https://github.com/assertible/deployments
Configurations for GitHub post-deployment testing with Assertible via CI
https://github.com/assertible/deployments
api-testing ci-automation circleci continuous-integration continuous-testing delivery-pipeline deployments testing travis-ci wercker
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Configurations for GitHub post-deployment testing with Assertible via CI
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/assertible/deployments
- Owner: assertible
- License: mit
- Created: 2016-07-08T01:37:58.000Z (over 9 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2017-05-06T01:57:08.000Z (almost 9 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-07-20T06:44:11.916Z (8 months ago)
- Topics: api-testing, ci-automation, circleci, continuous-integration, continuous-testing, delivery-pipeline, deployments, testing, travis-ci, wercker
- Homepage: https://assertible.com
- Size: 47.9 KB
- Stars: 13
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 7
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- jimsghstars - assertible/deployments - Configurations for GitHub post-deployment testing with Assertible via CI (Others)
README
Continuously test your web services
Post-deployment testing with Assertible
Assertible **extends your CI pipeline** to provide **automated
post-deployment API testing**. This repo will show you how to run
integration tests against your web app after deploying from CI.
_Don't have an Assertible account
yet? [Sign up for free](https://assertible.com/signup)._
## How it works
1. [Send a _deployment_ to the Assertible API](#send-a-deployment-to-the-assertible-api)
2. [View the result in a GitHub status check](#view-the-result-in-a-github-status-check) _(optional)_
Start by sending a deployment to
the [Assertible API](https://assertible.com/docs/guide/deployments)
after you deploy your app from CI. This will **initiate integration
tests** to run on your live web app, and reports any test failures.
When
you
[connect Assertible to a GitHub repo](#view-the-result-in-a-github-status-check),
the post deployment test results will show as a **status check** on
your commits and pull requests.
### Send a deployment to the Assertible API
The [Deployments API](https://assertible.com/docs/guide/deployments)
is used to **run integration tests** on your app after a deployment.
Tests can be run on different environments, like `staging` or `qa`, by
making a simple `POST` request:
```sh
curl -u $ASSERTIBLE_TOKEN: -XPOST "https://assertible.com/deployments" -d'{
"service": "'"${SERVICE}"'",
"environmentName": "'"${ENVIRONMENT}"'",
"version": "'"${VERSION}"'",
# Optional
"ref": "'"${COMMIT_ID}"'",
"github": true
}'
```
That's it! When you make that request, tests will be run against your
API to validate the new deployment.
Check out the [example configurations](#example-configurations) for
details on integrating the script with your CI/CD provider, like
TravisCI or Wercker.
### View the result in a GitHub status check
When you connect Assertible to a GitHub repo, status checks will be
shown for test results triggered by deployments. Setting up this part
is easy, just [sign in to Assertible](https://assertible.com/login),
and
[connect one of your web services to a repo](https://assertible.com/docs/guide/deployments#github).
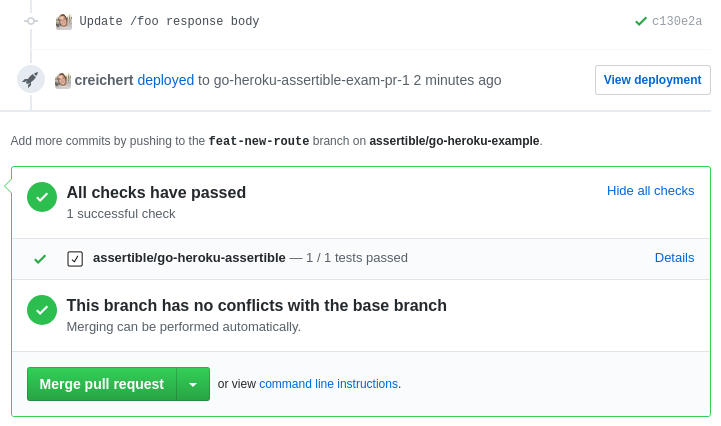
Assertible will send a status check to GitHub when
you
[send a deployment event to the API](#send-deployment-events-to-the-api). If
any of the tests fail, a failing status check will show on your
commits, and a passing status check will show if all tests pass.
## Example configurations
Below are some examples for integrating Assertible deployments with
various CI providers.
