https://github.com/alex-87/qaekwy-python
A modern, open-source Python framework for declarative constraint programming and combinatorial optimization.
https://github.com/alex-87/qaekwy-python
branch-and-bound client-library constraint-programming constraint-satisfaction-and-optimization constraint-satisfaction-problem csp csp-solver decision-making deep-first-search modeling modelling modelling-framework operational-research optimization python search-engine-optimization solver solver-algorithm
Last synced: 29 days ago
JSON representation
A modern, open-source Python framework for declarative constraint programming and combinatorial optimization.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/alex-87/qaekwy-python
- Owner: alex-87
- License: eupl-1.2
- Created: 2023-08-26T09:21:20.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2026-01-10T18:32:27.000Z (about 1 month ago)
- Last Synced: 2026-01-11T05:14:07.686Z (about 1 month ago)
- Topics: branch-and-bound, client-library, constraint-programming, constraint-satisfaction-and-optimization, constraint-satisfaction-problem, csp, csp-solver, decision-making, deep-first-search, modeling, modelling, modelling-framework, operational-research, optimization, python, search-engine-optimization, solver, solver-algorithm
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://docs.qaekwy.io
- Size: 197 KB
- Stars: 10
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Qaekwy Python
*A modern, open-source Python framework for declarative constraint programming and combinatorial optimization*.
 
## Overview
Qaekwy is a Python library designed for modeling and solving combinatorial optimization and constraint satisfaction problems.
It provides a clean, Pythonic interface for defining variables, constraints, and objectives, enabling a natural *define-and-solve* workflow. Qaekwy manages the interaction with the solver engine, allowing users to focus entirely on expressing the structure of their problems.
#### Perfect for
* 🎓 **Learning** — Model real problems in minutes
* 👩🏫 **Teaching** — Demonstrate CSP concepts with no setup
* 🔬 **Research & Prototyping** — Explore models, heuristics, and ideas fast
## 📚 Documentation
Visit the [Qaekwy Documentation](https://docs.qaekwy.io/) for guides, teaching resources, and detailed examples.
## 🚀 Quick Start
### Prerequisites
- Python 3.9+
- pip
### Installation
```shell
pip install qaekwy
```
### 🌱 Your First Model
```python
import qaekwy as qw
m = qw.Model()
x = m.integer_variable("x", (-10, 10))
y = m.integer_variable("y", (-10, 10))
z = m.integer_variable("z", (-10, 10))
m.constraint(x + 2*y + 3*z <= 15)
m.maximize(x)
m.solve_one(searcher="bab").pretty_print()
```
*Output*:
```text
----------------------------------------
Solution:
----------------------------------------
x: 10
y: 2
z: -4
----------------------------------------
```
## Capabilities
* **Declarative Modeling**
Define integer, float, and boolean variables, as well as arrays and matrices, to represent problems at a high semantic level.
* **Expressive Constraints**
Formulate arithmetic, logical, and conditional constraints using readable and maintainable Python expressions.
* **Optimization Objectives**
Specify minimization and maximization goals to guide the solver toward optimal solutions.
* **Search Configuration**
Configure solver behavior using explicit search strategies such as Depth-First Search and Branch-and-Bound, along with branching heuristics and cutoffs.
* **Cloud-Native Execution**
Transparent handling of model serialization and execution on the Qaekwy Cloud Solver instance.
## Examples
### 🔢 Constraint Programming -- Sudoku
Here is a complete example solving a [Sudoku](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sudoku) grid:
> The objective is to fill a 9 × 9 grid with digits so that each column, each row, and each
> of the nine 3 × 3 subgrids that compose the grid contains all of the digits from 1 to 9.
```python
import qaekwy as qw
# Initial Sudoku grid; 0 represents empty cells to be assigned by Qaekwy
my_problem = [
[0, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 9, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 6, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 9, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 1, 7, 0, 9],
[4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 5, 6, 1, 0, 8],
[0, 5, 9, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 5, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5, 7, 0]
]
# Instantiate the model
m = qw.Model()
# Create a 9x9 matrix of integer variables
# Each variable can take a value between 1 and 9 (inclusive)
grid = m.integer_matrix("grid", rows=9, cols=9, domain=(1, 9))
for i in range(9):
# Ensure all variables in row 'i' are unique
m.constraint_distinct(grid.row(i))
# Ensure all variables in column 'i' are unique
m.constraint_distinct(grid.col(i))
# Iterate over 3x3 blocks
for i in range(0, 9, 3):
for j in range(0, 9, 3):
# Extract the 3x3 block and enforce uniqueness
m.constraint_distinct(grid.slice(i, j, i + 3, j + 3))
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
# If the cell is not empty (0 represents empty in our data)
if my_problem[i][j] != 0:
# Constrain the model variable at [i][j] to equal the input value
m.constraint(grid[i][j] == my_problem[i][j])
# Solve the model and retrieve the first valid solution found
s = m.solve_one()
# Display the result
s.pretty_print()
```
*Output*:
```text
----------------------------------------
Solution:
----------------------------------------
grid: (9 x 9 matrix)
1 7 8 3 2 5 6 9 4
5 4 3 6 1 9 8 2 7
6 9 2 7 4 8 3 5 1
2 6 5 4 8 1 7 3 9
4 8 1 9 7 3 2 6 5
9 3 7 2 5 6 1 4 8
7 5 9 8 3 2 4 1 6
3 1 4 5 6 7 9 8 2
8 2 6 1 9 4 5 7 3
----------------------------------------
```
### 🎒 Optimization -- Knapsack Problem
Here is a complete example solving a basic resource allocation problem ([The Knapsack Problem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knapsack_problem)):
> Given a set of items, each with a weight and a value, determine which items to include in the
> collection so that the total weight is less than or equal to a given limit and the total value
> is as large as possible.
