https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NeuralGenetic
Building and training artificial neural networks (regression or classification) using the genetic algorithm.
https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NeuralGenetic
deep-learning genetic-algorithm neural-networks optimization pygad python
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
Building and training artificial neural networks (regression or classification) using the genetic algorithm.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NeuralGenetic
- Owner: ahmedfgad
- Created: 2019-01-24T13:47:06.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-02-04T22:40:43.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-07T12:06:23.344Z (6 months ago)
- Topics: deep-learning, genetic-algorithm, neural-networks, optimization, pygad, python
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://pygad.readthedocs.io
- Size: 1.28 MB
- Stars: 246
- Watchers: 10
- Forks: 90
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# NeuralGenetic: Training Neural Networks using the Genetic Algorithm
[NeuralGenetic](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NeuralGenetic) is a Python project for training neural networks using the genetic algorithm.
[NeuralGenetic](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NeuralGenetic) is part of the [PyGAD](https://pypi.org/project/pygad) library which is an open-source Python 3 library for implementing the genetic algorithm and optimizing machine learning algorithms. Both regression and classification neural networks are supported starting from PyGAD 2.7.0.
Check documentation of the [NeuralGenetic](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NeuralGenetic) project in the PyGAD's documentation: https://pygad.readthedocs.io/en/latest/gann.html
The library is under active development and more features are added regularly. If you want a feature to be supported, please check the **Contact Us** section to send a request.
# Donation
- [Credit/Debit Card](https://donate.stripe.com/eVa5kO866elKgM0144): https://donate.stripe.com/eVa5kO866elKgM0144
- [Open Collective](https://opencollective.com/pygad): [opencollective.com/pygad](https://opencollective.com/pygad)
- PayPal: Use either this link: [paypal.me/ahmedfgad](https://paypal.me/ahmedfgad) or the e-mail address ahmed.f.gad@gmail.com
- Interac e-Transfer: Use e-mail address ahmed.f.gad@gmail.com
# Tutorial Project
**IMPORTANT** If you are coming for the code of the tutorial titled [**Artificial Neural Networks Optimization using Genetic Algorithm with Python**](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/artificial-neural-networks-optimization-using-genetic-ahmed-gad), then it has been moved to the [Tutorial Project](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NeuralGenetic/tree/master/Tutorial Project) directory on 15 May 2020.
# Installation
To install [PyGAD](https://pypi.org/project/pygad), simply use pip to download and install the library from [PyPI](https://pypi.org/project/pygad) (Python Package Index). The library is at PyPI at this page https://pypi.org/project/pygad.
Install PyGAD with the following command:
```python
pip install pygad
```
To get started with PyGAD, please read the documentation at [Read The Docs](https://pygad.readthedocs.io/) https://pygad.readthedocs.io.
# PyGAD Source Code
The source code of the PyGAD' modules is found in the following GitHub projects:
- [pygad](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/GeneticAlgorithmPython): (https://github.com/ahmedfgad/GeneticAlgorithmPython)
- [pygad.nn](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NumPyANN): https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NumPyANN
- [pygad.gann](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NeuralGenetic): https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NeuralGenetic
- [pygad.cnn](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NumPyCNN): https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NumPyCNN
- [pygad.gacnn](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/CNNGenetic): https://github.com/ahmedfgad/CNNGenetic
- [pygad.kerasga](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/KerasGA): https://github.com/ahmedfgad/KerasGA
- [pygad.torchga](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/TorchGA): https://github.com/ahmedfgad/TorchGA
The documentation of PyGAD is available at [Read The Docs](https://pygad.readthedocs.io/) https://pygad.readthedocs.io.
# PyGAD Documentation
The documentation of the PyGAD library is available at [Read The Docs](https://pygad.readthedocs.io) at this link: https://pygad.readthedocs.io. It discusses the modules supported by PyGAD, all its classes, methods, attribute, and functions. For each module, a number of examples are given.
If there is an issue using PyGAD, feel free to post at issue in this [GitHub repository](https://github.com/ahmedfgad/GeneticAlgorithmPython) https://github.com/ahmedfgad/GeneticAlgorithmPython or by sending an e-mail to ahmed.f.gad@gmail.com.
If you built a project that uses PyGAD, then please drop an e-mail to ahmed.f.gad@gmail.com with the following information so that your project is included in the documentation.
- Project title
- Brief description
- Preferably, a link that directs the readers to your project
Please check the **Contact Us** section for more contact details.
