https://github.com/ai/size-limit
Calculate the real cost to run your JS app or lib to keep good performance. Show error in pull request if the cost exceeds the limit.
https://github.com/ai/size-limit
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
Calculate the real cost to run your JS app or lib to keep good performance. Show error in pull request if the cost exceeds the limit.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/ai/size-limit
- Owner: ai
- License: mit
- Created: 2017-06-25T05:18:40.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-21T14:19:35.000Z (12 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-05T20:51:54.376Z (10 months ago)
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 5.47 MB
- Stars: 6,703
- Watchers: 38
- Forks: 1,812
- Open Issues: 26
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- Front-End-Performance-Checklist - ai/size-limit: Prevent JS libraries bloat. If you accidentally add a massive dependency, Size Limit will throw an error.
- awesome-github-repos - ai/size-limit - Calculate the real cost to run your JS app or lib to keep good performance. Show error in pull request if the cost exceeds the limit. (JavaScript)
- awesome_frontend_development_resources - size-limit - Prevent JS libraries bloat. If you accidentally add a massive dependency, Size Limit will throw an error. (Build Tools / React Components)
- awesome-github-star - size-limit
- awesome-readme - ai/size-limit - Project logo, clear description, screenshot, step-by-step installing instructions. (Examples)
- awesome - size-limit - Prevent JS libraries bloat. If you accidentally add a massive dependency, Size Limit will throw an error. (Build Tools / React Components)
- awesome-ru - Size Limit - Инструмент для контроля размера JavaScript библиотек в CI. Автор: Андрей Ситник. (Веб-разработка)
- awesome-web-performance-budget - Size Limit - Calculate the real cost to run your JS app or lib to keep good performance. Show error in pull request if the cost exceeds the limit. (Build Tools to set up performance budget)
- awesome-web-dev-resources - size-limit
- my-awesome-list - size-limit
- awesome-readme - ai/size-limit - Project logo, clear description, screenshot, step-by-step installing instructions. (Examples)
- awesome - size-limit - Calculate the real cost to run your JS app or lib to keep good performance. Show error in pull request if the cost exceeds the limit. (JavaScript)
- awesome-anomaly-detection - Incorporating Feedback into Tree-based Anomaly Detection - KDD 2017 Workshop on Interactive Data Exploration and Analytics. (Deep Learning Method / FeedBack)
- fucking-awesome-readme - ai/size-limit - Project logo, clear description, screenshot, step-by-step installing instructions. (Examples)
- awesome-list - size-limit
README
# Size Limit [![Cult Of Martians][cult-img]][cult]

Size Limit is a performance budget tool for JavaScript. It checks every commit
on CI, calculates the real cost of your JS for end-users and throws an error
if the cost exceeds the limit.
* **ES modules** and **tree-shaking** support.
* Add Size Limit to **GitHub Actions**, **Circle CI** or another CI system
to know if a pull request adds a massive dependency.
* **Modular** to fit different use cases: big JS applications
that use their own bundler or small npm libraries with many files.
* Can calculate **the time** it would take a browser
to download and **execute** your JS. Time is a much more accurate
and understandable metric compared to the size in bytes.
Additionally, you can [customize time plugin] via config
for every check with network speed, latency and so on.
* Calculations include **all dependencies and polyfills**
used in your JS.

