https://github.com/afollestad/vvalidator
🤖 An easy to use form validator for Kotlin & Android.
https://github.com/afollestad/vvalidator
android androidx form kotlin validation
Last synced: 9 months ago
JSON representation
🤖 An easy to use form validator for Kotlin & Android.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/afollestad/vvalidator
- Owner: afollestad
- License: apache-2.0
- Archived: true
- Created: 2019-01-12T20:38:35.000Z (almost 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-02-21T05:03:23.000Z (almost 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-24T17:47:52.031Z (about 1 year ago)
- Topics: android, androidx, form, kotlin, validation
- Language: Kotlin
- Homepage: https://af.codes
- Size: 630 KB
- Stars: 658
- Watchers: 14
- Forks: 51
- Open Issues: 14
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
- License: LICENSE.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-kotlin - vvalidator - 🤖 An easy to use form validator for Kotlin & Android. (Libraries)
README
## VValidator (BETA)
*View Validator*, an easy-to-use form validation library for Kotlin & Android.
[  ](https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/afollestad/vvalidator)
[](https://www.codacy.com/app/drummeraidan_50/vvalidator?utm_source=github.com&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=afollestad/vvalidator&utm_campaign=Badge_Grade)
[](https://github.com/afollestad/vvalidator/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Android+CI%22)
[](https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html)
---
## Table of Contents
1. [Gradle Dependency](#gradle-dependency)
2. [The Basics](#the-basics)
3. [Field Types](#field-types)
1. [Input](#input)
2. [Input Layout](#input-layout)
3. [Checkable](#checkable)
4. [Spinner](#spinner)
5. [Seeker](#seeker)
4. [Assertion Descriptions](#assertion-descriptions)
5. [Validation Results](#validation-results)
6. [Error Handling](#error-handling)
7. [Submit With](#submit-with)
8. [Conditionals](#conditionals)
9. [Supporting Additional Views](#supporting-additional-views)
10. [Real Time Validation](#real-time-validation)
---
## Gradle Dependency
Add this to your module's `build.gradle` file:
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad:vvalidator:0.5.2'
}
```
---
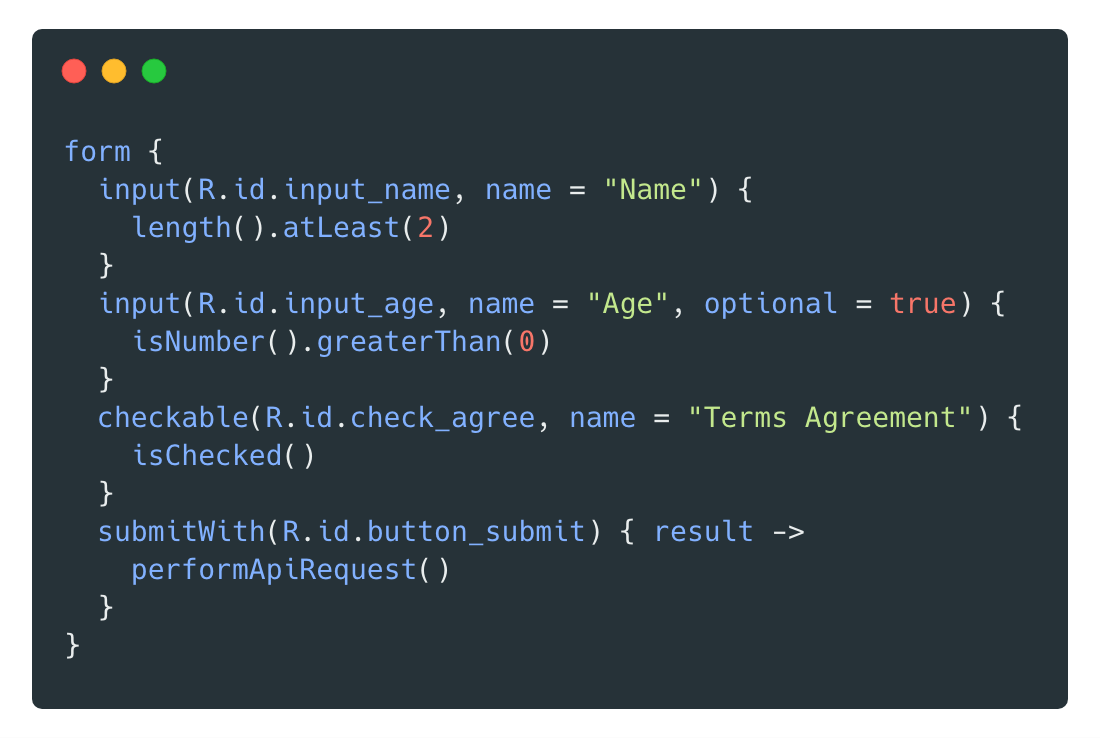
## The Basics
VValidator works automatically within any Activity or AndroidX Fragment.
```kotlin
class MyActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.my_layout)
form {
input(R.id.your_edit_text) {
isNotEmpty()
}
submitWith(R.id.submit) { result ->
// this block is only called if form is valid.
// do something with a valid form state.
