Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/alejo1630/4bar_mechanism
This Python Notebook is a tool to calculate the kinematic model (position, velocity and acceleration) for a 4-bar mechanism in several configurations
https://github.com/alejo1630/4bar_mechanism
4barmechanism jupyter-notebook kinematic-modeling python
Last synced: 8 days ago
JSON representation
This Python Notebook is a tool to calculate the kinematic model (position, velocity and acceleration) for a 4-bar mechanism in several configurations
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/alejo1630/4bar_mechanism
- Owner: alejo1630
- Created: 2023-07-02T22:29:58.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2023-10-01T18:50:40.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2023-10-01T22:32:33.751Z (about 1 year ago)
- Topics: 4barmechanism, jupyter-notebook, kinematic-modeling, python
- Language: Jupyter Notebook
- Homepage:
- Size: 7.67 MB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# 4 bar Mechanism
This Python Notebook is a tool to calculate the kinematic model (position, velocity and acceleration) for a 4-bar mechanism in several configurations
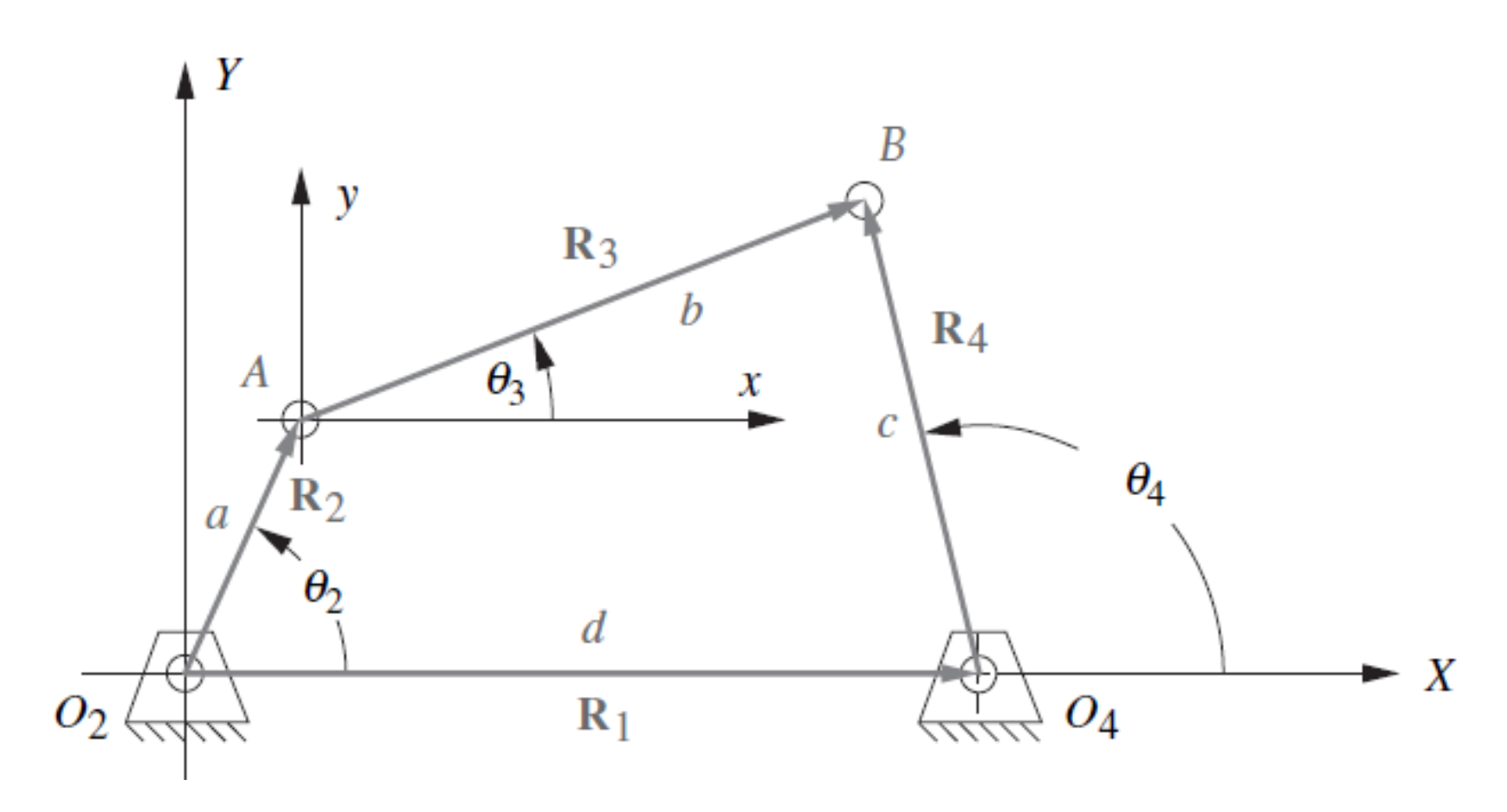
## 🔰 How does it work?
* User has to input the size of the 4 linkage bars $(a, b, c, d)$
* Linkage bars are classified based on their sizes
* $S:$ Shortest member
* $L:$ Longest member
* $P, Q:$ Remaining members
* Grashof condition is applied in order to classify the 4-bar mechanism
### Grashof Mechanism
$$S + L < P + Q$$
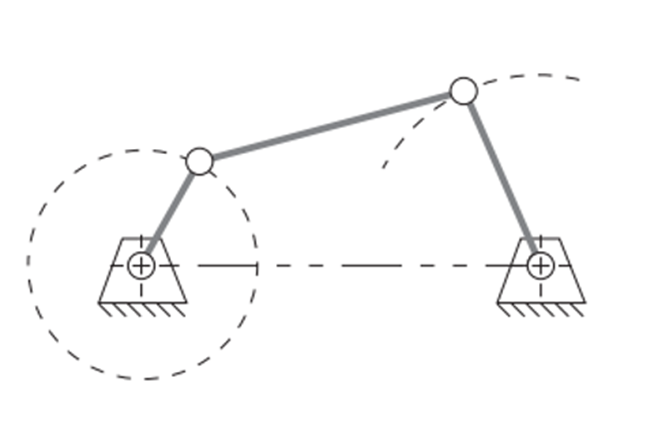
* **Crank and Rocker Mechanism**: Occurs when the ground link $d$ is the shortest member $(S)$
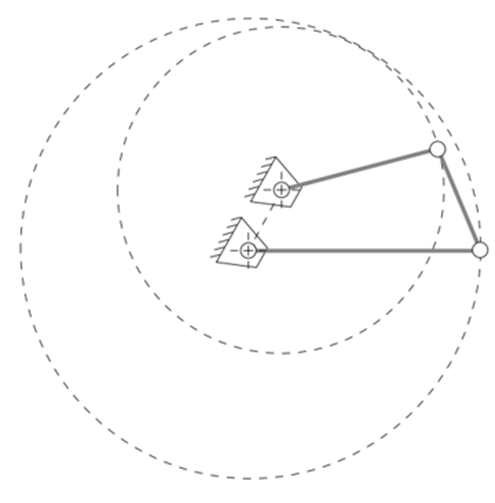
* **Double Crank Mechanism**: Occurs when linkage bars $a$ or $c$ are the shortest member $(S)$
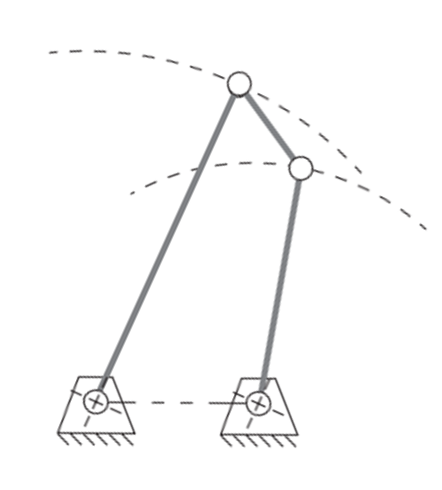
* **Double Rocker Mechanism**: Occurs when the couples link $b$ is the shortest member $(S)$
### Triple Rocker Mechanism
$$S + L > P + Q$$
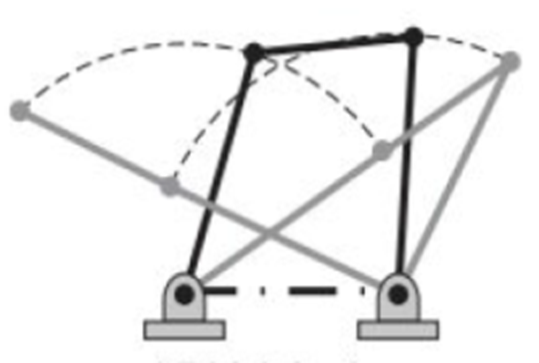
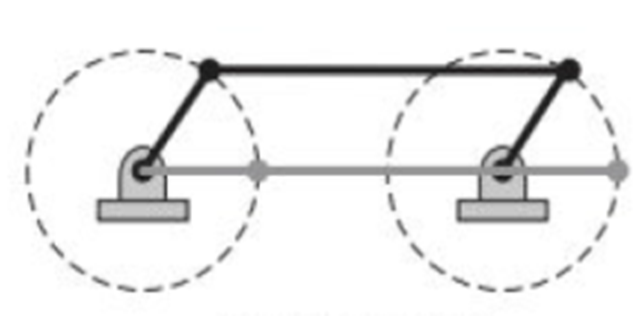
### Change Point State
$$S + L = P + Q$$
* User hast to enter the initial angular position, angular velocity and angular acceleration. In addtion, time and time-step have to be defined.