# Life Cycle of PyGAD
The next figure lists the different stages in the lifecycle of an instance of the `pygad.GA` class. Note that PyGAD stops when either all generations are completed or when the function passed to the `on_generation` parameter returns the string `stop`.
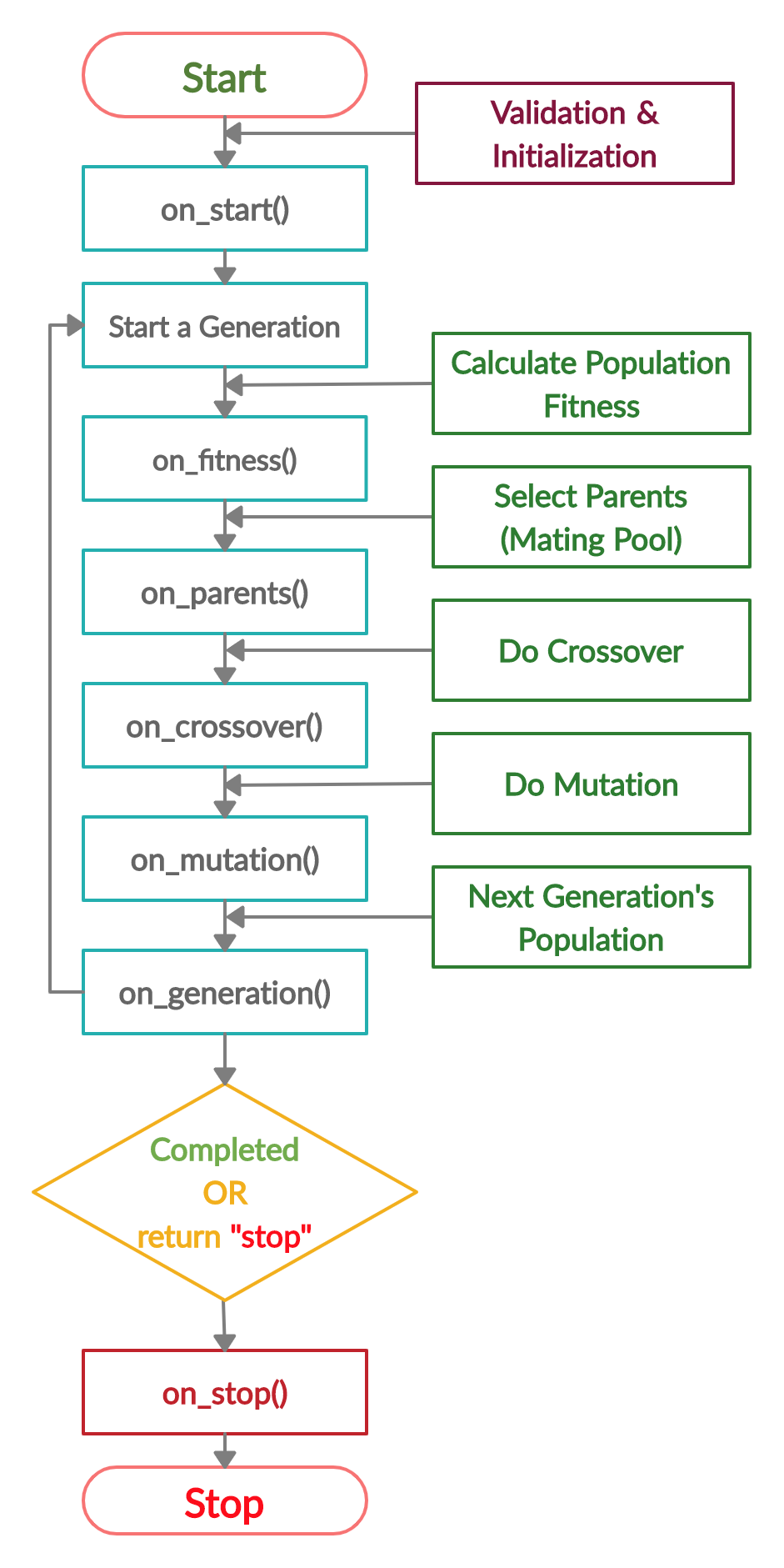
The next code implements all the callback functions to trace the execution of the genetic algorithm. Each callback function prints its name.
