https://github.com/athackst/vscode_ros2_workspace
A template for using VSCode as an IDE for ROS2 development.
https://github.com/athackst/vscode_ros2_workspace
docker ros2 vscode workspace
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
A template for using VSCode as an IDE for ROS2 development.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/athackst/vscode_ros2_workspace
- Owner: athackst
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2020-08-11T01:15:04.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: humble
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-26T23:02:47.000Z (8 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-13T20:39:14.340Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: docker, ros2, vscode, workspace
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://althack.dev/vscode_ros2_workspace
- Size: 882 KB
- Stars: 912
- Watchers: 22
- Forks: 184
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-ai-robotics - **VSCode ROS2 Workspace Template** - This template will get you set up using ROS2 with VSCode as your IDE. (ROS2 / Dev Tools)
- awesome-robotic-tooling - VS Code ROS2 Workspace Template - Template for using VSCode as an IDE for ROS2 development. (Development Environment / Template)
README
# VSCode ROS2 Workspace Template
This template will get you set up using ROS2 with VSCode as your IDE.
See [how I develop with vscode and ros2](https://www.allisonthackston.com/articles/vscode_docker_ros2.html) for a more in-depth look on how to use this workspace.
## Features
### Style
ROS2-approved formatters are included in the IDE.
* **c++** uncrustify; config from `ament_uncrustify`
* **python** autopep8; vscode settings consistent with the [style guide](https://docs.ros.org/en/humble/The-ROS2-Project/Contributing/Code-Style-Language-Versions.html)
### Tasks
There are many pre-defined tasks, see [`.vscode/tasks.json`](.vscode/tasks.json) for a complete listing. Feel free to adjust them to suit your needs.
Take a look at [how I develop using tasks](https://www.allisonthackston.com/articles/vscode_tasks.html) for an idea on how I use tasks in my development.
### Debugging
This template sets up debugging for python files, gdb for cpp programs and ROS launch files. See [`.vscode/launch.json`](.vscode/launch.json) for configuration details.
### Continuous Integration
The template also comes with basic continuous integration set up. See [`.github/workflows/ros.yaml`](/.github/workflows/ros.yaml).
To remove a linter just delete it's name from this line:
```yaml
matrix:
linter: [cppcheck, cpplint, uncrustify, lint_cmake, xmllint, flake8, pep257]
```
## How to use this template
### Prerequisites
You should already have Docker and VSCode with the remote containers plugin installed on your system.
* [docker](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/)
* [vscode](https://code.visualstudio.com/)
* [vscode remote containers plugin](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-vscode-remote.remote-containers)
### Get the template
Click on "use this template"
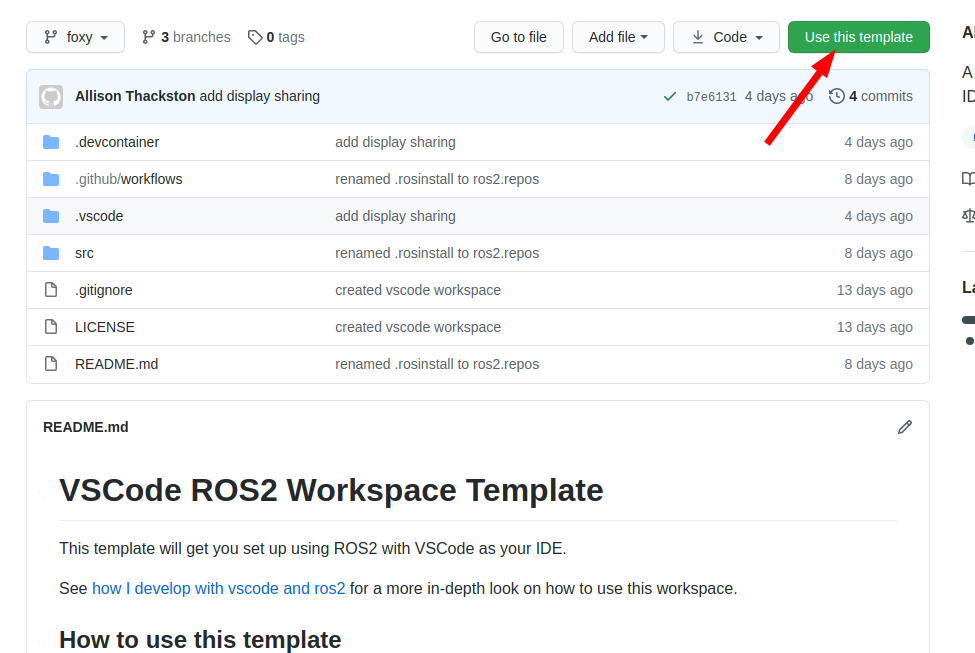
### Create your repository
On the next dialog, name the repository you would like to start and decide if you want all of the branches, or just the latest LTS: humble.
