Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/andrewrosss/nipype-generate-fieldmaps
Nipype workflow to generate fieldmaps from EPI acquisitions with differing phase-encoding directions
https://github.com/andrewrosss/nipype-generate-fieldmaps
epi fieldmap fsl neuroimaging neuroscience nipype phase-encoding topup
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
Nipype workflow to generate fieldmaps from EPI acquisitions with differing phase-encoding directions
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/andrewrosss/nipype-generate-fieldmaps
- Owner: andrewrosss
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-12-12T16:53:54.000Z (about 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-02-03T19:16:23.000Z (almost 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-10-27T00:15:33.892Z (about 2 months ago)
- Topics: epi, fieldmap, fsl, neuroimaging, neuroscience, nipype, phase-encoding, topup
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 175 KB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# nipype-generate-fieldmaps
Nipype workflow to generate fieldmaps from EPI acquisitions with differing phase-encoding directions
## Installation
```bash
pip install nipype-generate-fieldmaps
```
## Usage
### As a stand-alone workflow
```python
# create the workflow
wf = create_generate_fieldmaps_wf()
# wire-up the inputs
wf.inputs.inputnode.se_epi_pe1_file = my_se_epi_pe1_file # type: str | Path
wf.inputs.inputnode.se_epi_pe2_file = my_se_epi_pe2_file # type: str | Path
wf.inputs.inputnode.se_epi_pe1_sidecar_file = my_se_epi_pe1_sidecar_file # type: str | Path
wf.inputs.inputnode.se_epi_pe2_sidecar_file = my_se_epi_pe2_sidecar_file # type: str | Path
# set the output directory
wf.base_dir = my_output_dir # type: str | Path
# run it
wf.run()
```
### As a nested workflow
The nodes `node1`, `node2`, `some_other_node`, `maybe_a_4th_node`, `epi_node`, and `anat_node` are made up for demonstration purposes
```python
from nipype import Workflow
from nipype.interfaces.fsl import EpiReg
from nipype_generate_fieldmaps import create_generate_fieldmaps_wf
# parent workflow defined elsewhere
wf = Workflow(...)
# create the (sub-)workflow
fmap_wf = create_generate_fieldmaps_wf()
# connect the various nodes form the parent workflow to the nested fieldmap workflow
wf.connect(node1, 'out_file', fmap_wf, 'inputnode.se_epi_pe1_file')
wf.connect(node2, 'out', fmap_wf, 'inputnode.se_epi_pe2_file')
wf.connect(some_other_node, 'output_file', fmap_wf, 'inputnode.se_epi_pe1_sidecar_file')
wf.connect(maybe_a_4th_node, 'sidecar_file', fmap_wf, 'inputnode.se_epi_pe2_sidecar_file')
# connect the fieldmap workflow outputs to one (or more) node(s) in the parent workflow
# for example: EpiReg()
epireg = Node(EpiReg(out_base='epi2str.nii.gz'), name='epi_reg')
# from elsewhere
wf.connect(epi_node, 'my_epi_file' epireg, 'epi')
wf.connect(anat_node, 'my_t1_file', epireg, 't1_head')
wf.connect(anat_node, 'my_t1_brain_file', epireg, 't1_brain')
# from the fieldmap workflow!
wf.connect(fmap_wf, 'outputnode.fmap_rads_file', epireg, 'fmap')
wf.connect(fmap_wf, 'outputnode.fmap_mag_file', epireg, 'fmapmag')
wf.connect(fmap_wf, 'outputnode.fmap_mag_brain_file', epireg, 'fmapmagbrain')
wf.connect(fmap_wf, 'outputnode.echo_spacing', epireg, 'echospacing')
wf.connect(fmap_wf, 'outputnode.pe1_pedir', epireg, 'pedir')
```
### From the command line
```bash
$ nipype-generate-fieldmaps --help
usage: nipype-generate-fieldmaps [-h] [-v] se_epi_pe1 se_epi_pe2 se_epi_pe1_sidecar se_epi_pe2_sidecar out_dir
Generate fieldmaps from EPI acquisitions with differing phase-encoding directions
positional arguments:
se_epi_pe1 The spin-echo EPI file acquired in the 'first' phase-encoding direction
se_epi_pe2 The spin-echo EPI file acquired in the 'second' phase-encoding direction
se_epi_pe1_sidecar The JSON sidecar for the first spin-echo EPI file
se_epi_pe2_sidecar The JSON sidecar for the second spin-echo EPI file
out_dir The directory into which outputs are written
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --version show program's version number and exit
```
## Prerequisites
This workflow has a few requirements:
1. There are **two** acquisitions (i.e. `.nii.gz` files) acquired with **different** phase encodings, usually opposite phase encodings but this need not be the case.
