https://github.com/andreia/omgit
Git Quick Reference
https://github.com/andreia/omgit
cheatsheet cli git github quickreference reference
Last synced: 11 months ago
JSON representation
Git Quick Reference
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/andreia/omgit
- Owner: andreia
- Created: 2020-12-27T21:43:34.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-04-13T20:33:39.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-27T20:06:36.867Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: cheatsheet, cli, git, github, quickreference, reference
- Homepage:
- Size: 18.3 MB
- Stars: 24
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 9
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# OMGit! <3
Git Quick Reference
- [PDF Format](https://github.com/andreia/OMGit/blob/main/pdf/git_quick_reference.pdf)
- [Image Format](https://github.com/andreia/OMGit/blob/main/images/git_quick_reference.png)
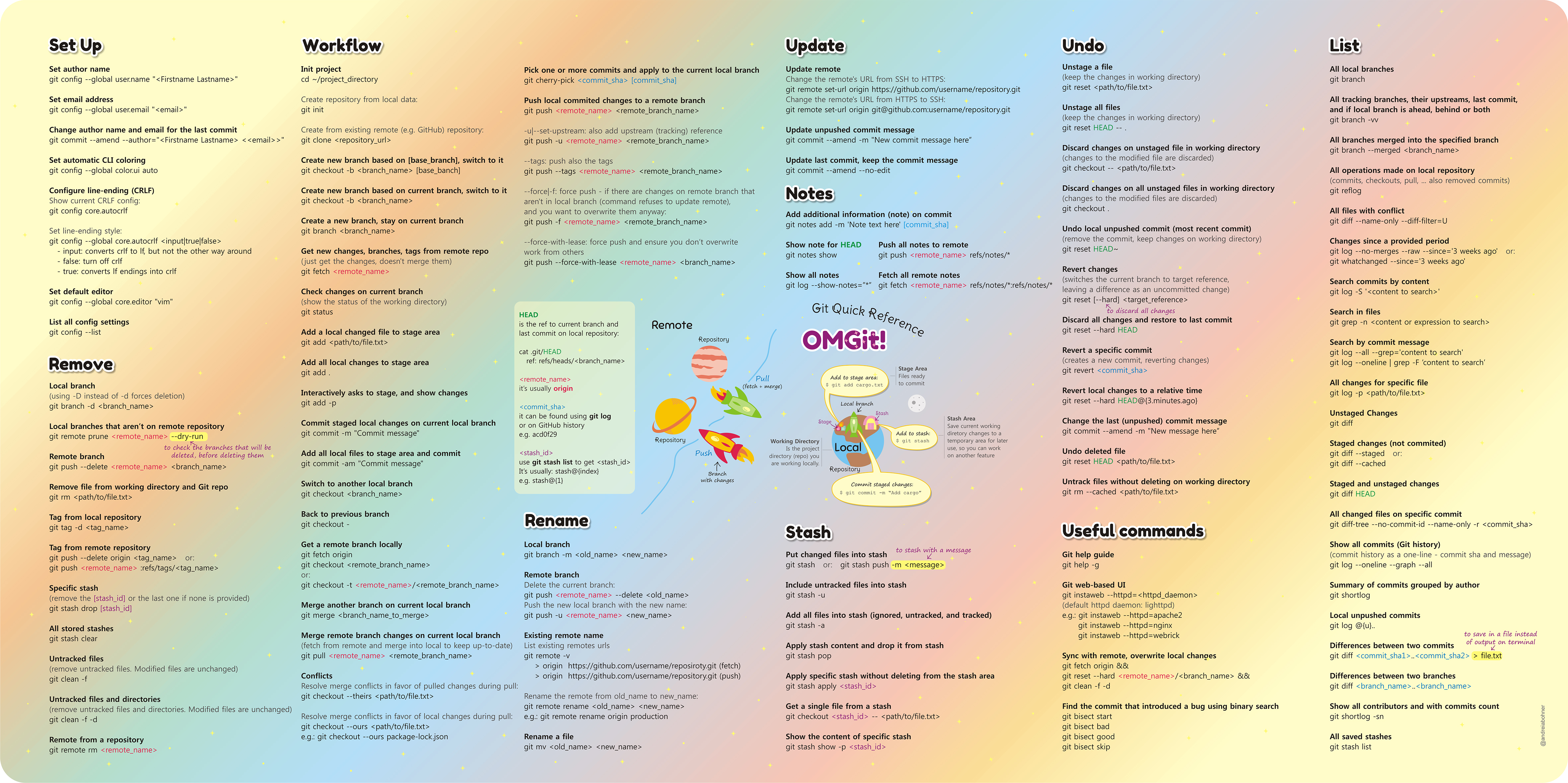
## Setting up
### Set author name
(to be show on version history)
```console
git config --global user.name ""
```
e.g.:
```console
git config --global user.name "Andréia Bohner"
```
### Set email address
```console
git config --global user.email ""
```
### Change author's name and email
```console
git commit --amend --author=" <>" --no-edit
```
### Set automatic CLI coloring for Git
```console
git config --global color.ui auto
```
### Configure line-ending (CRLF)
```console
git config core.autocrlf
```
show current CRLF config
```console
git config --global core.autocrlf
```
set line-ending style
- ```input```: convert crlf to lf on commit but not the other way around
- ```false```: turn off crlf
- ```true```: converts lf endings into crlf
e.g.:
```console
git config --global core.autocrlf input
```
### List all Git config settings
```console
git config --list
```
## Workflow
### Create a new repository from current local directory (local files)
```console
git init
```
### Create a new repository locally from a remote repository
```console
git clone
```
e.g:
```console
git clone https://github.com/path/repository.git
```
### Create a new branch
Create a new branch based on `[base_branch]` or on current branch if `[base_banch]` isn't informed
and check it out right away:
```console
git checkout -b [base_banch]
```
Create a new branch based on current branch and stays on current branch:
```console
git branch
```
### List all local branches
```console
git branch
```
### List all local and remote branches
```console
git branch -a
```
### List all tracking branches, their upstreams, last commit on branch, and if local branch is ahead, behind, or both
```console
git branch -vv
```
### List all branches merged into the specified branch
```console