}
}
}
}
```
The example above asserts that an edit text is not empty when a button a clicked. If that edit text
is not empty when the button is clicked, the callback that the comment is in is invoked.
---
## Field Types
### Input
The most basic type of supported view is an `EditText`.
```kotlin
form {
input(R.id.view_id, name = "Optional Name") {
isNotEmpty()
isUri()
isUri().hasScheme("file")
isUri().that { uri -> uri.getQueryParameter("q") != null }
isUrl() // isUri() with defaults to require http/https and a hostname
isEmail()
isNumber()
isNumber().lessThan(5)
isNumber().atMost(5)
isNumber().exactly(5)
isNumber().atLeast(5)
isNumber().greaterThan(5)
isDecimal()
isDecimal().lessThan(5.2)
isDecimal().atMost(5.2)
isDecimal().exactly(5.2)
isDecimal().atLeast(5.2)
isDecimal().greaterThan(5.2)
length().lessThan(5)
length().atMost(5)
length().exactly(5)
length().atLeast(5)
length().greaterThan(5)
contains("Hello, World!")
contains("Hello, World!").ignoreCase()
matches("/^(\+?\d{1,3}|\d{1,4})$/")
// Custom assertions
assert("expected something") { view -> true }
}
}
```
### Input Layout
This is basically identical to input. However, this targets
`TextInputLayout` views from the Google Material library. Errors
are shown differently by this view type and text is pulled
from the child `TextInputEditText` rather than the parent.
```kotlin
form {
inputLayout(R.id.view_id, name = "Optional Name") {
isNotEmpty()
isUri()
isUri().hasScheme("file")
isUri().that { uri -> uri.getQueryParameter("q") != null }
isUrl() // isUri() with defaults to require http/https and a hostname
isEmail()
isNumber()
isNumber().lessThan(5)
isNumber().atMost(5)
isNumber().exactly(5)
isNumber().atLeast(5)
isNumber().greaterThan(5)
isDecimal()
isDecimal().lessThan(5.2)
isDecimal().atMost(5.2)
isDecimal().exactly(5.2)
isDecimal().atLeast(5.2)
isDecimal().greaterThan(5.2)
length().lessThan(5)
length().atMost(5)
length().exactly(5)
length().atLeast(5)
length().greaterThan(5)
contains("Hello, World!")
contains("Hello, World!").ignoreCase()
matches("/^(\+?\d{1,3}|\d{1,4})$/")
// Custom assertions
assert("expected something") { view -> true }
}
}
```
### Checkable
More specifically, a `CompoundButton`. This includes `Switch`,
`RadioButton`, and `CheckBox` views.
```kotlin
form {
checkable(R.id.view_id, name = "Optional Name") {
isChecked()
isNotChecked()
// Custom assertions
assert("expected something") { view -> true }
}
}
```
### Spinner
A `Spinner` is Android's core drop down view. It attaches to an
adapter, and shows a list of options when tapped.
```kotlin
form {
spinner(R.id.view_id, name = "Optional Name") {
selection().exactly(1)
selection().lessThan(1)
selection().atMost(1)
selection().atLeast(1)
selection().greaterThan(1)
// Custom assertions
assert("expected something") { view -> true }
}
}
```
### Seeker
An `AbsSeekBar` includes Android's core `SeekBar` and `RatingBar` views. They allow you to select
a number either with a horizontally sliding view or with horizontal icons.
```kotlin
form {
seeker(R.id.view_id, name = "Optional Name") {
progress().exactly(1)
progress().lessThan(1)
progress().atMost(1)
progress().atLeast(1)
progress().greaterThan(1)
// Custom assertions
assert("expected something") { view -> true }
}
}
```
---
## Assertion Descriptions
All assertions expose a `description(String)` method, used to specify a custom message for
assertion validation errors. They end up in the `description` field of `FieldError` instances.
All assertions provide default validation failure messages, however they may not be what you want
to display to your app users.
```kotlin
form {
input(R.id.some_input) {
isNotEmpty().description("Please enter a value!")
}
spinner(R.id.some_spinner) {
selection()
.greaterThan(0)
.description("Please make a selection!")
}
}
```
---
## Validation Results
You get an instance of `FormResult` through the `submitWith(...)` callbacks. You can also get one
when you manually validate your form.
```kotlin
val myForm = form {
...
}
val result: FormResult = myForm.validate()
```
A call to `validate()` goes through all of your fields, making all of the set assertions, and propagating
errors through `onErrors` callbacks (which may or may not show errors in the UI automatically).
This result class gives you access to some detailed information.
```kotlin
val result: FormResult = // ...
val isSuccess: Boolean = result.success()
val hasErrors: Boolean = result.hasErrors()
val errors: List = result.errors()
val values: List> = result.values()
val singleValue: FieldValue<*> = result["Field Name"]
singleValue.asString()
singleValue.asInt()
singleValue.asLong()
singleValue.asFloat()
singleValue.asDouble()
singleValue.asBoolean()
```
Each instance of `FieldError` contains additional information:
```kotlin
val error: FieldError = // ...