2. The number of volumes in acquisition 1 (the first phase encoding direction) **equals** the number of volumes in acquisition 2 (the second phase encoding direction)
3. Each acquisition has a JSON sidecar. Specifically, this workflow requires that _each_ sidecar contain one of the following sets of properties. These properties are listed in the order in which the workflow will search:
- `PhaseEncodingDirection` and `TotalReadoutTime`, or
- `PhaseEncodingDirection`, `ReconMatrixPE`, and `EffectiveEchoSpacing`, or
- `PhaseEncodingDirection`, `ReconMatrixPE`, and `BandwidthPerPixelPhaseEncode`
If either JSON sidecar fails to contain at least one of the above sets of parameters the workflow will produce an error.
## I/O
This workflow requires 4 inputs to be connected to the node named `inputnode`:
- **`se_epi_pe1_file`**
The spin-echo EPI file acquired in the 'first' phase-encoding direction
- **`se_epi_pe2_file`**
The spin-echo EPI file acquired in the 'second' phase-encoding direction
- **`se_epi_pe1_sidecar_file`**
The JSON sidecar for the first spin-echo EPI file
- **`se_epi_pe2_sidecar_file`**
The JSON sidecar for the second spin-echo EPI file
This workflow also exposes the following outputs via the node named `outputnode`:
- **`acq_params_file`**
The computed file passed to the `--datain` option of `topup`
- **`corrected_se_epi_file`**
The `.nii.gz` image containing all _distortion corrected_ volumes from the two input acquisitions
- **`fmap_hz_file`**
The fieldmap in hertz (Hz)
- **`fmap_rads_file`**
The fieldmap in radians per second (rad/s)
- **`fmap_mag_file`**
The 'magnitude' image (mean image) computed by averaging all volumes in `corrected_se_epi_file`
- **`fmap_mag_brain_file`**
The result of applying brain-extraction to `fmap_mag_file`
- **`fmap_mag_brain_mask_file`**
The brain mask produced during the brain-extraction of `fmap_mag_file`
## Workflow diagram
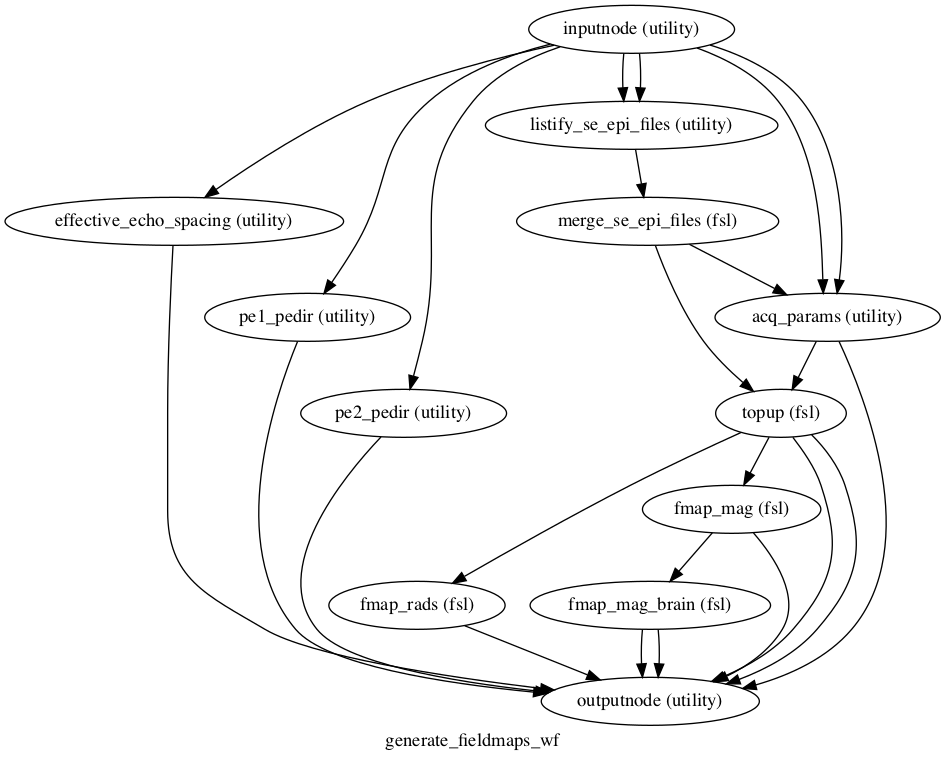
## Contributing
1. Have or install a recent version of `poetry` (version >= 1.1)
1. Fork the repo
1. Setup a virtual environment (however you prefer)
1. Run `poetry install`
1. Run `pre-commit install`
1. Add your changes
1. Commit your changes + push to your fork
1. Open a PR