https://github.com/alduron/automationtools
A set of tools for general automation
https://github.com/alduron/automationtools
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
A set of tools for general automation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/alduron/automationtools
- Owner: alduron
- Created: 2020-07-22T22:17:59.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2020-09-03T01:12:35.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-13T07:05:06.676Z (over 1 year ago)
- Language: PowerShell
- Size: 124 KB
- Stars: 7
- Watchers: 0
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- jimsghstars - alduron/automationtools - A set of tools for general automation (PowerShell)
README
- [AutomationTools](#automationtools)
- [Purpose](#purpose)
- [Config](#config)
- [config.json files](#configjson-files)
- [Reserved Config Names](#reserved-config-names)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [Write-Log](#write-log)
- [Anatomy](#Anatomy)
- [Log Levels](#log-levels)
- [To Console](#to-console)
- [To Log](#to-log)
- [To Event Log](#to-event-log)
- [Email Reporting](#email-reporting)
- [Send-JobReport](#send-jobreport)
- [Table Conversion and Templating](#table-conversion-and-templating)
- [Secrets](#secrets)
- [Add-Secret](#add-secret)
- [Get-Secret](#get-secret)
- [Remove-Secret](#remove-secret)
- [File Tools](#file-tools)
- [Resolve-Folder](#resolve-folder)
- [Resolve-File](#resolve-file)
- [Test-FolderWrite](#test-folderwrite)
- [Conversions](#conversions)
- [ConvertTo-Version](#convertto-version)
- [Convert-HashToPSObject](#convert-hashtopsobject)
- [Convert-ArrayToScriptBlock](#convert-arraytoscriptblock)
- [Utilities](#utilities)
- [Copy-PSObject](#copy-psobject)
- [Test-Elevation](#test-elevation)
- [Add-ToolConfig](#add-toolconfig)
- [Update-Config](#update-config)
- [Invoke-ScheduledTask](#invoke-scheduledtask)
- [Detailed Documentation](/docs)
# AutomationTools
A set of tools for general automation purposes
## Purpose
A collection of commonly used functions for automation tasks, as well as automatic handling of some commonly used items, including script and module config. These items are collected in order to help reduce the amount of repeat code written when writing new automation tasks.
## Config
By default, autmoationtools will ingest the config file included with the module. It will also search for a config file accompanying the current calling script and update the internal config with one or both of these files. The files will be overwritten in the order that they are added.
### config.json files
Config files are intended to be simple JSON structures that maintain a list of variables used by the currently running function. The focus behind the config file is to avoid having individuals or automations opening or editing files manually. Scripts can more easily be deployed with custom settings simply by including an accompanying `config.json` file.
AutomationTools can detect and ingest multiple `config.json` files. These files follow an order of importance where the file last to be consumed will contain the new current config value. By default, AutomationTools loads `config.json` located inside the module root, then `config.json` inside the calling script root directory, then any subsequent manually added files.
**First Load**
`config.json` inside module root
```
-Module Root
--ModuleFolder
--AutomationTools.psm1
--AutomationTools.psd1
--config.json
```
**Second Load**
`config.json` inside calling script root
```
-Script Root
--Script.ps1
--config.json
```
**Normal JSON structure**
```json
{
"ConfigVariableName":"ConfigVariableValue",
}
```
While these are intended to be simple structures, automationtools will ingest and assign more complicated structures. That said, if a complicated structure is required than it is most likely outside of the scope of config.