// view ID
val id: Int = error.id
// field/view name
val name: String = error.name
// assertion description - what the failure is
val description: String = error.description
// the class of the assertion that failed
val assertionType: KClass> = error.assertionType
```
---
## Error Handling
Input and Input Layout fields have default error handling because their underlying views have an
error property provided by Android. However, other view types do not. This library provides an
error hook for each field that you can use to display errors in the UI.
```kotlin
form {
checkable(R.id.view_id, name = "Optional Name") {
isChecked()
onErrors { view, errors ->
// `view` here is a CompoundButton.
// `errors` here is a List, which can be empty to notify that there are no longer
// any validation errors.
val firstError: FieldError? = errors.firstOrNull()
// Show firstError.toString() in the UI.
}
}
}
```
---
## Submit With
You can have this library automatically handle validating your form with the click of a `Button`:
```kotlin
form {
submitWith(R.id.button_id) { result ->
// Button was clicked and form is completely valid!
}
}
```
Or even a `MenuItem`:
```kotlin
val menu: Menu = // ...
form {
submitWith(menu, R.id.item_id) { result ->
// Item was clicked and form is completely valid!
}
}
```
---
## Conditionals
You can apply assertions conditionally. **Anything outside of a `conditional` block is still always
executed during validation.** This could be useful in many cases. One use case would be on fields that are optionally
visible. *If a field is not visible, it should not be validated.*
```kotlin
form {
input(R.id.input_site, name = "Site") {
conditional({ spinner.selectedItemPosition > 1 }) {
isUrl()
}
}
}
```
The `conditional(..)` block above only asserts the field is a URL if a spinner's selection is greater
than 1. Say the spinner makes the `input_site` field visible if its selection is > 1.
You can nest conditions as well:
```kotlin
form {
input(...) {
conditional(...) {
isNotEmpty()
conditional(...) {
length().greaterThan(0)
}
conditional(...) {
isNumber()
}
}
}
}
```
You may have noticed somewhere above that `input(...)` and `inputLayout(...)` have an optional
argument named `optional`. Internally, this uses `conditional` to only apply inner assertions if
the input field's text is not empty.
---
## Supporting Additional Views
If you need to support a view type that isn't supported out of the box, you can create custom
assertions and form fields.
First, you'd need an assertion class that goes with your view.
```kotlin
class MyView(context: Context) : EditText(context, null)
class MyAssertion : Assertion() {
override fun isValid(view: MyView): Boolean {
return view.text.isNotEmpty()
}
override fun defaultDescription(): String {
return "edit text should not be empty"
}
}
```
Then you'll need a custom `FormField` class:
```kotlin
class MyField(
container: ValidationContainer,
view: MyView,
name: String
) : FormField(container, id, name) {
init {
onErrors { myView, errors ->
// Do some sort of default error handling with views
}
}
// Your first custom assertion
fun myAssertion() = assert(MyAssertion())
override fun obtainValue(
id: Int,
name: String
): FieldValue? {
val currentValue = view.text as? CharSequence ?: return null
return TextFieldValue(
id = id,
name = name,
value = currentValue
)
}
override fun startRealTimeValidation(debounce: Int) {
// See the "Real Time Validation" section below.
// You'd want to begin observing input to the view this field attaches to,
// and call `validate()` on this field when it changes. You should respect the
// `debounce` parameter as well.
}
}
```
Finally, you can add an extension to `Form`:
```kotlin
fun Form.myView(
view: MyView,
name: String? = null,
builder: FieldBuilder
) {
val newField = MyField(
container = container.checkAttached(),
view = view,
name = name
)
builder(newField)
appendField(newField)
}
fun Form.myView(
@IdRes id: Int,
name: String? = null,
builder: FieldBuilder
) = myView(
view = container.getViewOrThrow(id),
name = name,
builder = builder
)
```
Now, you can use it:
```kotlin
form {
myView(R.id.seek_bar, name = "Optional Name") {
myAssertion()
}
}
```
When the form is validated, your assertion's `isValid(MyView)` method is executed. If it returns
false, this view is marked as erroneous in the validation results.
---
## Real Time Validation
This library provides an option to support real time validation. Rather than performing validation
when you call `validate()` on the `Form`, or `validate()` on an individual field, the library
makes these calls for you as the view's change.
```kotlin
form {
useRealTimeValidation()
input(R.id.your_edit_text) {
isNotEmpty()
}
}
```
With this example above, the form will automatically perform validation when the input field's
text changes. *Note that this does work with all field types, not just input fields.*
`useRealTimeValidation()` has an optional `Int` parameter that lets you set a custom debounce delay.
This delay is how much of a gap there is between a field's value changing and validation being
performed. This prevents too many validations from occurring in a row, such as a user is typing in
an input field - you wouldn't want to validate with every single letter input. *The default value
is 500 (milliseconds), or a half second.*
---
Another optional parameter on `useRealTimeValidation() is `disableSubmit`. When true,
the `submitWith` view or item you set will be enabled or disabled based on the real time
valid state of the overall form.
```kotlin
form {
useRealTimeValidation(disableSubmit = true)
input(R.id.your_edit_text) {
isNotEmpty()
}
submitWith(R.id.my_button) {
// Do something
}
}
```