https://github.com/andrejewski/reactbone
React extensions for Backbone
https://github.com/andrejewski/reactbone
Last synced: 8 months ago
JSON representation
React extensions for Backbone
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/andrejewski/reactbone
- Owner: andrejewski
- License: isc
- Created: 2014-02-17T01:16:42.000Z (about 12 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2014-08-13T14:28:46.000Z (over 11 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-06-12T01:13:51.733Z (9 months ago)
- Language: JavaScript
- Size: 301 KB
- Stars: 44
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-react - reactbone - React extensions for Backbone (React [🔝](#readme))
- awesome-react - reactbone - React extensions for Backbone
- awesome-react-cn - reactbone - React extensions for Backbone (Uncategorized / Uncategorized)
- awesome-learning-resources - reactbone - React extensions for Backbone (Uncategorized / Uncategorized)
README
Reactbone
=========
Reactbone extends [Backbone](http://backbonejs.org/) models and collections to better work with an immutable dependent such as [React](http://facebook.github.io/react/) by exposing two subclasses `ReactModel` and `ReactCollection`. These classes expose methods to allow a data hierarchy to be easily built between models and collections and expose access to the entire state of an application designed in such a way.
## Installation
### NPM
```bash
npm install reactbone
```
### Script
For the bundled version of Reactbone, use this repository's `reactbone.js`. It comes with its Backbone and Underscore dependencies.
```html
```
To create the bundle, install via NPM and build it with the build command, which uses Browserify.
```bash
npm run build
```
## Usage
Reactbone extends Backbone so it can be used anywhere Backbone would be used. The only difference is Reactbone adds its classes to Backbone.
```javascript
var Reactbone = require('reactbone');
Reactbone.Model; // just Backbone.Model
Reactbone.ReactModel;
Reactbone.Collection; // just Backbone.Collection
Reactbone.ReactCollection;
```
### Integrating with React
Reactbone makes plugging into React.js as simple and expressive as possible.
```javascript
var data = Application({name: 'color-me-shocked'}), // ReactModel
view = React.createClass({...});
data.on('change', function(model) {
var state = model.toReact();
React.renderComponent(view(state), document.body);
});
```
## Architecture
Reactbone is the middleground between Backbone and React. Any changes on the Backbone model hierarchy propogate up to Reactbone which then serializes the models into their JSON and helpers. That data can then be passed to React classes for rendering. Within React, helpers may be called (either manually or by user interaction) and may then change the underlying Backbone data, triggering the original data flow.
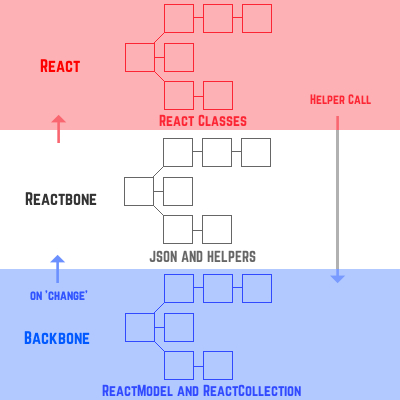
From the perspective of React, the data is immutable as an entirely new state is being passed to it on change from Backbone. The immutable data can also be used for snapshots, free undos and redos of application state, and all the other benefits of immutability. Yet, from the perspective of Backbone, the data is mutable and has the advantage of Underscore, Backbone, and plain JavaScript mutable functions. Reactbone harmonizes these two perspectives.
## ReactModel
### #property
- `property(name String) (Backbone.Model||Backbone.Collection)`
- `property(name String, component (Backbone.Model||Backbone.Collection)) this`
- `property(Object[name String]component(Backbone.Model||Backbone.Collection)) this`
ReactModel needs to know which objects attached to the model should be included in the data hierarchy. The `property` method accepts a name String and a component which is either a Backbone Model or Collection (or a subclasss of them), or a map of them if you have multiple. If you only pass a name String, the component at `model.properties[name]` or undefined will be returned.
The component will be watched for changes and those changes will be reflected through the parent model in the `change` and `change:#{name}` events where `name` was the String provided to the method.
The component can then be accessed on the parent model via `model[name]` or `model.name` where `name` was the String provided to the method.
The component's properties can then be set directly via setting them on the parent model. For instance, calling `model.set(name, {poop: 'poop'});` would be equivalent to calling `model[name].set({poop: 'poop'});` Setting values on a component the former way will not trigger `change:#{name}` but instead `change:_#{name}` as to not double trigger on any model listening for `change:#{name}`.
```javascript
var User = ReactModel.extend({
initialize: function() {
// setters
this.property('posts', new Posts({parent: this}));
this.property({
likes: new Likes({parent: this}),
comments: new Comments({parent: this})
});
// getter
var posts = this.property('posts');
}
});
```
### #helper
- `helper(name String) Function`
- `helper(name String, func Function) this`
- `helper(Object[name String]func Function) this`
Helpers are functions that will be added to the data representation of the model in the data hierarchy. These methods will allow React to communicate UI interactions back to the model. The `helper` method accepts a name String and a helper function, or a map of them if you have multiple. If a string is passed as a function parameter, the function at `model[func]` will be used. All functions are bound to the model with Underscore's `bind` function. If you only pass a name String, the function at `model.helpers[name]` or undefined will be returned.
```javascript
var User = ReactModel.extend({
initialize: function() {
// setters
this.helper('updateFirstName', this.updateFirstName);
this.helper('updateLastName', function(newLastName) {
this.set('lastName', lastName);
});
this.helper({
helperOne: function() {},
helperTwo: function() {}
});
// getter
var helper = this.helper('updateFirstName');
},
updateFirstName: function(newFirstName) {
this.set('firstName', newFirstName);
}
});
```
### #toReact
- `toReact() Object`
This is the only external function to be called in order to use Reactbone with React. This function returns the data hierarchy of the model along with all of its attached properties and associated helper functions. This function will recursively call `toReact` on all of its properties, defaulting to `toJSON` if not found. Example usage:
```javascript
var model = new Application({poop: 'poop'});
var root = document.getElementById('application'),
view = React.renderComponent(ApplicationView({data: model.toReact()}), root);
model.on('change', function(model, options) {
view.setProps({data: model.toReact()});
});
```
## ReactCollection
ReactCollection is not very extensive, it only exposes the `toReact` method, which is needed to match the ReactModel API. All it does is map over the collection, calling each model's own `toReact` (or `toJSON`) method.
## Contributing
Contributions are incredibly welcome as long as they are standardly applicable and pass the tests (or break bad ones). Tests are written in Mocha and assertions are done with the Node.js core `assert` module.
```bash
# running tests
npm run test
npm run test-spec # spec reporter
```
Follow me on [Twitter](https://twitter.com/compooter) for updates or just for the lolz and please check out my other [repositories](https://github.com/andrejewski) if I have earned it. I thank you for reading.