https://github.com/am-ash-or-am-i/c-programs
https://github.com/am-ash-or-am-i/c-programs
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/am-ash-or-am-i/c-programs
- Owner: AM-ash-OR-AM-I
- Created: 2023-09-13T03:41:03.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-01-09T17:52:50.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-01-10T18:23:46.304Z (over 1 year ago)
- Language: C
- Size: 860 KB
- Stars: 5
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# C Programming
## Code syntax
### Main function
```c
void main() {
// code
}
```
### Header files
```c
#include
```
### Input and output
```c
#include
void main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Hello world!\n");
}
```
## Structure in C
```c
struct name {
type member;
type member;
...
};
```
e.g.
```c
struct Student {
int regNo;
float marks;
char section;
};
```
- `struct Student` is the name of the structure
- It occupies 4 + 8 + 4 = 16 bytes of memory
### Using typedef
```c
typedef struct Student {
int regNo;
float marks;
char section;
} Student;
```
#### Union vs Struct
```c
// All can be assigned and used at the same time
struct struct_example {
int integer;
float decimal;
char name[20];
};
// Only any 1 of them can be assigned/used at a time
union union_example {
int integer;
float decimal;
char name[20];
};
int main() {
struct struct_example s;
union union_example u;
s.integer = 10;
s.decimal = 10.5;
strcpy(s.name, "Hello World!");
u.integer = 10;
u.decimal = 10.5;
strcpy(u.name, "Hello World!");
printf("struct_example: %d %f %s\n", s.integer, s.decimal, s.name);
printf("union_example: %d %f %s\n", u.integer, u.decimal, u.name);
return 0;
}
```
### Storage classes in c
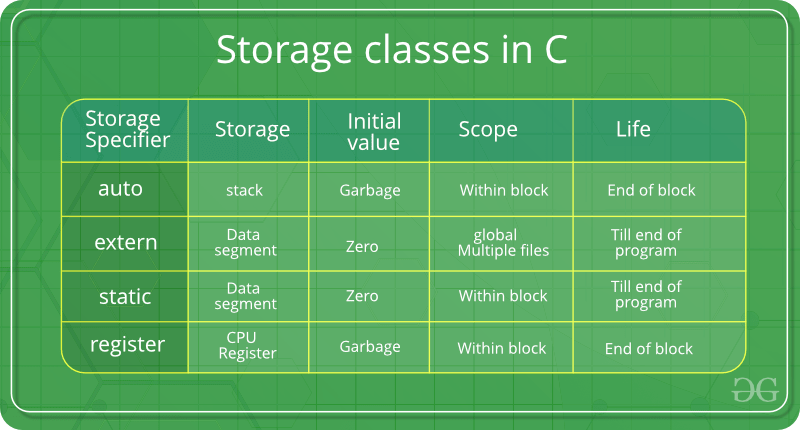
- Auto (Used by default)
- Slowest access
- Stored in stack
```c
int a = 32;
```
- Register
- Fastest access
- Used for variables that are accessed more times during program
```c
register int x = 324;
```
- Static
- Faster than auto
- Uses data segment
- Initialized only one during compilation
```c
static int x=324;
```
- Extern
- Global variable, can be accessed from any function
- Can be used to access global variable from another file
- file1.c
```c
int x = 324;
int main(){
extern int val;
printf("Global var %d", val);
}
```
- file2.c
```c
# include
# include "file1.c"
extern int x;
int main(){
printf("Global var %d", x);
}
```
## Pointers
- Wild pointer: pointer that has not been initialized
- Uninitialized pointers are known as wild pointers because they point to some arbitrary memory location and may cause a program to crash or behave unexpectedly.
```c
int *ptr;
*ptr = 32523;
printf("%d", *ptr);
```
- Dangling pointer: pointer that points to a memory location that has been deleted (or freed)
```c
int *ptr = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
*ptr = 32523;
free(ptr);
printf("%d", *ptr);
```
- Null pointer: pointer that has been initialized to NULL
- NULL is a macro defined in header file. It is an implementation-defined null pointer constant. It may be defined as 0 or ((void *)0). It is guaranteed that if NULL is defined as 0 then it will always be a null pointer constant.
```c
int *ptr = NULL;
printf("%d", *ptr);
```