https://github.com/asahi417/lm-vocab-trimmer
Vocabulary Trimming (VT) is a model compression technique, which reduces a multilingual LM vocabulary to a target language by deleting irrelevant tokens from its vocabulary. This repository contains a python-library vocabtrimmer, that remove irrelevant tokens from a multilingual LM vocabulary for the target language.
https://github.com/asahi417/lm-vocab-trimmer
bert gpt language-model model-compression nlp t5
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Vocabulary Trimming (VT) is a model compression technique, which reduces a multilingual LM vocabulary to a target language by deleting irrelevant tokens from its vocabulary. This repository contains a python-library vocabtrimmer, that remove irrelevant tokens from a multilingual LM vocabulary for the target language.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/asahi417/lm-vocab-trimmer
- Owner: asahi417
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-02-25T13:24:18.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-10-25T14:41:43.000Z (8 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-12-06T22:37:55.887Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: bert, gpt, language-model, model-compression, nlp, t5
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 17.4 MB
- Stars: 32
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
[](https://github.com/asahi417/lm-vocab-trimming/blob/master/LICENSE)
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/vocabtrimmer)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/vocabtrimmer/)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/vocabtrimmer/)
# Vocabulary Trimming
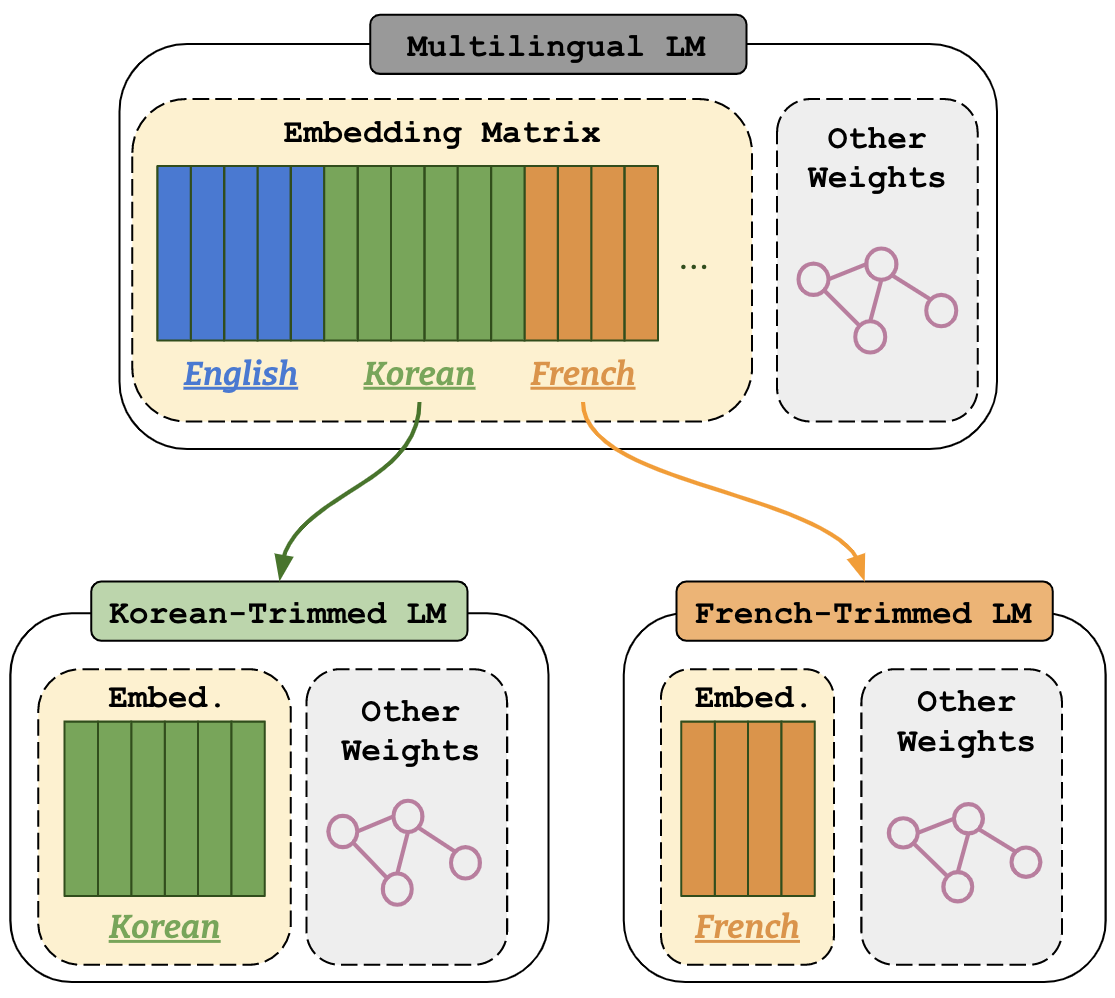
Figure 1: An illustration of vocabulary trimming to Korean and French.
