https://github.com/archo5/hlsloptconv
HLSL optimizing converter
https://github.com/archo5/hlsloptconv
compiler glsl glsl-shader hlsl optimizer shader transpiler
Last synced: 24 days ago
JSON representation
HLSL optimizing converter
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/archo5/hlsloptconv
- Owner: archo5
- License: mit
- Created: 2018-01-15T08:26:12.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2018-09-08T20:01:01.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-18T19:40:56.697Z (about 1 month ago)
- Topics: compiler, glsl, glsl-shader, hlsl, optimizer, shader, transpiler
- Language: C++
- Size: 271 KB
- Stars: 22
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 4
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
## HLSL Optimizing Converter
#### What is it?
This compiler takes HLSL 3.0/4.0 shader code and converts it to one of the following output formats:
* HLSL 3.0
* HLSL 4.0
* GLSL 1.40
* GLSL ES 1.0 (for WebGL 1)
It has an extensive test suite, including a [HTML5 WebGL 1 demo](http://archo.work/html5-hlsloptconvtest.htm) using a shader that has been compiled from HLSL, and a "four API test" for Windows featuring D3D9, D3D11, GL2 and GL3.1 running the same shader simultaneously:
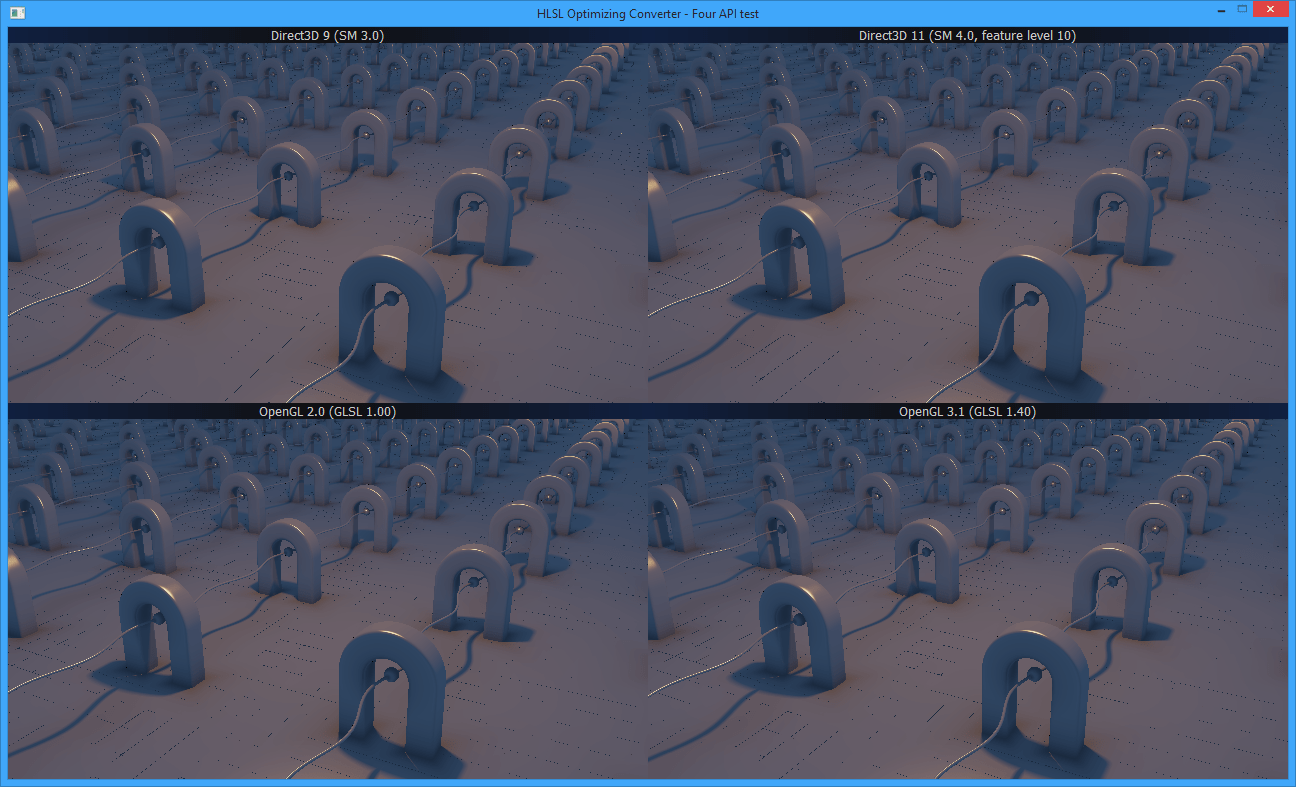
The main test suite checks most converted code with `glslangValidator` as well as does a before/after comparison with `fxc`, the DirectX shader compiler, to make sure that the meaning of the code is not lost in translation.
