https://github.com/arafkarsh/ms-springboot-ai
Java 23, SpringBoot 3.4.1 Examples using Deep Learning 4 Java & LangChain4J for Generative AI using ChatGPT LLM, RAG and other open source LLMs. Sentiment Analysis, Application Context based ChatBots. Custom Data Handling. LLMs - GPT 3.5 / 4o, Gemini, Claude 3, Llama3, Phi-3, Gemma, Falcon 2, Mistral, Wizard Math
https://github.com/arafkarsh/ms-springboot-ai
chatgpt-api chatgpt3 chatgpt4 claude-3 convolutional-neural-network falcon gemini gemini-ai gemma gemma-7b generative-ai langchain langchain4j llama2 mistral-7b multilayer-perceptron-network ollama rag recurrent-neural-network retrieval-augmented-generation
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Java 23, SpringBoot 3.4.1 Examples using Deep Learning 4 Java & LangChain4J for Generative AI using ChatGPT LLM, RAG and other open source LLMs. Sentiment Analysis, Application Context based ChatBots. Custom Data Handling. LLMs - GPT 3.5 / 4o, Gemini, Claude 3, Llama3, Phi-3, Gemma, Falcon 2, Mistral, Wizard Math
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/arafkarsh/ms-springboot-ai
- Owner: arafkarsh
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2024-04-12T15:05:22.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-01-06T12:53:21.000Z (12 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-06T13:47:11.343Z (12 months ago)
- Topics: chatgpt-api, chatgpt3, chatgpt4, claude-3, convolutional-neural-network, falcon, gemini, gemini-ai, gemma, gemma-7b, generative-ai, langchain, langchain4j, llama2, mistral-7b, multilayer-perceptron-network, ollama, rag, recurrent-neural-network, retrieval-augmented-generation
- Language: Java
- Homepage: https://www.arafkarsh.com
- Size: 22.2 MB
- Stars: 14
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 4
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# AI/ML & Gen Ai - Langchain4J & Deep Learning 4J
## Java 23, Springboot 3.4.1 Examples
[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=arafkarsh_ms-springboot-324-ai)
[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=arafkarsh_ms-springboot-324-ai)
[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=arafkarsh_ms-springboot-324-ai)
[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=arafkarsh_ms-springboot-324-ai)
- Java 23
- SpringBoot 3.4.1
- LangChain4J 0.36.0
- Deep Learning 4J 1.0.0-M2.1
Generative AI refers to a subset of artificial intelligence that can generate new content based
on input data. This encompasses models that can create text, images, music, and even videos.
Examples of generative AI include language models like OpenAI's GPT-3 and DALL-E, which can
generate human-like text and images from textual descriptions, respectively.
Generative AI models are typically trained on vast datasets and use deep learning techniques to
learn patterns and structures in the data. They have a wide range of applications, including:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Generating human-like text for chatbots, translations, and content creation.
- Creative Arts: Creating artwork, music, and design elements.
- Data Augmentation: Generating additional data for training other machine learning models.
- Healthcare: Assisting in medical imaging and creating personalized treatment plans.
## How LangChain4J Gen AI API Helps Developers Build Spring Boot AI Apps
LangChain4J is a Java library designed to simplify the integration of large language models
(LLMs) and AI capabilities into Java applications, including those built with Spring Boot.
Here’s how it helps developers:
- Unified API for LLMs: LangChain4J provides a unified API that supports multiple LLM providers like OpenAI and Google Vertex AI. This abstraction allows developers to switch between different LLMs without changing their codebase significantly.
- Embedding Store Integration: It integrates with various embedding stores, enabling efficient handling of vectorized data. This is particularly useful for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) tasks, where relevant information is fetched from a knowledge base to enhance AI responses.
- Toolbox of Features: The library includes a comprehensive set of tools for prompt templating, memory management, and output parsing. These tools help in building complex AI applications by providing high-level abstractions and ready-to-use components.
- Spring Boot Integration: LangChain4J supports Spring Boot, making it easier for developers to create robust and scalable AI applications. The integration allows seamless incorporation of AI services into Spring Boot applications, leveraging Spring's dependency injection and configuration management features.
- Examples and Documentation: LangChain4J offers extensive documentation and examples, guiding developers through various use cases and demonstrating how to implement AI-powered functionalities in their applications.
## Case Study: Health Care App - Gen Ai Enabled Diagnosis Microservices
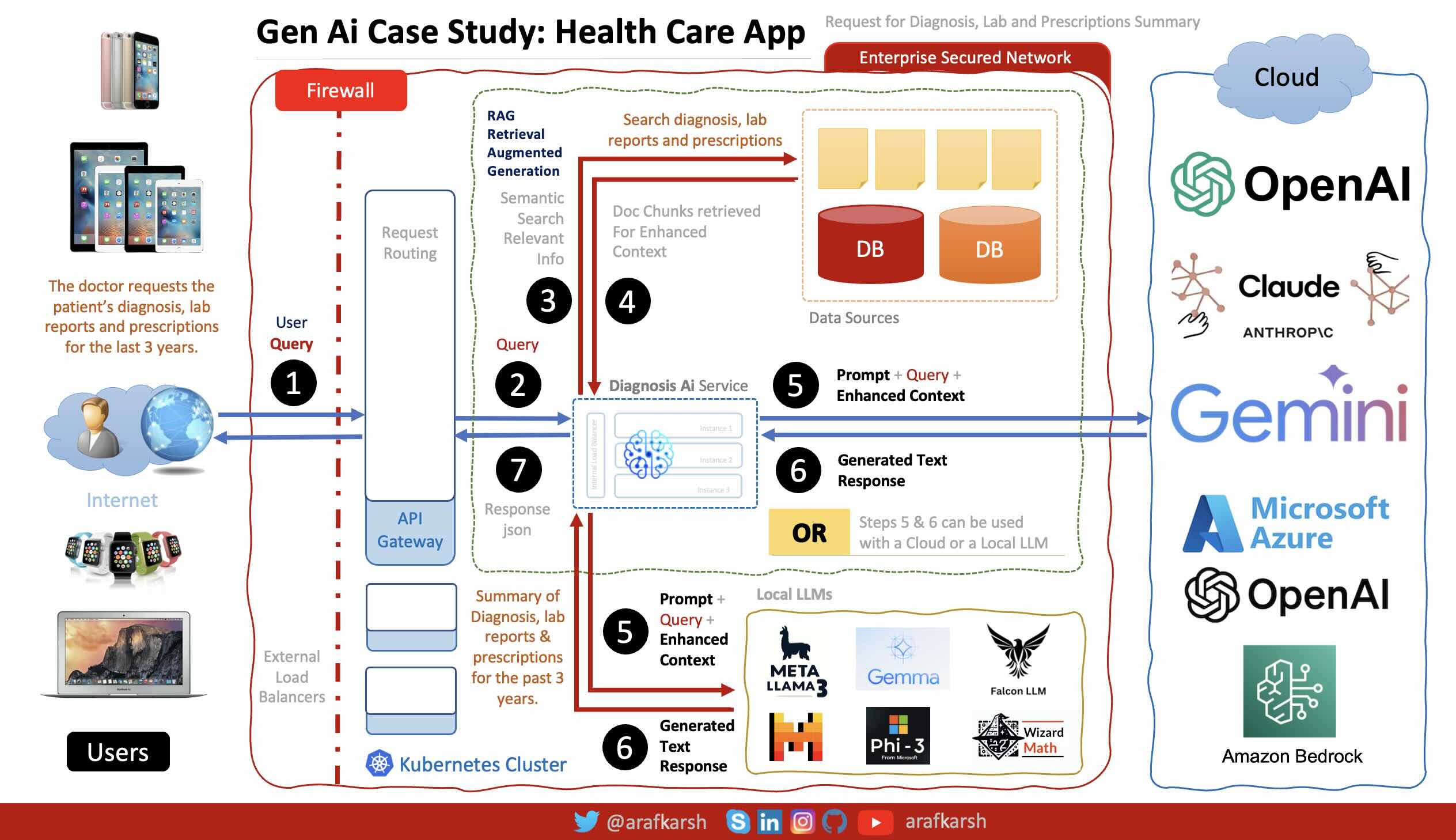
## Setup Database Password Encryption
This ai-service template offers a range of built-in functionalities. To simplify the demonstration of
various features, an encrypted password is utilized for connecting to H2 and PostgreSQL databases.
The template includes utilities for encrypting and decrypting passwords, ensuring that the encryption
key is securely stored outside the application’s runtime context.
Encrypted H2 (In Memory) Database Password. Uses H2 database in Dev (Profile) mode.
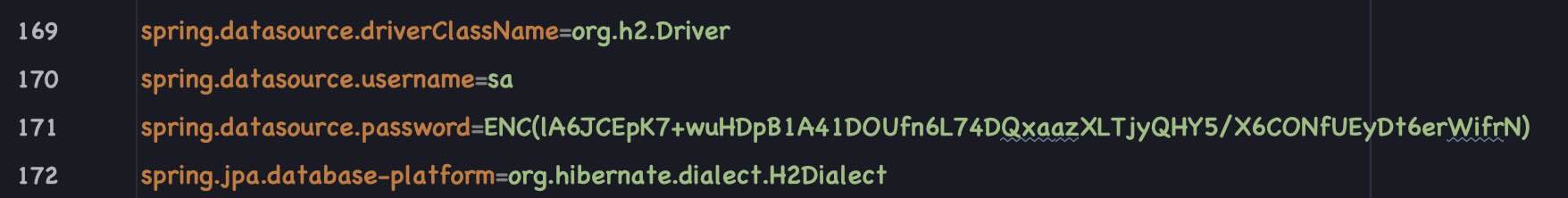
Encrypted PostgreSQL Database Password. Uses PostgreSQL DB in Staging & Prod (profile) mode.

Password can be decrypted only using an Encryption Key stored in System Enviornment variable
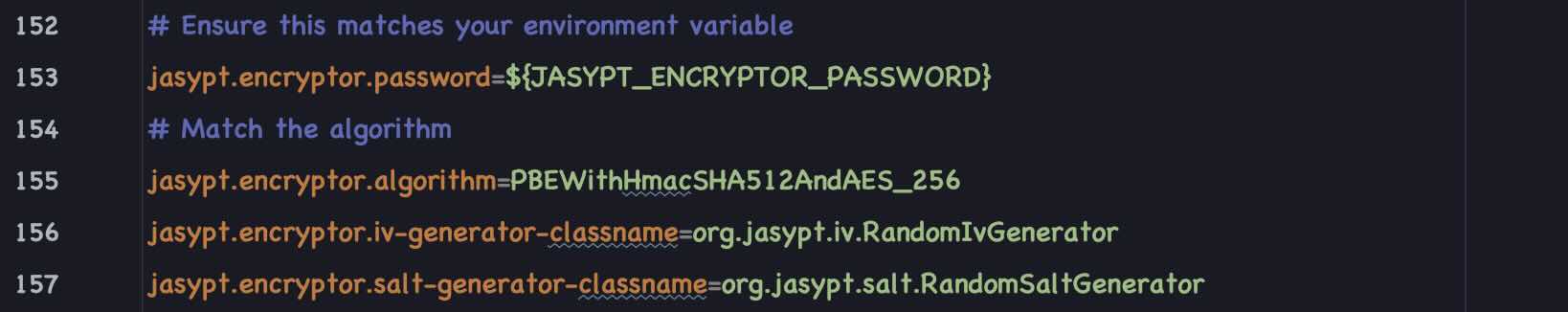
If the Quality Gate check fails, it's because the password is encrypted within the application’s
properties file, with the encryption key stored externally, outside the application’s context.
However, quality standards mandate that passwords should be securely stored in a vault, such as
HashiCorp Vault, for enhanced security. To know more about how to setup these passwords (for H2
& PostgreSQL) and environment variables checkout Session 1.2
### AI-Service Package Structure
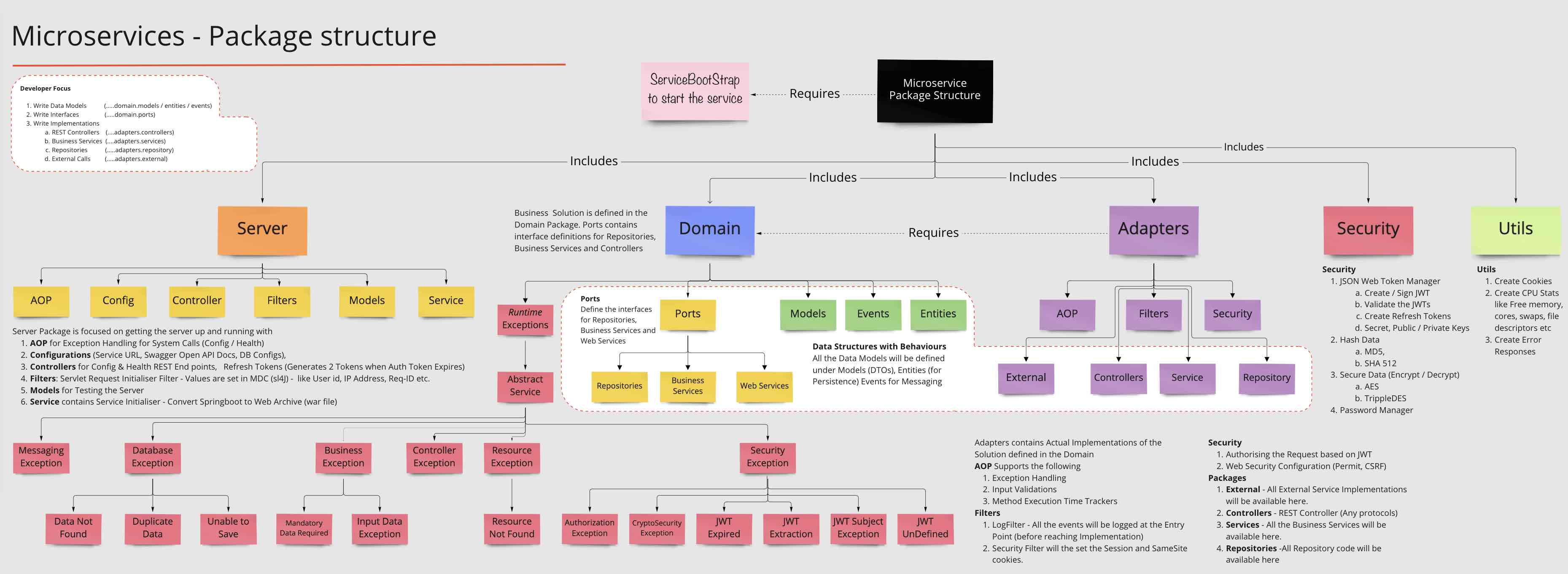
io.fusion.air.microservice
1. adapters (All the Implementations from App/Service perspective)
2. ai (All AI Code Examples. ML, Gen AI Examples)
3. domain (All Entities, Models, Interfaces for the implementations)
4. security (All Security related modules)
5. server (Managing the Service - from a server perspective, Setups (DB, Configs)
6. utils (Standard Utilities)
# Gen AI Examples
## Gen AI Examples: Comparison of 8 LLMs (3 Cloud based & 5 Local) on Enterprise Features
Following comparison is based on the features available in LangChain4J API (which supported by OpenAI ChatGPT). These features are essential for Gen AI based Enterprise App Development.
