pattern** or **Criteria pattern** is a design pattern that enables developers to filter a set of objects using different criteria and chaining them in a decoupled way through logical operations. This type of design pattern comes under *structural* pattern as this pattern combines multiple criteria to obtain single criteria.
**Filter design pattern** is useful where you want to add filters dynamically or you are implementing multiple functionalities and most of them require different filter criteria to filter something. In that case instead of hard coding the filters inside the functionalities, you can create filter criteria and re-use it wherever required.
```js
List laptops = LaptopFactory.manufactureInBulk();
AndCriteria searchCriteria = new AndCriteria(
new HardDisk250GBFilter(),
new MacintoshFilter(),
new I5ProcessorFilter());
List filteredLaptops = searchCriteria.meets(laptops);
```
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q3: What is Strategy pattern? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In **Strategy pattern**, a class behavior or its algorithm can be changed at run time. This type of design pattern comes under _behavior_ pattern.
In Strategy pattern, we create objects which represent various strategies and a context object whose behavior varies as per its strategy object. The strategy object changes the executing algorithm of the context object.

**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q4: What is Observer pattern? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Observer pattern** (also known as *Publish-Subscribe Pattern*) is used when there is one-to-many relationship between objects such as if one object is modified, its dependent objects are to be notified automatically. Observer pattern falls under _behavioral_ pattern category.
An object with a one-to-many relationship with other objects who are interested in its state is called the _subject_ or _publisher_. The _observers_ are notified whenever the state of the _subject_ changes and can act accordingly. The _subject_ can have any number of dependent _observers_ which it notifies, and any number of _observers_ can subscribe to the _subject_ to receive such notifications.
Observer pattern uses two actor classes:
* The Observer (os Subscriber) abstract class provides an `update()` method which will be called by the subject to notify it of the subject’s state change.
* The Subject (or Publisher) class is also an abstract class and defines four primary methods: `attach()`, `detach()`, `setState()`, and `notify()`

**Source:** _sitepoint.com_
#### Q5: When would you use the Builder Pattern? Why not just use a Factory Pattern? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q6: Why would I ever use a Chain of Responsibility over a Decorator? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q7: How is Bridge pattern is different from Adapter pattern? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q8: Explain difference between the Facade, Proxy, Adapter and Decorator design patterns? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q9: What's the difference between the Dependency Injection and Service Locator patterns? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 9 Questions Every Developer Should Ask On Interview
> Originally published on 👉 9 Questions Every Developer Should Ask On Interview | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What does the company do to nurture and train its employees? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
#### Q2: What is your stack? What is the rationale for/story behind this specific stack? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
#### Q3: What is the most fulfilling/exciting/technically complex project that you've worked on here so far? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
#### Q4: What makes your product competitive? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
#### Q5: There's "C++" (or Python, Swift or any other tech) in the job description. How will you estimate my proficiency in this tech in 3 months? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
#### Q6: How much time do you spend on new project development versus maintenance? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q7: What has been the worst technical blunder that has happened in the recent past? How did you guys deal with it? What changes were implemented afterwards to make sure it didn't happen again? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q8: What is the most costly technical decision made early on that the company is living with now? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q9: How long does the average engineer stay at the company? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) 9 Tricky Software Architecture Interview Questions
> Originally published on 👉 9 Tricky Software Architecture Interview Questions | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What does “program to interfaces, not implementations” mean? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Coding against interface* means, the client code always holds an Interface object which is supplied by a *factory*.
Any instance returned by the factory would be of type Interface which any factory candidate class must have implemented. This way the client program is not worried about implementation and the interface signature determines what all operations can be done.
This approach can be used to change the behavior of a program at run-time. It also helps you to write far better programs from the maintenance point of view.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q2: What are the differences between continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* Developers practicing **continuous integration** merge their changes back to the main branch as often as possible. By doing so, you avoid the integration hell that usually happens when people wait for release day to merge their changes into the release branch.
* **Continuous delivery** is an extension of continuous integration to make sure that you can release new changes to your customers quickly in a sustainable way. This means that on top of having automated your testing, you also have automated your release process and you can deploy your application at any point of time by clicking on a button.
* **Continuous deployment** goes one step further than continuous delivery. With this practice, every change that passes all stages of your production pipeline is released to your customers. There's no human intervention, and only a failed test will prevent a new change to be deployed to production.
**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q3: What does SOLID stand for? What are its principles? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**S.O.L.I.D** is an acronym for the first five object-oriented design (OOD) principles by Robert C. Martin.
* **S** - *Single-responsiblity principle*. A class should have one and only one reason to change, meaning that a class should have only one job.
* **O** - *Open-closed principle*. Objects or entities should be open for extension, but closed for modification.
* **L** - *Liskov substitution principle*. Let q(x) be a property provable about objects of x of type T. Then q(y) should be provable for objects y of type S where S is a subtype of T.
* **I** - *Interface segregation principle*. A client should never be forced to implement an interface that it doesn't use or clients shouldn't be forced to depend on methods they do not use.
* **D** - *Dependency Inversion Principle*. Entities must depend on abstractions not on concretions. It states that the high level module must not depend on the low level module, but they should depend on abstractions.