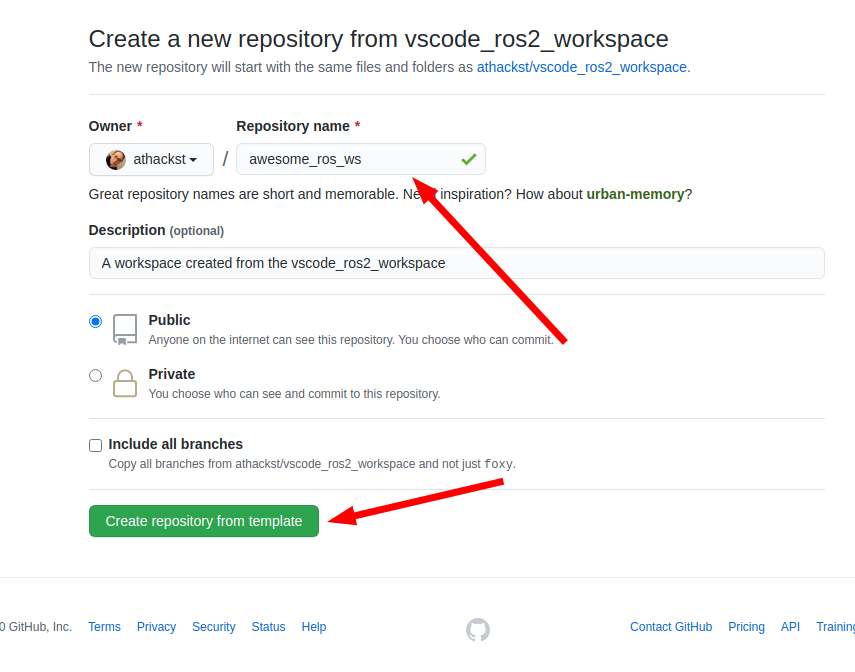
Github will then create a new repository with the contents of this one in your account. It grabs the latest changes as "initial commit".
### Clone your repo
Now you can clone your repo as normal
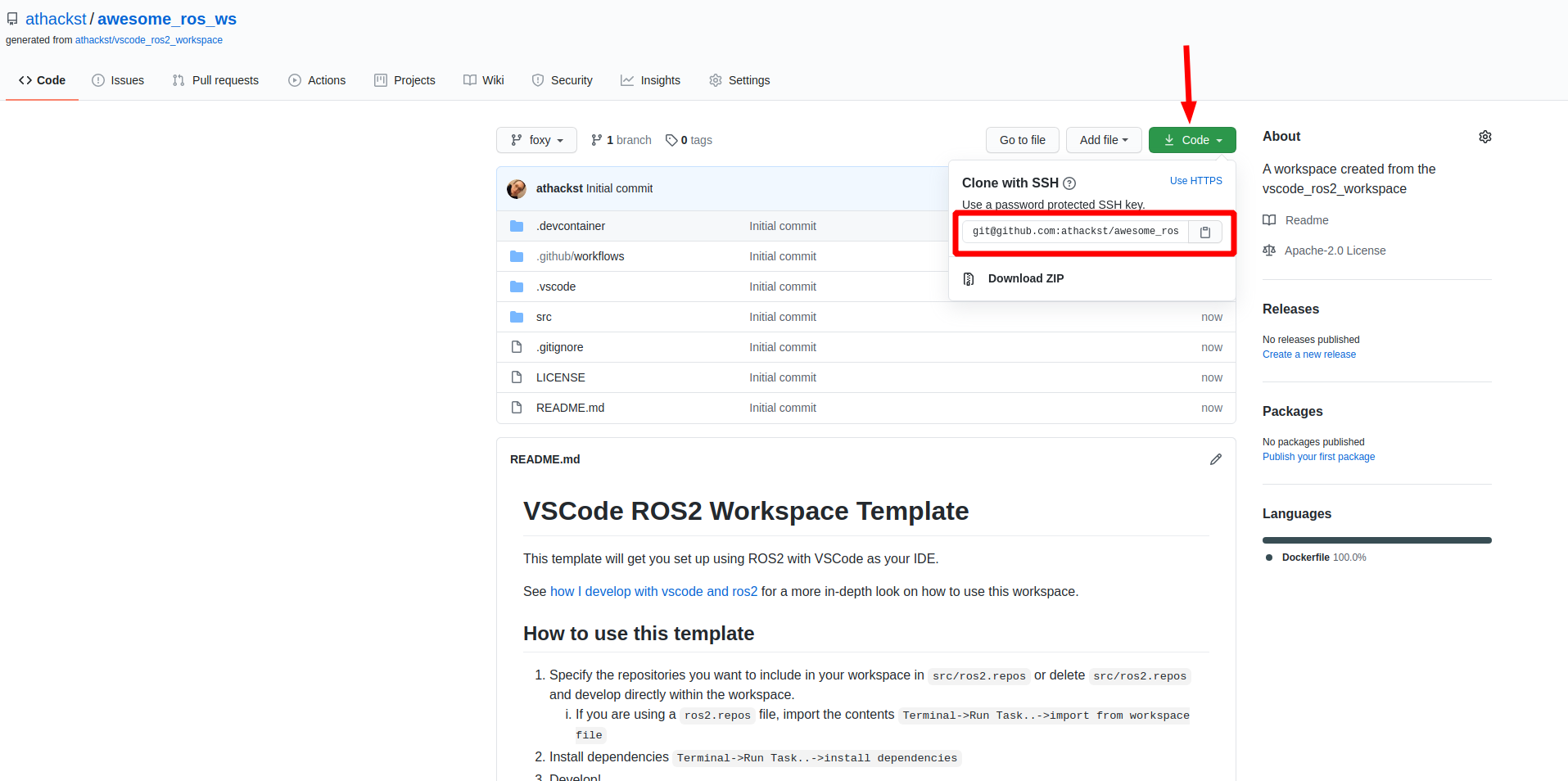
### Open it in vscode
Now that you've cloned your repo onto your computer, you can open it in VSCode (File->Open Folder).
When you open it for the first time, you should see a little popup that asks you if you would like to open it in a container. Say yes!
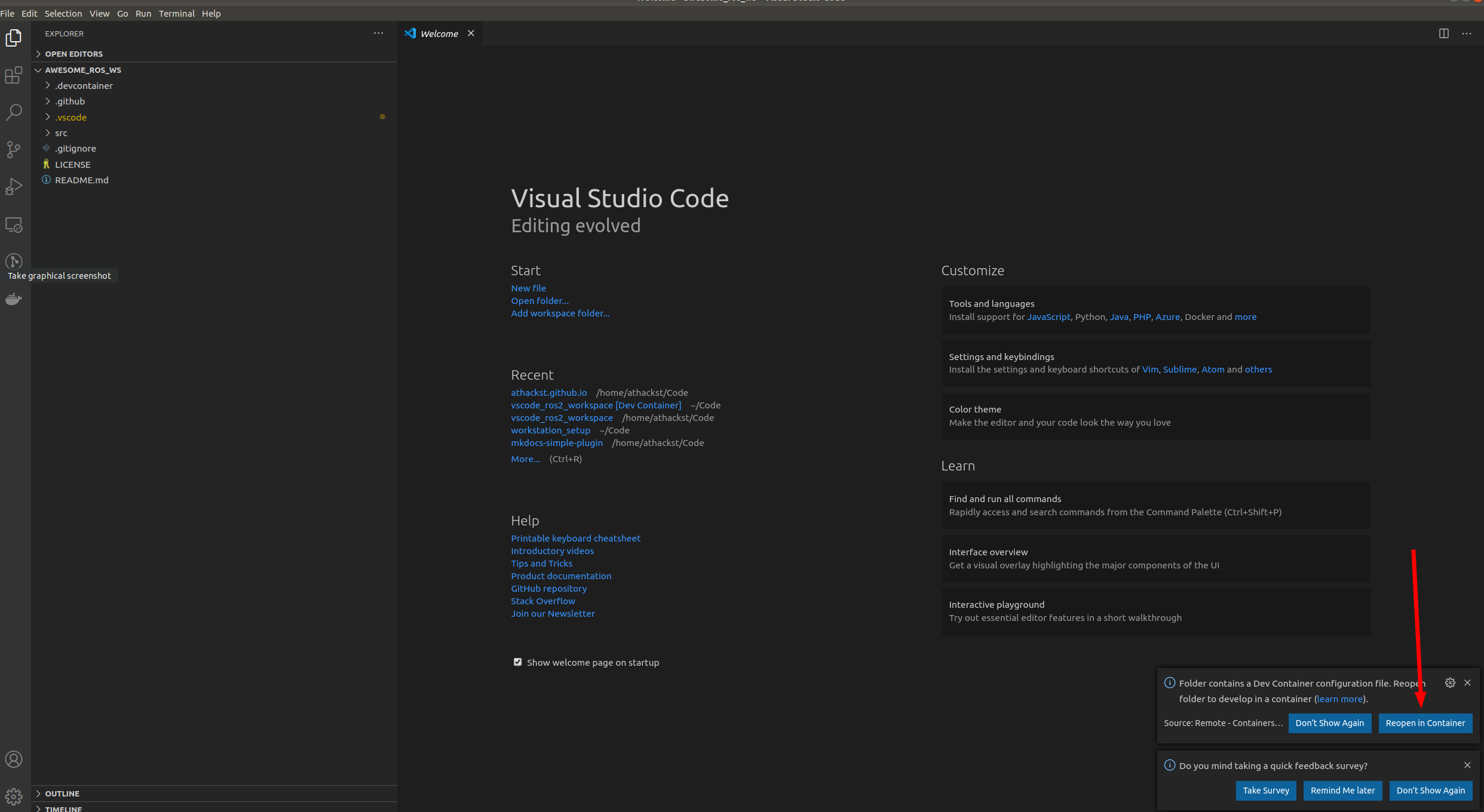
If you don't see the pop-up, click on the little green square in the bottom left corner, which should bring up the container dialog