[***Vocabulary Trimming (VT)***](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.15020) is a model compression technique, which reduces a multilingual LM vocabulary to a
target language by deleting irrelevant tokens from its vocabulary (see Figure 1).
This repository contains a python-library `vocabtrimmer`, that remove irrelevant tokens from a multilingual LM vocabulary for the target language.
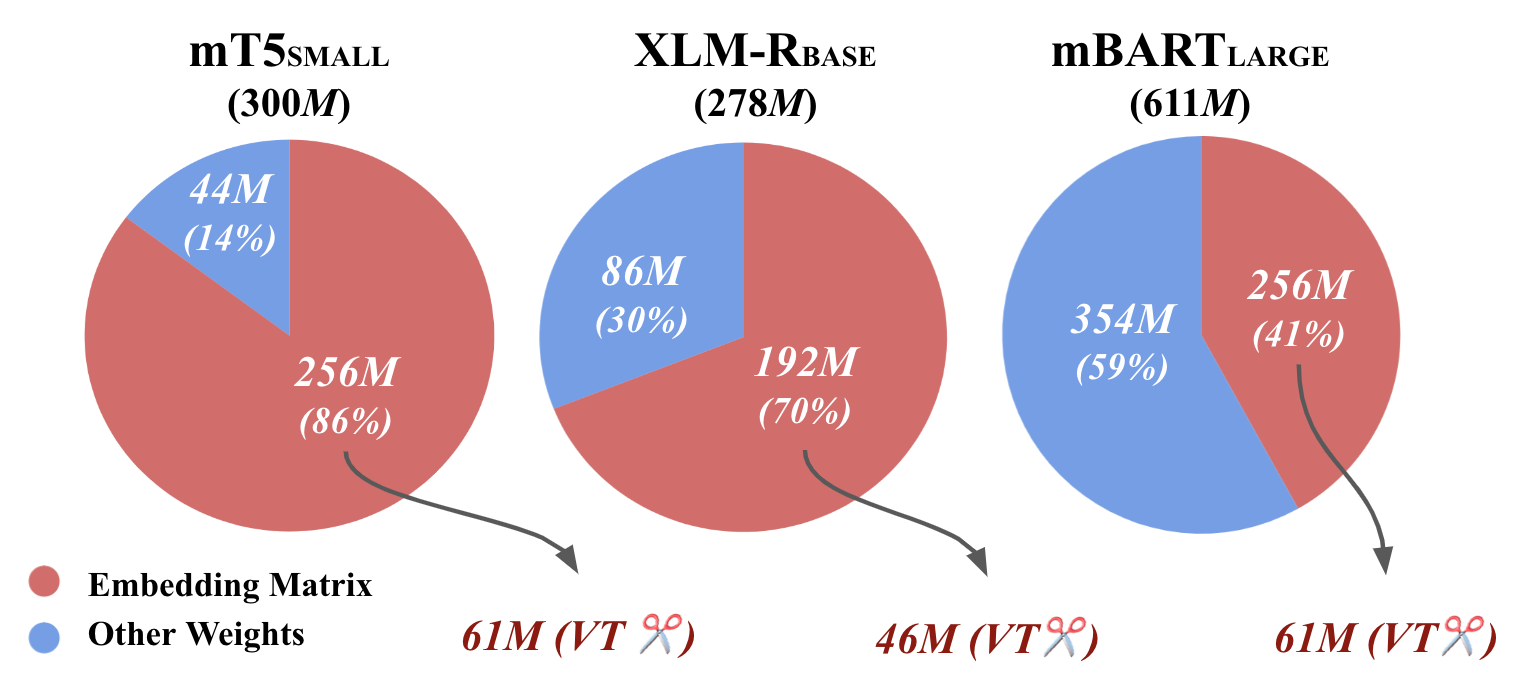
Figure 2: The ratio of the embedding matrix to the number of entire model parameters for each of multilingual LMs and the embedding matrix after VT with top-60 vocabulary.
The motivation behind VT is that a multilingual LM has a huge vocabulary to cover all languages, that results in a large model size (see Figure 2).
However, we don't need the bulk of those vocabularies, when we fine-tune the multilingual LM on a monolingual task in practice. Hence,
we can delete such un-used vocabularies to reduce the model size.
In theory, VT can compress any existing multilingual LM to build monolingual LMs in any language covered by the multilingual LM.
In our experiments, we show that VT can retain the original performance of the multilingual LM, while being smaller in size
(in general around 50% of the original vocabulary size is enough) than the original multilingual LM.