**Source:** _scotch.io_
#### Q4: What Is BASE Property Of A System? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q5: What Is CAP Theorem? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q6: Are you familiar with The Twelve-Factor App principles? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q7: What are heuristic exceptions? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q8: What Is Shared Nothing Architecture? How Does It Scale? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q9: What Does Eventually Consistent Mean? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) Angular Developer Resume Sample & Template (Download Word/PDF)
> Originally published on 👉 Angular Developer Resume Sample & Template (Download Word/PDF) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: career test ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
test
**Answer:**
test
## [[⬆]](#toc) Front End Developer Resume Sample & Template (Word, PDF)
> Originally published on 👉 Front End Developer Resume Sample & Template (Word, PDF) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: career test ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
test
**Answer:**
test
## [[⬆]](#toc) Guest Voice: The Solution For The CV Problem In IT Recruitment
> Originally published on 👉 Guest Voice: The Solution For The CV Problem In IT Recruitment | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: How do you spend your time outside work? ⭐
**Answer:**
## [[⬆]](#toc) JavaScript Developer Resume Sample & Template (2019 Update)
> Originally published on 👉 JavaScript Developer Resume Sample & Template (2019 Update) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: career test ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
test
**Answer:**
test
## [[⬆]](#toc) Node.js Error Handling: 7 Ways To Kill Them All
> Originally published on 👉 Node.js Error Handling: 7 Ways To Kill Them All | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: Explain some Error Handling approaches in Node.js you know about. Which one will you use? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
## [[⬆]](#toc) The Ultimate Guide to Transitioning to Remote Web Development
> Originally published on 👉 The Ultimate Guide to Transitioning to Remote Web Development | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: career test ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
test
**Answer:**
test
## [[⬆]](#toc) Top 26+ React Interview Questions (2018 Edition)
> Originally published on 👉 Top 26+ React Interview Questions (2018 Edition) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is React? ⭐
**Answer:**
React is an open-source JavaScript library created by Facebook for building complex, interactive UIs in web and mobile applications. React’s core purpose is to build UI components; it is often referred to as just the “V” (View) in an “MVC” architecture.
**Source:** _codementor.io_
#### Q2: What are the advantages of ReactJS? ⭐
**Answer:**
Below are the advantages of ReactJS:
1. Increases the application’s performance with Virtual DOM
2. JSX makes code is easy to read and write
3. It renders both on client and server side
4. Easy to integrate with other frameworks (Angular, BackboneJS) since it is only a view library
5. Easy to write UI Test cases and integration with tools such as JEST.
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q3: What are the major features of ReactJS? ⭐
**Answer:**
The major features of ReactJS are as follows,
- It uses **VirtualDOM** instead RealDOM considering that RealDOM manipulations are expensive.
- Supports **server-side rendering**
- Follows **Unidirectional** data flow or data binding
- Uses **reusable/composable** UI components to develop the view
**Source:** _https://github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q4: What is virtual DOM? ⭐
**Answer:**
**The virtual DOM (VDOM)** is an in-memory representation of Real DOM. The representation of a UI is kept in memory and synced with the “real” DOM. It’s a step that happens between the render function being called and the displaying of elements on the screen. This entire process is called reconciliation.
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q5: What’s the difference between an "Element" and a "Component" in React? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Simply put, a React element describes what you want to see on the screen. Not so simply put, a React element is an object representation of some UI.
A React component is a function or a class which optionally accepts input and returns a React element (typically via JSX which gets transpiled to a createElement invocation).
**Source:** _medium.freecodecamp.org/_
#### Q6: What are the limitations of ReactJS? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Below are the list of limitations:
1. React is just a view library, not a full-blown framework
2. There is a learning curve for beginners who are new to web development.
3. Integrating React.js into a traditional MVC framework requires some additional configuration
4. The code complexity increases with inline templating and JSX.
5. Too many smaller components leading to over-engineering or boilerplate
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q7: What is the difference between a Presentational component and a Container component? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Presentational components** are concerned with _how things look_. They generally receive data and callbacks exclusively via props. These components rarely have their own state, but when they do it generally concerns UI state, as opposed to data state.
* **Container components** are more concerned with _how things work_. These components provide the data and behavior to presentational or other container components. They call Flux actions and provide these as callbacks to the presentational components. They are also often stateful as they serve as data sources.
**Source:** _github.com/Pau1fitz_
#### Q8: How is React different from AngularJS (1.x)? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
For example, AngularJS (1.x) approaches building an application by extending HTML markup and injecting various constructs (e.g. Directives, Controllers, Services) at runtime. As a result, AngularJS is very opinionated about the greater architecture of your application — these abstractions are certainly useful in some cases, but they come at the cost of flexibility.
By contrast, React focuses exclusively on the creation of components, and has few (if any) opinions about an application’s architecture. This allows a developer an incredible amount of flexibility in choosing the architecture they deem “best” — though it also places the responsibility of choosing (or building) those parts on the developer.
**Source:** _codementor.io_
#### Q9: Describe how events are handled in React. ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
In order to solve cross browser compatibility issues, your event handlers in React will be passed instances of SyntheticEvent, which is React’s cross-browser wrapper around the browser’s native event. These synthetic events have the same interface as native events you’re used to, except they work identically across all browsers.