- [Heroku](#-heroku) ([website](https://heroku.com))
- [Travis CI](#-travis-ci) ([website](https://travis-ci.org))
- [Circle CI](#-circle-ci) ([website](https://circleci.com))
- [Wercker](#-wercker) ([website](http://www.wercker.com/))
- [Additional resources](#additional-resources)
- [Status badges!](#status-badges)
- [Example Projects](#example-projects)
##  Heroku
Heroku
If you're using Heroku Review Apps, this integration will work out of
the box with no additional
configuration. Just
[connect Assertible to a GitHub repo](#connect-to-a-repo) that has
Review Apps enabled, and open a PR. You should see a status check with
the result of your API tests. Learn how to enable this for your Heroku
app [here](https://devcenter.heroku.com/articles/github-integration)

##  Travis CI
Travis CI
> Note that the examples below assume that you have environment
> variables set. See
> the [environment variables section](#environment-variables).
If you deploy a website or API from Travis-CI (especially if you're
using the `deploy` or `after_success` steps), then it will be easy to
trigger a deployment event to run your Assertible tests. The sections
below describe some common use-cases:
**Sections**
- [Example `.travis.yml`](#example-travis-config)
- [Using the `after_deploy` step](#after_deploy)
- [Using `after_script` or `after_success`](#after_success)
### Example Travis config
You can see a runnable `.travis.yml` in the repo here:
- https://github.com/assertible/deployments/blob/master/.travis.yml
_Note: You can just copy the two lines below into your existing
configuration, if you have one. Otherwise, continue reading to
determine which setup will work best._
### `after_deploy`
If you use the [`deploy`](https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/deployment)
step in your Travis configuration then you can send a deployment event
from
the
[`after_deploy`](https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/customizing-the-build/#Deploying-your-Code) step,
like this:
```yaml
after_deploy:
- |
curl -u $ASSERTIBLE_TOKEN: -XPOST "https://assertible.com/deployments" -d'{
"service": "'"${ASSERTIBLE_SERVICE}"'",
"environmentName": "'"${ENVIRONMENT}"'",
"version": "'"${TRAVIS_COMMIT}"'",
"ref": "'"${TRAVIS_COMMIT}"'",
"github": true
}'
```
### `after_success`
If your `.travis.yml` runs a deployment during the
[`after_success`](https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/customizing-the-build/#The-Build-Lifecycle)
step, then you have two options:
- Add the following lines to the end of your existing `after_success`
script, or
- Copy the following lines to the `after_script` step in your
`.travis.yml`.
Example in the `after_script` step:
```yaml
after_script:
- |
curl -u $ASSERTIBLE_TOKEN: -XPOST "https://assertible.com/deployments" -d'{
"service": "'"${ASSERTIBLE_SERVICE}"'",
"environmentName": "'"${ENVIRONMENT}"'",
"version": "'"${TRAVIS_COMMIT}"'",
"ref": "'"${TRAVIS_COMMIT}"'",
"github": true
}'
```
Read more about `after_success`
step [here](https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/customizing-the-build/)
##  Circle CI
Circle CI
> Note that the examples below assume that you have environment
> variables set See
> the [environment variables section](#environment-variables).
If you deploy a website or API from Circle CI (especially if you're
using the `deployment` step), then it will be easy to trigger a
deployment event to run your integration tests. The sections below
describe the most common use-cases:
**Sections**
- [Example `circle.yml`](#example-circleci-config)
- [Using the `deployment` step](#deployment)
### Example CircleCI config
You can see a runnable `circle.yml` in the repo here:
- https://github.com/assertible/deployments/blob/master/circle.yml
### `deployment`
If your `circle.yml` runs a
[`deployment`](https://circleci.com/docs/configuration/#deployment)
step, add the following lines to the end of the `commands` section:
```yaml
deployment:
production:
branch: master
commands:
# - deploy your app normally here
- |
curl -u $ASSERTIBLE_TOKEN: -XPOST "https://assertible.com/deployments" -d'{
"service": "'"${ASSERTIBLE_SERVICE}"'",
"environmentName": "'"${ENVIRONMENT}"'",
"version": "'"${CIRCLE_SHA1}"'",
"ref": "'"${CIRCLE_SHA1}"'",
"github": true
}'
```
Read more about `deployment` step here:
https://circleci.com/docs/configuration/#deployment
##  Wercker
Wercker
> Note that the examples below assume that you have environment
> variables set See
> the [environment variables section](#environment-variables).
If you deploy your API or website from Wercker (especially if you're
using the `deployment` step), then it will be easy to run integration
tests after a deployment. The sections below describe the most common
workflows:
**Sections**
- [Example `wercker.yml`](#example-wercker-config)
- [Using the `deployment` step](#deploy-step)
### Example Wercker config
You can see a runnable `wercker.yml` in the
repo
[here](https://github.com/assertible/deployments/blob/master/wercker.yml).
