https://github.com/arangodb/nx-arangodb
The ArangoDB backend to NetworkX
https://github.com/arangodb/nx-arangodb
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
The ArangoDB backend to NetworkX
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/arangodb/nx-arangodb
- Owner: arangodb
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2024-04-26T23:57:40.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-06T00:34:50.000Z (3 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-07T00:13:43.366Z (2 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://nx-arangodb.readthedocs.io
- Size: 11.2 MB
- Stars: 13
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 5
- Open Issues: 7
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# nx-arangodb

[](https://dl.circleci.com/status-badge/redirect/gh/arangodb/nx-arangodb/tree/main)
[](https://github.com/arangodb/nx-arangodb/actions/workflows/analyze.yml)
[](https://nx-arangodb.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://pypi.org/project/nx-arangodb/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/nx-arangodb/)
[](https://github.com/arangodb/nx-arangodb/blob/main/LICENSE)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/nx-arangodb)
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/e5f56574-d3ef-452c-ab21-b47b3d5d5900
## What is this?
This is a [backend to NetworkX](https://networkx.org/documentation/stable/reference/backends.html) that offers [ArangoDB](https://github.com/arangodb/arangodb) as a [Persistence Layer to NetworkX Graphs](https://arangodb.com/introducing-the-arangodb-networkx-persistence-layer/):
1. Persist NetworkX Graphs to ArangoDB.
2. Reload NetworkX Graphs from ArangoDB.
2. Perform CRUD on ArangoDB Graphs via NetworkX.
3. Run algorithms (CPU & GPU) on ArangoDB Graphs via NetworkX.
Benefits of having ArangoDB as a backend to NetworkX include:
1. No need to re-create the graph every time you start a new session.
2. Access to GPU-accelerated graph analytics ([nx-cugraph](https://rapids.ai/nx-cugraph/)).
3. Access to a database query language ([Arango Query Language](https://arangodb.com/sql-aql-comparison/)).
4. Access to a visual interface for graph exploration ([ArangoDB Web UI](https://docs.arangodb.com/stable/components/web-interface/graphs/)).
5. Access to cross-collaboration on the same graph ([ArangoDB Cloud](https://docs.arangodb.com/stable/get-started/set-up-a-cloud-instance/)).
6. Access to efficient distribution of graph data ([ArangoDB SmartGraphs](https://docs.arangodb.com/stable/graphs/smartgraphs/)).

## Does this replace NetworkX?
Not really. This is a plugin to NetworkX, which means that you can use NetworkX as you normally would, but with the added benefit of persisting your graphs to a database.
```python
import os
import networkx as nx
import nx_arangodb as nxadb
os.environ["DATABASE_HOST"] = "http://localhost:8529"
os.environ["DATABASE_USERNAME"] = "root"
os.environ["DATABASE_PASSWORD"] = "openSesame"
os.environ["DATABASE_NAME"] = "_system"
G = nxadb.Graph(name="MyGraph")
G.add_node(1, foo='bar')
G.add_node(2, bar='foo')
G.add_edge(1, 2, weight=2)
res = nx.pagerank(G)
for k, v in res.items():
G.nodes[k]['pagerank'] = v
```
## Does this mean I need to learn ArangoDB?
No. You can use `nx-arangodb` without knowing anything about ArangoDB. The UX of `nx-arangodb` is designed to be as close as possible to the UX of NetworkX. See the ReadTheDocs for a list of features that are currently unsupported/in-development.
```python
import os
import networkx as nx
import nx_arangodb as nxadb
# os.environ ...
# Re-connect to the graph
G = nxadb.Graph(name="MyGraph")
assert G.number_of_nodes() == 2
assert G.number_of_edges() == 1
```
## How do I install it?
```bash
pip install nx-arangodb
```
### What if I want to use nx-cuGraph with it?
```bash
pip install nx-cugraph-cu12 --extra-index-url https://pypi.nvidia.com
pip install nx-arangodb
```
## How can I set up ArangoDB?
**1) Local Instance via Docker**
Appears on `localhost:8529` with the user `root` & password `openSesame`.
More info: [arangodb.com/download-major](https://arangodb.com/download-major/).
```bash
docker run -e ARANGO_ROOT_PASSWORD=openSesame -p 8529:8529 arangodb/arangodb
```
**2) ArangoDB Cloud Trial**
[ArangoGraph](https://dashboard.arangodb.cloud/home) is ArangoDB’s Cloud offering to use ArangoDB as a managed service.
A 14-day trial is available upon sign up.