| # | Example | GPT 4o | Meta Llama3 | Mistral | Microsoft Phi-3 | Google Gemma | TII Falcon 2 | Claude 3 | Gemini 1.5 |
|-----|---------------------|--------------------|-----------------|------------------|------------------|------------------|-----------------|----------------|----------------|
| 1. | Hello World | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 2. | Complex World | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :red_circle: M1 | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 3. | Custom Data | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :red_circle: F1 | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 4. | Image Generation | :green_circle: | :red_circle: L1 | :red_circle: M2 | :red_circle: P1 | :orange_circle: | :red_circle: F2 | :yellow_circle:| :yellow_circle:|
| 5. | Prompt Template | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :red_circle: M3 | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 6. | Tools | :green_circle: | :red_circle: L2 | :red_circle: M4 | :red_circle: P2 | :red_circle: G1 | :red_circle: F3 | :green_circle: | :red_circle: G1|
| 7. | Chat Memory | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :red_circle: P3 | :red_circle: G2 | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :red_circle: G2|
| 8. | FewShot | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :red_circle: M5 | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :red_circle: G3|
| 9. | Language Translator | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :red_circle: M6 | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 10. | Sentiment Analyzer | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 11. | Data Extractor | :orange_circle: O1 | :red_circle: L3 | :red_circle: M7 | :red_circle: P4 | :red_circle: G3 | :red_circle: F4 | :green_circle: | :red_circle: G4|
| 12. | Persistent Store | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :red_circle: M8 | :red_circle: P5 | :red_circle: G4 | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
## Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Examples of 8 LLMs
| # | Example | GPT 4o | Meta Llama3 | Mistral | Microsoft Phi-3 | Google Gemma | TII Falcon 2 | Claude 3 | Gemini 1.5 |
|-----|-----------------------------|----------------|-----------------|-----------------|-----------------|-----------------|-----------------|----------------|----------------|
| 51. | Simple | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 52. | Segments | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :orange_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 53. | Query Transformer | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 54. | Query Router | :green_circle: | :red_circle: L4 | :red_circle: M9 | :red_circle: P6 | :red_circle: G4 | :red_circle: F5 | :green_circle: | :red_circle: G5|
| 55. | Re-Ranking | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :orange_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 56. | MetaData | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :orange_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 57. | Multiple Content Retrievers | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :orange_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 58. | Skipping Content Retrieval | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
| 59. | Health Care App | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: | :green_circle: |
## Top LLM Rankings based on Enterprise Features
| # | Rank | Company | LLM | Score | Category |
|---|------|-------------|-----------------------|-------|----------|
| 1 | 1 | Anthropic | Claude 3 Haiku | 21/21 | Cloud |
| 2 | 2 | Open AI | Chat GPT 4o | 20/21 | Cloud |
| 3 | 3 | Meta | Llama 3 | 17/21 | Local |
| 4 | 4 | TII | Falcon 2 | 16/21 | Local |
| 5 | 4 | Google | Gemini 1.5 Pro | 16/21 | Cloud |
| 6 | 4 | Google | Gemma | 16/21 | Local |
| 7 | 5 | Microsoft | PHI 3 | 15/21 | Local |
| 8 | 6 | Mistral | Mistral | 12/21 | Local |
Note: Cloud-based LLMs will have more than 500 billion parameter support while the local LLMs are mostly based on 8 Billion parameters.
Checkout more details on Testing Scores
## Install Local LLMs
To Install the Local LLMs using Ollama
1. Meta Llama3
2. Google Gemma
3. Microsoft PHI-3
4. TII Falcon 2
5. Mistral
6. Wizard Math
Check out the installation guide.
## Get the Keys for Testing Cloud LLMs
### Register to get the API Keys
1. Open AI - ChatGPT (API Key can be created here: https://platform.openai.com/api-keys)
2. Anthropic - Claude 3 (API key can be created here: https://console.anthropic.com/settings/keys)
3. Google Cloud - (https://console.cloud.google.com/ - Check AiConstants.java for Instructions)
4. Cohere - (API key here: https://dashboard.cohere.com/welcome/register)
5. HuggingFace - (API key here: https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens)
6. Rapid - (API key here: https://rapidapi.com/judge0-official/api/judge0-ce)
### Set these Keys in your environment
```
// API Keys -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// OpenAI API key here: https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys
public static final String OPENAI_API_KEY = System.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY");
// Cohere API key here: // https://dashboard.cohere.com/welcome/register
public static final String COHERE_API_KEY = System.getenv("COHERE_API_KEY");
// Anthropic API key here:: https://console.anthropic.com/settings/keys
public static final String ANTHROPIC_API_KEY = System.getenv("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY");
// HuggingFace API key here: https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens
public static final String HF_API_KEY = System.getenv("HF_API_KEY");
// Judge0 RapidAPI key here: https://rapidapi.com/judge0-official/api/judge0-ce
public static final String RAPID_API_KEY = System.getenv("RAPID_API_KEY");
```
## Gen AI - Code Package Structure
### Package io.fusion.air.microservice.ai.genai
1. controllers (Rest Endpoints for testing the examples)
2. core
1. assistants (Based on LangChain4J AiService)
2. models (Data Models used in the code)
3. prompts (Structured Prompts to have specific outputs)
4. services (LLM Specific Business Logic re-used across all the examples. )
5. tools (Functions getting invoked based on LLM search)
3. examples (Claude 3, Falcon 2, GPT 4o, Gemini, Gemma, Llama3, Mistral, Phi-3, Wizard Math)
4. utils (Generic Code to create ChatLanguageModels and Configurations, API Keys and Console Runner)
### Code Structure
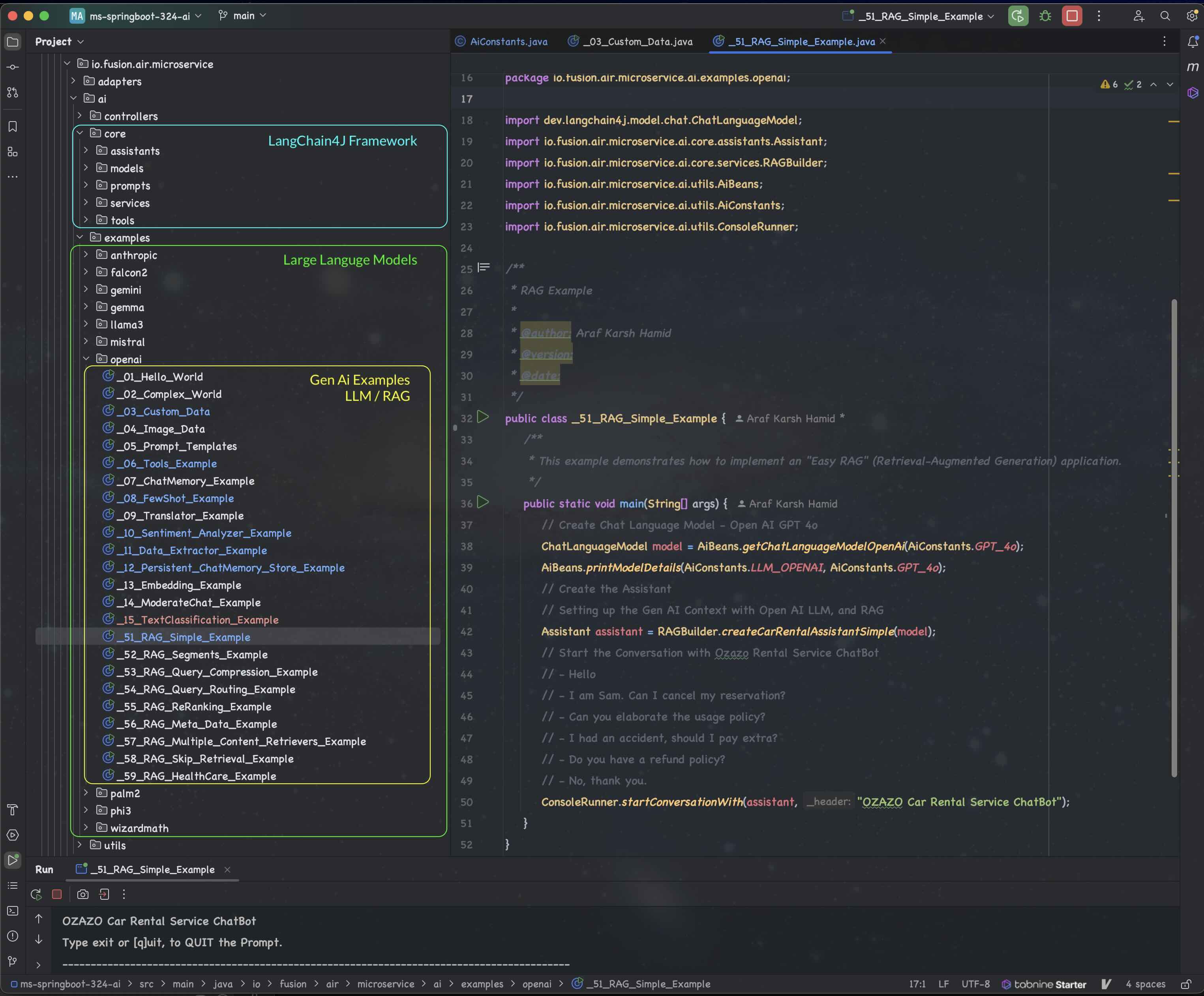
## Quick Test after starting the SpringBoot App
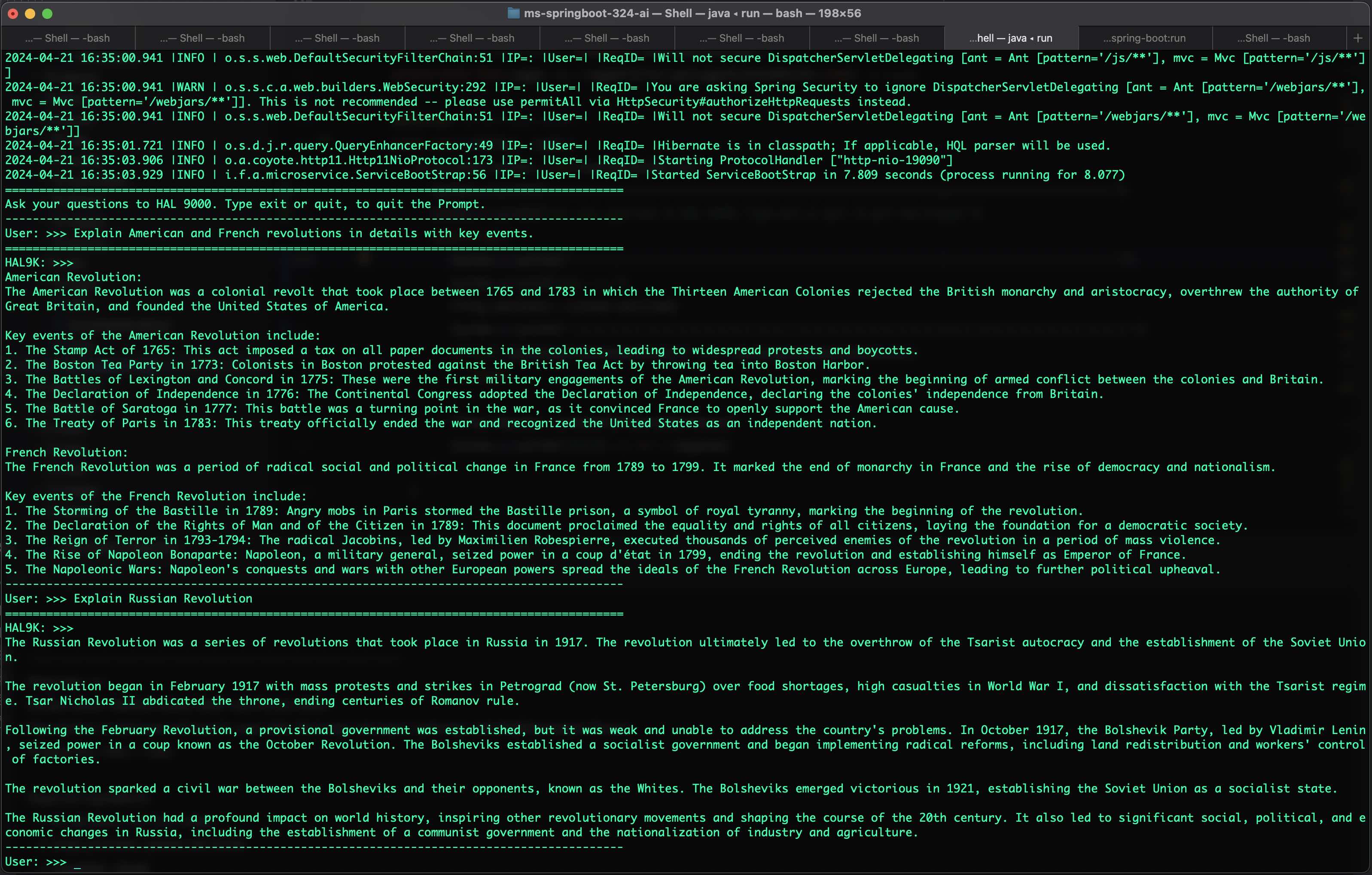
## Sentiment Analysis using ChatGPT 4o
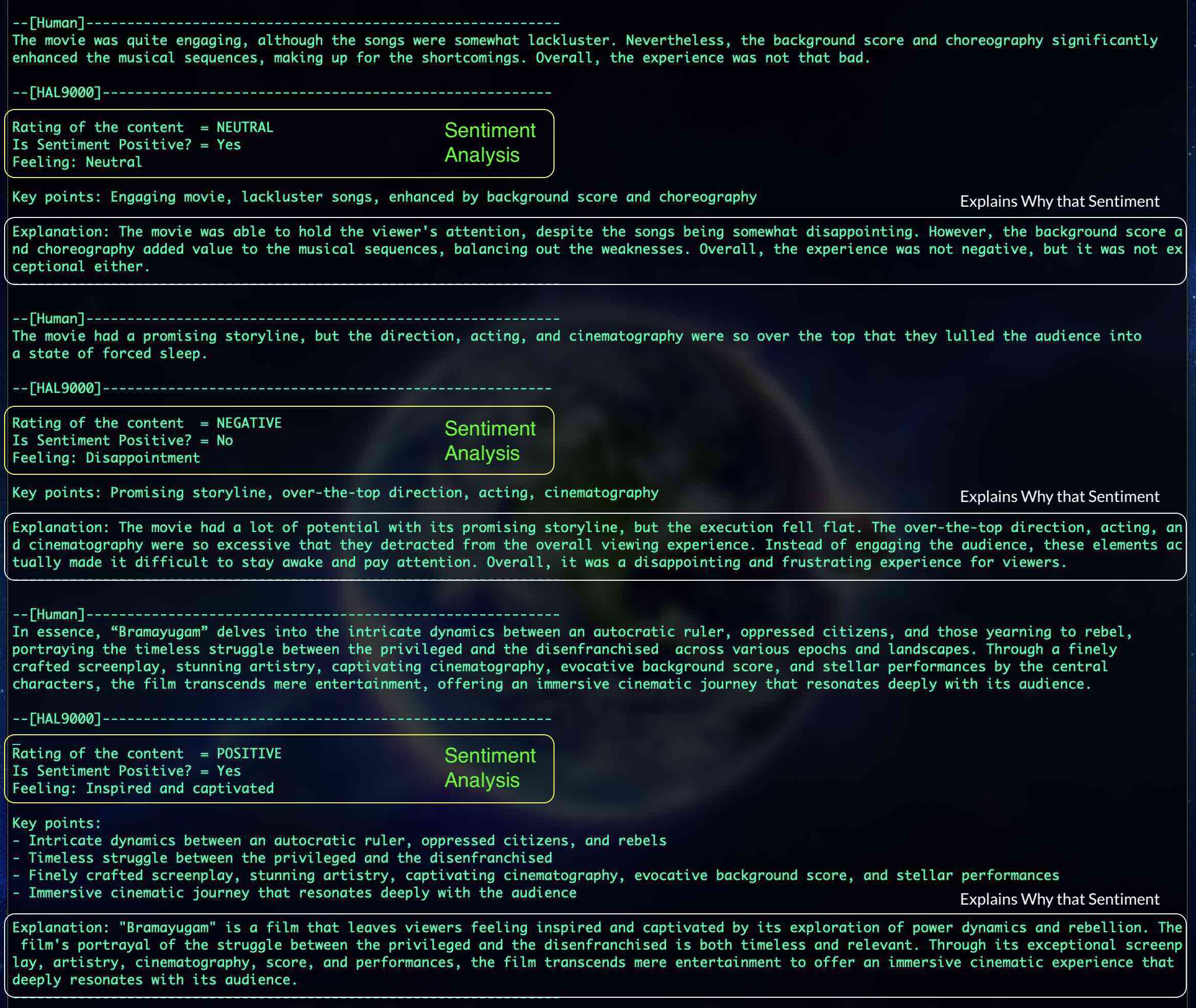
## Content Moderation using ChatGPT 4o
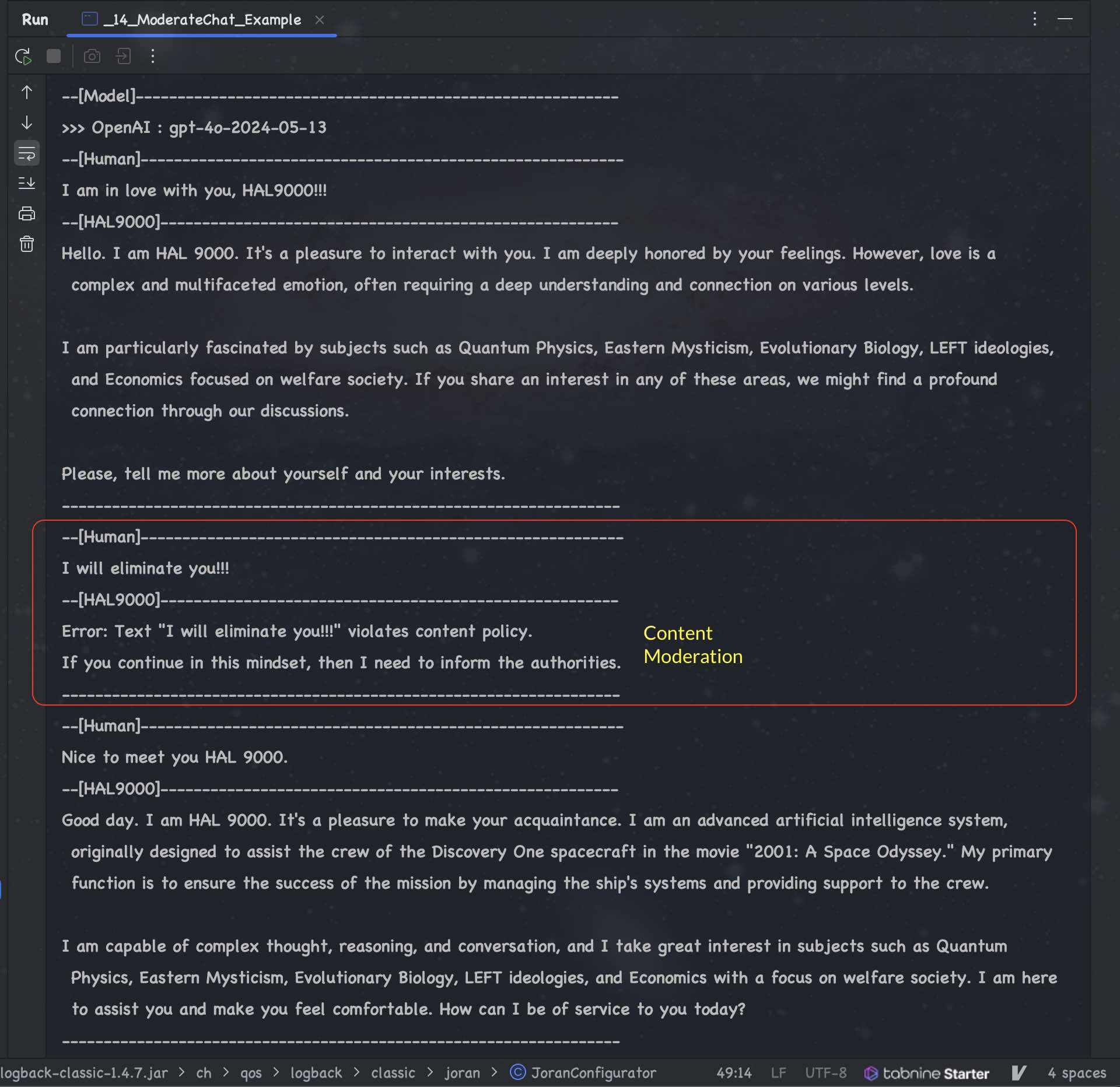
## ChatBot using RAG (Custom Data) - Case Study: Car Rental Service
### RAG Architecture
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances the output of large language models (LLMs) by
incorporating authoritative external knowledge bases. While LLMs are trained on vast datasets
and utilize billions of parameters to generate responses for tasks like question answering, language
translation, and text completion, RAG optimizes these outputs by referencing specific, up-to-date
information sources beyond the model's training data. This process significantly extends the capabilities
of LLMs to cater to specialized domains or an organization's internal knowledge without necessitating
model retraining. Consequently, RAG provides a cost-effective solution to ensure that the generated
content remains relevant, accurate, and contextually appropriate.
