https://github.com/aiff22/pynet-bokeh
Rendering Realistic Bokeh Images with PyNET
https://github.com/aiff22/pynet-bokeh
aperture blur blurred-background bokeh bokeh-effect camera computer-vision deep-learning image-processing image-reconstruction image-to-image-translation inference mobile photography photos pynet shallow-depth-of-field smartphones
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
Rendering Realistic Bokeh Images with PyNET
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/aiff22/pynet-bokeh
- Owner: aiff22
- License: other
- Created: 2020-06-10T21:16:17.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-12-12T17:53:36.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-24T15:18:24.302Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: aperture, blur, blurred-background, bokeh, bokeh-effect, camera, computer-vision, deep-learning, image-processing, image-reconstruction, image-to-image-translation, inference, mobile, photography, photos, pynet, shallow-depth-of-field, smartphones
- Language: Python
- Homepage: http://people.ee.ethz.ch/~ihnatova/pynet-bokeh.html
- Size: 5.87 MB
- Stars: 176
- Watchers: 9
- Forks: 30
- Open Issues: 7
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
## Rendering Natural Camera Bokeh Effect with Deep Learning

#### 1. Overview [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.05698.pdf) [[Project Webpage]](http://people.ee.ethz.ch/~ihnatova/pynet-bokeh.html) [[PyNET PyTorch]](https://github.com/aiff22/PyNET-PyTorch)
This repository provides the implementation of the deep learning-based bokeh effect rendering approach presented in [this paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.05698.pdf). The model is trained to map the standard **narrow-aperture images** into shallow depth-of-field photos captured with a professional Canon 7D DSLR camera. The presented approach is camera independent, **does not require any special hardware**, and can also be applied to the existing images. More visual results of this method on the presented EBB! dataset and its comparison to the **Portrait Mode** of the *Google Pixel Camera* app can be found [here](http://people.ee.ethz.ch/~ihnatova/pynet-bokeh.html#demo).
#### 2. Prerequisites
- Python: scipy, numpy, imageio and pillow packages
- [TensorFlow 1.x / 2.x](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/) + [CUDA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn)
- Nvidia GPU
#### 3. First steps
- Download the pre-trained [VGG-19 model](https://polybox.ethz.ch/index.php/s/7z5bHNg5r5a0g7k) and put it into `vgg_pretrained/` folder.
- Download the pre-trained [PyNET model](https://data.vision.ee.ethz.ch/ihnatova/public/ebb/PyNET_Bokeh_pretrained.zip) and put it into `models/original/` folder.
- Download the [EBB! dataset](http://people.ee.ethz.ch/~ihnatova/pynet-bokeh.html#dataset) and extract it into `ebb_dataset/` folder.
This folder should contain two subfolders: `train/` and `test/`
*Please note that Google Drive has a quota limiting the number of downloads per day. To avoid it, you can login to your Google account and press "Add to My Drive" button instead of a direct download. Please check [this issue](https://github.com/aiff22/PyNET/issues/4) for more information.*
#### 4. PyNET CNN
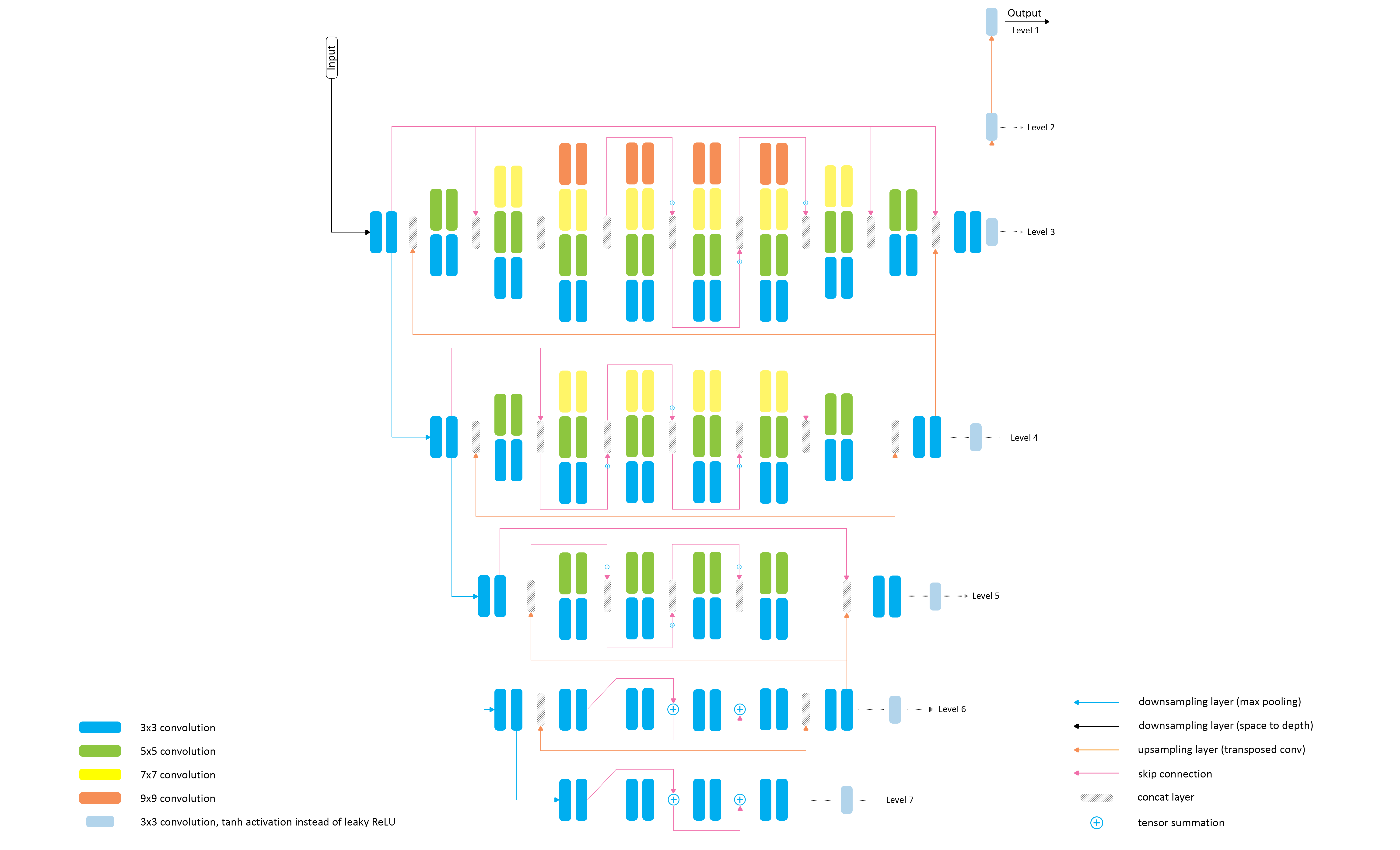
The proposed PyNET-based architecture has an inverted pyramidal shape and is processing the images at **seven different scales** (levels). The model is trained sequentially, starting from the lowest 7th layer, which allows to achieve good semantically-driven reconstruction results at smaller scales that are working with images of very low resolution and thus performing mostly global image manipulations. After the bottom layer is pre-trained, the same procedure is applied to the next level till the training is done on the original resolution. Since each higher level is getting **upscaled high-quality features** from the lower part of the model, it mainly learns to reconstruct the missing low-level details and refines the results. In this work, we additionally use two transposed convolutional layers on top of the main model (Levels 1, 2) that upsample the images to their target size.
