Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/agude/UMN-PhD-Thesis-Template
The LaTeX thesis template provided by the University of Minnesota, with various improvements.
https://github.com/agude/UMN-PhD-Thesis-Template
latex latex-template phd-thesis-template thesis-template university-of-minnesota
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
The LaTeX thesis template provided by the University of Minnesota, with various improvements.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/agude/UMN-PhD-Thesis-Template
- Owner: agude
- Created: 2015-05-06T01:48:10.000Z (almost 10 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-01-04T22:23:57.000Z (about 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2023-07-31T14:58:39.297Z (over 1 year ago)
- Topics: latex, latex-template, phd-thesis-template, thesis-template, university-of-minnesota
- Language: Perl
- Size: 260 KB
- Stars: 38
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 32
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- latex-templates - agude/<br>UMN-PhD-Thesis-Template - PhD-Thesis-Template?style=flat-square)<br/><br/> | The LaTeX thesis template provided by the University of Minnesota, with various improvements. | (Popular & New Non-LaTeX Templates / Thesis/Dissertation)
README
# University of Minnesota PhD Thesis Template
This repository contains an updated version of the UMN PhD Thesis Template.
## Prerequisites
### Build Locally
To build the thesis locally, on Ubuntu 18.04, you will need to install:
```bash
# Install the required packages
sudo apt-get install \
texlive-latex-base \
texlive-latex-extra \
texlive-fonts-recommended \
texlive-pictures \
texlive-science \
```
You can then build the thesis with `make`:
```bash
make
```
This will produce a `thesis.pdf` in the root directory of your repository,
along with all the intermediate build files. You can instead run:
```bash
make tidy
```
To just produce the PDF.
### Build On Github
The easiest way to build the PDF is to use [Github Actions][actions]. This
will build the thesis and produce a PDF all within Github. The repository
already contains the correct configuration files, but you will need to enable
actions in Github.
[actions]: https://help.github.com/en/actions
Once this is done, you can click on the _"Actions"_ tab at the top of the
repository on Github.
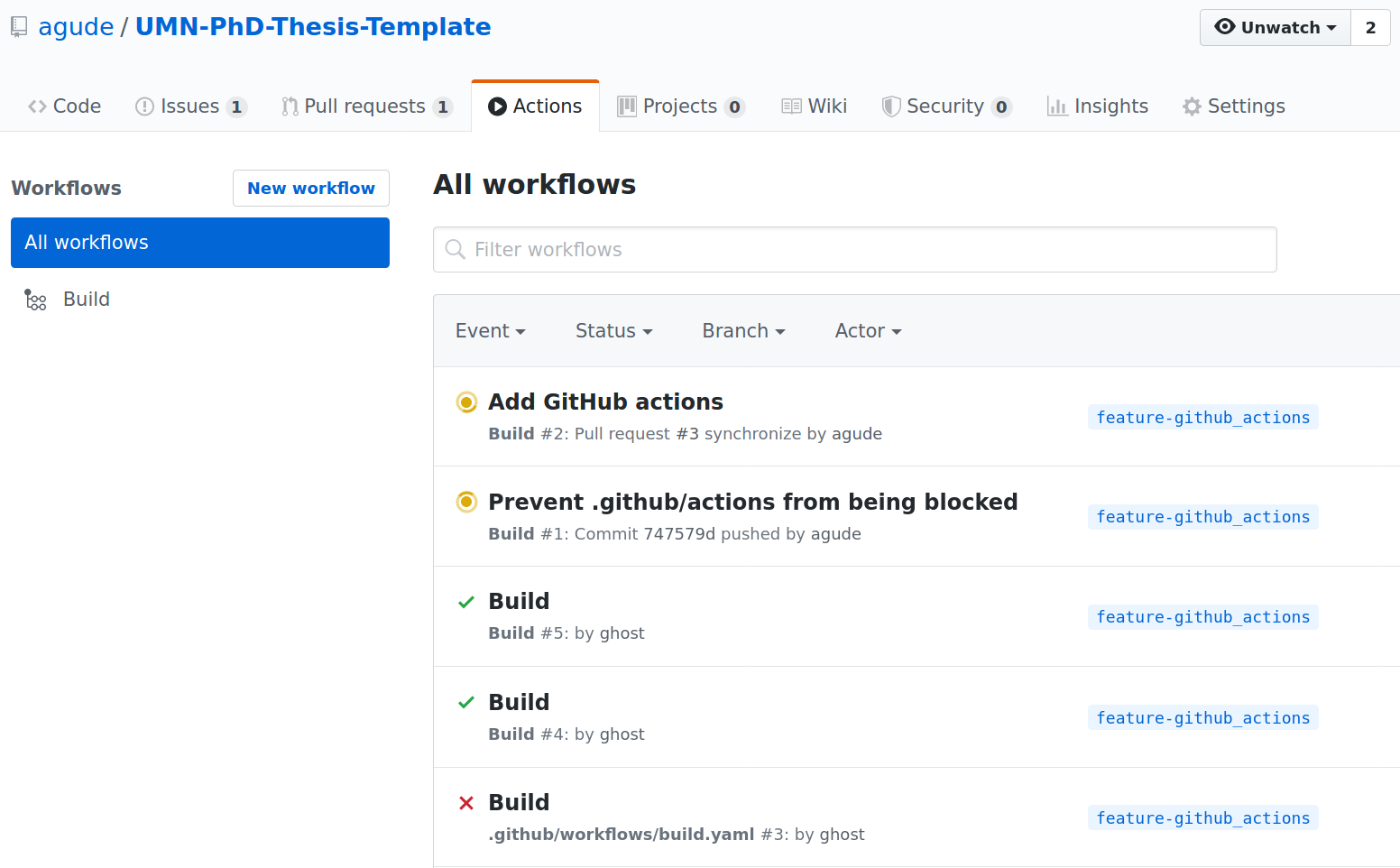
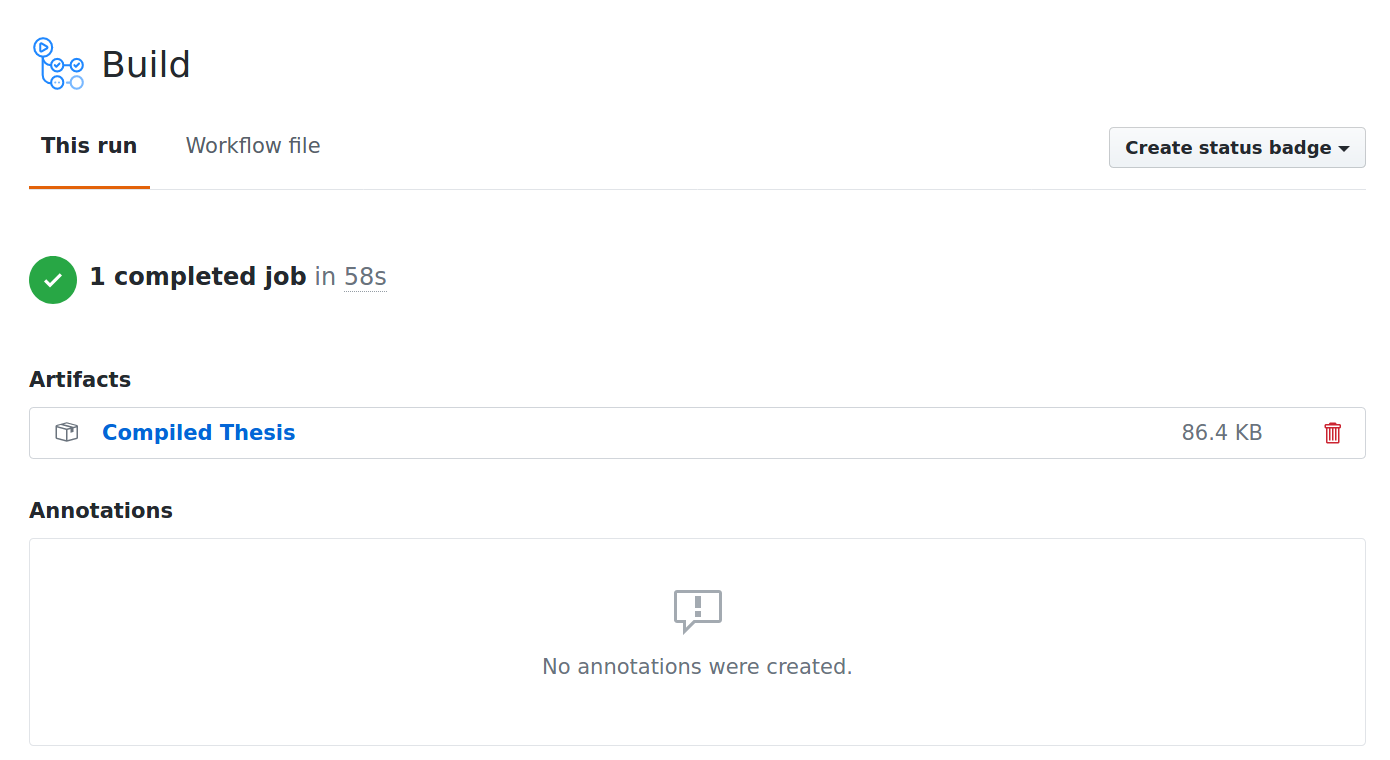
There you'll see a list of build jobs. The ones with green check marks have
completed successfully. Clicking on one will bring you to the build page,
where there will be a section titled **Artifacts**. Click on "Compiled Thesis"
to download a zip file containing the PDF.