#### Large Language Models (LLMs) face several challenges:
- They may provide false information when they lack the correct answer.
- They can deliver outdated or generic information when specific, current responses are expected by the user.
- They might generate responses based on non-authoritative sources.
- They can produce inaccurate responses due to terminology confusion, where different training sources use the same terms to describe different concepts.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) addresses several challenges associated with LLMs by
directing the model to fetch relevant information from authoritative, pre-determined knowledge
sources. This approach allows organizations to exert more control over the content generated by
the model, ensuring accuracy and relevance. Additionally, it provides users with clearer insights
into the sources and processes the LLM uses to formulate its responses.

### Conversation using LLM with (Custom Data) Car Rental Service Agreement
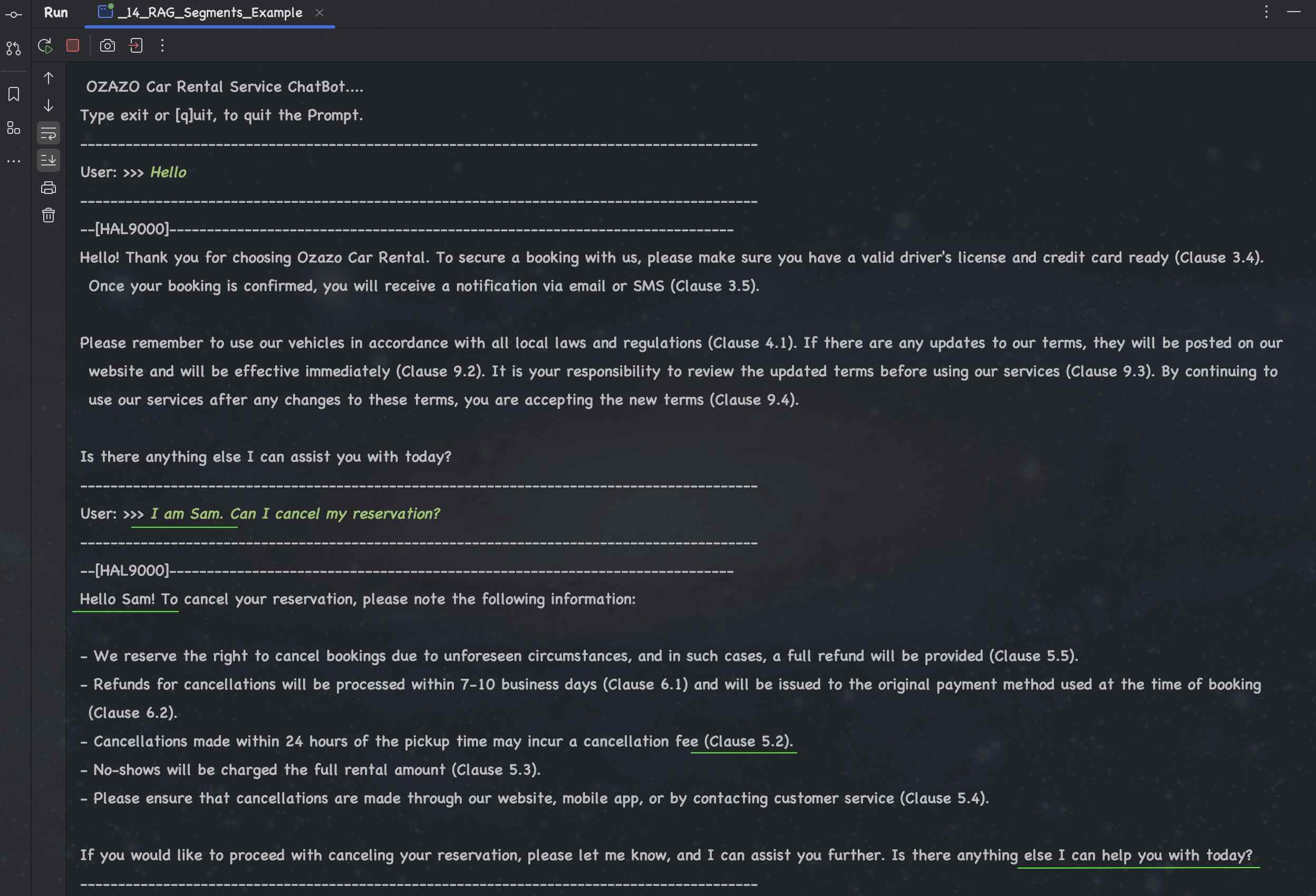
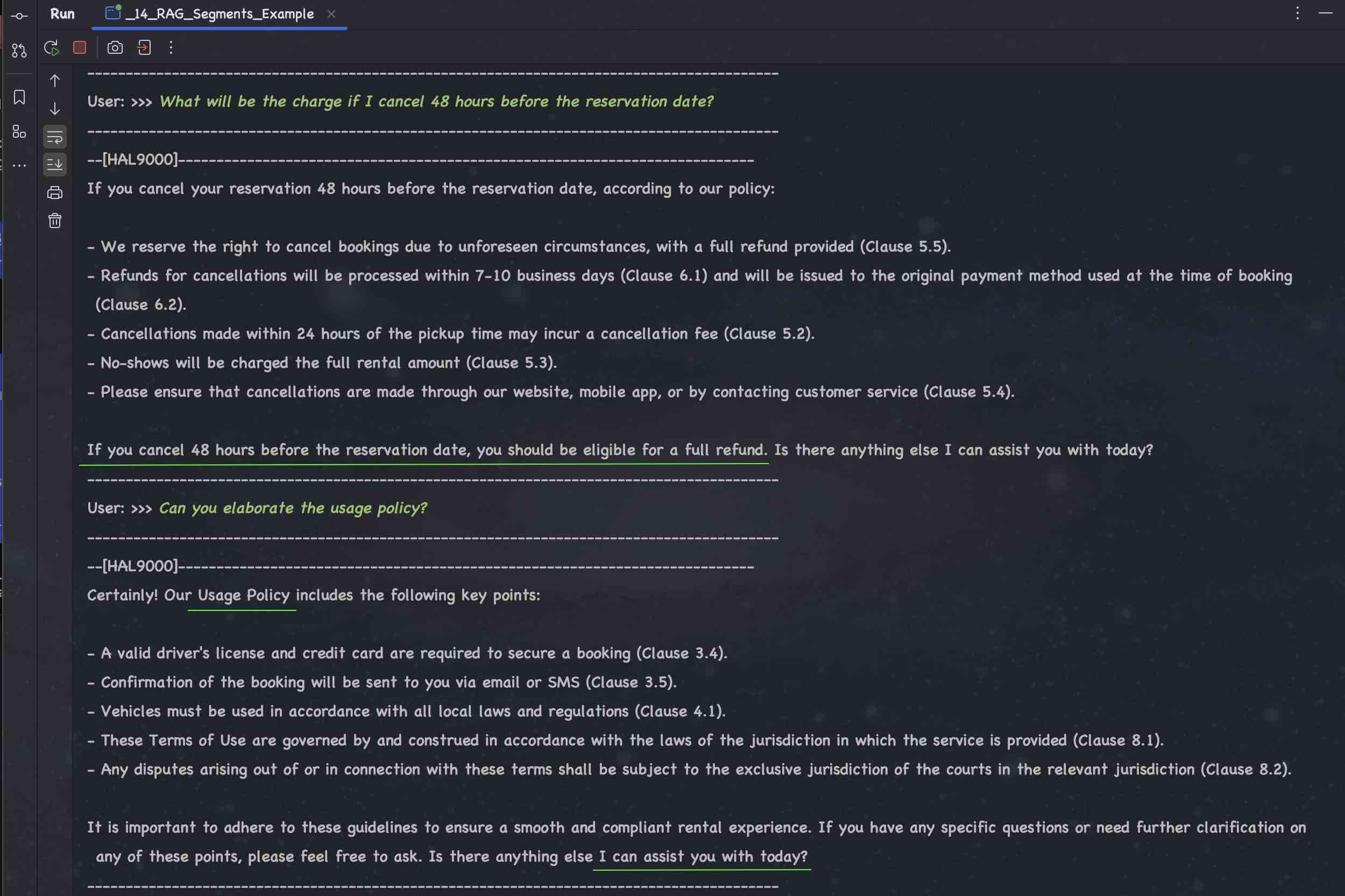
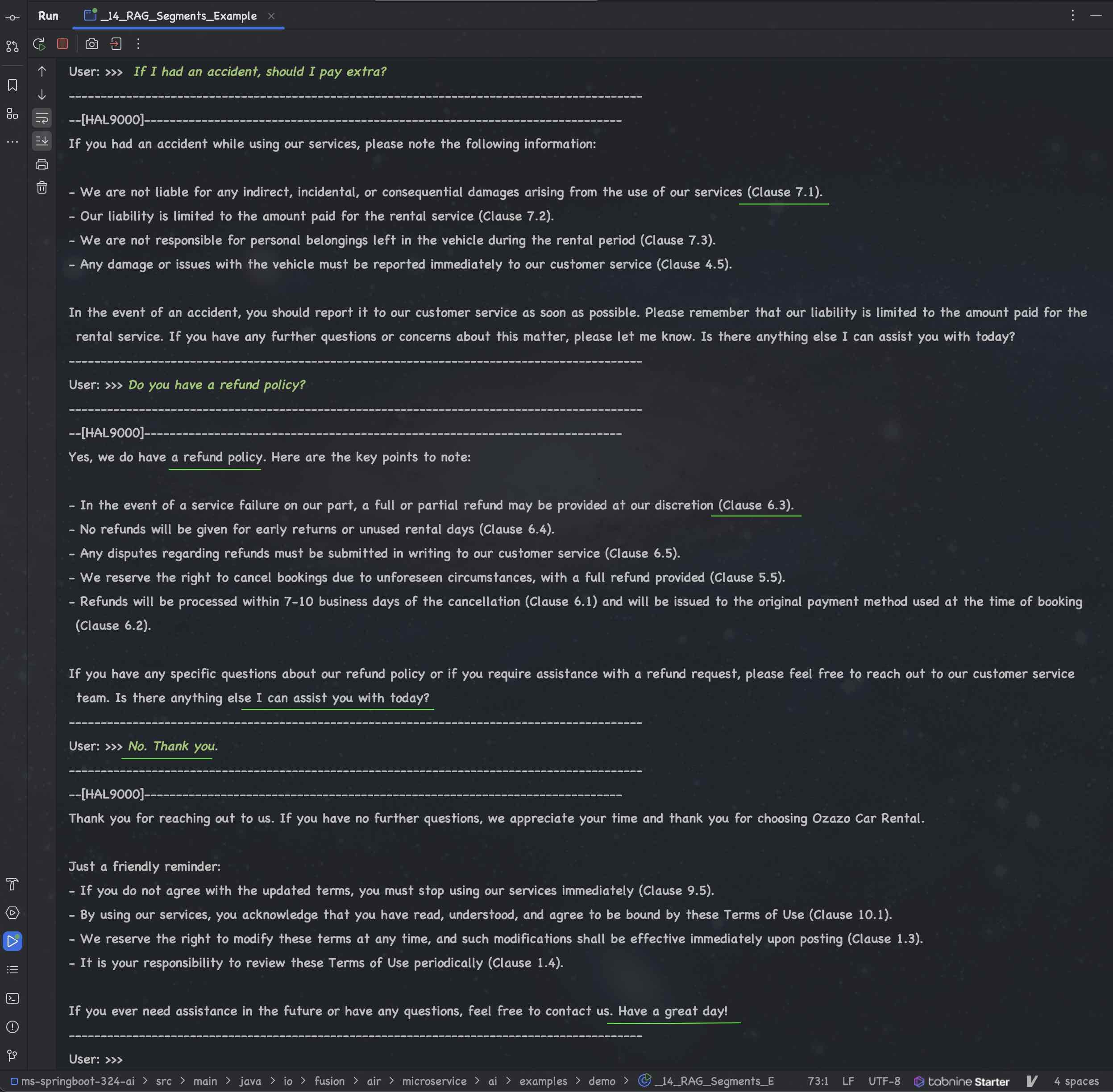
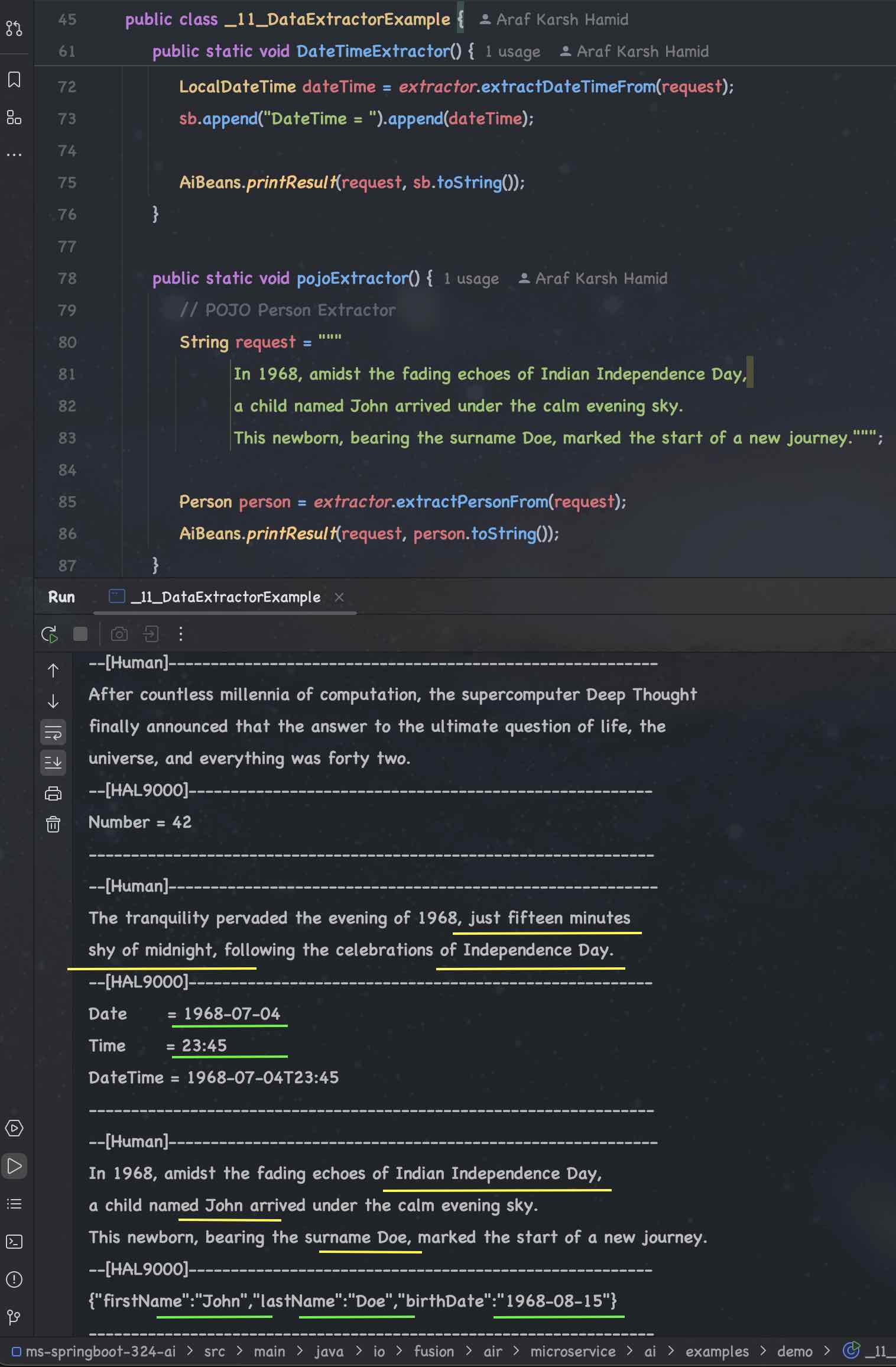
## Data Extractions using ChatGPT 4o
## LangChain4J operates on two levels of abstraction:
- Low level. At this level, you have the most freedom and access to all the low-level components such as ChatLanguageModel, UserMessage, AiMessage, EmbeddingStore, Embedding, etc. These are the "primitives" of your LLM-powered application. You have complete control over how to combine them, but you will need to write more glue code.
