https://github.com/austinsonger/react-google-apps-script-
https://github.com/austinsonger/react-google-apps-script-
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/austinsonger/react-google-apps-script-
- Owner: austinsonger
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-12-03T01:24:45.000Z (10 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-12-03T01:24:47.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-09T18:35:25.860Z (7 months ago)
- Language: JavaScript
- Size: 354 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
Built with React v18 and Vite for best-in-class frontend development.
[]()
[](https://github.com/enuchi/React-Google-Apps-Script/issues)
[](https://github.com/enuchi/React-Google-Apps-Script/pulls)
[](/LICENSE)
🚀 This is your boilerplate project for developing React apps inside Google Sheets, Docs, Forms and Slides projects. It's perfect for personal projects and for publishing complex add-ons in the Google Workspace Marketplace.
---
## 📝 Table of Contents
- [About](#about)
- [Install](#install)
- [Prerequisites](#prerequisites)
- [Getting started](#getting-started)
- [Deploy](#deploy)
- [Local Development](#local-development)
- [Using React DevTools](#dev-tools)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [The included sample app](#the-included-sample-app)
- [Typescript](#new-typescript)
- [Adding packages](#adding-packages)
- [Styles](#styles)
- [Modifying scopes](#modifying-scopes)
- [Calling server-side Google Apps Script functions](#calling-server-side-google-apps-script-functions)
- [Autocomplete](#Autocomplete)
- [Authors](#authors)
- [Acknowledgments](#acknowledgement)
[Google Apps Script](https://developers.google.com/apps-script/overview) is Google's Javascript-based development platform for building applications and add-ons for Google Sheets, Docs, Forms and other Google Apps.
Google Apps Scripts lets you add custom [user interfaces inside dialog windows](https://developers.google.com/apps-script/guides/html). Using this template, it's easy to run [React](https://reactjs.org/) apps inside these dialogs, and build everything from small projects to advanced add-ons that can be published in the Google Workspace Marketplace.

This repo is a boilerplate project for developing React apps with Google Apps Script projects. You can use this starter template to build your own React apps and deploy them inside Google Sheets, Docs, Forms and Slides for use in dialogs and sidebars. Sample code is provided showing how your React app can interact with the underlying Google Apps Script server-side code.
Read on to get started with your own project!
These instructions will get you set up with a copy of the React project code on your local machine. It will also get you logged in to `clasp`, which lets you manage script projects from the command line.
See [deploy](#deploy) for notes on how to deploy the project and see it live in a Google Spreadsheet.
- Make sure you're running at least [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/en/download/) v18 and [yarn (classic)](https://classic.yarnpkg.com/lang/en/docs/install/).
- You'll need to enable the Google Apps Script API. You can do that by visiting [script.google.com/home/usersettings](https://script.google.com/home/usersettings).
- To use live reload while developing, you'll need to serve your files locally using HTTPS. See [local development](#local-development) below for instructions on setting up your local environment.
Full steps to getting your local environment set up, deploying your app, and also running your app locally for local development are shown in the video below:
https://github.com/enuchi/React-Google-Apps-Script/assets/31550519/83622b83-0d0e-43de-a589-36f96d51c9c4
**1.** First, let's clone the repo and install the dependencies. This project is published as a public template, so you can also fork the repo or select "Use this template" in GitHub.
```bash
git clone https://github.com/enuchi/React-Google-Apps-Script.git
cd React-Google-Apps-Script
yarn install
```
**2.** Next, we'll need to log in to [clasp](https://github.com/google/clasp), which lets us manage our Google Apps Script projects locally.
```bash
yarn run login
```
**3.** Now let's run the setup script to create a New spreadsheet and script project from the command line.
```bash
yarn run setup
```
Alternatively, you can use an existing Google Spreadsheet and Script file instead of creating a new one.
See instructions here for using an existing project.
You will need to update the `.clasp.json` file in the root of this project with the following three key/value pairs (see .clasp.json.SAMPLE for reference):
```json
{
"scriptId": "1PY037hPcy................................................",
"parentId": ["1Df30......................................."],
"rootDir": "./dist"
}
```
- `scriptId`: Your existing script project's `scriptId`. You can find it by opening your spreadsheet, selecting **Tools > Script Editor** from the menubar, then **File > Project properties**, and it will be listed as "Script ID".
- `parentId`: An array with a single string, the ID of the parent file (spreadsheet, doc, etc.) that the script project is bound to. You can get this ID from the url, where the format is usually `https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/{id}/edit`. This allows you to run `npm run open` and open your file directly from the command line.
