https://github.com/asyml/fortehealth
The project is in the incubation stage and still under development. ForteHealth is a flexible and powerful ML workflow builder for biomedical and clinical scenarios. This is part of the CASL project: http://casl-project.ai/
https://github.com/asyml/fortehealth
biomedical-named-entity-recognition clinical-nlp clinical-text-processing data-processing deep-learning information-retrieval machine-learning natural-language natural-language-processing python
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
The project is in the incubation stage and still under development. ForteHealth is a flexible and powerful ML workflow builder for biomedical and clinical scenarios. This is part of the CASL project: http://casl-project.ai/
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/asyml/fortehealth
- Owner: asyml
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2022-02-04T06:08:44.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-03-22T01:41:39.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-18T00:57:54.842Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: biomedical-named-entity-recognition, clinical-nlp, clinical-text-processing, data-processing, deep-learning, information-retrieval, machine-learning, natural-language, natural-language-processing, python
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.98 MB
- Stars: 12
- Watchers: 10
- Forks: 5
- Open Issues: 21
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
Download •
Quick Start •
Contribution Guide •
License •
Documentation •
Publication
-----------------
**ForteHealth is in the incubation stage and still under development**
**Bring good software engineering to your Biomedical/Clinical ML solutions, starting from Data!**
**ForteHealth** is a biomedical and clinical domain centric framework designed to engineer complex ML workflows for several tasks including, but not limited to, Medical Entity Recognition, Negation Context Analysis and ICD Coding. ForteHealth allows practitioners to build ML components in a composable and modular way. It works in conjunction with Forte and Forte-wrappers project, and leverages the tools defined there to execute general tasks vital in the biomedical and clinical use cases.
## Installation
To install from source:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/asyml/ForteHealth.git
cd ForteHealth
pip install .
```
To install some Forte adapter for some existing [libraries](https://github.com/asyml/forte-wrappers#libraries-and-tools-supported):
Install from PyPI:
```bash
pip install forte.health
```
Some tools are pre-requisites to a few tasks in our pipeline. For example, forte.spacy and stave maybe needed
for a pipeline that implements NER with visualisation and so on, depending on the use case.
```bash
# To install other tools. Check here https://github.com/asyml/forte-wrappers#libraries-and-tools-supported for available tools.
pip install forte.spacy
pip install stave
```
Some components or modules in forte may require some [extra requirements](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/setup.py#L45):
Install ScispaCyProcessor:
```bash
pip install 'forte.health[scispacy_processor]'
```
Install TemporalNormalizingProcessor:
```bash
pip install 'forte.health[normalizer_processor]'
```
## Quick Start Guide
Writing biomedical NLP pipelines with ForteHealth is easy. The following example creates a simple pipeline that analyzes the sentences, tokens, and medical named entities from a discharge note.
Before we start, make sure the SpaCy wrapper is installed.
Also, make sure you have input text files in the ```input_path``` directory that are passed through to the processors.
```bash
pip install forte.spacy
```
Let's look at an example of a full fledged medical pipeline:
```python
from fortex.spacy import SpacyProcessor
from forte.data.data_pack import DataPack
from forte.data.readers import PlainTextReader
from forte.pipeline import Pipeline
from ft.onto.base_ontology import Sentence, EntityMention
from ftx.medical.clinical_ontology import NegationContext, MedicalEntityMention
from fortex.health.processors.negation_context_analyzer import (
NegationContextAnalyzer,
)
pl = Pipeline[DataPack]()
pl.set_reader(PlainTextReader())
pl.add(SpacyProcessor(), config={
"processors": ["sentence", "tokenize", "pos", "ner", "umls_link"],
"medical_onto_type": "ftx.medical.clinical_ontology.MedicalEntityMention",
"umls_onto_type": "ftx.medical.clinical_ontology.UMLSConceptLink",
"lang": "en_ner_bc5cdr_md"
})
pl.add(NegationContextAnalyzer())
pl.initialize()
```
Here we have successfully created a pipeline with a few components:
* a `PlainTextReader` that reads data from text files, given by the `input_path`
* a `SpacyProcessor` that calls SpaCy to split the sentences, create tokenization,
pos tagging, NER and umls_linking
* finally, the processor `NegationContextAnalyzer` detects negated contexts
Let's see it run in action!
```python
for pack in pl.process_dataset(input_path):
for sentence in pack.get(Sentence):
medical_entities = []
for entity in pack.get(MedicalEntityMention, sentence):
for ent in entity.umls_entities:
medical_entities.append(ent)
negation_contexts = [
(negation_context.text, negation_context.polarity)
for negation_context in pack.get(NegationContext, sentence)
]
print("UMLS Entity Mentions detected:", medical_entities, "\n")
print("Entity Negation Contexts:", negation_contexts, "\n")
```
We have successfully created a simple pipeline. In the nutshell, the `DataPack`s are
the standard packages "flowing" on the pipeline. They are created by the reader, and
then pass along the pipeline.
Each processor, such as our `SpacyProcessor` `NegationContextAnalyzer`,
interfaces directly with `DataPack`s and do not need to worry about the
other part of the pipeline, making the engineering process more modular.