The evaluation is performed over four NLP tasks (two generative and two classification tasks) among four widely used multilingual
LMs in seven languages. Finally, we show that this methodology can keep the best of both monolingual and multilingual
worlds by keeping a small size as monolingual models without the need for specifically retraining them, and even
limiting potentially harmful social biases. Please check those experimental results as wel as the technical detail in our paper,
["An Efficient Multilingual Language Model Compression through Vocabulary Trimming, 2023,"](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.15020). To reproduce the results in our paper, please check [here](https://github.com/asahi417/lm-vocab-trimmer/tree/main/experiments).
**NEWS:** Our paper ["An Efficient Multilingual Language Model Compression through Vocabulary Trimming, 2023,"](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.15020) got accepted by findings of [EMNLP 2023](https://2023.emnlp.org/).
## Get Started 🚀
Let's install `lmqg` via pip first.
```shell
pip install vocabtrimmer
```
## Vocabulary Trimming with `vocabtrimmer`
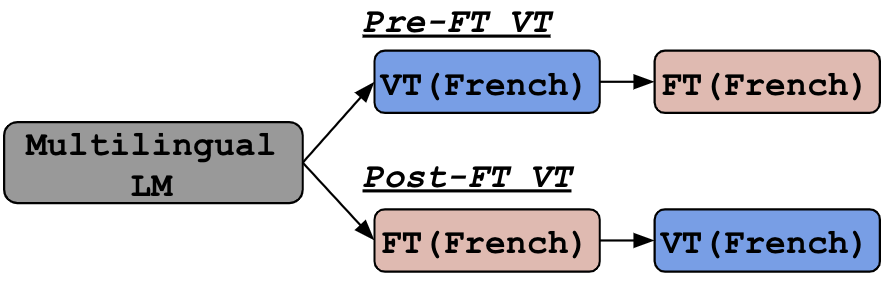
Figure 3: Comparisons of Pre-FT vs Post-FT in an example of fine-tuning on a task in French.
As a default, VT relies on [mC4](https://huggingface.co/datasets/vocabtrimmer/mc4_validation), to find a set of language-specific
tokens and the frequency of each token.
The practical usage of VT is to apply it to a multilingual LM before fine-tuning (pre-FT VT) or after fine-tuning (post-FT VT).
Both should work well in general, but post-VT is more robust and it suits, if you already have a model as no additional training is required.
Otherwise, pre-FT VT would be an option as it could reduce the time to fine-tune the model.
See the comparison of pre/post-FT VT in our [paper]([paper-link](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.1502)).
### VT in Command-Line
The `vocabtrimmer` provides following command-line interface to trim a multilingual LM vocabulary.
```bash
vocabtrimmer-trimming -m MODEL -l LANGUAGE -p PATH_TO_SAVE [-v TARGET_VOCAB_SIZE] [--repo-id REPO_ID]
arguments:
-m, --model, model name on huggingface or path to local model
-l, --language, language code of tokens to keep
-p, --path-to-save, directly to save model
-v, --target-vocab-size, [optinoal] vocab size after mining
--repo-id, [optinoal] huggingface repo id to push after trimming
```
Following command trims the vocabulary of `google/mt5-small` to French with top-60k vocabulary.
```bash
vocabtrimmer-trimming -m "google/mt5-small" -l "fr" -v 60000 -p "ckpts/mt5-small-trimmed-fr-60000"
```
The vocabulary size of multilingual LMs is usually 250k (XLM-R, mBART, mT5), and we recommend setting the target vocabulary size to 60k,
the effective vocabulary size. Less vocabulary size than 60k may cause performance degradation, but can retain the original performance in some cases
(check our [paper](paper-link)). If the target vocabulary size is not specified, it will use whole vocabulary that is appeared in the mC4 dataset or the specified target corpus.
### VT in Python
The `vocabtrimmer` provides an API to trim a multilingual LM via python.
Following command trims the vocabulary of `google/mt5-small` to French with top-60k vocabulary.
```python
import vocabtrimmer
trimmer = vocabtrimmer.VocabTrimmer("google/mt5-small")
trimmer.trim_vocab(
path_to_save="ckpts/mt5-small-trimmed-fr-60000",
language="fr",
target_vocab_size=60000)
```
## Citation
Please cite following paper if you use any resource and see the code to reproduce the model if needed.
```
@inproceedings{ushio2023efficient,
title = "An Efficient Multilingual Language Model Compression through Vocabulary Trimming",
author = "Ushio, Asahi and
Zhou, Yi and
Camacho-Collados, Jose",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP): Findings",
month = Dec,
year = "2023",
address = "",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
}
```