- `rootDir`: This should always be `"./dist"`, i.e. the local build folder that is used to store project files.
Next, let's deploy the app so we can see it live in Google Spreadsheets.
https://github.com/enuchi/React-Google-Apps-Script/assets/31550519/0c67c4b8-e3f5-4345-8460-470e9211aeb9
Run the deploy command. You may be prompted to update your manifest file. Type 'yes'.
```bash
yarn run deploy
```
The deploy command will build all necessary files using production settings, including all server code (Google Apps Script code), client code (React bundle), and config files. All bundled files will be outputted to the `dist/` folder, then pushed to the Google Apps Script project.
Now open Google Sheets and navigate to your new spreadsheet (e.g. the file "My React Project"). You can also run `yarn run open`. Make sure to refresh the page if you already had it open. You will now see a new menu item appear containing your app!
We can develop our client-side React apps locally, and see our changes directly inside our Google Spreadsheet dialog window.
There are two steps to getting started: installing a certificate (first time only), and running the start command.
1. Generating a certificate for local development
Install the mkcert package:
```bash
# mac:
brew install mkcert
# windows:
choco install mkcert
```
[More install options here.](https://github.com/FiloSottile/mkcert#installation)
Then run the mkcert install script:
```bash
mkcert -install
```
Create the certs in your repo:
```
yarn run setup:https
```
2. Now you're ready to start:
```bash
yarn run start
```
The start command will create and deploy a development build, and serve your local files.
After running the start command, navigate to your spreadsheet and open one of the menu items. It should now be serving your local files. When you make and save changes to your React app, your app will reload instantly within the Google Spreadsheet, and have access to any server-side functions!