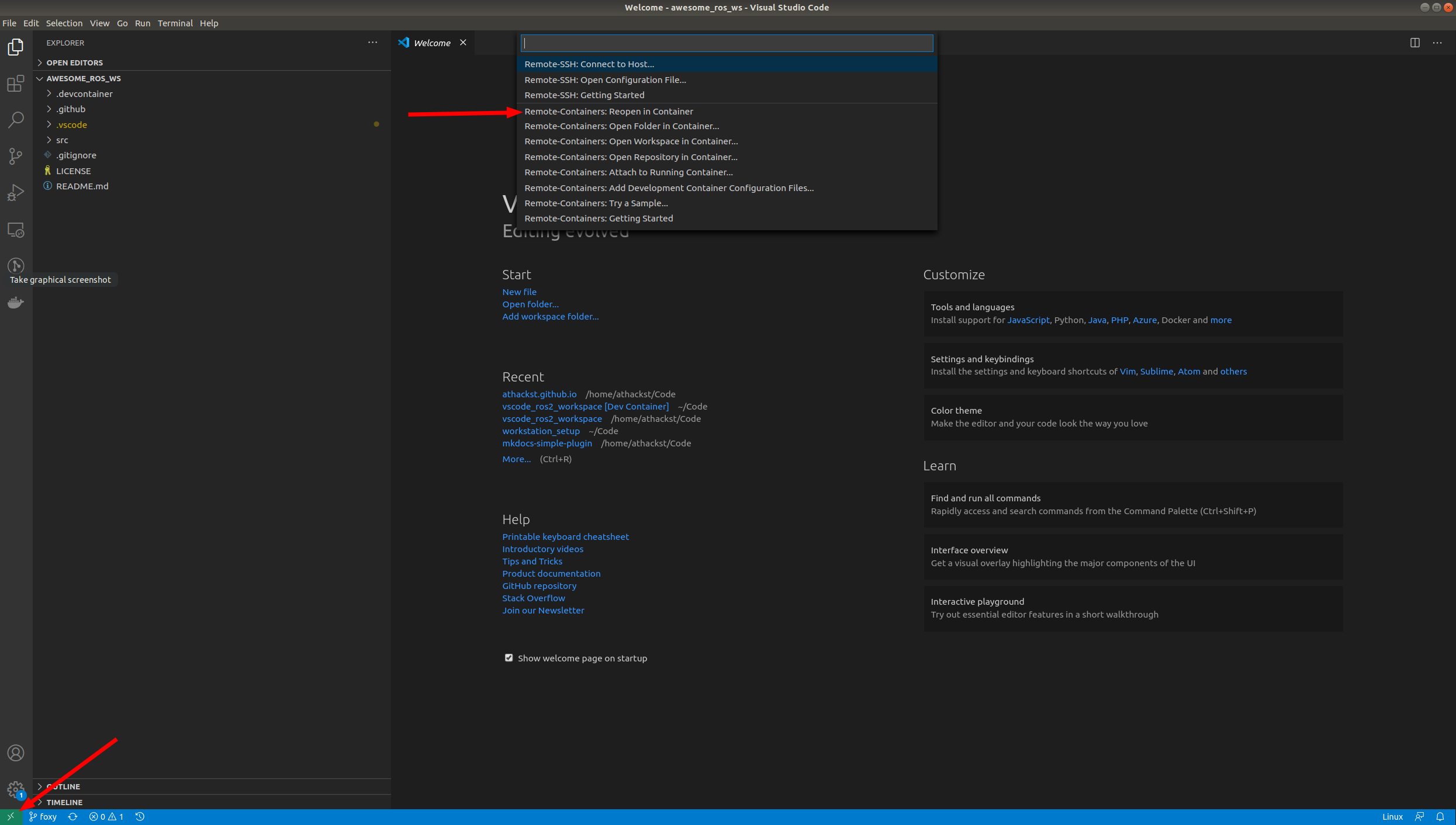
In the dialog, select "Remote Containers: Reopen in container"
VSCode will build the dockerfile inside of `.devcontainer` for you. If you open a terminal inside VSCode (Terminal->New Terminal), you should see that your username has been changed to `ros`, and the bottom left green corner should say "Dev Container"
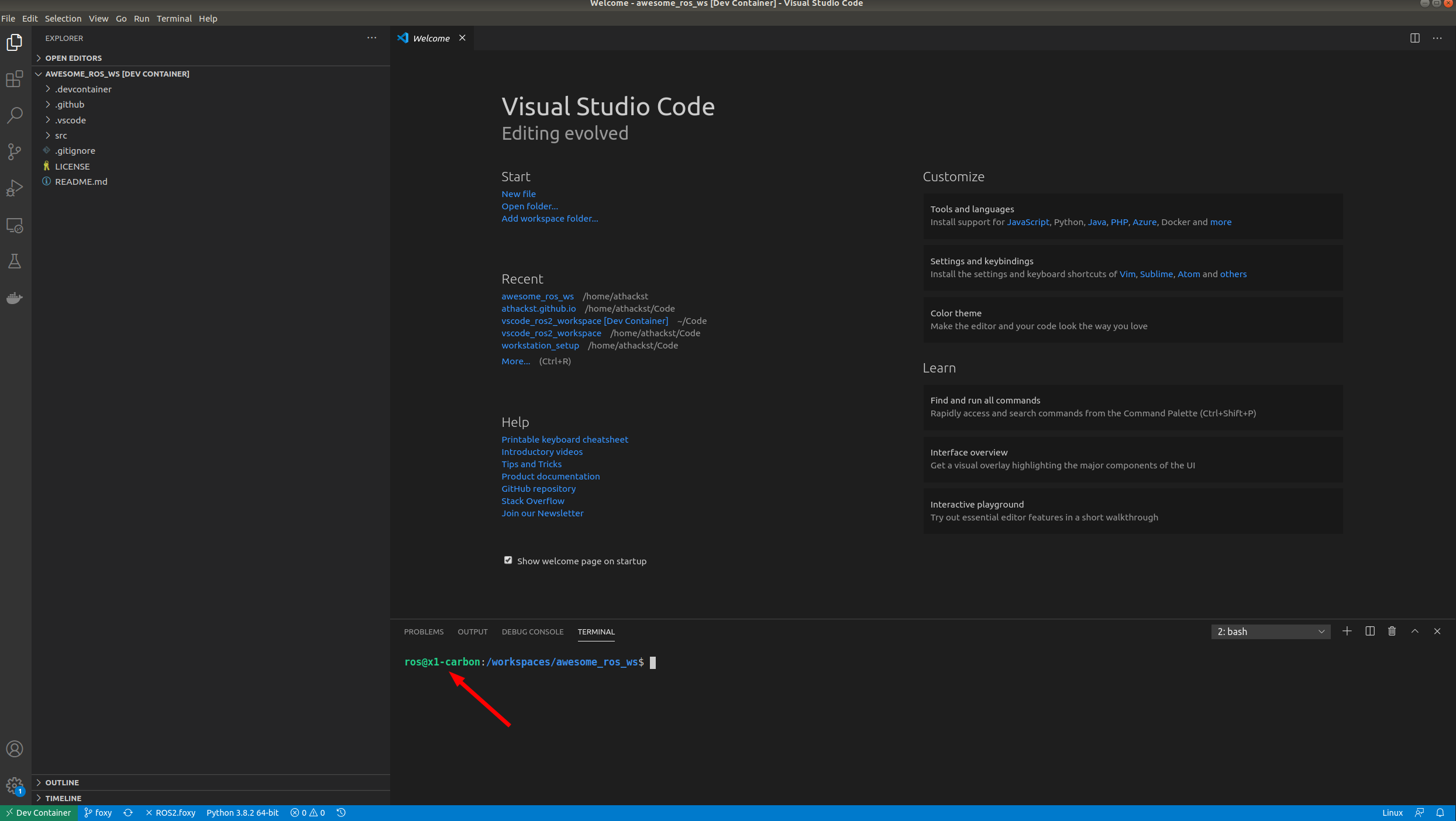
### Update the template with your code
1. Specify the repositories you want to include in your workspace in `src/ros2.repos` or delete `src/ros2.repos` and develop directly within the workspace.
2. If you are using a `ros2.repos` file, import the contents `Terminal->Run Task..->import from workspace file`