* The kinematics models is derived using the vectorial representation of the 4 bar mechanism, getting the **Freudenstein's Equations**
### Position Analysis
Position analysis is performed solving the following equations. One of the three angles had to have been defined by the user, so it would be a system of two equations and two unknowns.
**Real Part**
$$a\cos{\theta_2} + b\cos{\theta_3} - c\cos{\theta_4} - d = 0$$
**Imaginary Part**
$$a\sin{\theta_2} + b\sin{\theta_3} - c\sin{\theta_4} = 0$$
Due to the angles are related with trigonometric functions, Newton-Raphson method is used for solving the equations.

### Velocity Analysis
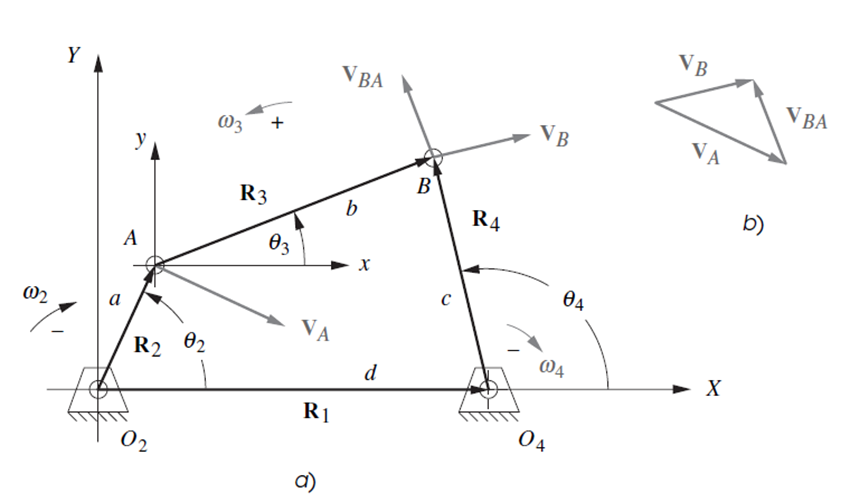
The velocity analysis is performed based on the following systems of linear equations
**Real Part**
$$-a\omega_2\sin{\theta_2} - b\omega_3\sin{\theta_3} + c\omega_4\sin{\theta_4} = 0$$
**Imaginary Part**
$$a\omega_2\cos{\theta_2} + b\omega_3\cos{\theta_3} - c\omega_4\cos{\theta_4} = 0$$
## Acceleration Analysis
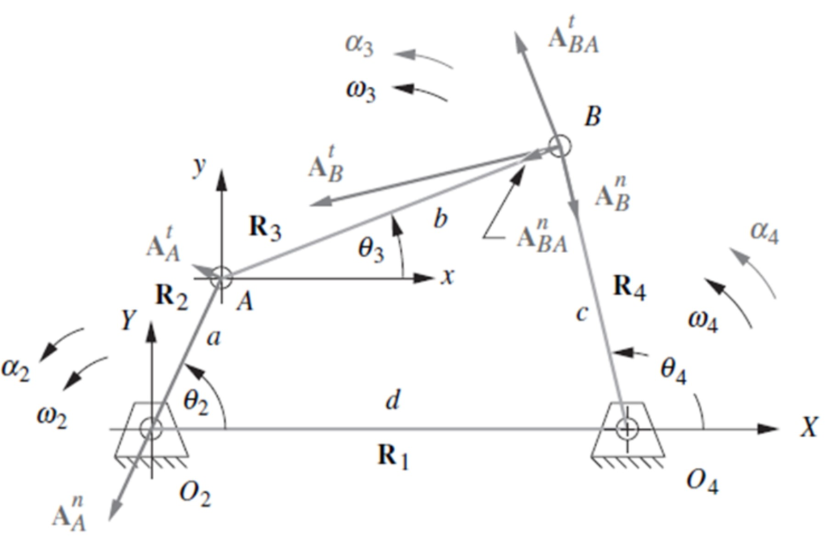
The acceleration analysis is performed based on the following systems of linear equations
**Real Part**
$$-a\alpha_2\sin{\theta_2}-a\omega_2^2\cos{\theta_2}-b\alpha_3\sin{\theta_3}-b\omega_3^2\cos{\theta_3}+c\alpha_4\sin{\theta_4}+c\omega_4^2\cos{\theta_4} = 0$$
**Imaginary Part**
$$a\alpha_2\cos{\theta_2}-a\omega_2^2\sin{\theta_2}+b\alpha_3\cos{\theta_3}-b\omega_3^2\sin{\theta_3}-c\alpha_4\cos{\theta_4}+c\omega_4^2\sin{\theta_4} = 0$$