```python
import qaekwy as qw
# 1. Setup the Model
m = qw.Model()
weights = [2, 3, 4, 5]
values = [3, 4, 5, 6]
limit = 7
n_items = len(weights)
# 2. Define Decision Variables (0 = exclude, 1 = include)
selected = [
m.integer_variable(f"item_{i}", domain=(0, 1))
for i in range(n_items)
]
# 3. Apply Constraints
# Total weight must not exceed the limit
current_weight = sum(weights[i] * selected[i] for i in range(n_items))
m.constraint(current_weight <= limit)
# 4. Define Objective
# Maximize total value
total_value = m.integer_variable(
name="total_value",
expression=sum(values[i] * selected[i] for i in range(n_items)),
branch_val=qw.BranchIntegerVal.VAL_MAX # Forces the solver to try higher values first
)
m.maximize(total_value)
# 5. Solve
solution = m.solve_one(searcher="bab") # Branch-and-Bound
print(f"Max Value: {solution.total_value}")
# Output: Max Value: 9
```
## 💡 Core Concepts
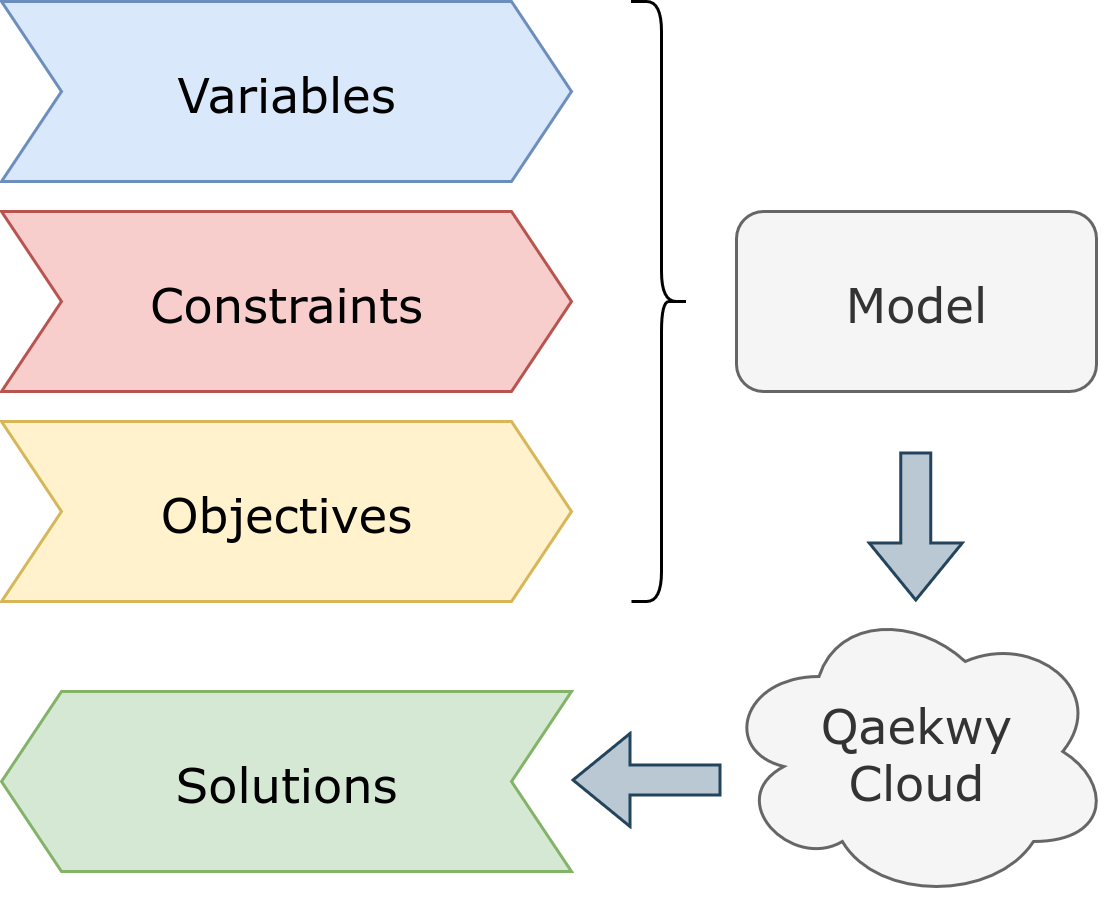
### The Model
The `qw.Model` acts as the container for your variables and constraints. It also manages the interaction with
the underlying solver engine.