What’s mildly interesting is that React doesn’t actually attach events to the child nodes themselves. React will listen to all events at the top level using a single event listener. This is good for performance and it also means that React doesn’t need to worry about keeping track of event listeners when updating the DOM.
**Source:** _tylermcginnis.com_
#### Q10: What is state in ReactJS? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**State** of a component is an object that holds some information that may change over the lifetime of the component. We should always try to make our state as simple as possible and minimize the number of stateful components.
Let's create user component with message state,
```js
class User extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
message: "Welcome to React world",
}
}
render() {
return (
{this.state.message}
);
}
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q11: What is the difference between state and props? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Both **props** and **state** are plain JavaScript objects. While both of them hold information that influences the output of render, they are different in their functionality with respect to component. i.e,
* Props get passed to the component similar to function parameters
* state is managed within the component similar to variables declared within a function.
**Source:** _https://github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q12: What can you tell me about JSX? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
When Facebook first released React to the world, they also introduced a new dialect of JavaScript called JSX that embeds raw HTML templates inside JavaScript code. JSX code by itself cannot be read by the browser; it must be transpiled into traditional JavaScript using tools like Babel and webpack. While many developers understandably have initial knee-jerk reactions against it, JSX (in tandem with ES2015) has become the defacto method of defining React components.
```js
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
let props = this.props;
return (
);
}
}
```
**Source:** _codementor.io_
#### Q13: Why should not we update the state directly? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
If you try to update state directly then it won’t re-render the component.
```js
//Wrong
This.state.message =”Hello world”;
```
Instead use `setState()` method. It schedules an update to a component’s state object. When state changes, the component responds by re-rendering
```js
//Correct
This.setState({message: ‘Hello World’});
```
**Note:** The only place you can assign the state is constructor.
**Source:** _https://github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q14: What are the different phases of ReactJS component lifecycle? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
There are four different phases of React component’s lifecycle:
1. **Initialization:** In this phase react component prepares setting up the initial state and default props.
2. **Mounting:** The react component is ready to mount in the browser DOM. This phase covers **componentWillMount** and **componentDidMount** lifecycle methods.
3. **Updating:** In this phase, the component get updated in two ways, sending the new props and updating the state. This phase covers **shouldComponentUpdate, componentWillUpdate and componentDidUpdate** lifecycle methods.
4. **Unmounting:** In this last phase, the component is not needed and get unmounted from the browser DOM. This phase include **componentWillUnmount** lifecycle method.

**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q15: What are error boundaries in ReactJS (16)? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Error boundaries are React components that catch JavaScript errors anywhere in their child component tree, log those errors, and display a fallback UI instead of the component tree that crashed.
A class component becomes an error boundary if it defines a new lifecycle method called `componentDidCatch(error, info)`
```js
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { hasError: false };
}
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
// Display fallback UI
this.setState({ hasError: true });
// You can also log the error to an error reporting service
logErrorToMyService(error, info);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// You can render any custom fallback UI
return
Something went wrong.
;}
return this.props.children;
}
}
```
After that use it as a regular component
```js
```
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q16: Why ReactJS uses className over class attribute? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**class** is a keyword in javascript and JSX is an extension of javascript. That's the principal reason why React uses `className` instead of class.
```js
render() {
return Menu
}
```
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q17: What is the difference between a controlled component and an uncontrolled component? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q18: What is wrong with this code? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q19: Why would you use forceUpdate in a React component? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q20: Describe Flux vs MVC? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q21: Explain some difference between Flux and AngularJS (1.x) approach ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q22: What is a pure function? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q23: What is Redux? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Redux** is a predictable state container for JavaScript apps based on the Flux design pattern. Redux can be used together with ReactJS, or with any other view library. It is tiny (about 2kB) and has no dependencies.
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q24: What is Flux? ⭐
**Answer:**
**Flux** is an application design paradigm used as a replacement for the more traditional mvc pattern. It is not a framework or a library but a new kind of architecture that complements React and the concept of Unidirectional Data Flow. Facebook used this pattern internally when working with React The workflow between dispatcher, stores and views components with distinct inputs and outputs as follows:

**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q25: How to access redux store outside a react component? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Yes.You just need to export the store from the module where it created with `createStore`. Also, it shouldn't pollute the global window object
```js
store = createStore(myReducer);
export default store;
```
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
#### Q26: What are the downsides of Redux over Flux? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Instead of saying downsides we can say that there are few compromises of using Redux over Flux. Those are as follows:
1. **You will need to learn avoiding mutations:**
Flux is un-opinionated about mutating data, but Redux doesn't like mutations and many packages complementary to Redux assume you never mutate the state. You can enforce this with dev-only packages like redux-immutable-state-invariant, Immutable.js, or your team to write non-mutative code.
2. **You're going to have to carefully pick your packages:**
While Flux explicitly doesn't try to solve problems such as undo/redo, persistence, or forms, Redux has extension points such as middleware and store enhancers, and it has spawned a young but rich ecosystem. This means most packages are new ideas and haven't received the critical mass of usage yet
3. **There is no nice Flow integration yet:**
Flux currently lets you do very impressive static type checks which Redux doesn't support yet.