git branch --merged
```
### Get new changes, branches, and tags from remote repository
(just get the changes, it doesn't merge them)
```console
git fetch
```
it's usually:
```console
git fetch origin
```
### Check changes on current branch
```console
git status
```
Show the status of your working directory:
- new, staged, and modified files.
- current branch name
- current commit identifier
- changes pending to commit
### Add a local changed file to stage area
```console
git add
```
### Add all local changes to stage area
```console
git add .
```
### Commit staged local changes on current local branch
```console
git commit -m "commit message"
```
### Add all local files to stage area and commit, with one line:
```console
git commit -am "Commit message"
```
Equivalent to:
```console
git add .
git commit -m "Commit message"
```
### Add missing file on last local commit
```console
git add missing_file.txt
git commit --amend --no-edit
```
### Empty commit
```console
git commit --allow-empty
```
### Change to another local branch
```console
git checkout
```
### Back to the previous branch
```console
git checkout -
```
or:
```console
git checkout @{-1}
```
### Get a remote branch locally
```console
git fetch origin
git checkout
```
or:
```console
git checkout -t origin/
```
### Merge another local branch on current local branch
```console
git merge
```
### Merge changes from a remote branch on current local branch
(fetch from remote and merge into local)
```console
git pull origin
```
#### Pick a commit from a branch and apply it to another
```console
git cherry-pick
```
### Conflicts
#### Resolve merge conflicts in favor of pulled changes during a pull
```console
git checkout --theirs
```
#### Resolve merge conflicts in favor of my local changes during a pull
```console
git checkout --ours
```
E.g.:
```console
git checkout --ours package-lock.json
```
### Push local changes to a remote branch
```console
git push origin
```
- `-u`: add upstream (tracking) reference
```console
git push -u origin
```
- `--tags`: push also the tags
```console
git push --tags origin
```
- `--force`: if there are changes on remote branch that aren't in local branch (command refuses to update the remote), and you want to overwrite them:
```console
git push --force origin
```
Note: You can use `HEAD` instead of ``:
```console
git push origin HEAD
```
HEAD is the current branch on your local repository:
```console
cat .git/HEAD
ref: refs/heads/
```
### Force push and ensure you don't overwrite work from others
```console
git push --force-with-lease origin
```
### List all operations made on local repository
e.g.: commits, checkouts, pull, ... (also list removed commits with `git reset`, `git rebase`, ...)