```python
import pygad
import numpy
function_inputs = [4,-2,3.5,5,-11,-4.7]
desired_output = 44
def fitness_func(ga_instance, solution, solution_idx):
output = numpy.sum(solution*function_inputs)
fitness = 1.0 / (numpy.abs(output - desired_output) + 0.000001)
return fitness
fitness_function = fitness_func
def on_start(ga_instance):
print("on_start()")
def on_fitness(ga_instance, population_fitness):
print("on_fitness()")
def on_parents(ga_instance, selected_parents):
print("on_parents()")
def on_crossover(ga_instance, offspring_crossover):
print("on_crossover()")
def on_mutation(ga_instance, offspring_mutation):
print("on_mutation()")
def on_generation(ga_instance):
print("on_generation()")
def on_stop(ga_instance, last_population_fitness):
print("on_stop()")
ga_instance = pygad.GA(num_generations=3,
num_parents_mating=5,
fitness_func=fitness_function,
sol_per_pop=10,
num_genes=len(function_inputs),
on_start=on_start,
on_fitness=on_fitness,
on_parents=on_parents,
on_crossover=on_crossover,
on_mutation=on_mutation,
on_generation=on_generation,
on_stop=on_stop)
ga_instance.run()
```
Based on the used 3 generations as assigned to the `num_generations` argument, here is the output.
```
on_start()
on_fitness()
on_parents()
on_crossover()
on_mutation()
on_generation()
on_fitness()
on_parents()
on_crossover()
on_mutation()
on_generation()
on_fitness()
on_parents()
on_crossover()
on_mutation()
on_generation()
on_stop()
```
# Example
Check the [PyGAD's documentation](https://pygad.readthedocs.io/en/latest/gann.html) for information about the implementation of this example.
```python
import numpy
import pygad
import pygad.nn
import pygad.gann
def fitness_func(ga_instance, solution, sol_idx):
global GANN_instance, data_inputs, data_outputs
predictions = pygad.nn.predict(last_layer=GANN_instance.population_networks[sol_idx],
data_inputs=data_inputs)
correct_predictions = numpy.where(predictions == data_outputs)[0].size
solution_fitness = (correct_predictions/data_outputs.size)*100
return solution_fitness
def callback_generation(ga_instance):
global GANN_instance, last_fitness
population_matrices = pygad.gann.population_as_matrices(population_networks=GANN_instance.population_networks,
population_vectors=ga_instance.population)
GANN_instance.update_population_trained_weights(population_trained_weights=population_matrices)
print("Generation = {generation}".format(generation=ga_instance.generations_completed))
print("Fitness = {fitness}".format(fitness=ga_instance.best_solution()[1]))
print("Change = {change}".format(change=ga_instance.best_solution()[1] - last_fitness))
last_fitness = ga_instance.best_solution()[1].copy()
# Holds the fitness value of the previous generation.
last_fitness = 0
# Preparing the NumPy array of the inputs.
data_inputs = numpy.array([[1, 1],
[1, 0],
[0, 1],
[0, 0]])
# Preparing the NumPy array of the outputs.
data_outputs = numpy.array([0,
1,
1,
0])
# The length of the input vector for each sample (i.e. number of neurons in the input layer).
num_inputs = data_inputs.shape[1]
# The number of neurons in the output layer (i.e. number of classes).
num_classes = 2
# Creating an initial population of neural networks. The return of the initial_population() function holds references to the networks, not their weights. Using such references, the weights of all networks can be fetched.
num_solutions = 6 # A solution or a network can be used interchangeably.
GANN_instance = pygad.gann.GANN(num_solutions=num_solutions,
num_neurons_input=num_inputs,
num_neurons_hidden_layers=[2],
num_neurons_output=num_classes,
hidden_activations=["relu"],
output_activation="softmax")
# population does not hold the numerical weights of the network instead it holds a list of references to each last layer of each network (i.e. solution) in the population. A solution or a network can be used interchangeably.
# If there is a population with 3 solutions (i.e. networks), then the population is a list with 3 elements. Each element is a reference to the last layer of each network. Using such a reference, all details of the network can be accessed.
population_vectors = pygad.gann.population_as_vectors(population_networks=GANN_instance.population_networks)
# To prepare the initial population, there are 2 ways:
# 1) Prepare it yourself and pass it to the initial_population parameter. This way is useful when the user wants to start the genetic algorithm with a custom initial population.