**Source:** _github.com/sudheerj_
## [[⬆]](#toc) Top 60+ MEAN Stack Developer Interview Questions And Answers (2019 Edition)
> Originally published on 👉 Top 60+ MEAN Stack Developer Interview Questions And Answers (2019 Edition) | FullStack.Cafe
#### Q1: What is Routing Guard in Angular? ⭐
**Answer:**
Angular’s route guards are interfaces which can tell the router whether or not it should allow navigation to a requested route. They make this decision by looking for a true or false return value from a class which implements the given guard interface.
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q2: What is a service, and when will you use it? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Angular services* are singleton objects which get instantiated only once during the lifetime of an application. They contain methods that maintain data throughout the life of an application, i.e. data does not get refreshed and is available all the time. The main objective of a service is to organize and share business logic, models, or data and functions with different components of an Angular application.
The *separation of concerns* is the main reason why Angular services came into existence. An Angular service is a stateless object and provides some very useful functions.
**Source:** _dzone.com_
#### Q3: How to bundle an Angular app for production? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**OneTime Setup**
* `npm install -g @angular/cli`
* `ng new projectFolder` creates a new application
**Bundling Step**
* `ng build --prod` (run in command line when directory is `projectFolder`)
* flag `prod` _bundle for production
_bundles are generated by default to_ **_projectFolder/dist/_**
**Deployment**
You can get a preview of your application using the `ng serve --prod` command that starts a local HTTP server such that the application with production files is accessible using [http://localhost:4200](http://localhost:4200).
For a production usage, you have to deploy all the files from the `dist` folder in the HTTP server of your choice.
**Source:** _medium.com_
#### Q4: What's new in Angular 6 and why shall we upgrade to it? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **Angular Elements** - Angular Elements is a project that lets you wrap your Angular components as Web Components and embed them in a non-Angular application.
* **New Rendering Engine: Ivy** - increases in speed and decreases in application size.
* **Tree-shakeable providers** - a new, recommended, way to register a provider, directly inside the @Injectable() decorator, using the new `providedIn` attribute
* **RxJS 6** - Angular 6 now uses RxJS 6 internally, and requires you to update your application also. RxJS released a library called rxjs-compat, that allows you to bump RxJS to version 6.0 even if you, or one of the libraries you’re using, is still using one of the “old” syntaxes.
* **ElementRef``** - in Angular 5.0 or older, is that the said ElementRef had its nativeElement property typed as any. In Angular 6.0, you can now type ElementRef more strictly.
* **Animations** - The polyfill web-animations-js is not necessary anymore for animations in Angular 6.0, except if you are using the AnimationBuilder.
* **i18n** - possibility to have “runtime i18n”, without having to build the application once per locale.
**Source:** _ninja-squad.com_
#### Q5: What is AOT? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The Angular Ahead-of-Time compiler pre-compiles application components and their templates during the build process.
Apps compiled with AOT launch faster for several reasons.
* Application components execute immediately, without client-side compilation.
* Templates are embedded as code within their components so there is no client-side request for template files.
* You don't download the Angular compiler, which is pretty big on its own.
* The compiler discards unused Angular directives that a tree-shaking tool can then exclude.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q6: What is Redux and how does it relate to an Angular app? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Redux** is a way to manage application state and improve maintainability of asynchronicity in your application by providing a single source of truth for the application state, and a unidirectional flow of data change in the application. `ngrx/store` is one implementation of Redux principles.
**Source:** _github.com/WebPredict_
#### Q7: How to set headers for every request in Angular? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q8: Just-in-Time (JiT) vs Ahead-of-Time (AoT) compilation. Explain the difference. ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q9: Do you know how you can run angularJS and angular side by side? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q10: What is a Grid System in CSS? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A grid system is a structure that allows for content to be stacked both vertically and horizontally in a consistent and easily manageable fashion. Grid systems include two key components: rows and columns.
Some Grid Systems:
* Simple Grid
* Pure
* Flexbox Grid
* Bootstrap
* Foundation
**Source:** _sitepoint.com_
#### Q11: How is responsive design different from adaptive design? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Both *responsive* and *adaptive* design attempt to optimize the user experience across different devices, adjusting for different viewport sizes, resolutions, usage contexts, control mechanisms, and so on.
**Responsive design** works on the principle of flexibility — a single fluid website that can look good on any device. Responsive websites use *media queries*, *flexible grids*, and *responsive images* to create a user experience that flexes and changes based on a multitude of factors. Like a single ball growing or shrinking to fit through several different hoops.
**Adaptive design** is more like the modern definition of progressive enhancement. Instead of one flexible design, adaptive design detects the device and other features, and then provides the appropriate feature and layout based on a *predefined set of viewport sizes* and other characteristics. The site detects the type of device used, and delivers the pre-set layout for that device. Instead of a single ball going through several different-sized hoops, you’d have several different balls to use depending on the hoop size.
**Source:** _codeburst.io_
#### Q12: Explain the basic rules of CSS Specificity ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q13: What is the difference between Linear Search and Binary Search? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* A **linear search** looks down a list, one item at a time, without jumping. In complexity terms this is an `O(n)` search - the time taken to search the list gets bigger at the same rate as the list does.
* A **binary search** is when you start with the middle of a sorted list, and see whether that's greater than or less than the value you're looking for, which determines whether the value is in the first or second half of the list. Jump to the half way through the sublist, and compare again etc. In complexity terms this is an `O(log n)` search - the number of search operations grows more slowly than the list does, because you're halving the "search space" with each operation.