**3) Temporary Cloud Instance via Python**
A temporary cloud database can be provisioned using the [adb-cloud-connector](https://github.com/arangodb/adb-cloud-connector?tab=readme-ov-file#arangodb-cloud-connector) python package.
```python
# !pip install adb-cloud-connector
import os
from adb_cloud_connector import get_temp_credentials
credentials = get_temp_credentials()
os.environ["DATABASE_HOST"] = credentials["url"]
os.environ["DATABASE_USERNAME"] = credentials["username"]
os.environ["DATABASE_PASSWORD"] = credentials["password"]
os.environ["DATABASE_NAME"] = credentials["dbName"]
# ...
```
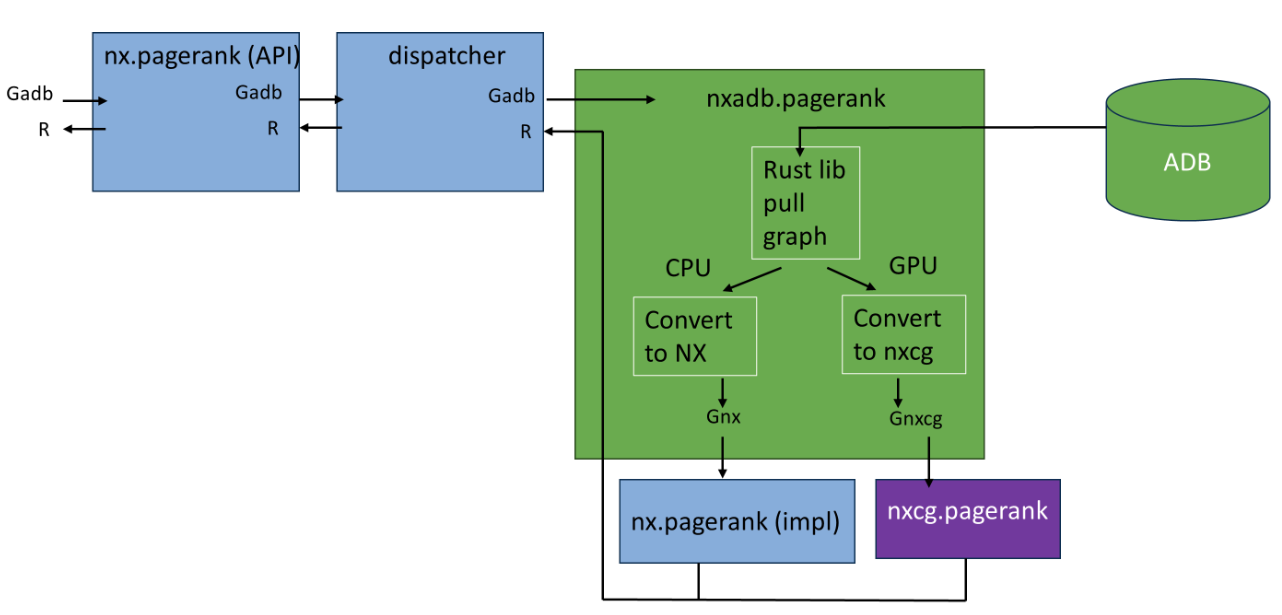
## How does algorithm dispatching work?
`nx-arangodb` will automatically dispatch algorithm calls to either CPU or GPU based on if [nx-cugraph](https://rapids.ai/nx-cugraph/) is installed. We rely on a rust-based library called [phenolrs](https://github.com/arangoml/phenolrs) to retrieve ArangoDB Graphs as fast as possible.
You can also force-run algorithms on CPU even if `nx-cugraph` is installed:
```python
import os
import networkx as nx
import nx_arangodb as nxadb
# os.environ ...
G = nxadb.Graph(name="MyGraph")
# Option 1: Use Global Config
nx.config.backends.arangodb.use_gpu = False
nx.pagerank(G)
nx.betweenness_centrality(G)
# ...
nx.config.backends.arangodb.use_gpu = True
# Option 2: Use Local Config
nx.pagerank(G, use_gpu=False)
nx.betweenness_centrality(G, use_gpu=False)
```
## Can I create an ArangoDB Graph from an existing NetworkX Graph?
Yes, this is actually the recommended way to start using `nx-arangodb`:
```python
import os
import networkx as nx
import nx_arangodb as nxadb
# os.environ ...
G_nx = nx.karate_club_graph()
G_nxadb = nxadb.Graph(
incoming_graph_data=G_nx,
name="MyKarateGraph"
)
assert G_nxadb.number_of_nodes() == G_nx.number_of_nodes()
assert G_nxadb.number_of_edges() == G_nx.number_of_edges()
```