### Reserved Config Names
There are several defaults that automationtools uses that can be easily overwritten in the default config. These include:
* `ModuleRoot` - The root location of the module
* `LogRoot` - The root location of the logging location
* `LogName` - The name of the log file
* `MaxLogCount` - The maximum amount of logs retained in memory, defaulted to 30,000
* `EventSource` - The name of the Windows Event Source name
* `SMTPServer` - The server address for SMTP messages
* `SMTPFrom` - The sending address for SMTP messaages
* `SMTPPort` - The port to be used with the SMTP server
* `SMTPUseSSL` - The flag to indicate if SMTP should be using SSL
* `TemplatesRoot` - The root location for HTML templates
* `DefaultJobReportTemplate` - The location of the default Send-JobReport template
* `HTMLHelpers` - Helpers for replacing content inside HTML templats
* `DefaultToLog` - Indicator of whether or not all non-SYS/VRB messages should be sent to log file
* `DefaultToConsole` - Indicator of whether or not all non-SYS/VRB messages should be sent to console
* `DefaultToEvent` - Indicator of whether or not all non-SYS/VRB messages should be sent to the Windows Event Log
* `DefaultEventID` - The default Event ID to be given to the Windows Event Log should one not be included in the message
* `DefaultSYSConsole` - Indicator of whether or not all SYS messages should be sent to the console
* `DefaultSYSLog` - Indicator of whether or not all SYS messages should be sent to log
* `DefaultSYSEvent` - Indicator of whether or not all SYS messages should be sent to the Windows Event Log
* `DefaultVRBConsole` - Indicator of whether or not all VRB messages should be sent to the console
* `DefaultVRBLog` - Indicator of whether or not all VRB messages should be sent to log
* `DefaultVRBEvent` - Indicator of whether or not all VRB messages should be sent to the Windows Event Log
* `MinimumPSVersion` - The minimum PS version that tools will support
* `RunLocation` - The location of the calling entity, this value will be either `SCRIPT` or `CONSOLE`
* `RunFile` - The name of the script currently calling, this defaults to blank if `RunLocation` is blank
* `InvokeRoot` - The root of the script currently calling automationtools
* `InvokeSecrets` - The location of the current secrets.json file used for Add-Secret,Get-Secret, and Remove-Secret
### Usage
Module root config loading happens automatically at time of import. Script-level config load happens simply by calling the module's `Get-Config` function. Additional config files should be loaded prior to calling `Get-Config` by calling the `Add-ToolConfig` function.
If you're adding a third or additional config file:
```powershell
Add-ToolConfig -Path "C:\Path\To\New\config.json"
$Config = Get-Config
```
For normal operation use:
```powershell
$Config = Get-Config
```
Any changes to the config after this point will require `Get-Config` be called again as this is a snapshot of the living config inside AutomationTools.
## Write-Log
[Details](/docs/Write-Log.md)
`Write-Log` is a single-point of communication between an automation and various external publishing sources. It is intended to unify output across various locations for quick diagnosis, error capture, and reporting. This maintained log is defaulted to 30,000 logs before being rewritten.
### Anatomy
The standard output for log information reads as follows
**Standard Log**
```powershell
Write-Log -Message "Example Message" -Type INF -Console
```
Outputs
```
INF | 07/22/20 18:07:26 | Example Message
```
This contains a log level, a datetime stamp, and the included message. There are several scenarios where the message will be further formatted to include unique data, one of which is error capture.
**Error capture**
```powershell
$_ | Write-Log -Message "Could not find [$FileName]" -Type ERR -Console
```
Outputs
```
ERR | 07/22/20 13:46:02 | Could not find [File.txt]. Exception [File not found] was thrown in [C:\Script.ps1] at line [$Content = Get-Content $FileName], line number [35], position [8].
