https://github.com/apple/tensor-visualizer
A Jupyter widget to visualize tensor data in notebooks.
https://github.com/apple/tensor-visualizer
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
A Jupyter widget to visualize tensor data in notebooks.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/apple/tensor-visualizer
- Owner: apple
- License: other
- Created: 2024-08-23T22:08:52.000Z (11 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-28T01:03:00.000Z (11 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-06T20:57:57.607Z (3 months ago)
- Language: Svelte
- Homepage:
- Size: 126 KB
- Stars: 52
- Watchers: 6
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
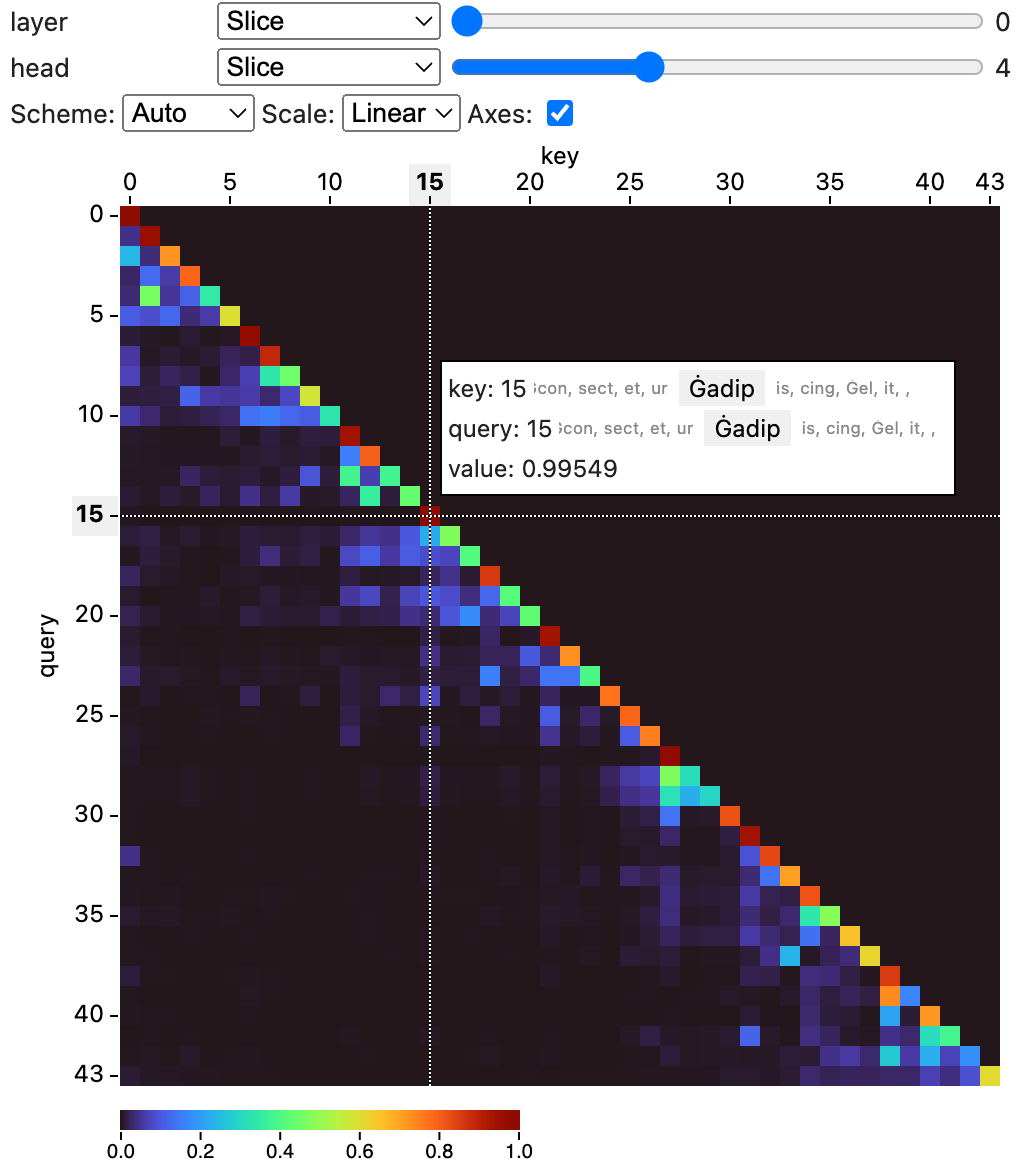
# Tensor Visualizer
This is a package to visualize tensor data in notebooks.
## Install
Install the package from the [Python Package Index (PyPI)](https://pypi.org/project/tensor-visualizer/).
```bash
pip install tensor-visualizer
```
## Usage
You can use this widget in a notebook to visualize tensor data.
The widget supports numpy `ndarray`s, PyTorch and Tensorflow tensors,
as well as MLX tensors.
```python
from tensor_visualizer import TensorVisualizer
# Visualize a 4-dimensional numpy array.
import numpy as np
data = np.random.randn(5, 10, 10, 10)
widget = TensorVisualizer(data)
widget
```
```python
from tensor_visualizer import TensorVisualizer
# Visualize a 4-dimensional torch tensor.
import torch
data = torch.randn((5, 10, 10, 10))
widget = TensorVisualizer(data)
widget
```
You can name dimensions with the `names` argument:
```python
TensorVisualizer(data, names=["batch", "channel", "height", "width"])
```
and label indices for the dimensions with the `labels` argument:
```python
TensorVisualizer(
data,
names=["batch", "channel", "height", "width"],
labels=[["b1", "b2", "b3"], ["ch1", "ch2"]]
)
```
By default the widget infers the color scale automatically from your data. To configure the color scale, you can set the `scale_domain`, `scale_type`, and `scale_scheme` properties:
```python
# Set the scale domain to [1, 100], log scale,
# and use the viridis color scheme.
w = TensorVisualizer(data, scale_domain=[1, 100], scale_type="log", scale_scheme="viridis")
# You can also set it after creating the widget
w.scale_domain = [0, 1]
```
If you are using inferred scales, you can access the inferred scale properties with `current_scale_domain`, `current_scale_type`, and `current_scale_scheme`. These properties are available only after the widget has been shown.
You may use the `permute` argument the re-order the tensor dimensions in the visualization. For instance, `permute=[2, 0, 1, 3]` shows dimension 2 first, then dimension 0, 1, and 3. The last two dimensions are used in the heatmap.
### Parameters
| Name | Description |
| --------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `tensor` | The tensor to visualize. |
| `names` | The names for dimensions in the tensor. |
| `labels` | Lists of labels for dimensions in the tensor. |
| `default_views` | Specify the default views for each dimension, supported options are: `slice`, `small-multiples`, `min`, `max`, and `mean`. |
| `scale_domain` | Specify the scale domain. If unspecified, the widget will infer the domain automatically. |
| `scale_type` | Specify the scale type (linear or log). The default is linear. |
| `scale_scheme` | Specify the scale color scheme. If unspecified, the widget will infer the scheme automatically. |
| `permute` | Permute the order of the tensor's dimensions. |
## Development
This project consists of a Svelte library for the frontend component, and Python code for the widget.
To setup for frontend development, run:
```bash
npm install
npm run dev
```
You'll get a development server (usually at )
that hosts an demo page of the frontend component.
To build the frontend package, run:
```bash
npm run build
```
To build the Python package, run:
```bash
hatch build
```
To develop the widget, you can start a Jupyter Lab instance and load the example notebooks in the `examples` folder:
```bash
hatch run jupyter lab
```