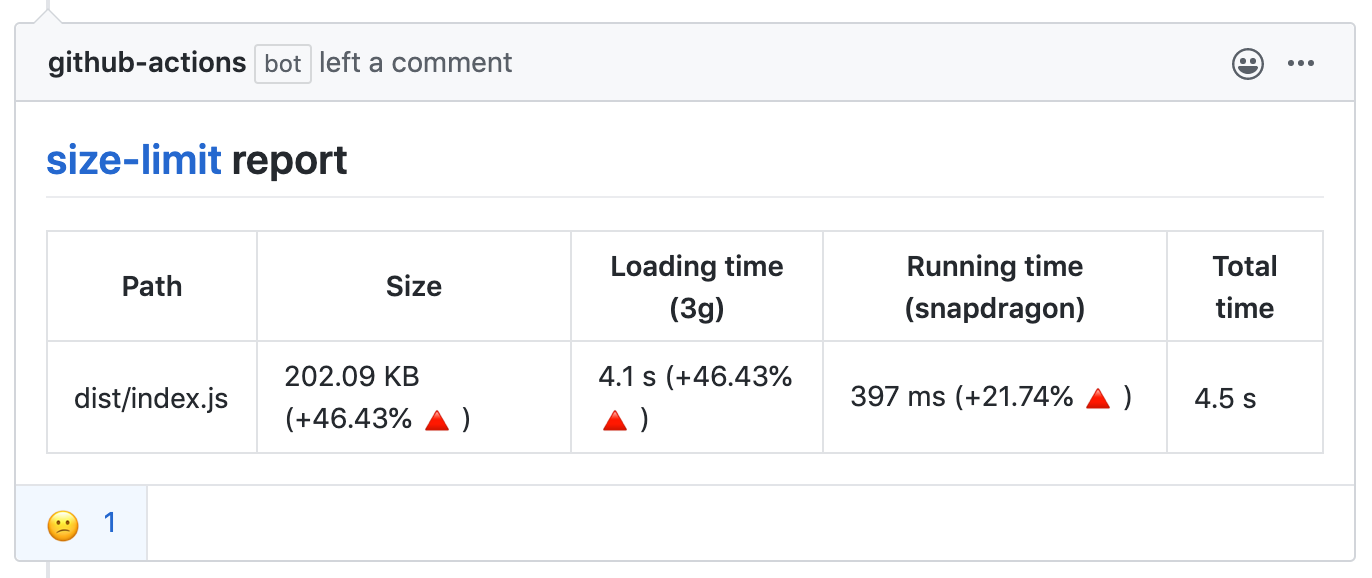
With **[GitHub action]** Size Limit will post bundle size changes as a comment
in pull request discussion.
With `--why`, Size Limit can tell you *why* your library is of this size
and show the real cost of all your internal dependencies.
We are using [Statoscope] for this analysis.

[GitHub action]: https://github.com/andresz1/size-limit-action
[Statoscope]: https://github.com/statoscope/statoscope
[cult-img]: http://cultofmartians.com/assets/badges/badge.svg
[cult]: http://cultofmartians.com/tasks/size-limit-config.html
[customize time plugin]: https://github.com/ai/size-limit/packages/time#customize-network-speed
## Who Uses Size Limit
* [MobX](https://github.com/mobxjs/mobx)
* [Material-UI](https://github.com/callemall/material-ui)
* [Ant Design](https://github.com/ant-design/ant-design/)
* [Autoprefixer](https://github.com/postcss/autoprefixer)
* [PostCSS](https://github.com/postcss/postcss) reduced
[25% of the size](https://github.com/postcss/postcss/commit/150edaa42f6d7ede73d8c72be9909f0a0f87a70f).
* [Browserslist](https://github.com/browserslist/browserslist) reduced
[25% of the size](https://github.com/browserslist/browserslist/commit/640b62fa83a20897cae75298a9f2715642531623).
* [EmojiMart](https://github.com/missive/emoji-mart) reduced
[20% of the size](https://github.com/missive/emoji-mart/pull/111)
* [nanoid](https://github.com/ai/nanoid) reduced
[33% of the size](https://github.com/ai/nanoid/commit/036612e7d6cc5760313a8850a2751a5e95184eab).
* [React Focus Lock](https://github.com/theKashey/react-focus-lock) reduced
[32% of the size](https://github.com/theKashey/react-focus-lock/pull/48).
* [Logux](https://github.com/logux) reduced
[90% of the size](https://github.com/logux/logux-client/commit/62b258e20e1818b23ae39b9c4cd49e2495781e91).
## How It Works
1. Size Limit contains a CLI tool, 3 plugins (`file`, `webpack`, `time`)
and 3 plugin presets for popular use cases (`app`, `big-lib`, `small-lib`).
A CLI tool finds plugins in `package.json` and loads the config.
2. If you use the `webpack` plugin, Size Limit will bundle your JS files into
a single file. It is important to track dependencies and webpack polyfills.
It is also useful for small libraries with many small files and without
a bundler.
3. The `webpack` plugin creates an empty webpack project, adds your library
and looks for the bundle size difference.
4. The `time` plugin compares the current machine performance with that of
a low-priced Android devices to calculate the CPU throttling rate.
5. Then the `time` plugin runs headless Chrome (or desktop Chrome if it’s
available) to track the time a browser takes to compile and execute your JS.
Note that these measurements depend on available resources and might
be unstable. [See here](https://github.com/mbalabash/estimo/issues/5)
for more details.
## Usage
### JS Applications
Suitable for applications that have their own bundler and send the JS bundle
directly to a client (without publishing it to npm). Think of a user-facing app
or website, like an email client, a CRM, a landing page or a blog with
interactive elements, using React/Vue/Svelte lib or vanilla JS.