#### The Variables
Here are examples of variable creation in the model:
```python
# A single integer between 0 and 100
capacity = m.integer_variable("capacity", domain=(0, 100))
# A 9x9 Grid (Matrix) for Sudoku-like problems
grid = m.integer_matrix("grid", rows=9, cols=9, domain=(1, 9))
```
#### The Constraints
Constraints are logical assertions that must be true in any valid solution.
```python
# Arithmetic
m.constraint(x * 2 < qw.math.power(y, 2) + 5)
```
### Modeling Capabilities
Qaekwy supports:
* Conditional constraints
```python
m.constraint_if_then_else(
condition=x + y <= 7,
then_constraint=z >= 2,
else_constraint=z <= 2
)
```
* Logical expressions
```python
m.constraint(
(qw.math.absolute(z) == qw.math.power(x-(y+1),2)) | (z >= 4)
)
```
* Arrays and Matrices
```python
arr = m.integer_array("arr", 3, (0,100))
m.constraint(arr[1] < x + 1)
mat = m.integer_matrix("mat", rows=2, cols=3, domain=(0,50))
m.constraint(sum(mat.col(0)) > arr[2])
```
*...and more, visit the [Qaekwy Documentation](https://docs.qaekwy.io/)*
### Solving & Execution
- `solve_one()` — find one feasible or optimal solution
- `solve()` — returns a list of solutions
- `minimize(...)` / `maximize(...)` — Set one or more objectives on variables
- Searchers such as DFS, Branch-and-Bound, etc.
- Cloud-based Solver instance (*please, refer to [Terms & Conditions](https://docs.qaekwy.io/docs/terms-and-conditions/)*)
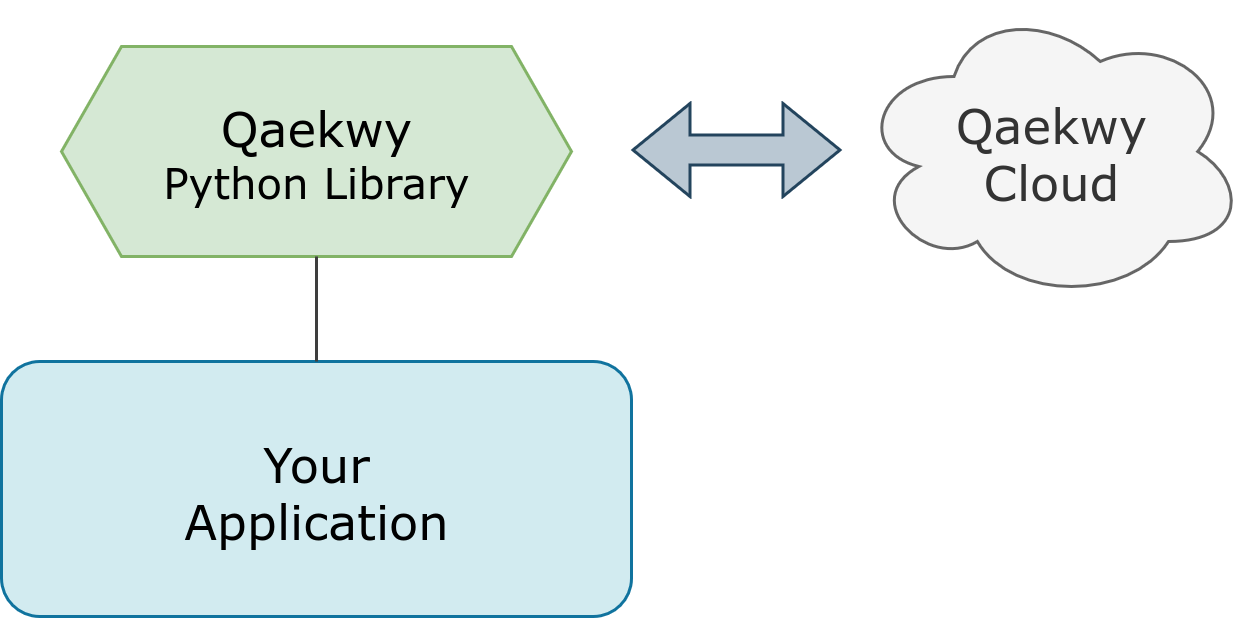
#### Integration
The model is then sent to the Qaekwy Cloud Engine through REST API.
## License
- Released under the [European Union Public Licence 1.2 (EUPL 1.2)](https://joinup.ec.europa.eu/collection/eupl/eupl-text-eupl-12).
- Qaekwy Cloud Instance [Terms & Conditions](https://docs.qaekwy.io/docs/terms-and-conditions/).