# 2) Assign valid integer values to the sol_per_pop and num_genes parameters. If the initial_population parameter exists, then the sol_per_pop and num_genes parameters are useless.
initial_population = population_vectors.copy()
num_parents_mating = 4 # Number of solutions to be selected as parents in the mating pool.
num_generations = 500 # Number of generations.
mutation_percent_genes = 5 # Percentage of genes to mutate. This parameter has no action if the parameter mutation_num_genes exists.
parent_selection_type = "sss" # Type of parent selection.
crossover_type = "single_point" # Type of the crossover operator.
mutation_type = "random" # Type of the mutation operator.
keep_parents = 1 # Number of parents to keep in the next population. -1 means keep all parents and 0 means keep nothing.
init_range_low = -2
init_range_high = 5
ga_instance = pygad.GA(num_generations=num_generations,
num_parents_mating=num_parents_mating,
initial_population=initial_population,
fitness_func=fitness_func,
mutation_percent_genes=mutation_percent_genes,
init_range_low=init_range_low,
init_range_high=init_range_high,
parent_selection_type=parent_selection_type,
crossover_type=crossover_type,
mutation_type=mutation_type,
keep_parents=keep_parents,
on_generation=callback_generation)
ga_instance.run()
# After the generations complete, some plots are showed that summarize how the outputs/fitness values evolve over generations.
ga_instance.plot_fitness()
# Returning the details of the best solution.
solution, solution_fitness, solution_idx = ga_instance.best_solution()
print("Parameters of the best solution : {solution}".format(solution=solution))
print("Fitness value of the best solution = {solution_fitness}".format(solution_fitness=solution_fitness))
print("Index of the best solution : {solution_idx}".format(solution_idx=solution_idx))
if ga_instance.best_solution_generation != -1:
print("Best fitness value reached after {best_solution_generation} generations.".format(best_solution_generation=ga_instance.best_solution_generation))
# Predicting the outputs of the data using the best solution.
predictions = pygad.nn.predict(last_layer=GANN_instance.population_networks[solution_idx],
data_inputs=data_inputs)
print("Predictions of the trained network : {predictions}".format(predictions=predictions))
# Calculating some statistics
num_wrong = numpy.where(predictions != data_outputs)[0]
num_correct = data_outputs.size - num_wrong.size
accuracy = 100 * (num_correct/data_outputs.size)
print("Number of correct classifications : {num_correct}.".format(num_correct=num_correct))
print("Number of wrong classifications : {num_wrong}.".format(num_wrong=num_wrong.size))
print("Classification accuracy : {accuracy}.".format(accuracy=accuracy))
```
# For More Information
There are different resources that can be used to get started with the genetic algorithm and building it in Python.
## Tutorial: Implementing Genetic Algorithm in Python
To start with coding the genetic algorithm, you can check the tutorial titled [**Genetic Algorithm Implementation in Python**](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/genetic-algorithm-implementation-python-ahmed-gad) available at these links:
- [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/genetic-algorithm-implementation-python-ahmed-gad)
- [Towards Data Science](https://towardsdatascience.com/genetic-algorithm-implementation-in-python-5ab67bb124a6)