Show instructions
1. Install the preset:
```sh
npm install --save-dev size-limit @size-limit/file
```
2. Add the `size-limit` section and the `size` script to your `package.json`:
```diff
+ "size-limit": [
+ {
+ "path": "dist/app-*.js"
+ }
+ ],
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack ./webpack.config.js",
+ "size": "npm run build && size-limit",
"test": "vitest && eslint ."
}
```
3. Here’s how you can get the size for your current project:
```sh
$ npm run size
Package size: 30.08 kB with all dependencies, minified and brotlied
```
4. Now, let’s set the limit. Add 25% to the current total size and use that as
the limit in your `package.json`:
```diff
"size-limit": [
{
+ "limit": "35 kB",
"path": "dist/app-*.js"
}
],
```
5. Add the `size` script to your test suite:
```diff
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack ./webpack.config.js",
"size": "npm run build && size-limit",
- "test": "vitest && eslint ."
+ "test": "vitest && eslint . && npm run size"
}
```
6. If you don’t have a continuous integration service running, don’t forget
to add one — start with GitHub Actions.
### JS Application and Time-based Limit
File size limit (in kB) is not the best way to describe your JS application
cost for developers. Developers will compare the size of the JS bundle
with the size of images. But browsers need much more time to parse 100 kB
of JS than 100 kB of an image since JS compilers are very complex.
This is why Size Limit support time-based limit. It runs headless Chrome
to track the time a browser takes to compile and execute your JS.
Show instructions
1. Install the preset:
```sh
npm install --save-dev size-limit @size-limit/preset-app
```
2. Add the `size-limit` section and the `size` script to your `package.json`:
```diff
+ "size-limit": [
+ {
+ "path": "dist/app-*.js"
+ }
+ ],
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack ./webpack.config.js",
+ "size": "npm run build && size-limit",
"test": "vitest && eslint ."
}
```
3. Here’s how you can get the size for your current project:
```sh
$ npm run size
Package size: 30.08 kB with all dependencies, minified and brotlied
Loading time: 602 ms on slow 3G
Running time: 214 ms on Snapdragon 410
Total time: 815 ms
```
4. Now, let’s set the limit. Add 25% to the current total time and use that as
the limit in your `package.json`:
```diff
"size-limit": [
{
+ "limit": "1 s",
"path": "dist/app-*.js"
}
],
```
5. Add the `size` script to your test suite:
```diff
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack ./webpack.config.js",
"size": "npm run build && size-limit",
- "test": "vitest && eslint ."
+ "test": "vitest && eslint . && npm run size"
}
```
6. If you don’t have a continuous integration service running, don’t forget
to add one — start with GitHub Actions.
### Big Libraries
JS libraries > 10 kB in size.
This preset includes headless Chrome, and will measure your lib’s execution
time. You likely don’t need this overhead for a small 2 kB lib, but for larger
ones the execution time is a more accurate and understandable metric that
the size in bytes. Libraries like [React] are good examples for this preset.
Show instructions
1. Install preset:
```sh
npm install --save-dev size-limit @size-limit/preset-big-lib
```
2. Add the `size-limit` section and the `size` script to your `package.json`:
```diff
+ "size-limit": [
+ {
+ "path": "dist/react.production-*.js"
+ }
+ ],
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack ./scripts/rollup/build.js",
+ "size": "npm run build && size-limit",
"test": "vitest && eslint ."
}
```
3. If you use ES modules you can test the size after tree-shaking with `import`
option:
```diff
"size-limit": [
{
"path": "dist/react.production-*.js",
+ "import": "{ createComponent }"
}
],
```
4. Here’s how you can get the size for your current project:
```sh
$ npm run size
Package size: 30.08 kB with all dependencies, minified and brotlied
Loading time: 602 ms on slow 3G
Running time: 214 ms on Snapdragon 410
Total time: 815 ms
```
5. Now, let’s set the limit. Add 25% to the current total time and use that
as the limit in your `package.json`:
```diff
"size-limit": [
{
+ "limit": "1 s",
"path": "dist/react.production-*.js"
}
],
```
6. Add a `size` script to your test suite:
```diff
"scripts": {
"build": "rollup ./scripts/rollup/build.js",
"size": "npm run build && size-limit",
- "test": "vitest && eslint ."
+ "test": "vitest && eslint . && npm run size"
}
```
7. If you don’t have a continuous integration service running, don’t forget
to add one — start with GitHub Actions.