#### 5. Training the model
The model is trained level by level, starting from the lowest (7th) one:
```bash
python train_model.py level=
```
Obligatory parameters:
>```level```: **```7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1```**
Optional parameters and their default values:
>```batch_size```: **```50```** - batch size [small values can lead to unstable training]
>```train_size```: **```4894```** - the number of training images randomly loaded each 1000 iterations
>```eval_step```: **```1000```** - each ```eval_step``` iterations the accuracy is computed and the model is saved
>```learning_rate```: **```5e-5```** - learning rate
>```restore_iter```: **```None```** - iteration to restore (when not specified, the last saved model for PyNET's ```level+1``` is loaded)
>```num_train_iters```: **```5K, 5K, 20K, 20K, 30K, 80K, 100K (for levels 5 - 0)```** - the number of training iterations
>```vgg_dir```: **```vgg_pretrained/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat```** - path to the pre-trained VGG-19 network
>```dataset_dir```: **```ebb_dataset/```** - path to the folder with the **EBB! dataset**
Below we provide the commands used for training the model on the Nvidia Tesla V100 GPU with 16GB of RAM. When using GPUs with smaller amount of memory, the batch size and the number of training iterations should be adjusted accordingly:
```bash
python train_model.py level=7 batch_size=50 num_train_iters=5000
python train_model.py level=6 batch_size=50 num_train_iters=5000
python train_model.py level=5 batch_size=40 num_train_iters=20000
python train_model.py level=4 batch_size=14 num_train_iters=20000
python train_model.py level=3 batch_size=9 num_train_iters=30000
python train_model.py level=2 batch_size=9 num_train_iters=80000
python train_model.py level=1 batch_size=5 num_train_iters=100000
```
#### 6. Test the provided pre-trained models on full-resolution test EBB! images
```bash
python test_model.py orig=true
```
Optional parameters:
>```use_gpu```: **```true```**,**```false```** - run the model on GPU or CPU
>```dataset_dir```: **```ebb_dataset/```** - path to the folder with the **EBB! dataset**
#### 7. Validate the obtained model on full-resolution test EBB! images
```bash
python test_model.py
```
Optional parameters:
>```restore_iter```: **```None```** - iteration to restore (when not specified, the last saved model for level=`````` is loaded)
>```use_gpu```: **```true```**,**```false```** - run the model on GPU or CPU
>```dataset_dir```: **```ebb_dataset/```** - path to the folder with the **EBB! dataset**
#### 8. Folder structure
>```models/``` - logs and models that are saved during the training process
>```models/original/``` - the folder with the provided pre-trained PyNET model
>```ebb_dataset/``` - the folder with the EBB! dataset
>```results/``` - visual results for image crops that are saved while training
>```results/full-resolution/``` - full-resolution image results saved during the testing
>```vgg-pretrained/``` - the folder with the pre-trained VGG-19 network
>```load_dataset.py``` - python script that loads training data
>```model.py``` - PyNET implementation (TensorFlow)
>```train_model.py``` - implementation of the training procedure
>```test_model.py``` - applying the pre-trained model to full-resolution test images and computing the numerical results
>```utils.py``` - auxiliary functions
>```vgg.py``` - loading the pre-trained vgg-19 network
#### 9. License
Copyright (C) 2020 Andrey Ignatov. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the [CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 (Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International)](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
The code is released for academic research use only.
#### 10. Citation
```
@article{ignatov2020rendering,
title={Rendering Natural Camera Bokeh Effect with Deep Learning},
author={Ignatov, Andrey and Patel, Jagruti and Timofte, Radu},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops},
pages={0--0},
year={2020}
}
```
#### 11. Any further questions?
```
Please contact Andrey Ignatov (andrey@vision.ee.ethz.ch) for more information
```