## Additional Packages
The thesis template comes with some useful additional packages. They are
described below.
### `cleveref`
[`cleveref`](https://www.ctan.org/pkg/cleveref?lang=en) is a package designed
to make cross referencing easier. Unlike `\ref`, `\cref` automatically adds
the prefix required for the object being referenced. For example,
`\cref{fig:my_fig}` will produce text like "figure 1" whereas
`\ref{fig:my_fig}` would simply produce "1" and require you to fill in the
"figure".
Additionally, `cleveref` can handle multiple references at once.
`\cref{fig:my_fig,fig:my_fig2}` produces "figures 1 and 2".
In the [main thesis file](thesis_masters.tex), the following is set:
```latex
\newcommand{\creflastconjunction}{, and } % Always use the serial comma
```
This includes the serial comma in lists, so that
`\cref{fig:my_fig,fig:my_fig2,fig_other_fig}` produces "figures 1, 2, and 3"
instead of "figures 1, 2 and 3".
Additionally, the package is passed the option `noabbrev` which causes it to
print the full prefix instead of an abbreviation ("figure" vs "fig.").
### `SIunitx`
[`SIunitx`](https://www.ctan.org/pkg/siunitx?lang=en) formats SI units. It
provides the `\SI{}` command, which is used as follows:
```latex
\SI{3.8}{\tesla}
\SI{14}{\kilo\tonne}
\SI{14.6}{\meter\squared}
\SI{8}{\tera\eV}
```
There are various abbreviations for units (such as `\SI{8}{\TeV}`) and the
formatting of the numbers can be controlled in detail. Additionally, it
provides `\SIrange{1}{5}{\meter}` which produces "1m to 5m" and
`\SIlist{1;2;3}{\kelvin}` which produces "1K, 2K, and 3K".
The package also provides `\num{12345}` which will format numbers (just like
`\SI`) but without adding units. The previous example produces "12,345" for
instance.
In the [main thesis file](thesis_masters.tex), the following default options
are set:
```latex
% Configure the siunitx package
\sisetup{
group-separator = {,}, % Use , to separate groups of digits, like 12,345
list-final-separator = {, and } % Always use the serial comma in \SIlist
}
```
`group-separator` makes the package separate groups of digits with commas (so
12,345.0), and `list-final-separator` uses the serial comma in lists ("1K, 2K,
and 3K", not "1K, 2K and 3K").
The way in which units are displayed can also be redefined, as has been done
`\electronvolt` in [the macros file](my_definitions.tex):
```latex
% Define a better looking eV by moving the V slightly left
\DeclareSIUnit\electronvolt{e\hspace{-0.08em}V}
```
### `booktabs`
[`booktabs`](https://www.ctan.org/pkg/booktabs?lang=en) adds options to make
nicer tables. It defines `\toprule`, `\midrule`, and `\bottomrule` which add
rules of varying thickness and with additional vertical space.
An example table using these commands is shown below. The `@{}` removes extra
space on the end of the tables (so that the rules start and end flush with the
text instead of hanging over) and the `\spacerows{1.2}` command is defined in
[the macros file](my_definitions.tex) and adds extra space between the rows.
```latex
\begin{table}[h]
\centering
\spacerows{1.2}
\begin{center}
\begin{tabular}{@{}l r@{}}
\toprule
Mode & Fraction $\left( \Gamma_{i} / \Gamma \right)$ \\
\midrule
$\Ztoqq$ & $69.91 \pm 0.06\%$ \\
$\Ztoee$ & $3.363 \pm 0.004\%$ \\
$\Ztomumu$ & $3.366 \pm 0.007\%$ \\
$\Ztotautau$ & $3.370 \pm 0.008\%$ \\
$\Ztonunu$ & $20.00 \pm 0.06\%$ \\
\bottomrule
\end{tabular}
\caption{
Selected decay modes of the Z boson.
}
\label{table:z_decays}
\end{center}
\end{table}
```