```
Additional routing and formatting can occur based off of log level, so it is important to use proper log levels
### Log Levels
* `INF` - Information, maps to Information inside Event Log
* `WRN` - Warning, maps to Warning inside Event Log
* `ERR` - Error, maps to Error inside Event Log
* `HDR` - Header, maps to Information inside Event Log and is used to mark new jobs
* `CON` - Connection, maps to SuccessAudit inside Event Log
* `DIS` - Disconnection, maps to SuccessAudit inside Event Log
* `RES` - Result, maps to Information inside Event Log, used to automatically determine job results
* `SYS` - System, maps to Information inside Event Log. This is intended for hidden Module-Level logging
* `VRB` - Verbose, maps to Information inside Event Log. This is intended to use and display with the -Verbose flag on advanced functions
Both `SYS` and `VRB` are hidden from console view by default as they are intended to be used for Verbose logging and/or debugging
### To Console
**Config Controls**
`DefaultToConsole`
`DefaultSYSConsole`
`DefaultVRBConsole`
```powershell
Write-Log -Message "Example Message" -Type INF -Console
```
Outputs directly to PowerShell console, if available
### To Log
**Config Controls**
`LogRoot`
`LogName`
`DefaultToLog`
`DefaultSYSLog`
`DefaultVRBLog`
```powershell
Write-Log -Message "Example Message" -Type INF -Log
```
Outputs directly to Log file located in `$Config.LogRoot`
```powershell
Write-Log -Message "Example Message" -Type INF -Log -SecondaryLog $Path
```
Outputs directly to Log file located in `$Config.LogRoot` as well as a log file located in `$Path`
```powershell
Write-Log -Message "Example Message" -Type INF -Log -Path $Path
```
Outputs directly to Log file located in `$Path`
### To Event Log
**Config Controls**
`EventSource`
`DefaultEventID`
`DefaultVRBEvent`
`DefaultToEvent`
`DefaultSYSEvent`
`DefaultVRBEvent`
```powershell
Write-Log -Message "Example Message" -Type INF -EventLog
```
Outputs directly to Event Log with source in `$Config.EventSource` with Event ID `$Config.DefaultEventID`
```powershell
Write-Log -Message "Example Message" -Type INF -EventLog -Source "NewSource" -EventID 9001
```
Outputs directly to Event Log with source `NewSource` and Event ID `9001`
**NOTE**: You must have elevated privileges to create a new source in the Event Log
```powershell
Write-Log -Message "Example Message" -Type INF -Log -Path $Path
```
Outputs directly to Log file located in `$Path`
## Email Reporting
**Config Controls**
`SMTPServer`
`SMTPFrom`
`SMTPPort`
`SMTPUseSSL`
`DefaultJobReportTemplate`
Sending email reports is sometimes a necessary evil. Some base-level convenience tools have been added into AutomationTools in order to speed up the repetitive processes. These tools now include auto-table highlighting, table injection, and formatting.
### Send-JobReport
[Details](/docs/Send-JobReport.md)
```powershell