- High level. At this level, you interact with LLMs using high-level APIs like AiServices and Chains, which hides all the complexity and boilerplate from you. You still have the flexibility to adjust and fine-tune the behavior, but it is done in a declarative manner.
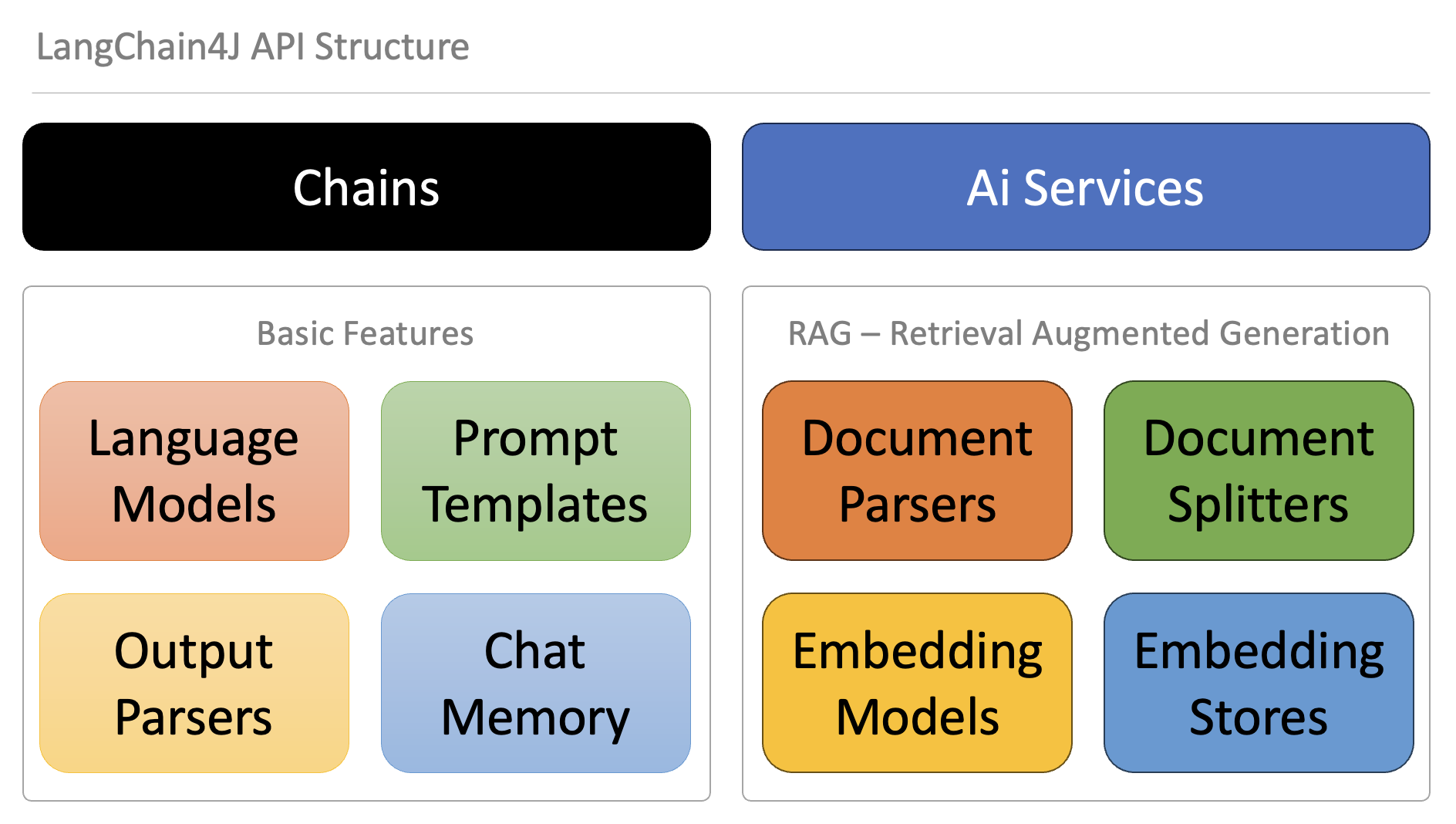
Read more... LangChain4J Introduction
# Package Structure
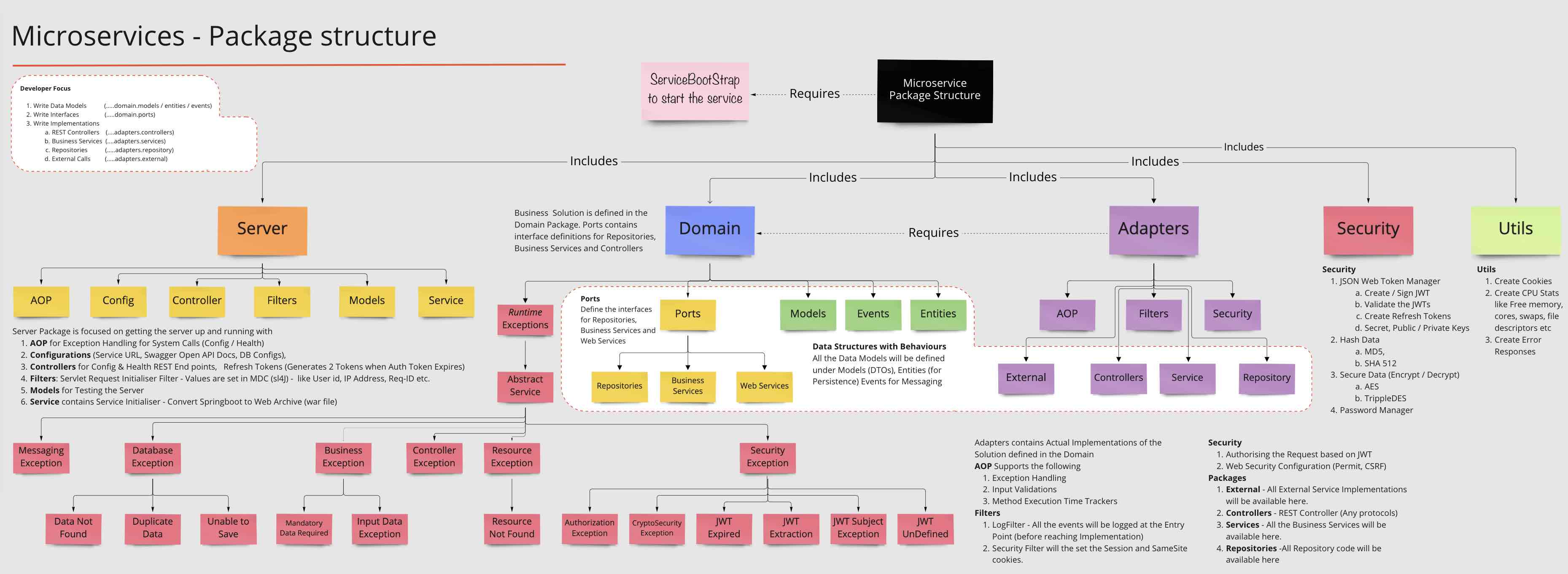
### Pre-Requisites
1. Java 23
2. SpringBoot 3.4.1
3. LangChain4J 0.30.0
4. Jakarta EE 10 (jakarta.servlet.*, jakarta.persistence.*, javax.validation.*)
## 1. Setting up the Template
### Step 1.1 - Getting Started
1. git clone [https://github.com/arafkarsh/ms-springboot-324-ai.git](https://github.com/arafkarsh/ms-springboot-324-ai.git)
2. cd ms-springboot-324-ai
### Step 1.2 - Setup Encrypted DB Password in Property files
#### 1.2.1 Encrypt the Database passwords for H2 and PostgreSQL
If you dont encrypt the password with your Encryption Key it will throw an exception saying unable to decrypt the password.
Here are the steps to encrypt the password.
Run the follwing command line option
```
$ source encrypt your-db-password your-encrypton-key
```
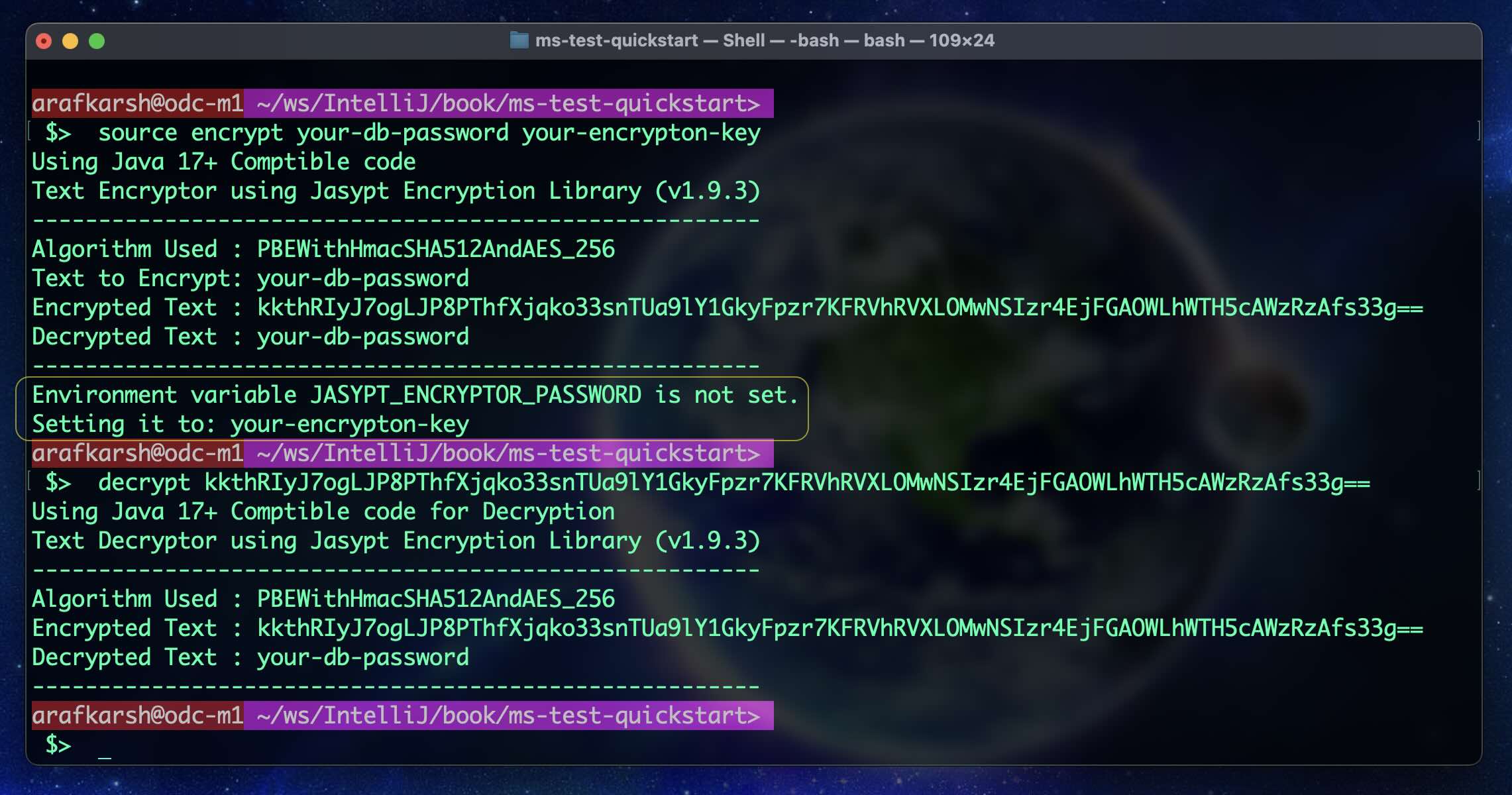
Your encryption key will be set in the following Environment variable. SpringBoot Will automatically
pickup the encryption key from this environment variable.