Comparing the two:
- Binary search requires the input data to be sorted; linear search doesn't
- Binary search requires an *ordering* comparison; linear search only requires equality comparisons
- Binary search has complexity `O(log n)`; linear search has complexity O(n)
- Binary search requires random access to the data; linear search only requires sequential access (this can be very important - it means a linear search can *stream* data of arbitrary size)
**Source:** _wikipedia.org_
#### Q14: What is Dependency Injection? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Dependency injection* makes it easy to create loosely coupled components, which typically means that components consume functionality defined by interfaces without having any first-hand knowledge of which implementation classes are being used.
*Dependency injection* makes it easier to change the behavior of an application by changing the components that implement the interfaces that define application features. It also results in components that are easier to isolate for unit testing.
**Source:** _Pro ASP.NET Core MVC 2_
#### Q15: What is Inversion of Control? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Inversion of control* is a broad term but for a software developer it's most commonly described as a pattern used for decoupling components and layers in the system.
For example, say your application has a text editor component and you want to provide spell checking. Your standard code would look something like this:
```js
public class TextEditor {
private SpellChecker checker;
public TextEditor() {
this.checker = new SpellChecker();
}
}
```
What we've done here creates a dependency between the TextEditor and the SpellChecker. In an IoC scenario we would instead do something like this:
```js
public class TextEditor {
private IocSpellChecker checker;
public TextEditor(IocSpellChecker checker) {
this.checker = checker;
}
}
```
You have *inverted control* by handing the responsibility of instantiating the spell checker from the TextEditor class to the caller.
```js
SpellChecker sc = new SpellChecker; // dependency
TextEditor textEditor = new TextEditor(sc);
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q16: What is Prototype pattern? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Prototype pattern* refers to creating duplicate object while keeping performance in mind. This pattern involves implementing a prototype interface which tells to create a clone of the current object.

*The Prototype pattern* is used when creation of object directly is costly. For example, an object is to be created after a costly database operation. We can cache the object, returns its clone on next request and update the database as and when needed thus reducing database calls.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q17: Which are the top DevOps tools? Which tools have you worked on? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The most popular DevOps tools are:
* **Git**: Version Control System tool
* **Jenkins**: Continuous Integration tool
* **Selenium**: Continuous Testing tool
* **Puppet, Chef, Ansible**: Configuration Management and Deployment tools
* **Nagios**: Continuous Monitoring tool
* **Docker**: Containerization tool
**Source:** _edureka.co_
#### Q18: What does Containerization mean? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Containerisation* is a type of *virtualization* strategy that emerged as an alternative to traditional hypervisor-based virtualization.
In containerization, the operating system is shared by the different containers rather than cloned for each virtual machine. For example Docker provides a container virtualization platform that serves as a good alternative to hypervisor-based arrangements.
**Source:** _linoxide.com_
#### Q19: What's the difference between a blue/green deployment and a rolling deployment? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* In **Blue Green Deployment**, you have TWO complete environments.
One is Blue environment which is running and the Green environment to which you want to upgrade. Once you swap the environment from blue to green, the traffic is directed to your new green environment. You can delete or save your old blue environment for backup until the green environment is stable.
* In **Rolling Deployment**, you have only ONE complete environment. The code is deployed in the subset of instances of the same environment and moves to another subset after completion.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q20: How does the Centralized Workflow work? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The **Centralized Workflow** uses a central repository to serve as the single point-of-entry for all changes to the project. The default development branch is called master and all changes are committed into this branch.
Developers start by cloning the central repository. In their own local copies of the project, they edit files and commit changes. These new commits are stored locally.
To publish changes to the official project, developers *push* their local master branch to the central repository. Before the developer can publish their feature, they need to *fetch* the updated central commits and rebase their changes on top of them.
Compared to other workflows, the Centralized Workflow has no defined pull request or forking patterns.
**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q21: Could you explain the Gitflow workflow? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Gitflow workflow employs two parallel *long-running* branches to record the history of the project, `master` and `develop`:
* **Master** - is always ready to be released on LIVE, with everything fully tested and approved (production-ready).
* **Hotfix** - Maintenance or “hotfix” branches are used to quickly patch production releases. Hotfix branches are a lot like release branches and feature branches except they're based on `master` instead of `develop`.
* **Develop** - is the branch to which all feature branches are merged and where all tests are performed. Only when everything’s been thoroughly checked and fixed it can be merged to the `master`.
* **Feature** - Each new feature should reside in its own branch, which can be pushed to the `develop` branch as their parent one.

**Source:** _atlassian.com_
#### Q22: Explain the main difference between REST and GraphQL ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The main and most important difference between REST and GraphQL is that *GraphQL is not dealing with dedicated resources, instead everything is regarded as a graph and therefore is connected and can be queried to app exact needs*.