- [KDnuggets](https://www.kdnuggets.com/2018/07/genetic-algorithm-implementation-python.html)
[This tutorial](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/genetic-algorithm-implementation-python-ahmed-gad) is prepared based on a previous version of the project but it still a good resource to start with coding the genetic algorithm.
[](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/genetic-algorithm-implementation-python-ahmed-gad)
## Tutorial: Introduction to Genetic Algorithm
Get started with the genetic algorithm by reading the tutorial titled [**Introduction to Optimization with Genetic Algorithm**](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/introduction-optimization-genetic-algorithm-ahmed-gad) which is available at these links:
* [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/introduction-optimization-genetic-algorithm-ahmed-gad)
* [Towards Data Science](https://www.kdnuggets.com/2018/03/introduction-optimization-with-genetic-algorithm.html)
* [KDnuggets](https://towardsdatascience.com/introduction-to-optimization-with-genetic-algorithm-2f5001d9964b)
[](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/introduction-optimization-genetic-algorithm-ahmed-gad)
## Tutorial: Build Neural Networks in Python
Read about building neural networks in Python through the tutorial titled [**Artificial Neural Network Implementation using NumPy and Classification of the Fruits360 Image Dataset**](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/artificial-neural-network-implementation-using-numpy-fruits360-gad) available at these links:
* [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/artificial-neural-network-implementation-using-numpy-fruits360-gad)
* [Towards Data Science](https://towardsdatascience.com/artificial-neural-network-implementation-using-numpy-and-classification-of-the-fruits360-image-3c56affa4491)
* [KDnuggets](https://www.kdnuggets.com/2019/02/artificial-neural-network-implementation-using-numpy-and-image-classification.html)
[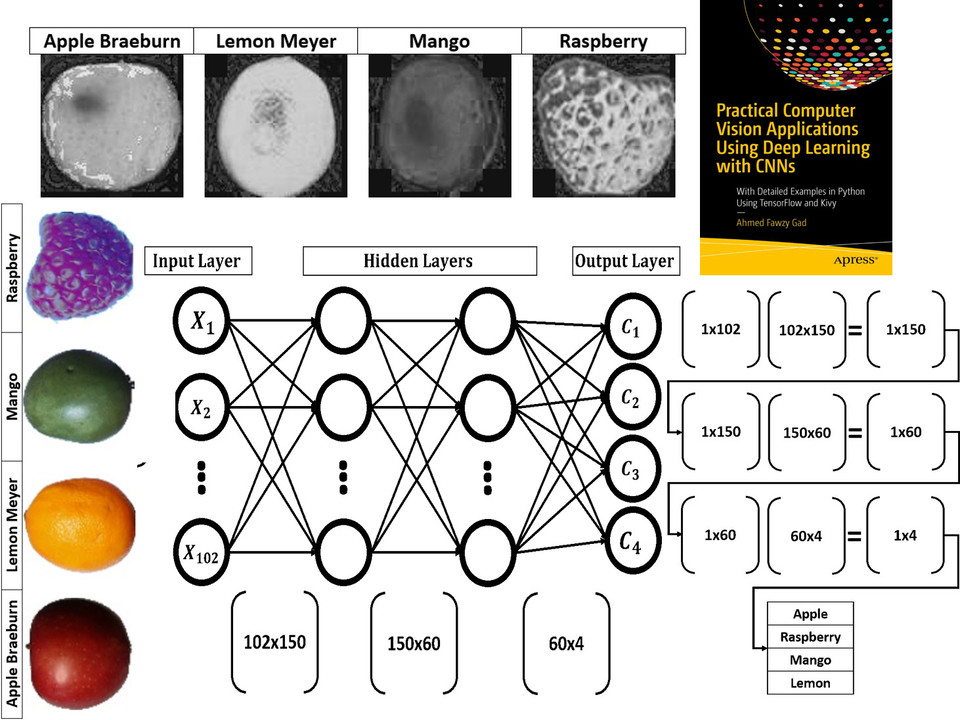](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/artificial-neural-network-implementation-using-numpy-fruits360-gad)
## Tutorial: Optimize Neural Networks with Genetic Algorithm
Read about training neural networks using the genetic algorithm through the tutorial titled [**Artificial Neural Networks Optimization using Genetic Algorithm with Python**](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/artificial-neural-networks-optimization-using-genetic-ahmed-gad) available at these links:
- [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/artificial-neural-networks-optimization-using-genetic-ahmed-gad)
- [Towards Data Science](https://towardsdatascience.com/artificial-neural-networks-optimization-using-genetic-algorithm-with-python-1fe8ed17733e)
- [KDnuggets](https://www.kdnuggets.com/2019/03/artificial-neural-networks-optimization-genetic-algorithm-python.html)
[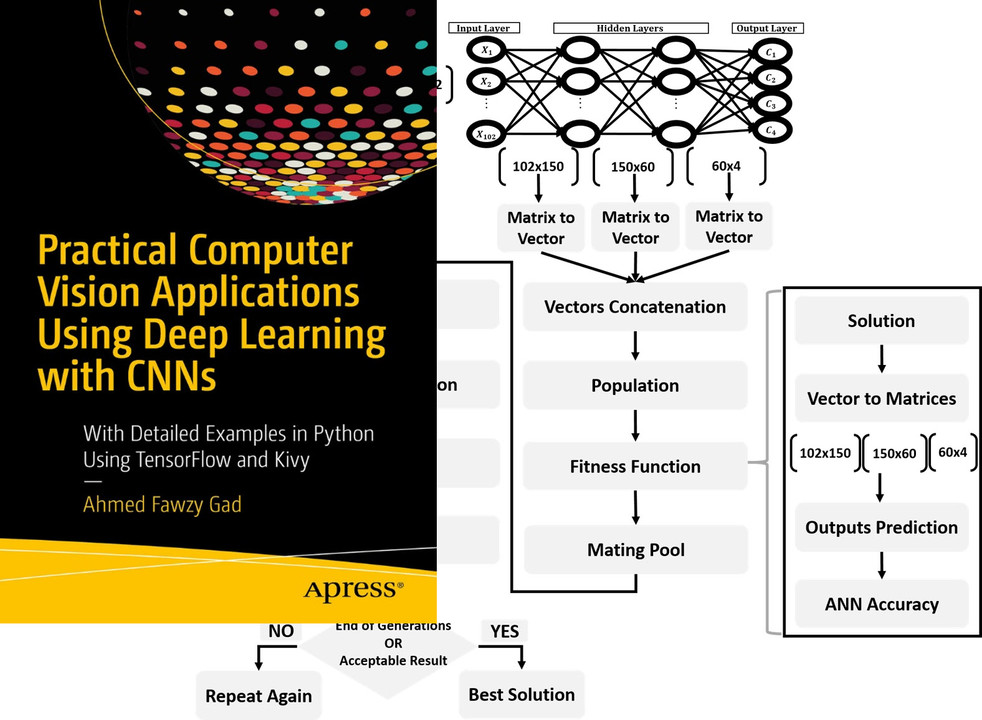](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/artificial-neural-networks-optimization-using-genetic-ahmed-gad)
## Tutorial: Building CNN in Python
To start with coding the genetic algorithm, you can check the tutorial titled [**Building Convolutional Neural Network using NumPy from Scratch**](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/building-convolutional-neural-network-using-numpy-from-ahmed-gad) available at these links:
- [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/building-convolutional-neural-network-using-numpy-from-ahmed-gad)
- [Towards Data Science](https://towardsdatascience.com/building-convolutional-neural-network-using-numpy-from-scratch-b30aac50e50a)
- [KDnuggets](https://www.kdnuggets.com/2018/04/building-convolutional-neural-network-numpy-scratch.html)
- [Chinese Translation](http://m.aliyun.com/yunqi/articles/585741)
[This tutorial](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/building-convolutional-neural-network-using-numpy-from-ahmed-gad)) is prepared based on a previous version of the project but it still a good resource to start with coding CNNs.
[](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/building-convolutional-neural-network-using-numpy-from-ahmed-gad)
## Tutorial: Derivation of CNN from FCNN
Get started with the genetic algorithm by reading the tutorial titled [**Derivation of Convolutional Neural Network from Fully Connected Network Step-By-Step**](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/derivation-convolutional-neural-network-from-fully-connected-gad) which is available at these links:
* [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/derivation-convolutional-neural-network-from-fully-connected-gad)
* [Towards Data Science](https://towardsdatascience.com/derivation-of-convolutional-neural-network-from-fully-connected-network-step-by-step-b42ebafa5275)
* [KDnuggets](https://www.kdnuggets.com/2018/04/derivation-convolutional-neural-network-fully-connected-step-by-step.html)
[](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/derivation-convolutional-neural-network-from-fully-connected-gad)
## Book: Practical Computer Vision Applications Using Deep Learning with CNNs
You can also check my book cited as [**Ahmed Fawzy Gad 'Practical Computer Vision Applications Using Deep Learning with CNNs'. Dec. 2018, Apress, 978-1-4842-4167-7**](https://www.amazon.com/Practical-Computer-Vision-Applications-Learning/dp/1484241665) which discusses neural networks, convolutional neural networks, deep learning, genetic algorithm, and more.
Find the book at these links:
- [Amazon](https://www.amazon.com/Practical-Computer-Vision-Applications-Learning/dp/1484241665)
- [Springer](https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-1-4842-4167-7)
- [Apress](https://www.apress.com/gp/book/9781484241660)
- [O'Reilly](https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/practical-computer-vision/9781484241677)
- [Google Books](https://books.google.com.eg/books?id=xLd9DwAAQBAJ)

# Citing PyGAD - Bibtex Formatted Citation
If you used PyGAD, please consider adding a citation to the following paper about PyGAD:
```
@misc{gad2021pygad,
title={PyGAD: An Intuitive Genetic Algorithm Python Library},
author={Ahmed Fawzy Gad},
year={2021},
eprint={2106.06158},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.NE}
}
```
# Contact Us
* E-mail: ahmed.f.gad@gmail.com
* [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/ahmedfgad)
* [Amazon Author Page](https://amazon.com/author/ahmedgad)
* [Heartbeat](https://heartbeat.fritz.ai/@ahmedfgad)
* [Paperspace](https://blog.paperspace.com/author/ahmed)
* [KDnuggets](https://kdnuggets.com/author/ahmed-gad)
* [TowardsDataScience](https://towardsdatascience.com/@ahmedfgad)
* [GitHub](https://github.com/ahmedfgad)