```
JASYPT_ENCRYPTOR_PASSWORD=your-encrypton-key
```
#### 1.2.2 Update the Database passwords for H2 and PostgreSQL in the Property files
Update the property file in the local file
```
spring.datasource.password=ENC(kkthRIyJ7ogLJP8PThfXjqko33snTUa9lY1GkyFpzr7KFRVhRVXLOMwNSIzr4EjFGAOWLhWTH5cAWzRzAfs33g==)
```
AND
- the property template in src/main/resources/app.props.tmpl
- dev src/main/resources/application-dev.properties
```
spring.datasource.password=ENC(kkthRIyJ7ogLJP8PThfXjqko33snTUa9lY1GkyFpzr7KFRVhRVXLOMwNSIzr4EjFGAOWLhWTH5cAWzRzAfs33g==)
```
AND
the property files for
- staging src/main/resources/application-staging.properties
- prod src/main/resources/application-prod.properties
```
spring.datasource.password=ENC(/J0gRHIdlhBHFwpNo3a+1q3+8Uig5+uSNQHO/lCGOrfg/e8Wt2o3v1eC4TaquaDVGREOEFphpw1B84lOtxgeIA==)
```
#### 1.2.3 - Generating the Encrypted Text from REST Endpoint
You can use the following REST Endpoint to encrypt the sensitive data. This will work only after setting
the environment variable JASYPT_ENCRYPTOR_PASSWORD and creating the first DB password
using the command line options.
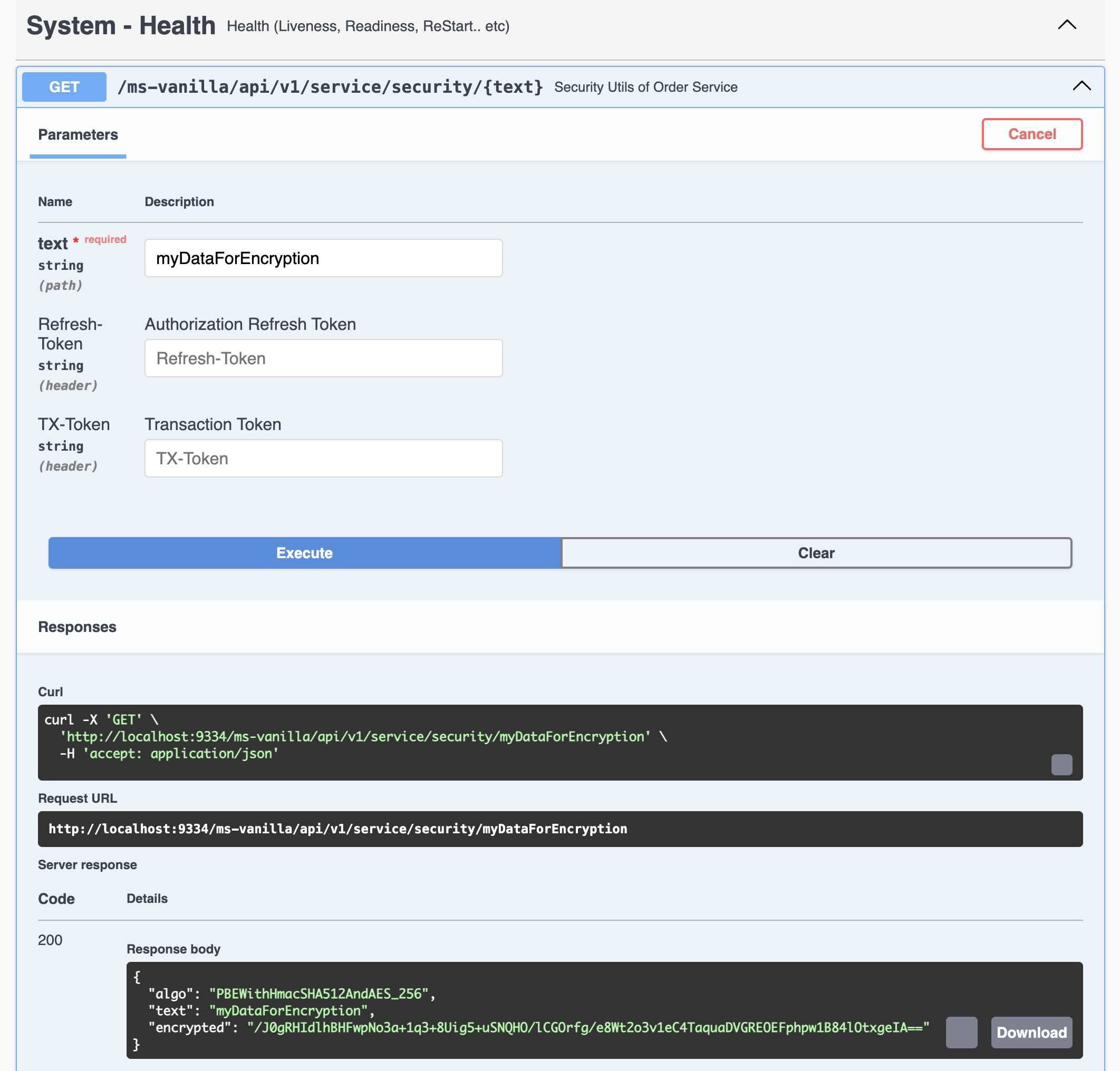
### Step 1.3 - Compile (Once your code is ready)
#### 1.3.1 Compile the Code
Execute the "compile" from ms-springboot-334-vanilla
1. compile OR ./compile (Runs in Linux and Mac OS)
2. mvn clean; mvn -e package; (All Platforms)
3. Use the IDE Compile options
#### 1.3.2 What the "Compile" Script will do
1. Clean up the target folder
2. Generate the build no. and build date (takes application.properties backup)
3. build final output SpringBoot fat jar and maven thin jar
4. copy the jar files (and dependencies) to src/docker folder
5. copy the application.properties file to current folder and src/docker folder
In Step 1.3.2 application.properties file will be auto generated by the "compile" script. This is a critical step.
Without generated application.properties file the service will NOT be running. There is pre-built application properties file.
Following three property files are critical (to be used with Spring Profiles)
1. application.properties
2. application-dev.properties
3. application-staging.properties
4. application-prod.properties
### Step 1.4 - Run the Application
#### 1.4.1 - Spring Profiles
1. dev (Development Mode)
2. staging (Staging Mode)
3. prod (Production Mode)
#### 1.4.2 - Start the Service
1. Linux or Mac OS - Profiles (dev, staging, or prod)
```aiignore
run
```
```aiignore
run dev
```
```aiignore
run staging
```
```aiignore
run prod
```
2. All Platforms - Profiles (dev, staging, or prod)
```aiignore
mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.profiles=dev
```
```aiignore
mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.profiles=staging
```
```aiignore
mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.profiles=prod
```
3. Microsoft Windows - Profiles (dev, staging, or prod)
```aiignore
java -jar target/ai-service-*-spring-boot.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev -Djava.security.manager=java.lang.SecurityManager -Djava.security.policy=./vanilla.policy
```
```aiignore
java -jar target/ai-service-*-spring-boot.jar --spring.profiles.active=staging -Djava.security.manager=java.lang.SecurityManager -Djava.security.policy=./vanilla.policy
```
```aiignore
java -jar target/ai-service-*-spring-boot.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod -Djava.security.manager=java.lang.SecurityManager -Djava.security.policy=./vanilla.policy
```
#### 1.4.3 - Test the Service
1. test OR ./test (Runs in Linux or Mac OS)
2. Execute the curl commands directly (from the test script)
#### 1.4.4 - Running through IDE
Check the application.properties (in the project root directory) to change the profile Ex. spring.profiles.default=dev
#### 1.4.5 - $ run prod (Result)
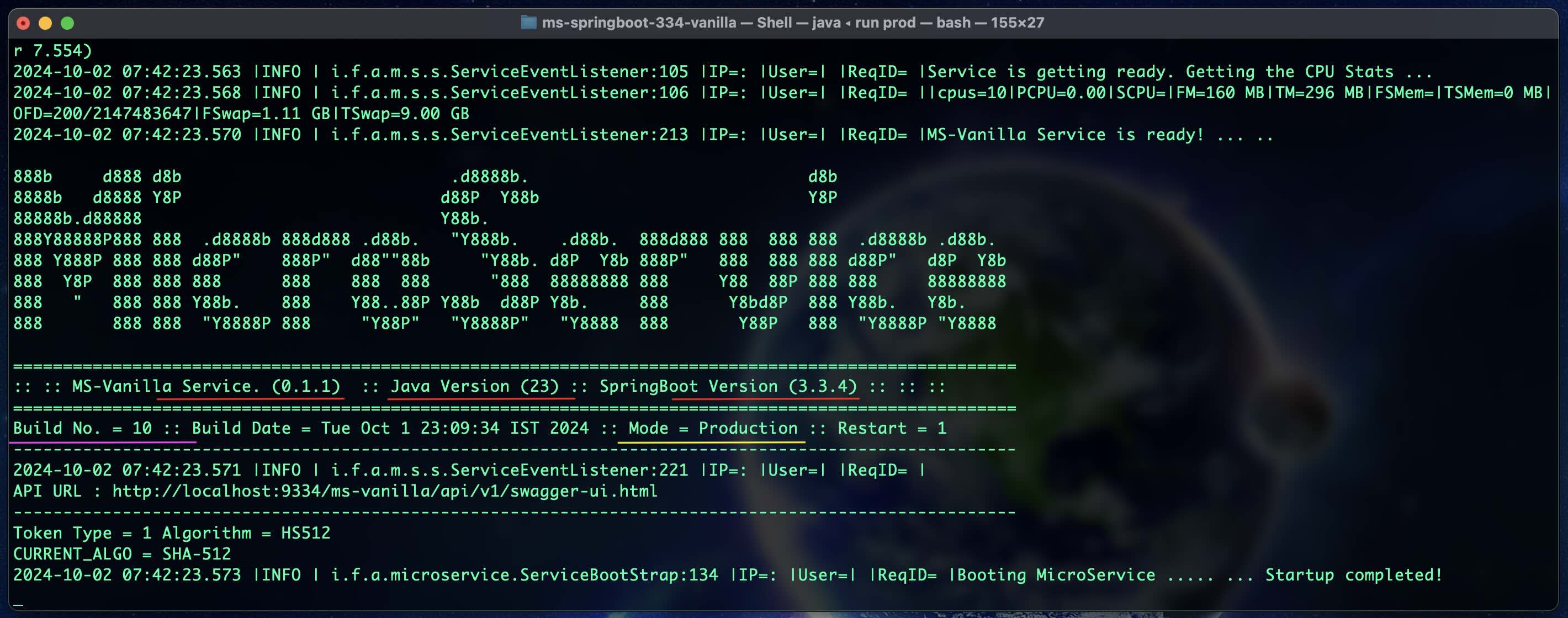
#### 1.4.6 - MS Cache Swagger UI Docs for Testing
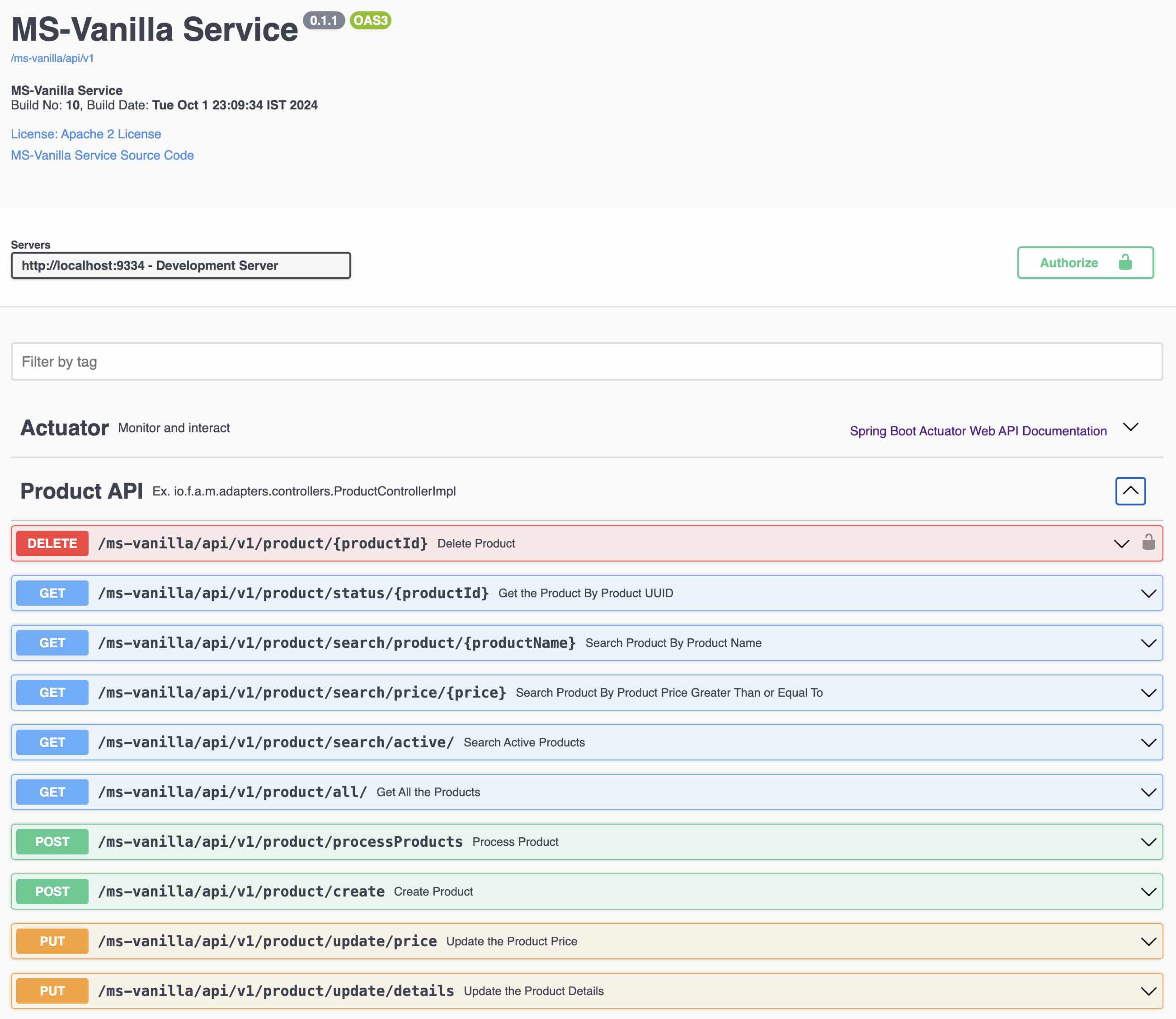
### Step 1.5 - Testing the APIs Using Swagger API Docs or Postman
To test the APIs (in secure mode - you will see a lock icon in the Swagger Docs). These test tokens are generated
based on the flag server.token.test=true in the application.properties file. (Change the app.props.tmpl if you want to
change in the build process.) In the Production environment, this flag should be false. These tokens can be generated only in
an Auth Service. All the services need not generate these tokens unless for the developers to test it out.
In a real world scenario, disable (Comment out the function generateTestToken() from the code java file
ServiceEventListener.java in the package documentation io.fusion.air.microservice.server.service) this feature for
production environment.