**Source:** _medium.com/codingthesmartway-com-blog_
#### Q23: Are there any disadvantages to GraphQL? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q24: Describe the difference between a 'cookie', 'sessionStorage' and 'localStorage'. ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
All the above-mentioned technologies are key-value storage mechanisms on the client side. They are only able to store values as strings.
| | `cookie` | `localStorage` | `sessionStorage` |
| -------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- | -------------- | ---------------- |
| Initiator | Client or server. Server can use `Set-Cookie` header | Client | Client |
| Expiry | Manually set | Forever | On tab close |
| Persistent across browser sessions | Depends on whether expiration is set | Yes | No |
| Sent to server with every HTTP request | Cookies are automatically being sent via `Cookie` header | No | No |
| Capacity (per domain) | 4kb | 5MB | 5MB |
| Accessibility | Any window | Any window | Same tab |
**Source:** _developer.mozilla.org_
#### Q25: What are the building blocks of HTML5? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q26: What is Scope in JavaScript? ⭐
**Answer:**
In JavaScript, each function gets its own *scope*. Scope is basically a collection of variables as well as the rules for how those variables are accessed by name. Only code inside that function can access that function's scoped variables.
A variable name has to be unique within the same scope. A scope can be nested inside another scope. If one scope is nested inside another, code inside the innermost scope can access variables from either scope.
#### Q27: How would you use a closure to create a private counter? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
You can create a function within an outer function (a closure) that allows you to update a private variable but the variable wouldn't be accessible from outside the function without the use of a helper function.
```js
function counter() {
var _counter = 0;
// return an object with several functions that allow you
// to modify the private _counter variable
return {
add: function(increment) { _counter += increment; },
retrieve: function() { return 'The counter is currently at: ' + _counter; }
}
}
// error if we try to access the private variable like below
// _counter;
// usage of our counter function
var c = counter();
c.add(5);
c.add(9);
// now we can access the private variable in the following way
c.retrieve(); // => The counter is currently at: 14
```
**Source:** _coderbyte.com_
#### Q28: Could you explain the difference between ES5 and ES6 ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
* **ECMAScript 5 (ES5)**: The 5th edition of ECMAScript, standardized in 2009. This standard has been implemented fairly completely in all modern browsers
* **ECMAScript 6 (ES6)/ ECMAScript 2015 (ES2015)**: The 6th edition of ECMAScript, standardized in 2015. This standard has been partially implemented in most modern browsers.
Here are some key differences between ES5 and ES6:
* **Arrow functions** & **string interpolation**:
Consider:
```js
const greetings = (name) => {
return `hello ${name}`;
}
```
and even:
```js
const greetings = name => `hello ${name}`;
```
* **Const**.
Const works like a constant in other languages in many ways but there are some caveats. Const stands for ‘constant reference’ to a value. So with const, you can actually mutate the properties of an object being referenced by the variable. You just can’t change the reference itself.
```js
const NAMES = [];
NAMES.push("Jim");
console.log(NAMES.length === 1); // true
NAMES = ["Steve", "John"]; // error
```
* **Block-scoped variables**.
The new ES6 keyword `let` allows developers to scope variables at the block level.
`Let` doesn’t hoist in the same way `var` does.
* **Default parameter values**
Default parameters allow us to initialize functions with default values. A default is used when an argument is either omitted or undefined — meaning null is a valid value.
```js
// Basic syntax
function multiply (a, b = 2) {
return a * b;
}
multiply(5); // 10
```
* ** Class Definition and Inheritance**
ES6 introduces language support for classes (`class` keyword), constructors (`constructor` keyword), and the `extend` keyword for inheritance.
* **for-of operator**
The for...of statement creates a loop iterating over iterable objects.
* **Spread Operator**
For objects merging
```js
const obj1 = { a: 1, b: 2 }
const obj2 = { a: 2, c: 3, d: 4}
const obj3 = {...obj1, ...obj2}
```
* **Promises**
Promises provide a mechanism to handle the results and errors from asynchronous operations. You can accomplish the same thing with callbacks, but promises provide improved readability via method chaining and succinct error handling.
```js
const isGreater = (a, b) => {
return new Promise ((resolve, reject) => {
if(a > b) {
resolve(true)
} else {
reject(false)
}
})
}
isGreater(1, 2)
.then(result => {
console.log('greater')
})
.catch(result => {
console.log('smaller')
})
```
* **Modules exporting & importing**
Consider module exporting:
```js
const myModule = { x: 1, y: () => { console.log('This is ES5') }}
export default myModule;
```
and importing:
```js
import myModule from './myModule';
```
#### Q29: Given two strings, return true if they are anagrams of one another ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
For example: `Mary` is an anagram of `Army`
**Answer:**
```js
var firstWord = "Mary";
var secondWord = "Army";
isAnagram(firstWord, secondWord); // true
function isAnagram(first, second) {
// For case insensitivity, change both words to lowercase.
var a = first.toLowerCase();
var b = second.toLowerCase();
// Sort the strings, and join the resulting array to a string. Compare the results
a = a.split("").sort().join("");
b = b.split("").sort().join("");
return a === b;
}
```
**Source:** _https://github.com/kennymkchan_
#### Q30: How would you create a private variable in JavaScript? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q31: Compare SQL databases and MongoDB at a high level. ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
SQL databases store data in form of tables, rows, columns and records. This data is stored in a pre-defined data model which is not very much flexible for today's real-world highly growing applications. MongoDB in contrast uses a flexible structure which can be easily modified and extended.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q32: What is BSON in MongoDB? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**BSON** is a binary serialization format used to store documents and make remote procedure calls in MongoDB. BSON extends the JSON model to provide additional data types, ordered fields, and to be efficient for encoding and decoding within different languages.