```console
git reflog
```
### Have to work on another branch. What to do with the changes on current branch?
Move them to stash: a place to temporarily store the modified and staged files in order to change branches.
#### Put the current working directory changes into stash, for later use
```console
git stash
```
#### Put the current working directory changes into stash with a message
```console
git stash push -m
```
#### Put the current working directory changes into stash, including untracked files
```console
git stash -u
```
or
```console
git stash push -u
```
or
```console
git stash push --include-untracked
```
#### Add all changed files of the current working directory into stash (ignored, untracked, and tracked)
```console
git stash -a
```
or
```console
git stash --all
```
or
```console
git stash push --all
```
#### List all saved stashes
```console
git stash list
```
#### Show the contents of a specific stash in patch form
```console
git stash show -p
```
#### Get the stored stash content into working directory, and drop it from stash.
```console
git stash pop
```
#### Apply the content of a specific stash without removing it from the stashed list
```console
git stash apply
```
## Checking changes
### Unstaged changes
```console
git diff
```
### Changes staged but not commited
```console
git diff --staged
```
or
```console
git diff --cached
```
### Staged and unstaged changes
```console
git diff HEAD
```
### All files with conflict
```console
git diff --name-only --diff-filter=U
```
### Show only changed files
```console
git show --name-only
```
### Changes since a provided period
```console
git log --no-merges --raw --since='2 weeks ago'
```
or:
```console
git whatchanged --since='2 weeks ago'
```
### Search commits by content
```console
git log -S ''
```
### Search by commit message
```console
git log --all --grep='content to search'
```
or
```console
git log --oneline | grep -F 'content to search'
```
### Search all changes for specific file
```console
git log -p
```
### All changed files on specific commit
```console
git diff-tree --no-commit-id --name-only -r
```
### Show all commits (Git history)
(history as a one-line short message - sha & message)
```console
git log --oneline --graph --all
```
### Summary of the commits grouped by author
(with the first line of each commit message)
```console
git shortlog
```
## Rename Things
### Rename a local branch
```console
git branch -m
```
### Rename a remote branch
1. Delete the current remote branch:
```console
git push origin --delete
```
2. Push the new local branch with the new name:
```console
git push -u origin
```
### Rename an existing remote name
List your existing remotes to get the name of the remote you want to change:
```console
git remote -v
> origin https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git (fetch)
> origin https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git (push)
```
Rename the remote from `old_name` to `new_name`:
```console
git remote rename
```
E.g.:
```console
git remote rename origin production
```
Check that the remote URL has changed:
```console
git remote -v
> production https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git (fetch)
> production https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git (push)
```
### Rename the remote url of an existing local repository to match the renamed remote repository
To rename the existing local repository accordingly to the remote you can first
rename the repository directory (optional) and then, to rename the remote URL
to the new name:
List your existing remotes:
```console
git remote -v
> origin https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git (fetch)
> origin https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git (push)
```
Rename the remote URL to `new_url`:
```console
git remote set-url
```
- `` could be `origin` or `upstream` for example
- `` could be the HTTPS or SSH URL
Change the `origin` remote's HTTPS URL e.g.:
```console
git remote set-url origin https://github.com/USERNAME/NEW-REPOSITORY.git
```
Change the `origin` remote's SSH URL e.g.:
```console
git remote set-url origin git@github.com:USERNAME/NEW-REPOSITORY.git
```
Check that the remote URL has changed:
```console
git remote -v
> origin https://github.com/USERNAME/NEW-REPOSITORY.git (fetch)
> origin https://github.com/USERNAME/NEW-REPOSITORY.git (push)
```
### Rename a file
```console
git mv
git commit -m "renamed"
git push origin main
```
## Undo Things
### Unstage a file
(retain the changes in working directory)
```console
git reset HEAD
```
### Unstage all files
(retain the changes in working directory)
```console
git reset HEAD -- .