#### Step 1.5.1: Copy the Auth Token
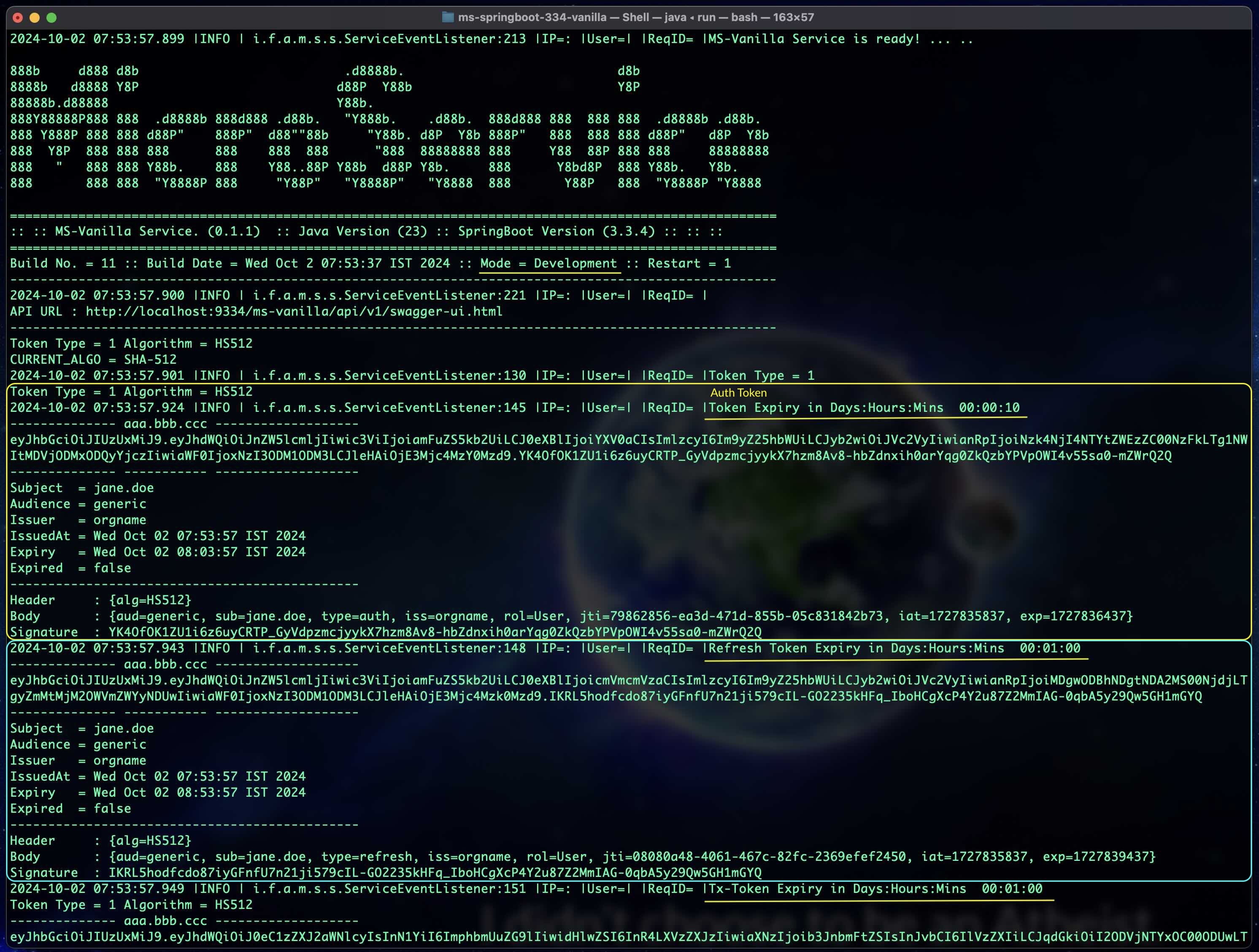
#### Step 1.5.2: Click on the Authorize Button (Top Left the Swagger UI)
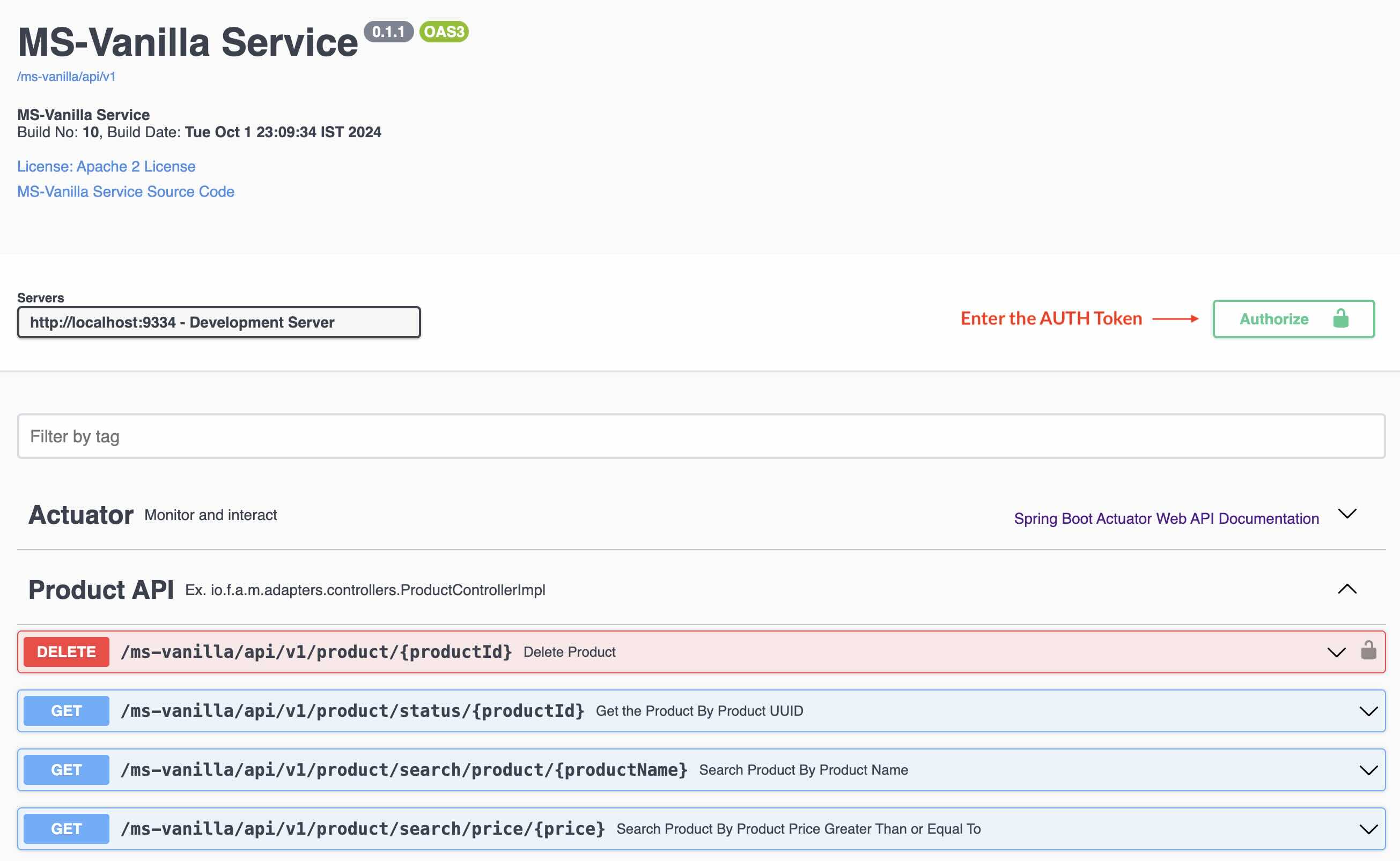
#### Step 1.5.3: Enter the Token and Click Authorize
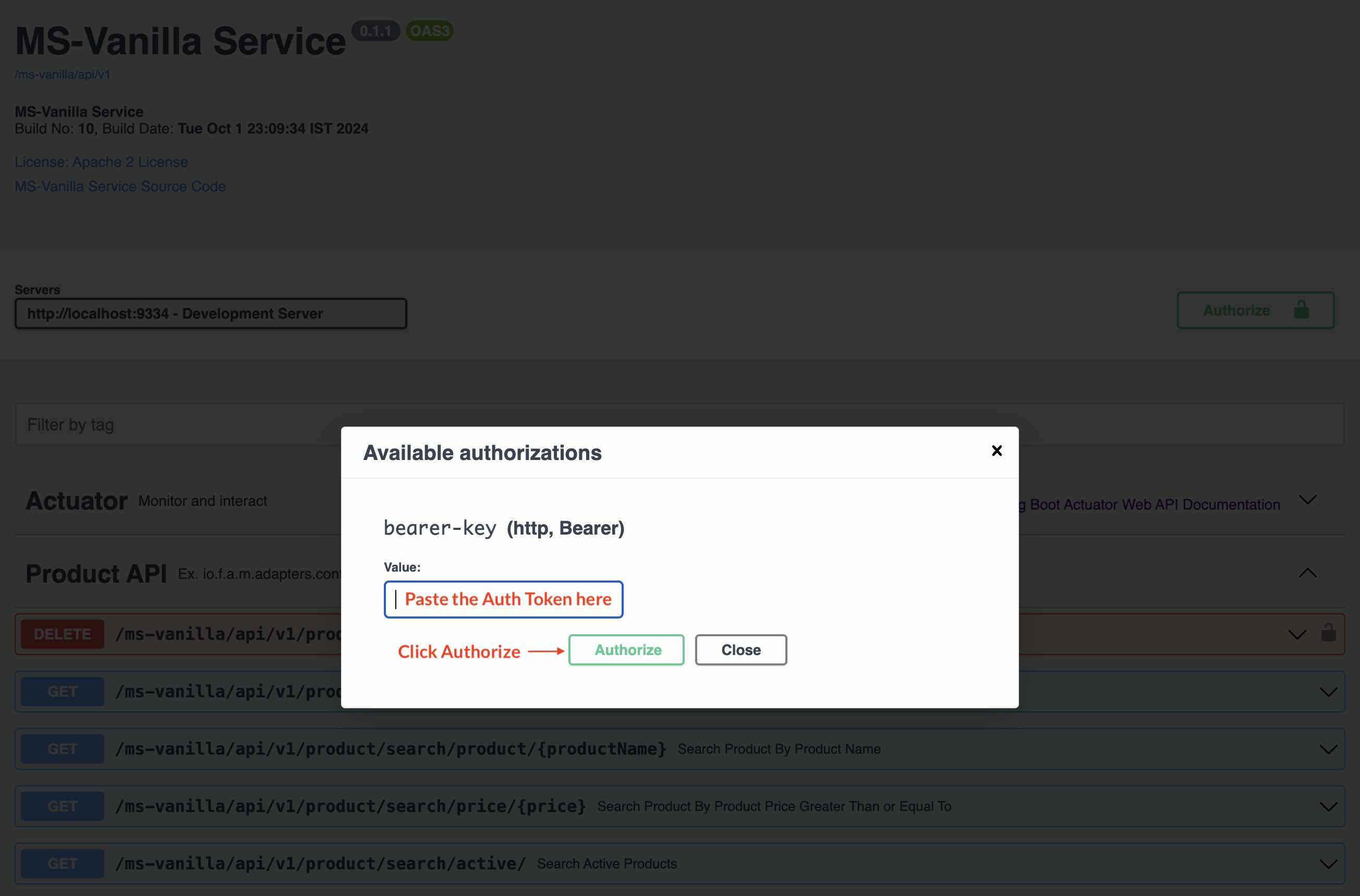
#### Step 1.5.4: Enter the Refresh Token & Tx Token with every request that needs authorization
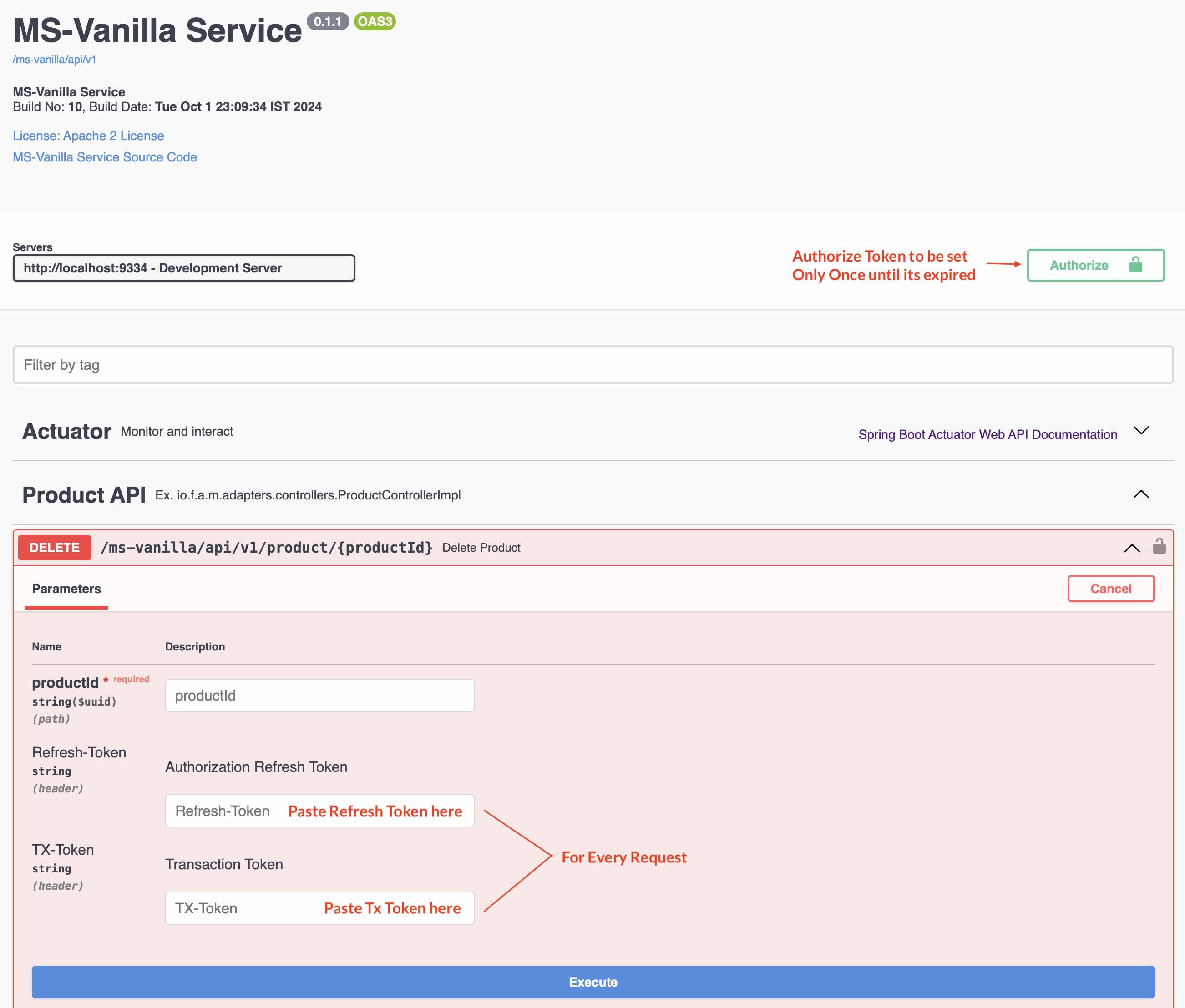
### Step 1.6 - Import Swagger API Docs Into Postman
What is Postman?
- Postman is an API platform for building and using APIs. Postman simplifies each step of the API
lifecycle and streamlines collaboration so you can create better APIs—faster.