**Source:** _mongodb.com_
#### Q33: What are Indexes in MongoDB? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Indexes support the efficient execution of queries in MongoDB. Without indexes, MongoDB must perform a collection scan, i.e. scan every document in a collection, to select those documents that match the query statement. If an appropriate index exists for a query, MongoDB can use the index to limit the number of documents it must inspect.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q34: What does MongoDB not being ACID compliant really mean? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
It's actually not correct that MongoDB is not ACID-compliant. On the contrary, MongoDB is ACID-compilant at the document level.
Any update to a single document is
* **Atomic**: it either fully completes or it does not
* **Consistent**: no reader will see a "partially applied" update
* **Isolated**: again, no reader will see a "dirty" read
* **Durable**: (with the appropriate write concern)
What MongoDB doesn't have is *transactions* - that is, multiple-document updates that can be rolled back and are ACID-compliant.
Multi-document transactions, scheduled for MongoDB 4.0 in Summer 2018*, will feel just like the transactions developers are familiar with from relational databases – multi-statement, similar syntax, and easy to add to any application.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q35: What is Aggregation in MongoDB? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
*Aggregations* operations process data records and return computed results. Aggregation operations group values from multiple documents together, and can perform a variety of operations on the grouped data to return a single result. MongoDB provides three ways to perform aggregation:
* the aggregation pipeline,
* the map-reduce function,
* and single purpose aggregation methods and commands.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q36: How to query MongoDB with “like”? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
I want to query something as SQL's like query:
```js
select *
from users
where name like '%m%'
```
How to do the same in MongoDB?
**Answer**
```js
db.users.find({"name": /.*m.*/})
// or
db.users.find({"name": /m/})
```
You're looking for something that contains "m" somewhere (SQL's `'%'` operator is equivalent to Regexp's `'.*'`), not something that has "m" anchored to the beginning of the string.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q37: How can I combine data from multiple collections into one collection? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
MongoDB 3.2 allows one to combine data from multiple collections into one through the `$lookup` aggregation stage.
```js
db.books.aggregate([{
$lookup: {
from: "books_selling_data",
localField: "isbn",
foreignField: "isbn",
as: "copies_sold"
}
}])
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q38: How do I perform the SQL JOIN equivalent in MongoDB? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Mongo is not a relational database, and the devs are being careful to recommend specific use cases for $lookup, but at least as of 3.2 doing join is now possible with MongoDB. The new $lookup operator added to the aggregation pipeline is essentially identical to a left outer join:
```js
{
$lookup:
{
from: ,
localField: ,
foreignField: ,
as:
}
}
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q39: How to query MongoDB with %like%? ⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
I want to query something as SQL's like query:
```sql
select *
from users
where name like '%m%'
```
How to do the same in MongoDB?
**Answer:**
```js
db.users.find({name: /a/}) //like '%a%'
db.users.find({name: /^pa/}) //like 'pa%'
db.users.find({name: /ro$/}) //like '%ro'
```
Or using Mongoose:
```js
db.users.find({'name': {'$regex': 'sometext'}})
```
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com_
#### Q40: What are the benefits of using Node.js? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Following are main benefits of using Node.js
* **Aynchronous and Event Driven** - All APIs of Node.js library are aynchronous that is non-blocking. It essentially means a Node.js based server never waits for a API to return data. Server moves to next API after calling it and a notification mechanism of Events of Node.js helps server to get response from the previous API call.
* **Very Fast** - Being built on Google Chrome's V8 JavaScript Engine, Node.js library is very fast in code execution.
* **Single Threaded but highly Scalable** - Node.js uses a single threaded model with event looping. Event mechanism helps server to respond in a non-bloking ways and makes server highly scalable as opposed to traditional servers which create limited threads to handle requests. Node.js uses a single threaded program and same program can services much larger number of requests than traditional server like Apache HTTP Server.
* **No Buffering** \- Node.js applications never buffer any data. These applications simply output the data in chunks.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q41: What is a blocking code? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
If application has to wait for some I/O operation in order to complete its execution any further then the code responsible for waiting is known as blocking code.
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q42: How can you avoid callback hells? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
To do so you have more options:
* **modularization**: break callbacks into independent functions
* use _Promises_
* use `yield` with _Generators_ and/or _Promises_
**Source:** _tutorialspoint.com_
#### Q43: What's the event loop? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**The event loop** is what allows Node.js to perform non-blocking I/O operations — despite the fact that JavaScript is single-threaded — by offloading operations to the system kernel whenever possible.

Every I/O requires a callback - once they are done they are pushed onto the event loop for execution. Since most modern kernels are multi-threaded, they can handle multiple operations executing in the background. When one of these operations completes, the kernel tells Node.js so that the appropriate callback may be added to the poll queue to eventually be executed.
**Source:** _blog.risingstack.com_
#### Q44: How does Node.js handle child threads? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Node.js, in its essence, is a single thread process. It does not expose child threads and thread management methods to the developer. Technically, Node.js does spawn child threads for certain tasks such as asynchronous I/O, but these run behind the scenes and do not execute any application JavaScript code, nor block the main event loop.