Send-JobReport -To "testemail@testdomain.com" -Subject "This is a test report" -Pretty
```

Row highlighting is automatically included when using the `-Pretty` switch. Behind the scenes this uses the Row and Cell match flags from the table conversion and templating section below.
### Table Conversion and Templating
[Convert-ArrayListToHTML Details](/docs/Convert-ArrayListToHTMLTable.md)
[Add-TablesToHTMLJobTemplate Details](/docs/Add-TablesToHTMLJobTemplate.md)
[Send-HTMLEmail Details](/docs/Send-HTMLEmail.md)
```powershell
$Tables = New-Object System.Collections.Generic.List[PSCustomObject]
$Table1 = Convert-ArrayListToHTMLTable -List $TestData1 -TableName "Foods" -WarnRowMatch "1|3" -FailRowMatch "3" -FailCellMatch "Cookies 6" -Limit 10
$Table2 = Convert-ArrayListToHTMLTable -List $TestData2 -TableName "Animals" -SuccessCellMatch "Snake|Hippo 3|Elephant 1" -WarnCellMatch "Hippo 1" -Limit 10
$Tables.Add($Table1)
$Tables.Add($Table2)
$Template = Add-TablesToHTMLJobTemplate -TableList $Tables -Description "This is a description of the email as a whole"
Send-HTMLEmail -HTMLData ($Template | Out-String) -Subject "Testing" -To "testemail@testdomain.com"
```
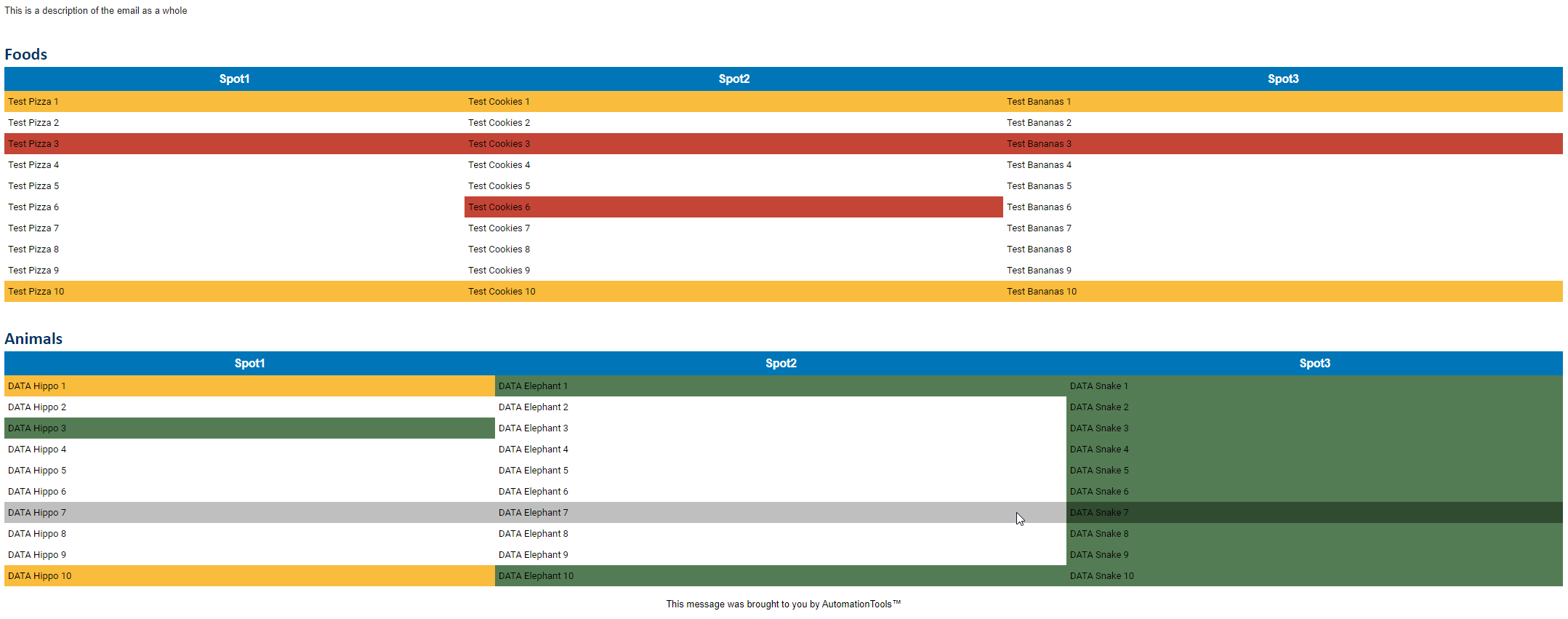
`Convert-ArrayListToHTMLTable` now supports conditional formatting with regex row and cell matching via the following commands
* `FailRowMatch` - Scans the row for regex match and fails the entire row based on match conditions
* `SuccessRowMatch` - Scans the row for regex match and succeeds the entire row based on match conditions
* `WarnRowMatch` - Scans the row for regex match and warns the entire row based on match conditions
* `FailCellMatch` - Scans each cell for regex match and fails the individual cell based on match conditions
* `SuccessCellMatch` - Scans each cell for regex match and succeeds the individual cell based on match conditions
* `WarnCellMatch` - Scans each cell for regex match and warns the individual cell based on match conditions
## Secrets
**Config Controls**
`InvokeSecrets`
For general script testing purposes credentials are often required. AutomationTools will assist in storage, retrevial, and removal of credential combinations. For now this is a simple JSON file with username/secure string pairs, but it will eventually be moved into the Winows Credentials Store. There are security concerns with both solutions, so this is by no means intended for production purposes. It is only intended for use in organizing commonly used credential sets while testing and debugging
**NOTE**: It is important to add an ignore rule for secrets.json inside gitignore
### Add-Secret
[Details](/docs/Add-Secret.md)
```powershell
$Credential = Get-Credential
Add-Secret -Name "CredentialSetName" -Credential $Credential
```
This will create a username/secure string pair in the root of the calling script or console named `secrets.json`. These credentials can only be used on the origin box by the origin user.