### `deploy` step
If your `wercker.yml` runs
a [`deployment`](http://old-devcenter.wercker.com/articles/deployment/)
step, add the following lines as the very last step in a `script`:
```yaml
deploy:
steps:
# This is where you would normally run your deployment. Right
# after this, we will tell Assertible about the deployment, and
# tests will be run against the app.
- script:
code:
- |
curl -u $ASSERTIBLE_TOKEN: -XPOST "https://assertible.com/deployments" -d'{
"service": "'"${ASSERTIBLE_SERVICE}"'",
"environmentName": "'"${ENVIRONMENT}"'",
"version": "'"${WERCKER_GIT_COMMIT}"'",
"ref": "'"${WERCKER_GIT_COMMIT}"'",
"github": true
}'
```
Read more about `deployment`
step [here](http://old-devcenter.wercker.com/articles/deployment/).
## Environment variables
The examples above assume you have some environment variables set:
- `ASSERTIBLE_TOKEN`
- `ASSERTIBLE_SERVICE`
You can get this information from the _Deployments_ tab of your web
service in
the [Assertible dashboard](https://assertible.com/dashboard).
### Travis CI
Set these environment variables in
your
[Travis-CI repository settings](https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/environment-variables/#Defining-Variables-in-Repository-Settings).
### CircleCI CI
Set these environment variables in
your
[Circle CI repository settings](https://circleci.com/docs/environment-variables/).
### Wercker
Set these environment variables in
your
[Wercker project settings](http://devcenter.wercker.com/docs/environment-variables/creating-env-vars).
## Additional resources
These links provide more information on the underlying technology and
services that make this work:
- [Assertible - Getting Started](https://assertible.com/docs)
- [Setting up Assertible and GitHub Deployments](https://assertible.com/docs#github-deployments)
- [Deployments API documentation](https://assertible.com/docs/guide/deployments)
**Alternatives**
Sometimes you don't use GitHub, or sending deployment events isn't
always possible. Assertible also supports a standalone Trigger URL
that you can use to run your tests from outside the Assertible
dashboard. For more information, see
the [documentation](https://assertible.com/docs#trigger-url)
## Status Badges
Assertible
has [status badges](https://assertible.com/docs#test-badges) for your
web services and tests to display the current state of your
application. The badges can be retrieved from within
your [Assertible dashboard](https://assertible.com/login). Here's what
they look like:
[](https://assertible.com/docs/guide/web-services#web-service-badges)
Nice! Pick yours up today and add it to your repository -- or learn
more in the [documentation](https://assertible.com/docs#test-badges)
## Example projects
There are some open source projects using Assertible with this
configuration; if you're a visual learner then one of these might be
helpful:
- [Node.js example app](https://github.com/assertible/nodejs-example)
This repo provides an example of a complete continuous integration,
deployment, and post-deployment testing pipeline using a Node.js example
app. [Check out the tutorial](https://assertible.com/blog/set-up-continuous-testing-with-nodejs)
- [Ruby API example](https://github.com/assertible/ruby-example)
This is an example of an automated post-deployment testing pipeline
on staging and production environments, with a sample Ruby API.
The project uses Codehsip, Heroku, and assertible.
- [Go API example on Heroku](https://github.com/assertible/go-heroku-example) This
example uses a Go API that is deployed to Heroku and Review
Apps. Since Heroku apps work out-of-the-box, there's no need for a
script. [Check out the blog post](https://assertible.com/blog/automate-smoke-tests-for-a-go-api-on-heroku)
- [reichertbrothers.com](https://github.com/rbros/rbros.github.io)
reichertbrothers.com is the website for a Haskell consulting
company. The website is deployed to GitHub Pages from a Travis-CI
build. Once the site has been successfuly deployed, a deployment
event is triggered and Assertible's post-deployment tests will run.
- [CheckAFlip](http://checkaflip.com)
CheckAFlip is a tool for quickly learning the best price at which to
buy or sell any item. The app is deployed from Heroku and, after
deploying, Heroku sends a deployment success event and Assertible
test's get run.
_Have an open source project using Assertible for post deployment
testing? Open a PR to add it to the list, or open an issue!_
## License
All of the code snippets in this repository are licensed under
MIT. [View the license](https://github.com/assertible/deployments/blob/master/LICENSE)
---
> [assertible.com](http://assertible.com) ·
> GitHub [@assertible](https://github.com/assertible) ·
> Twitter [@AssertibleApp](https://twitter.com/AssertibleApp)