If threading support is desired in a Node.js application, there are tools available to enable it, such as the ChildProcess module.
**Source:** _lazyquestion.com_
#### Q45: When should I use EventEmitter? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Whenever it makes sense for code to *subscribe* to something rather than get a callback from something. The typical use case would be that there's multiple blocks of code in your application that may need to do something when an event happens.
**Source:** _stackoverflow.com/_
#### Q46: Explain usage of NODE_ENV ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q47: How would you scale Node application? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q48: Explain some Error Handling approaches in Node.js you know about. Which one will you use? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q49: Why should you separate Express 'app' and 'server'? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q50: What is the difference between Classes and Interfaces in Typescript? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
We use classes as object factories. A class defines a blueprint of what an object should look like and act like and then implements that blueprint by initialising class properties and defining methods. Classes are present throughout all the phases of our code.
Unlike classes, an interface is a virtual structure that only exists within the context of TypeScript. The TypeScript compiler uses interfaces solely for type-checking purposes. Once code is transpiled to its target language, it will be stripped from interfaces.
A class may define a factory or a singleton by providing initialisation to its properties and implementation to its methods, an interface is simply a structural contract that defines what the properties of an object should have as a name and as a type.
**Source:** _toddmotto.com_
#### Q51: What is "Decorators" in TypeScript? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A *Decorator* is a special kind of declaration that can be attached to a class declaration, method, accessor, property, or parameter. Decorators are functions that take their target as the argument. With decorators we can run arbitrary code around the target execution or even entirely replace the target with a new definition.
There are 4 things we can decorate in ECMAScript2016 (and Typescript): constructors, methods, properties and parameters.
**Source:** _www.sparkbit.pl_
#### Q52: Does TypeScript support all object oriented principles? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
The answer is **YES**. There are 4 main principles to Object Oriented Programming:
* Encapsulation,
* Inheritance,
* Abstraction, and
* Polymorphism.
TypeScript can implement all four of them with its smaller and cleaner syntax.
**Source:** _jonathanmh.com_
#### Q53: How TypeScript is optionally statically typed language? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
TypeScript is referred as *optionally statically typed*, which means you can ask the compiler to ignore the type of a variable. Using `any` data type, we can assign any type of value to the variable. TypeScript will not give any error checking during compilation.
Consider:
```js
var unknownType: any = 4;
unknownType = "Okay, I am a string";
unknownType = false; // A boolean.
```
**Source:** _http://www.talkingdotnet.com_
#### Q54: What is the difference between "interface vs type" statements? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Details:**
```js
interface X {
a: number
b: string
}
type X = {
a: number
b: string
};
```
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q55: How would you overload a class constructor in TypeScript? ⭐⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
Read Full Answer on 👉 FullStack.Cafe
#### Q56: What is CORS and how to enable one? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
A request for a resource (like an image or a font) outside of the origin is known as a *cross-origin request*. CORS (cross-origin resource sharing) manages cross-origin requests. CORS allows servers to specify who (i.e., which origins) can access the assets on the server, among many other things.
**Access-Control-Allow-Origin** is an HTTP header that defines which foreign origins are allowed to access the content of pages on your domain via scripts using methods such as XMLHttpRequest.
For example, if your server provides both a website and an API intended for XMLHttpRequest access on a remote websites, only the API resources should return the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header. Failure to do so will allow foreign origins to read the contents of any page on your origin.
```sh
# Allow any site to read the contents of this JavaScript library, so that subresource integrity works
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
```
**Source:** _infosec.mozilla.org_
#### Q57: What is Cross Site Scripting (XSS)? ⭐⭐
**Answer:**
By using **Cross Site Scripting (XSS)** technique, users executed malicious scripts (also called payloads) unintentionally by clicking on untrusted links and hence, these scripts pass cookies information to attackers.
**Source:** _allabouttesting.org_
#### Q58: What is ClickJacking? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**ClickJacking** is an attack that fools users into thinking they are clicking on one thing when they are actually clicking on another. The attack is possible thanks to HTML frames (iframes).
Its other name, user interface (UI) redressing, better describes what is going on. Users think they are using a web page’s normal UI, but in fact there is a hidden UI in control; in other words, the UI has been redressed. When users click something they think is safe, the hidden UI performs a different action.
**Source:** _synopsys.com_
#### Q59: What is Cross-Site Request Forgery? ⭐⭐⭐
**Answer:**
**Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)** is an attack that forces authenticated users to submit a request to a Web application against which they are currently authenticated.
A CSRF attack tricks the victim into clicking a URL that contains a maliciously crafted, unauthorized request for a particular Web application. The user’s browser then sends this maliciously crafted request to a targeted Web application. The request also includes any credentials related to the particular website (e.g., user session cookies). If the user is in an active session with a targeted Web application, the application treats this new request as an authorized request submitted by the user.
**How to prevent**
To defeat a CSRF attack, applications need a way to determine if the HTTP request is legitimately generated via the application’s user interface. The best way to achieve this is through a CSRF token. A CSRF token is a secure random token (e.g., synchronizer token or challenge token) that is used to prevent CSRF attacks. The token needs to be unique per user session and should be of large random value to make it difficult to guess.
**Source:** _synopsys.com_