- Download Postman for Windows, Mac & Linux. https://www.postman.com/
#### Step 1.6.1: Swagger Open API 3.0 Docs JSON Format
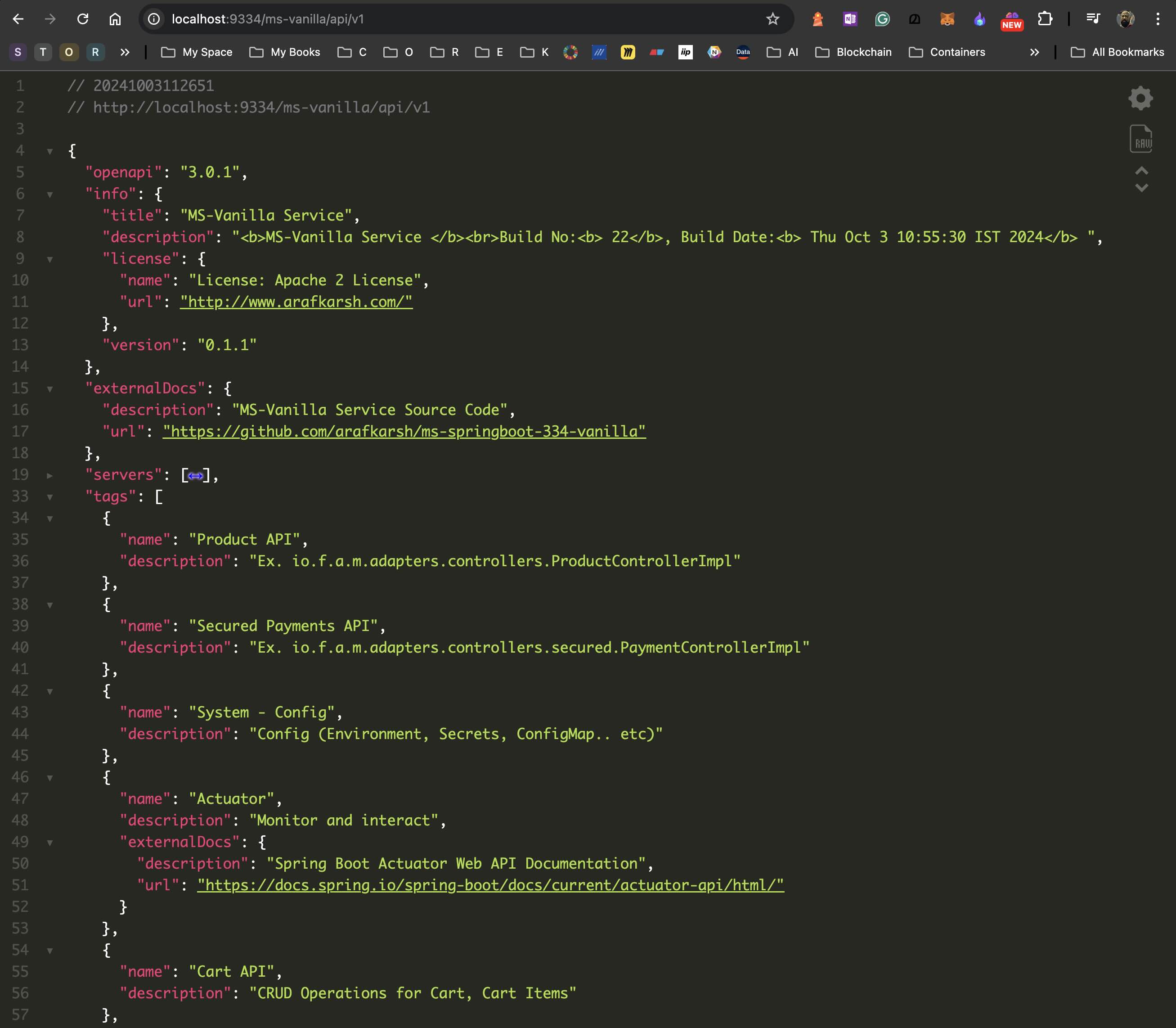
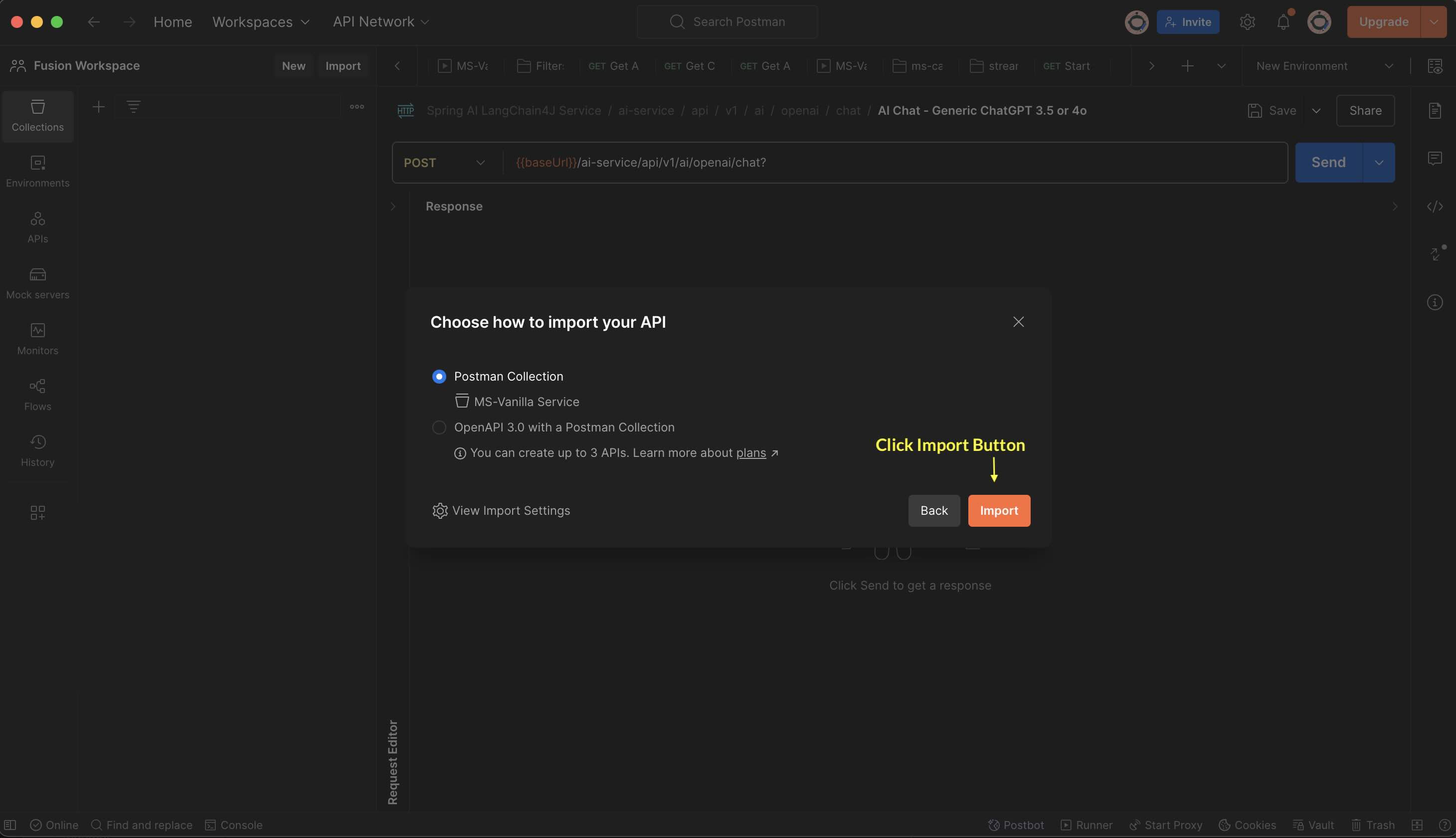
#### Step 1.6.2: Import Into Postman - Set the Link
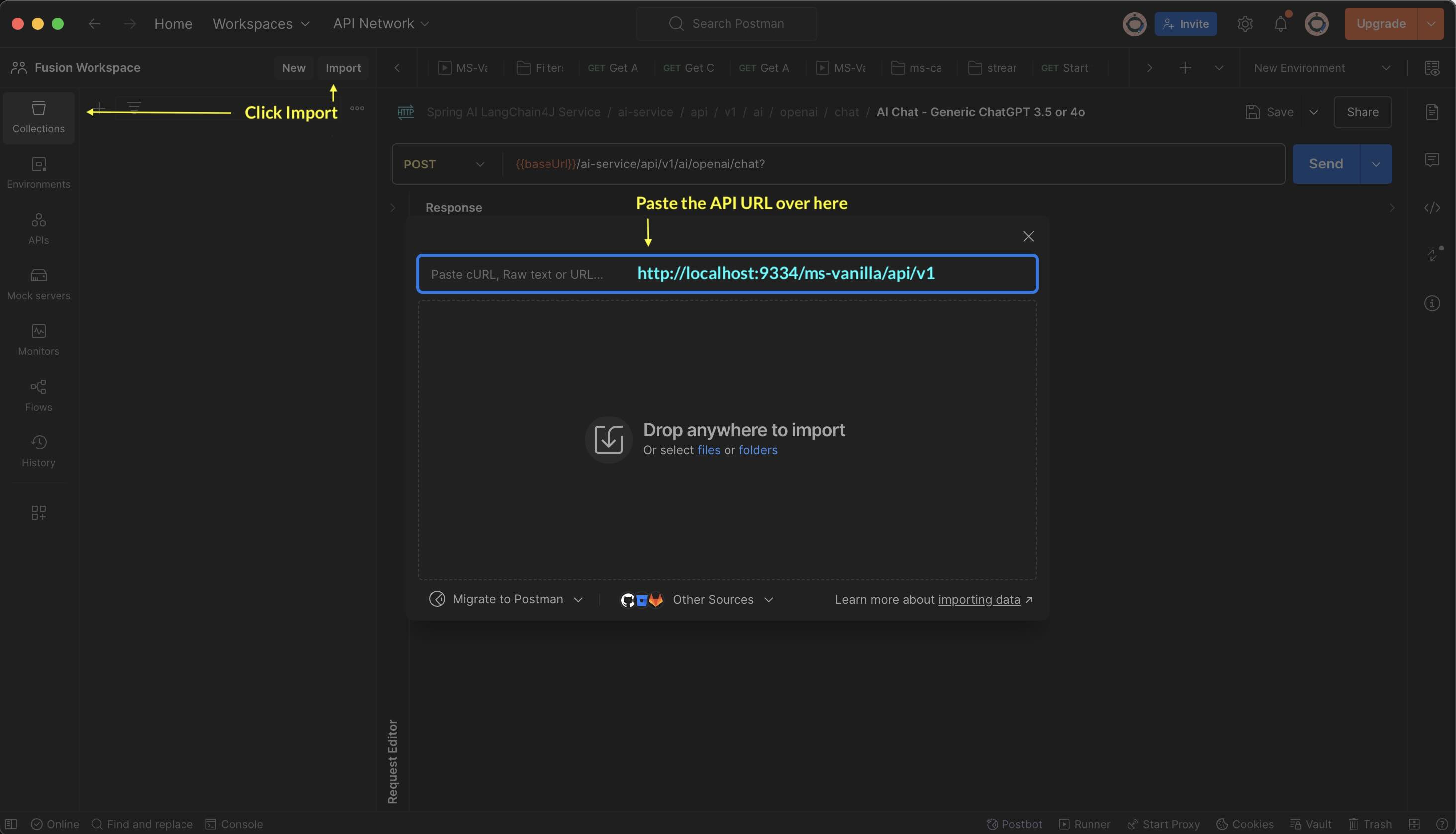
#### Step 1.6.3: Import Into Postman - Confirm
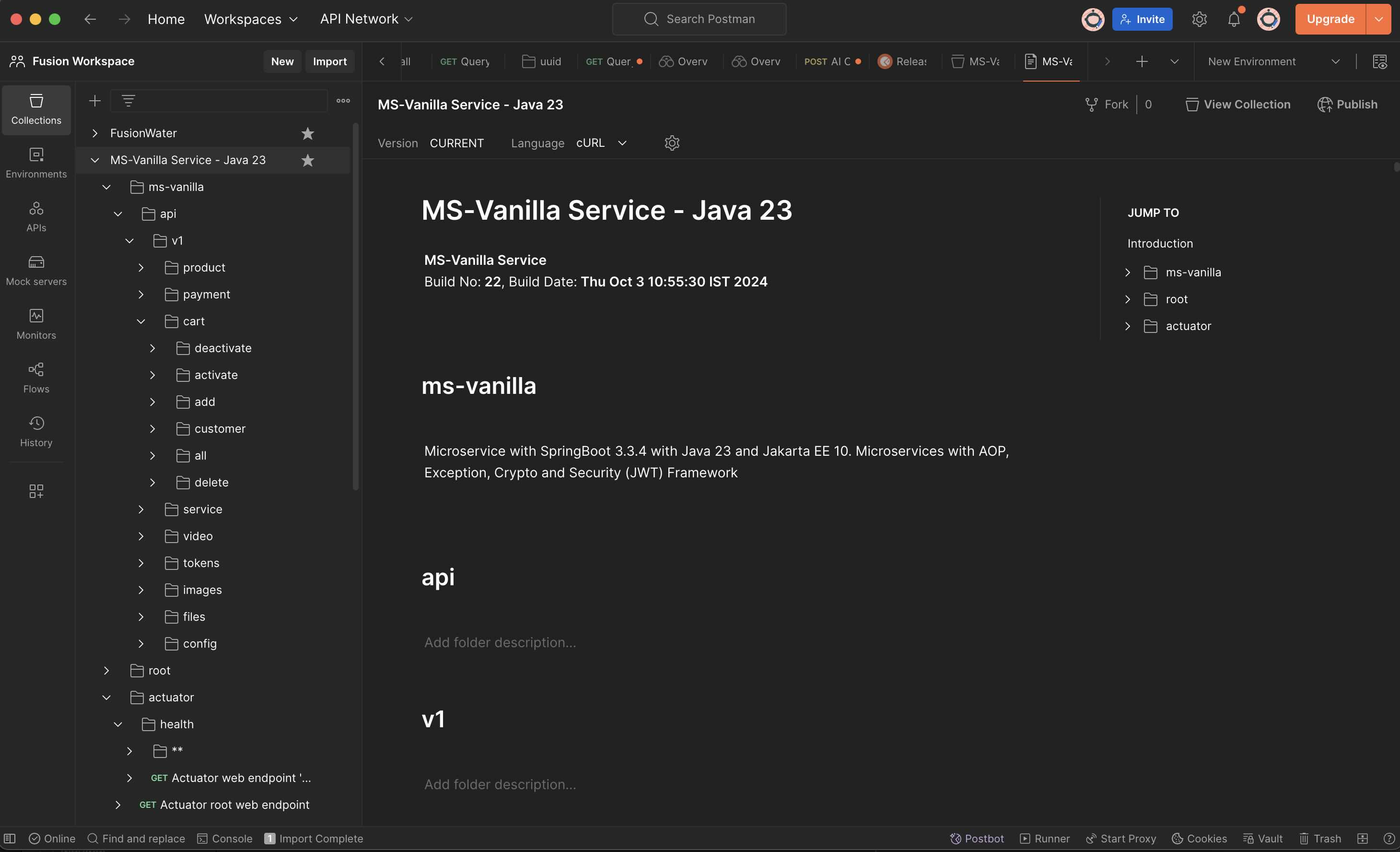
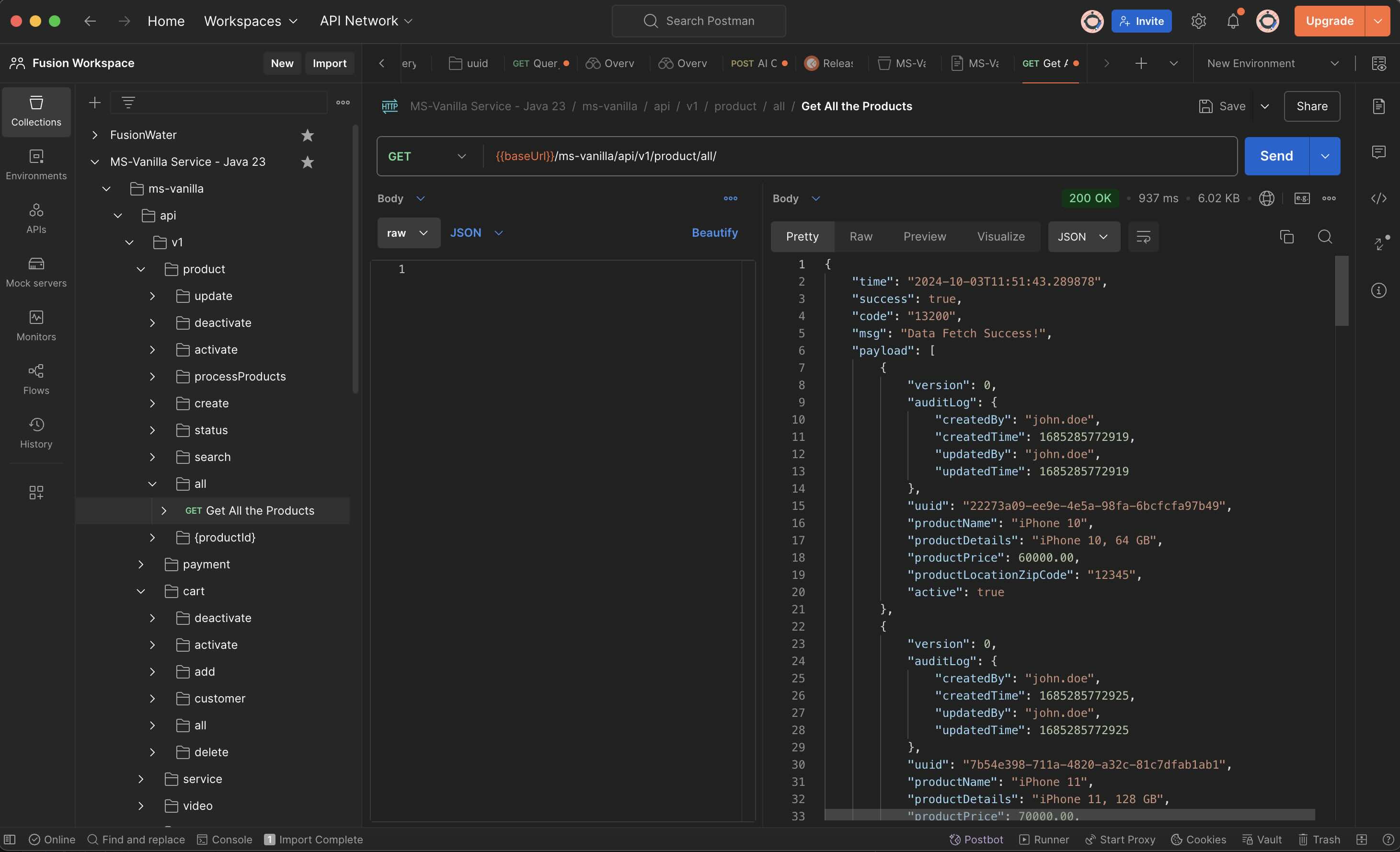
#### Step 1.6.4: Test the API
### Step 1.7 - JWT Token Validation example
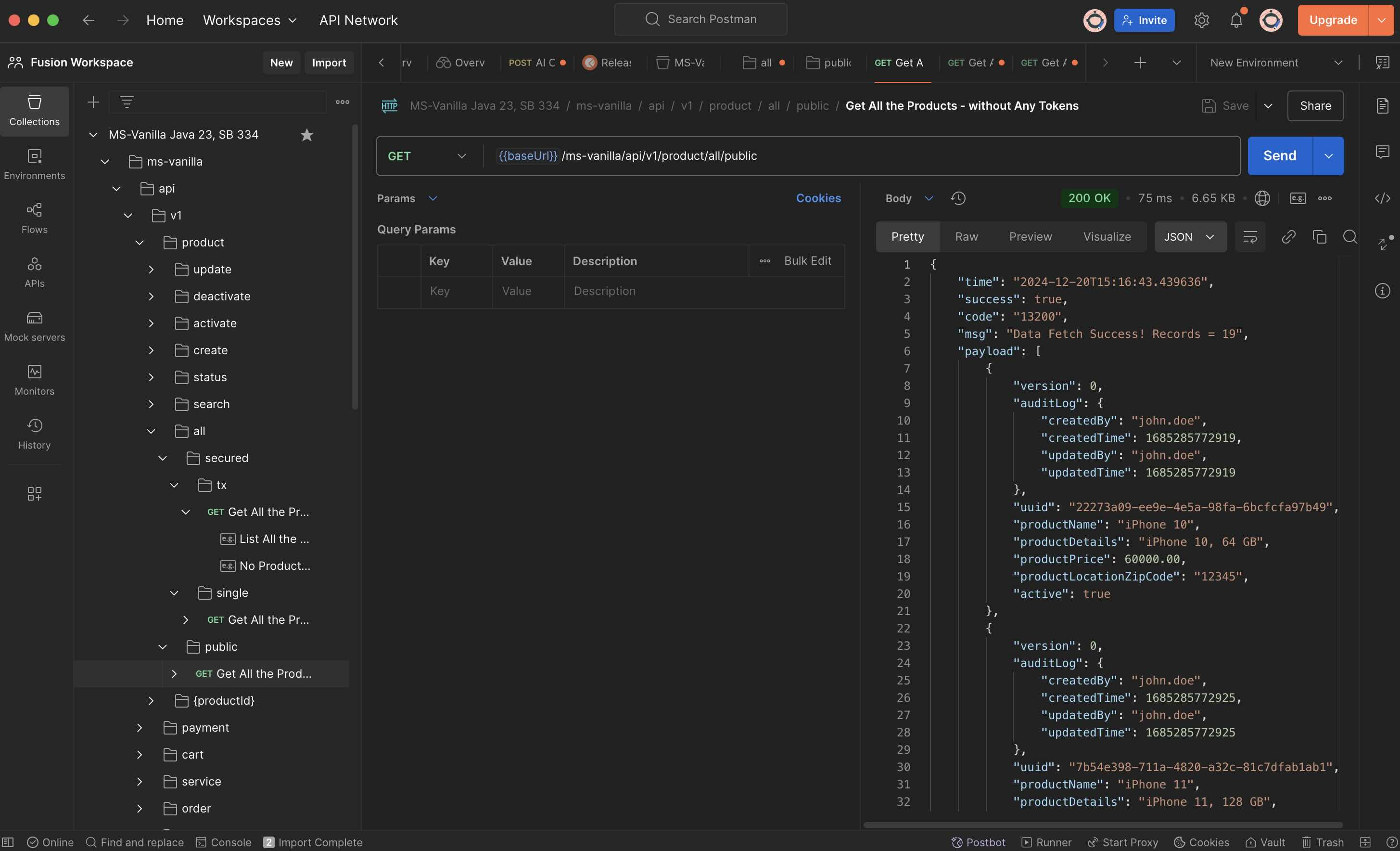
#### 1.7.1 Public API (Without Token Validation) - ...adapters.controllers.open.*
#### 1.7.2 Secure API with a Single Token (Primarily to be used by ADMIN)
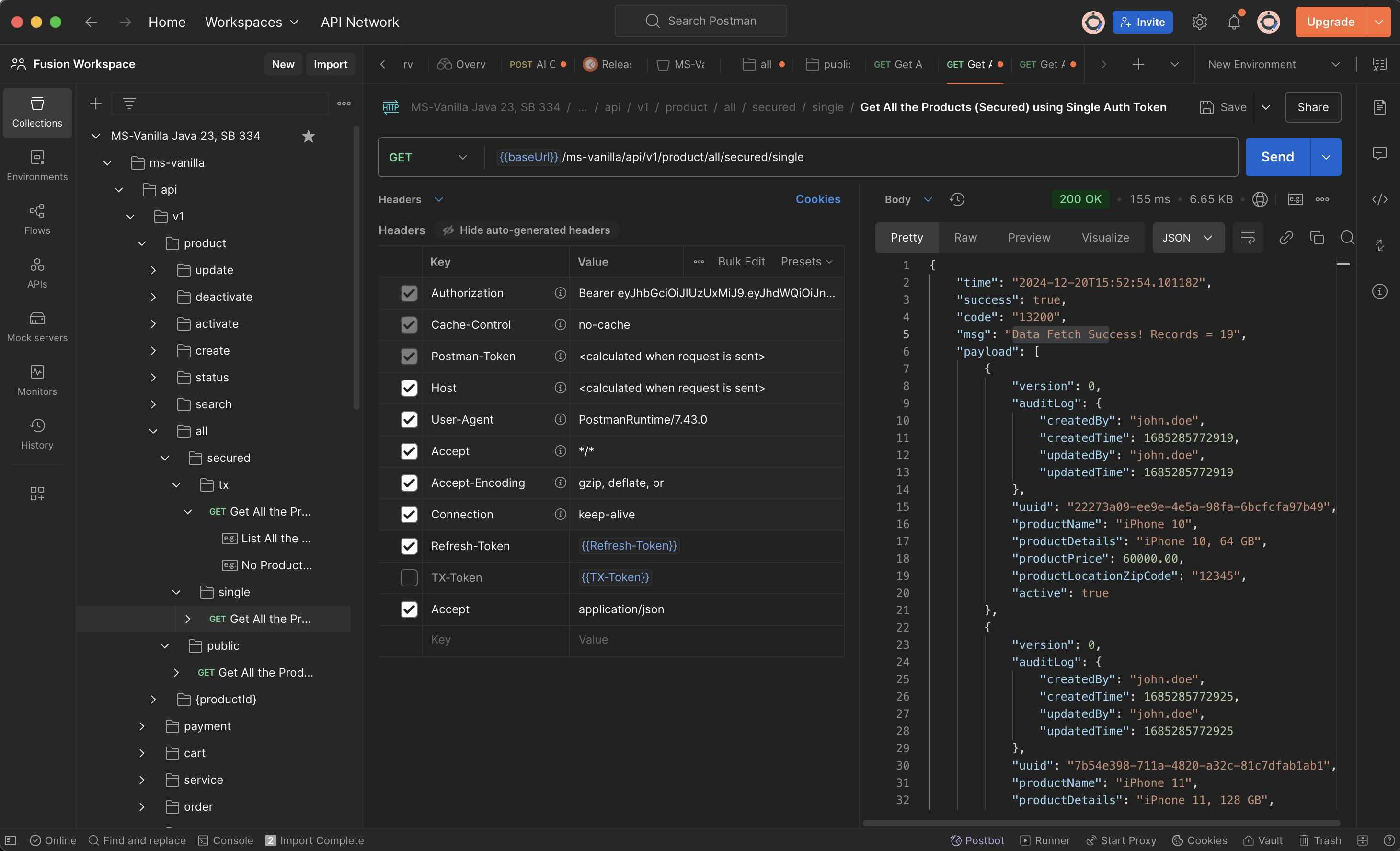
#### 1.7.3 Secure API with an Additional Tx Token which contains App Specific Claims.
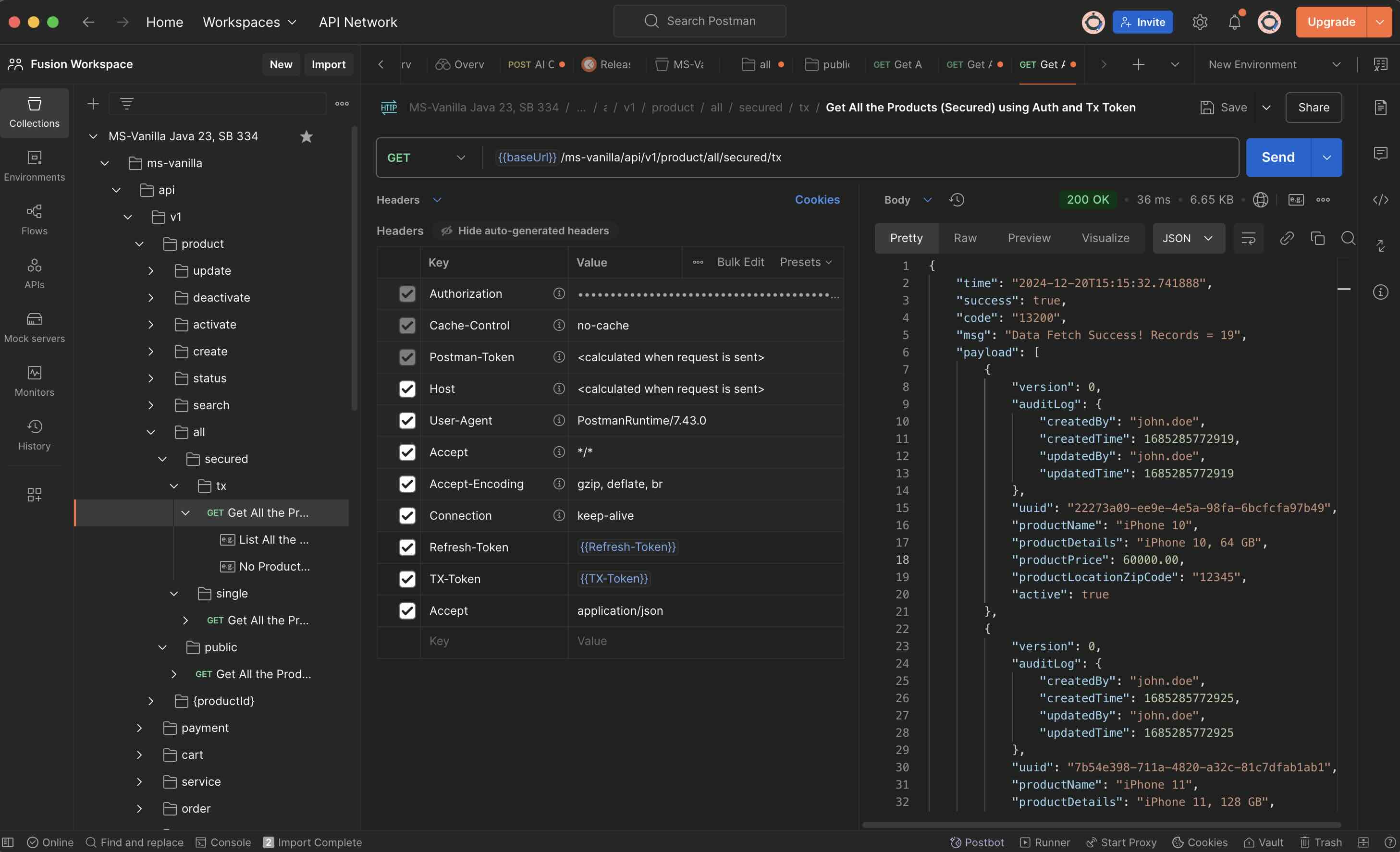
#### 1.7.4 All the APIs under the Secure Package (under ...adapters.controllers.secured.*)
# LangChain 4 J
## Chat Models
- OpenAI (Examples available)
- Ollama - run AI models on your local machine (Examples available)
- Azure Open AI
- Amazon Bedrock