### Get-Secret
[Details](/docs/Get-Secret.md)
```powershell
$Credentials = Get-Secret -Name "CredentialSetName"
```
This will get a username/secure string pair in the root of the calling script or console named `secrets.json`. These credentials can only be retrieved on the origin box by the origin user.
### Remove-Secret
[Details](/docs/Remove-Secret.md)
```powershell
Remove-Secret -Name "CredentialSetName"
```
This will remove the username/secure string pair from the secrets.json file.
## File Tools
AutomationTools has a few file management tools used to remove the thought process behind nested folders not existing. These tools are simple but reduce some repeat code.
### Resolve-Folder
[Details](/docs/Resolve-Folder.md)
```powershell
Resolve-Folder -Path "C:\Test\Folder\Location"
```
Tests if the folder structure exists, and creates it if it does not. This is recursive
### Resolve-File
[Details](/docs/Resolve-File.md)
```powershell
Resolve-File -Path "C:\Test\Folder\Location\testFile.txt"
```
Tests if the file exists, and creates it if it does not. This is recursive
### Test-FolderWrite
[Details](/docs/Test-FolderWrite.md)
```powershell
Test-FolderWrite -Path "C:\TestFolder"
```
Tests if the current user has write permission to the specified folder. The test does not create a file, but opens and closes a file stream
## Conversions
A few common conversion tools for use in general scripts
### ConvertTo-Version
[Details](/docs/ConvertTo-Version.md)
```powershell
"1.0.0.1" | ConvertTo-Version
```
Outputs a `Version` object, useful for quickly comparing different versions levels of various softwares or files
### Convert-HashToPSObject
[Details](/docs/Convert-HashToPSObject.md)
```powershell
$Hash | Convert-HashToPSObject
```
Outputs a `PSObject` given a standard hash. It will preserve nesting
### Convert-ArrayToScriptBlock
[Details](/docs/Convert-ArrayToScriptBlock.md)
```powershell
$Array = @(
"netstat",
"-ano"
)
$Array | Convert-ArrayToScriptBlock
```
Outputs a `ScriptBlock` given a standard array. This is useful in mocking `Invoke-Command` calls dynamically
## Utilities
A small collection of general purpose utilities
### Copy-PSObject
[Details](/docs/Copy-PSObject.md)
```powershell
[PSObject]$Template
$NewObj = $Template | Copy-PSObject
```
Returns a copy of the given `PSObject`. Generally assigning a `PSObject` to two variables creates a reference and not a new object
### Test-Elevation
[Details](/docs/Test-Elevation.md)
```powershell
Test-Elevation
```
Returns a `bool` of the current user's administration status. The principal to check can be overwritten with `-RoleOverride`
### Add-ToolConfig
[Details](/docs/Add-ToolConfig.md)
```powershell
Add-ToolConfig -Path "C:\Path\To\New\Config.json"
```
Adds contents of the json file into AutomationTools config
### Update-Config
[Details](/docs/Update-Config.md)
```powershell
Update-Config -Name "TestAdd" -Value "TestValue"
```
Adds an ad-hawk config element to the AutomationTools config variable
### Invoke-ScheduledTask
[Details](/docs/Invoke-ScheduledTask.md)
```powershell
Invoke-ScheduledTask -TaskName "Test" -ComputerName "TargetComputer"
```
Invokes a scheduled task on a remote machine via CIM session. Has an optional paramter `-Wait` that will wait for the Scheduled Task to finish. This is an older function and will be upgraded in the future