The above mentioned code snippet has been taken from the [Examples](https://github.com/asyml/ForteHealth/tree/master/examples/mimic_iii) folder.
To learn more about the details, check out of [documentation](https://asyml-forte.readthedocs.io/)!
The classes used in this guide can also be found in this repository or
[the Forte Wrappers repository](https://github.com/asyml/forte-wrappers/tree/main/src/spacy)
## And There's More
The data-centric abstraction of Forte opens the gate to many other opportunities.
Go to [this](https://github.com/asyml/forte#and-theres-more) link for more information
To learn more about these, you can visit:
* [Examples](https://github.com/asyml/ForteHealth/tree/master/examples)
* [Documentation](https://asyml-forte.readthedocs.io/)
* Currently we are working on some interesting [tutorials](https://asyml-forte.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index_toc.html), stay tuned for a full set of documentation on how to do NLP with Forte!
## Contributing
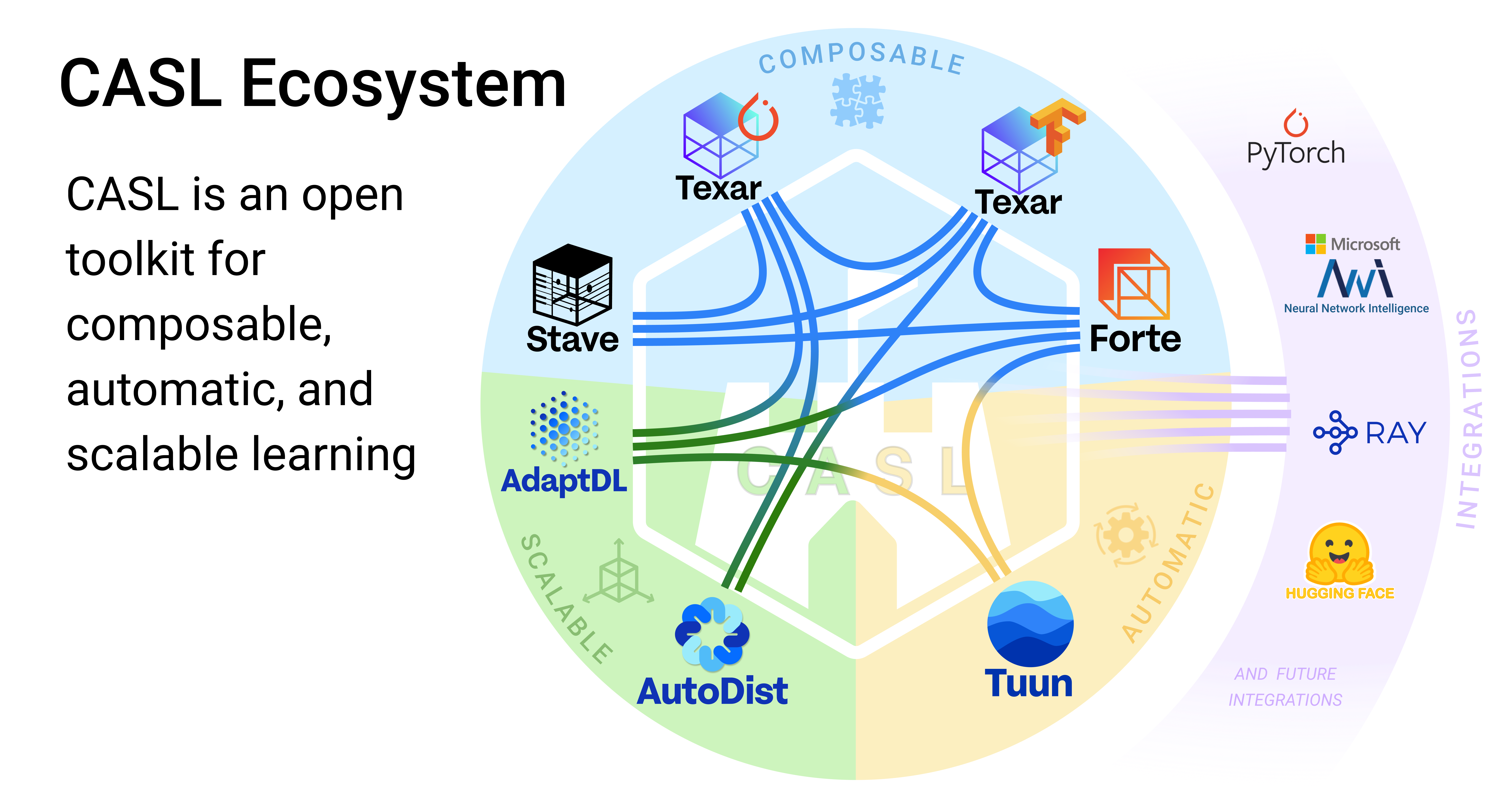
This project is part of the [CASL Open Source](http://casl-project.ai/) family.
If you are interested in making enhancement to Forte, please first go over our [Code of Conduct](https://github.com/asyml/ForteHealth/master/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md) and [Contribution Guideline](https://github.com/asyml/ForteHealth/master/CONTRIBUTING.md)
## About
### Supported By



### License
[Apache License 2.0](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/LICENSE)