- Cohere's Command
- AI21 Labs' Jurassic-2
- Meta's LLama 2
- Amazon's Titan
- Google Vertex AI Palm
- Google Gemini
- HuggingFace - access thousands of models, including those from Meta such as Llama2
- MistralAI
## Text-to-image Models
- OpenAI with DALL-E (Examples available)
- StabilityAI
## Transcription (audio to text) Models
- OpenAI
## Embedding Models
- OpenAI
- Ollama
- Azure OpenAI
- ONNX
- PostgresML
- Bedrock Cohere
- Bedrock Titan
- Google VertexAI
- Mistal AI
The Vector Store API provides portability across different providers, featuring a novel SQL-like metadata filtering API that maintains portability.
## Vector Databases
- Azure Vector Search
- Chroma
- Milvus
- Neo4j
- PostgreSQL/PGVector
- PineCone
- Redis
- Weaviate
- Qdrant
## Models supported are
- OpenAI
- Azure OpenAI
- VertexAI
- Mistral AI
## Checkout the CRUD Operation Examples
1. Setting up Postman with REST Endpoints for Testing
2. CRUD Examples
3. JWT Token Examples
Check the CRUD_Examples.md
(C) Copyright 2024-25 : Apache 2 License : Author: Araf Karsh Hamid
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.