8. Add the library size to docs, it will help users to choose your project:
```diff
# Project Name
Short project description
* **Fast.** 10% faster than competitor.
+ * **Small.** 15 kB (minified and brotlied).
+ [Size Limit](https://github.com/ai/size-limit) controls the size.
```
### Small Libraries
JS libraries < 10 kB in size.
This preset will only measure the size, without the execution time, so it’s
suitable for small libraries. If your library is larger, you likely want
the Big Libraries preset above. [Nano ID] or [Storeon] are good examples
for this preset.
Show instructions
1. First, install `size-limit`:
```sh
npm install --save-dev size-limit @size-limit/preset-small-lib
```
2. Add the `size-limit` section and the `size` script to your `package.json`:
```diff
+ "size-limit": [
+ {
+ "path": "index.js"
+ }
+ ],
"scripts": {
+ "size": "size-limit",
"test": "vitest && eslint ."
}
```
3. Here’s how you can get the size for your current project:
```sh
$ npm run size
Package size: 177 B with all dependencies, minified and brotlied
```
4. If your project size starts to look bloated, run `--why` for analysis:
```sh
npm run size -- --why
```
> We use [Statoscope](https://github.com/statoscope/statoscope) as bundle analyzer.
5. Now, let’s set the limit. Determine the current size of your library,
add just a little bit (a kilobyte, maybe) and use that as the limit
in your `package.json`:
```diff
"size-limit": [
{
+ "limit": "9 kB",
"path": "index.js"
}
],
```
6. Add the `size` script to your test suite:
```diff
"scripts": {
"size": "size-limit",
- "test": "vitest && eslint ."
+ "test": "vitest && eslint . && npm run size"
}
```
7. If you don’t have a continuous integration service running, don’t forget
to add one — start with GitHub Actions.
8. Add the library size to docs, it will help users to choose your project:
```diff
# Project Name
Short project description
* **Fast.** 10% faster than competitor.
+ * **Small.** 500 bytes (minified and brotlied). No dependencies.
+ [Size Limit](https://github.com/ai/size-limit) controls the size.
```
[Storeon]: https://github.com/ai/storeon/
[Nano ID]: https://github.com/ai/nanoid/
[React]: https://github.com/facebook/react/
## Reports
Size Limit has a [GitHub action] that comments and rejects pull requests based
on Size Limit output.
1. Install and configure Size Limit as shown above.
2. Add the following action inside `.github/workflows/size-limit.yml`
```yaml
name: "size"
on:
pull_request:
branches:
- master
jobs:
size:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
CI_JOB_NUMBER: 1
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v1
- uses: andresz1/size-limit-action@v1
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
```
## Config
### Plugins and Presets
Plugins or plugin presets will be loaded automatically from `package.json`.
For example, if you want to use `@size-limit/webpack`, you can just use
`npm install --save-dev @size-limit/webpack`, or you can use our preset
`@size-limit/preset-big-lib`.
Plugins:
* `@size-limit/file` checks the size of files with Brotli (default), Gzip
or without compression.
* `@size-limit/webpack` adds your library to empty webpack project
and prepares bundle file for `file` plugin.
* `@size-limit/webpack-why` adds reports for `webpack` plugin
about your library is of this size to show the cost of all your
dependencies.
* `@size-limit/webpack-css` adds css support for `webpack` plugin.
* `@size-limit/esbuild` is like `webpack` plugin, but uses `esbuild`
to be faster and use less space in `node_modules`.
* `@size-limit/esbuild-why` add reports for `esbuild` plugin
about your library is of this size to show the cost of all your
dependencies.
* `@size-limit/time` uses headless Chrome to track time to execute JS.
Plugin presets:
* `@size-limit/preset-app` contains `file` and `time` plugins.
* `@size-limit/preset-big-lib` contains `webpack`, `file`, and `time` plugins.
* `@size-limit/preset-small-lib` contains `esbuild` and `file` plugins.
#### Third-Party Plugins
Third-party plugins and presets named starting with `size-limit-` are also supported.
For example:
* [`size-limit-node-esbuild`](https://github.com/un-ts/size-limit/tree/main/packages/node-esbuild)
is like `@size-limit/esbuild` but for Node libraries.
* [`size-limit-preset-node-lib`](https://github.com/un-ts/size-limit/tree/main/packages/preset-node-lib)
is like `@size-limit/preset-small-lib` but for Node libraries which contains
above `node-esbuild` and core `file` plugins.