3. Install dependencies `Terminal->Run Task..->install dependencies`
4. (optional) Adjust scripts to your liking. These scripts are used both within tasks and CI.
* `setup.sh` The setup commands for your code. Default to import workspace and install dependencies.
* `build.sh` The build commands for your code. Default to `--merge-install` and `--symlink-install`
* `test.sh` The test commands for your code.
5. Develop!
## FAQ
### WSL2
#### The gui doesn't show up
This is likely because the DISPLAY environment variable is not getting set properly.
1. Find out what your DISPLAY variable should be
In your WSL2 Ubuntu instance
```
echo $DISPLAY
```
2. Copy that value into the `.devcontainer/devcontainer.json` file
```jsonc
"containerEnv": {
"DISPLAY": ":0",
}
```
#### I want to use vGPU
If you want to access the vGPU through WSL2, you'll need to add additional components to the `.devcontainer/devcontainer.json` file in accordance to [these directions](https://github.com/microsoft/wslg/blob/main/samples/container/Containers.md)
```jsonc
"runArgs": [
"--network=host",
"--cap-add=SYS_PTRACE",
"--security-opt=seccomp:unconfined",
"--security-opt=apparmor:unconfined",
"--volume=/tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix",
"--volume=/mnt/wslg:/mnt/wslg",
"--volume=/usr/lib/wsl:/usr/lib/wsl",
"--device=/dev/dxg",
"--gpus=all"
],
"containerEnv": {
"DISPLAY": "${localEnv:DISPLAY}", // Needed for GUI try ":0" for windows
"WAYLAND_DISPLAY": "${localEnv:WAYLAND_DISPLAY}",
"XDG_RUNTIME_DIR": "${localEnv:XDG_RUNTIME_DIR}",
"PULSE_SERVER": "${localEnv:PULSE_SERVER}",
"LD_LIBRARY_PATH": "/usr/lib/wsl/lib",
"LIBGL_ALWAYS_SOFTWARE": "1" // Needed for software rendering of opengl
},
```
### Repos are not showing up in VS Code source control
This is likely because vscode doesn't necessarily know about other repositories unless you've added them directly.
```
File->Add Folder To Workspace
```
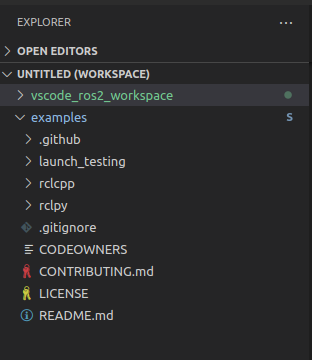
Or you've added them as a git submodule.

To add all of the repos in your *.repos file, run the script
```bash
python3 .devcontainer/repos_to_submodules.py
```
or run the task titled `add submodules from .repos`