#### Features:
* Built-in preprocessor
* Built-in validator (variable access, casts, overload resolution etc.)
* Basic constant propagation
* Removal of unused functions, branches and variables
#### What is missing (and may or may not appear later)?
* Parsing support for the following intrinsics: `frexp`, `lit`, `modf`, `noise`, `sincos`, `transpose`
* Non-square matrix emulation for GLSL ES 1.0
* Array emulation for GLSL ES 1.0
* Geometry shader support
* Validation of certain syntax constructs such as register notation
* Incomplete cbuffer packoffset support
#### Important notes:
* To compile HLSL SM4 shaders generated by this library, use `d3dcompiler_43.dll` or newer. Older versions do not support non-numeric return values needed for sampler emulation.
#### Other differences from HLSL 3.0:
* `static [const]` requires an initialization expression, but it is disallowed to have one for just `const` or other types. This is to avoid creating constants that are not actually initialized in the shader, but just look like they might be.
* `tex1D/tex2D/tex3D/texCUBE` overloads that work same as their `*grad` versions are not recognized.
* Shadow/comparison samplers and intrinsics from newer specifications have been added:
* `sampler1Dcmp`, `sampler2Dcmp`, `samplerCUBEcmp` - comparison sampler types
* `tex*[lod0]cmp` intrinsics - sample the red channel of sampler `s` using coordinates `c`, compare each sampled value using sampler's comparison settings and reference value `z` before filtering. The `lod0` variant limits sampling to the first level of detail (overriding sampler's mipmapping settings).
* `tex1Dcmp(sampler1Dcmp s, float c, float z)`
* `tex1Dlod0cmp(sampler1Dcmp s, float c, float z)`
* `tex2Dcmp(sampler2Dcmp s, float2 c, float z)`
* `tex2Dlod0cmp(sampler2Dcmp s, float2 c, float z)`
* `texCUBEcmp(samplerCUBEcmp s, float3 c, float z)`
* `texCUBElod0cmp(samplerCUBEcmp s, float3 c, float z)`
* `mod` from GLSL is also supported, since it differs from HLSL's `fmod` and has certain use cases.
#### Inherent incompatibilities between shader languages/APIs:
* `pow` intrinsic has different (reduced) output guarantees when converted to GLSL (do not use with `x < 0`).
* [`sampler1D`, `tex1D`] are converted to [`sampler2D`, `texture2D`] for GLSL ES 1.0 (there are no 1D textures).
* `tex3D*` intrinsics are not supported for GLSL ES 1.0 (there are no 3D textures).
* Floating point `%` (modulus) works differently in GLSL than in HLSL (see differences.md), though the main guarantee (defined values when both signs are equal) still holds.
* Storage addressing features are often incompatible. It is the responsibility of the user to link attributes by semantic/name and uniforms or buffers to their slots where the shader cannot, using the data provided.
#### Other planned improvements:
* removal of STL to improve compile times (~80% done)
* improved optimization capabilities