* [`nx-size-limit`](https://github.com/LironHazan/nx-size-limit)
is an [NX](https://nx.dev/community) build system community plugin.
### Limits Config
Size Limits supports three ways to define limits config.
1. `size-limit` section in `package.json`:
```json
"size-limit": [
{
"path": "index.js",
"import": "{ createStore }",
"limit": "500 ms"
}
]
```
2. or a separate `.size-limit.json` config file:
```js
[
{
"path": "index.js",
"import": "{ createStore }",
"limit": "500 ms"
}
]
```
3. or a more flexible `.size-limit.js` or `.size-limit.cjs` config file:
```js
module.exports = [
{
path: "index.js",
import: "{ createStore }",
limit: "500 ms"
}
]
```
4. or types `.size-limit.ts`:
```ts
import type { SizeLimitConfig } from '../../packages/size-limit'
module.exports = [
{
path: "index.js",
import: "{ createStore }",
limit: "500 ms"
}
] satisfies SizeLimitConfig
```
Each section in the config can have these options:
* **path**: relative paths to files. The only mandatory option.
It could be a path `"index.js"`, a [pattern] `"dist/app-*.js"`
or an array `["index.js", "dist/app-*.js", "!dist/app-exclude.js"]`.
* **import**: partial import to test tree-shaking. It could be `"{ lib }"`
to test `import { lib } from 'lib'`, `*` to test all exports,
or `{ "a.js": "{ a }", "b.js": "{ b }" }` to test multiple files.
* **limit**: size or time limit for files from the `path` option. It should be
a string with a number and unit, separated by a space.
Format: `100 B`, `10 kB`, `500 ms`, `1 s`.
* **name**: the name of the current section. It will only be useful
if you have multiple sections.
* **message**: an optional custom message to display additional information,
such as guidance for resolving errors, relevant links, or instructions
for next steps when a limit is exceeded.
* **entry**: when using a custom webpack config, a webpack entry could be given.
It could be a string or an array of strings.
By default, the total size of all entry points will be checked.
* **webpack**: with `false` it will disable webpack.
* **running**: with `false` it will disable calculating running time.
* **gzip**: with `true` it will use Gzip compression and disable
Brotli compression.
* **brotli**: with `false` it will disable any compression.
* **config**: a path to a custom webpack config.
* **ignore**: an array of files and dependencies to exclude from
the project size calculation.
* **modifyWebpackConfig**: (.size-limit.js only) function that can be used
to do last-minute changes to the webpack config, like adding a plugin.
* **compareWith**: path to `stats.json` from another build to compare
(when `--why` is using).
* **uiReports**: custom UI reports list (see [Statoscope docs]).
If you use Size Limit to track the size of CSS files, make sure to set
`webpack: false`. Otherwise, you will get wrong numbers, because webpack
inserts `style-loader` runtime (≈2 kB) into the bundle.
Also, you avoid having a config and pass the limit to CLI:
```sh
npm install --save-dev @size-limit/file
npx size-limit --limit "10 kB" dist/bundle.js
```
Additionally, you can specify a custom path to your configuration file when running the CLI:
```sh
npx size-limit --config configs/size-limit.json
```
[Statoscope docs]: https://github.com/statoscope/statoscope/tree/master/packages/webpack-plugin#optionsreports-report
[pattern]: https://github.com/SuperchupuDev/tinyglobby
## Analyze with `--why`
You can run `size-limit --why` to analyze the bundle.
You will need to install `@size-limit/esbuild-why` or `@size-limit/webpack-why`
depends on which bundler you are using (default is `esbuild`).
For `@size-limit/esbuild-why`,
it will generate a `esbuild-why.html` at the current directory & open it in the browser.
If you also specify `--save-bundle `,
the report will be generated inside ``.
If you have multiple sections in your config,
the files will be named `esbuild-why-{n}.html`,
or you can give it a custom name:
```jsonc
[
{
"name": "cjs",
/* snap */
},
{
"name": "esm",
/* snap */
}
]
```
This will produce `esbuild-why-cjs.html` and `esbuild-why-esm.html` respectively.
For `@size-limit/webpack-why`,
it will generate the report and open it in the browser automatically.
## JS API
```js
const sizeLimit = require('size-limit')
const filePlugin = require('@size-limit/file')
const webpackPlugin = require('@size-limit/webpack')
sizeLimit([filePlugin, webpackPlugin], [filePath]).then(result => {
result //=> { size: 12480 }
})
```