```
### Discard changes on unstaged file in working directory
(changes to the modified file are discarded)
```console
git checkout --
```
### Discard changes on all unstaged files in working directory
(changes to the modified files are discarded)
```console
git checkout .
```
### Undo local unpushed commit
(most recent commit)
Keep the work done on last commit (files will show in the stage
area as an uncommitted change):
```console
git reset --soft HEAD^
```
```console
git reset HEAD~
```
```console
git reset HEAD
```
Delete all the work done on last commit:
```console
git reset --hard HEAD~1
```
### Reverting changes
```console
git reset [--hard]
```
Switch the current branch to the target reference,
leaving a difference as an uncommitted change:
```console
git reset origin/master
```
Switch the current branch to the target reference,
discarding all changes
```console
git reset --hard origin/master
```
### Reverting changes of a specific commit
(Create a new commit, reverting changes from the specified commit.
It generates an inversion of changes.)
```console
git revert
```
### Reverting local changes to a relative time
```console
git reset --hard HEAD@{3.minutes.ago}
```
### Change the last (unpushed) commit message
```console
git commit --amend -m "New message here"
```
### Untrack files without deleting on working directory
```console
git rm --cached
```
### Discard all uncommitted changes on local working directory
(uncommitted changes will be removed)
```console
git restore .
```
### Revert local commits added on wrong branch and add them to the correct branch
```console
git branch
git reset --hard
git checkout
```
Example: add local commits on correct `fix_typo` branch, remove them from the `master` branch, and checkout `fix_typo` branch:
```console
git branch fix_typo
git reset --hard origin/master
git checkout fix_typo
```
## Removing
### Remove local branch
```console
git branch -d
```
- `-D` instead of `-d` forces deletion
### Remove remote branch
```console
git push --delete
```
e.g.:
```console
git push --delete origin my_remote_branch
```
### Remove file from working directory and Git repo
```console
git rm
```
### Remove a tag from local repository
```console
git tag -d
```
### Remove a tag from remote repository
```console
git push --delete origin
```
or:
```console
git push origin :refs/tags/tag_name
```
### Remove changes from stash
Remove the `[stash_name]` informed or the last one if none is provided.
```console
git stash drop [stash_name]
```
e.g.:
```console
git stash drop stash@{0}
```
### Remove all stored stashes
```console
git stash clear
```
### Remove untracked files
(Remove untracked files. Modified files are unchanged)
```console
git clean -f
```
### Remove untracked files and directories
(Remove untracked files and directories. Modified files are unchanged)
```console
git clean -f -d
```
## Tagging
Types of tags:
- `lightweight`: just the commit checksum stored in a file, i.e., a pointer to a specific commit
- `annotated`: stored as full objects in Git (checksummed; contain the tagger name, email, and date; have a tagging message; and can be signed and verified with GNU Privacy Guard - GPG).
### List all tags
```console
git tag
```
### Show the current tag you are
```console
git describe --tags
```
### Create a lightweight tag for current commit or for [commit sha], if informed.
```console
git tag [commit_sha]
```
### Create an annoted tag for current commit if [commit sha] it's not informed
```console
git tag -a [commit_sha] [-m "tagging_message"]
```
e.g.:
```console
git tag -a v2.1 -m "version 2.1"
```
### Show tag data with the commit that was tagged
```console
git show
```
e.g.:
```console
git show v2.1
```
## Remote
### List all remote references
```console
git remote
```
### Change the remote's URL from SSH to HTTPS:
```console
git remote set-url origin https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
```
### Change the remote's URL from HTTPS to SSH:
```console
git remote set-url origin git@github.com:USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
```
## Notes
### Add object notes
```console
git notes add -m 'Note message here'
```
### Show all notes
```console
git log --show-notes='*'
```
## More useful commands
### Git help guide
```console
git help -g
```
### Git web-based UI
```console
git instaweb --httpd apache2
git instaweb --httpd nginx
git instaweb --httpd=webrick
```
### Sync with remote, overwrite local changes
```console
git fetch origin && git reset --hard origin/ && git clean -f -d
```
### Find the commit that has introduced a bug in the code (using binary search)
```console
git bisect start
git bisect bad
git bisect good
```
## References
- https://git-scm.com/
- https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/getting-started-with-git/managing-remote-repositories