https://github.com/enuchi/React-Google-Apps-Script/assets/31550519/981604ac-bdea-489d-97fa-72e6d24ba6dd
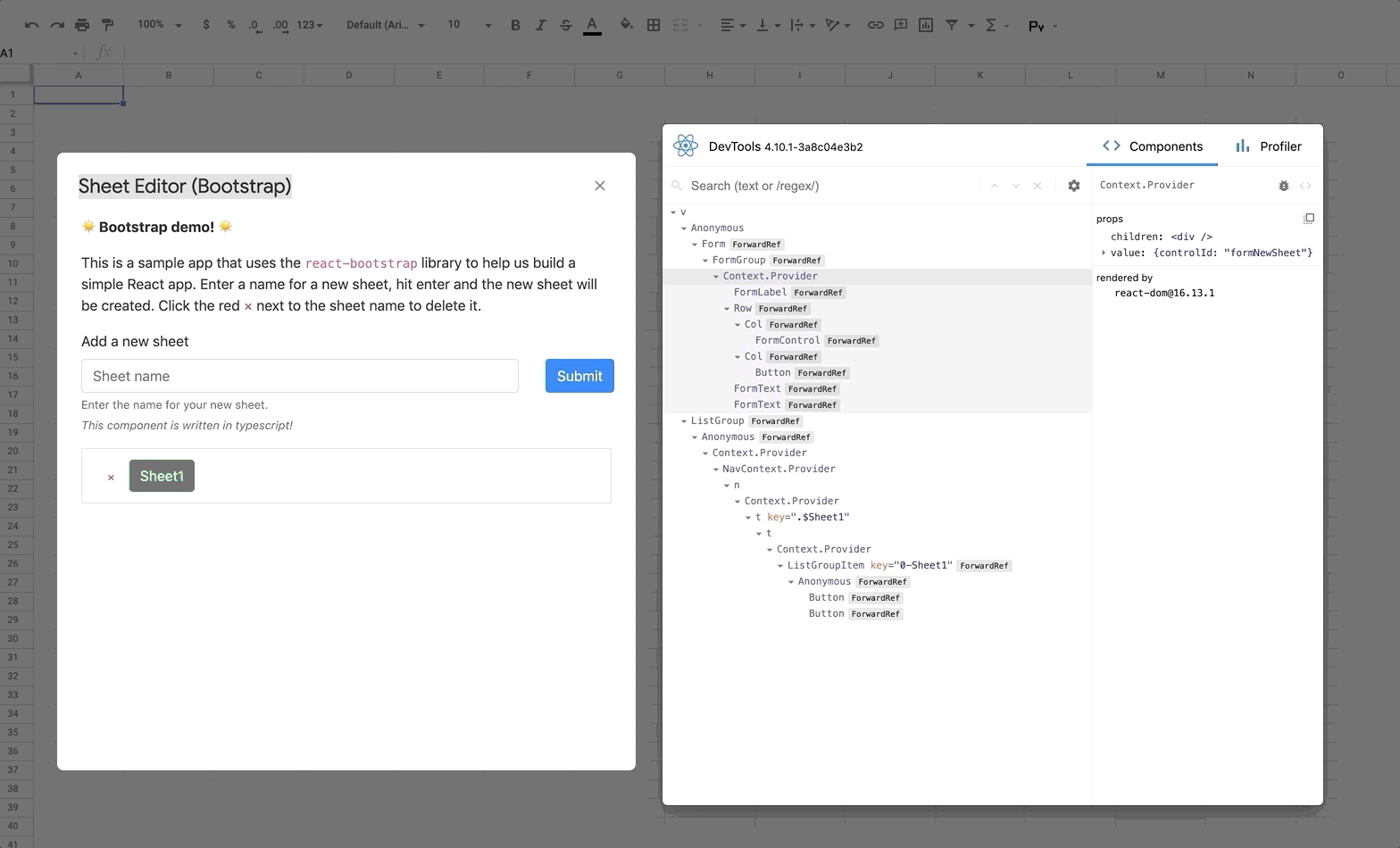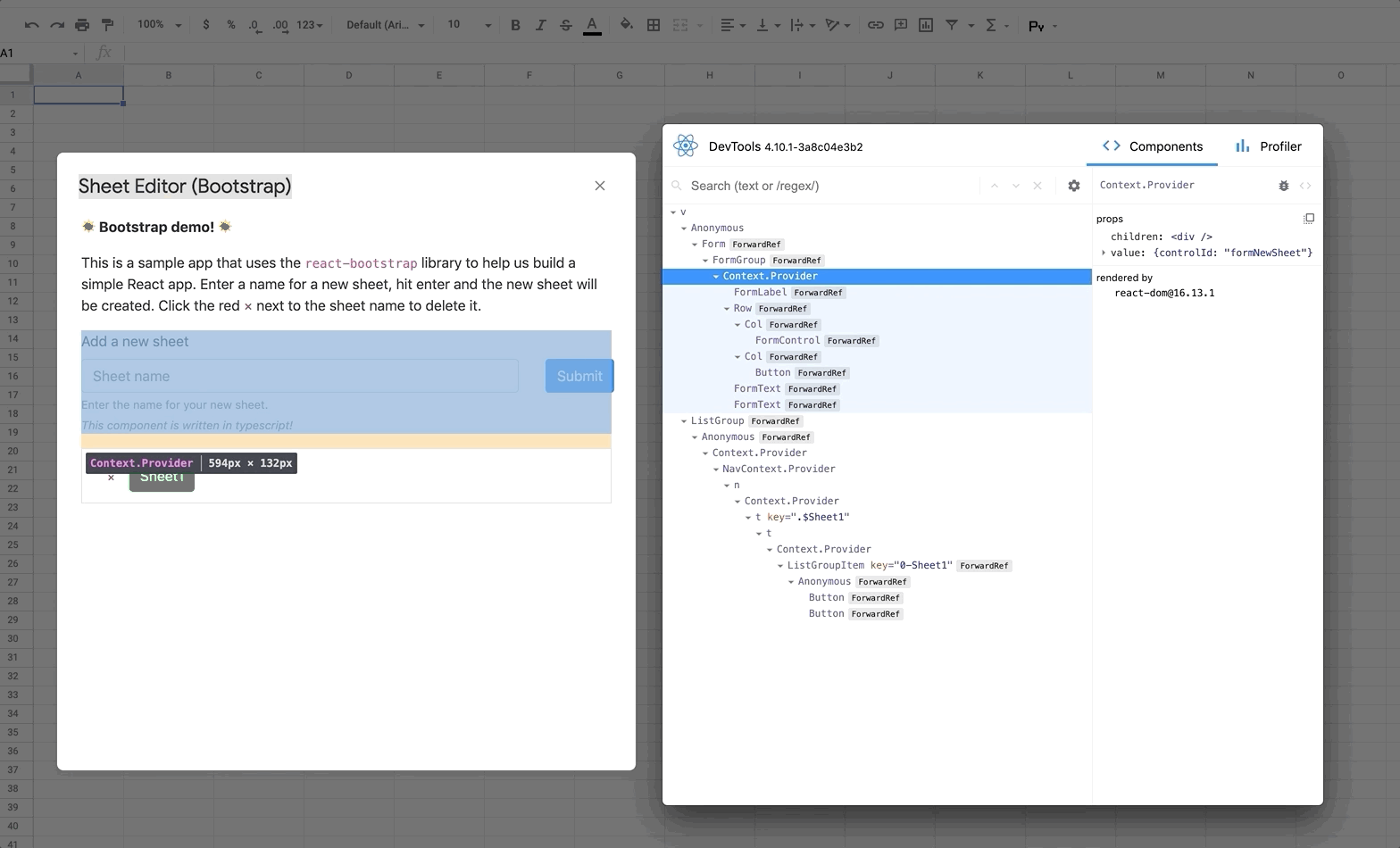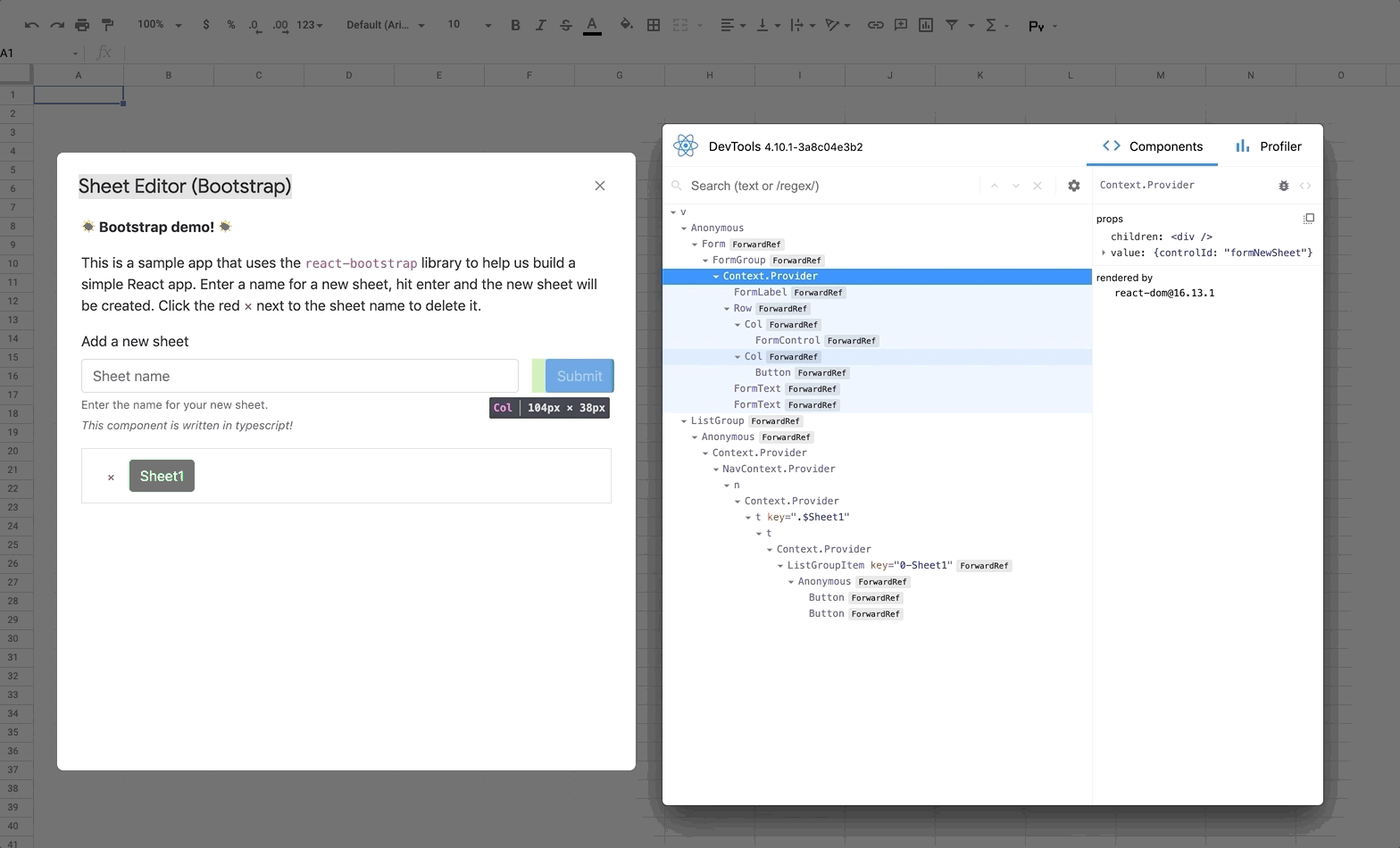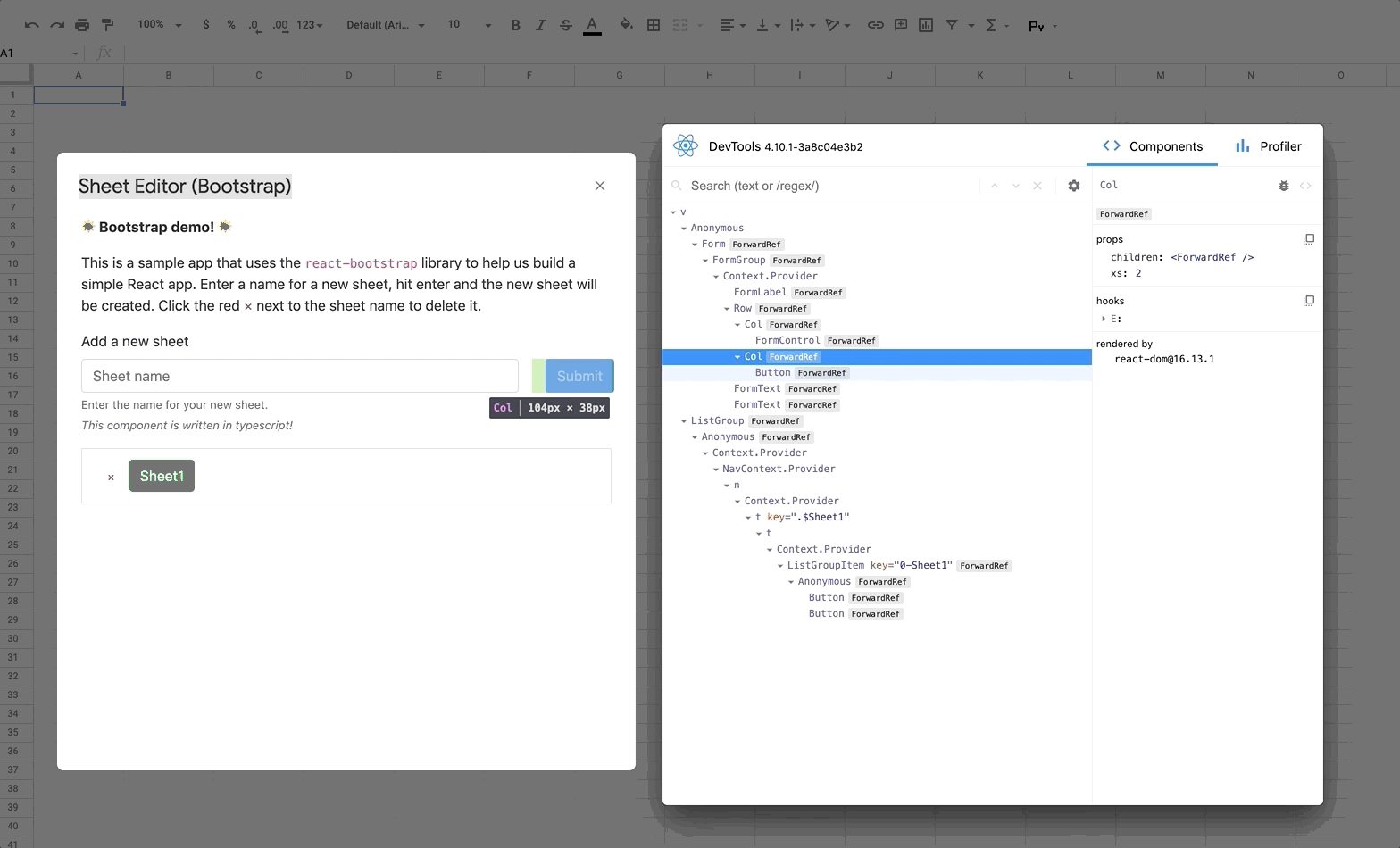
React DevTools is a tool that lets you inspect the React component hierarchies during development.
Instructions for installing React DevTools
You will need to use the "standalone" version of React DevTools since our React App is running in an iframe ([more details here](https://github.com/facebook/react/tree/master/packages/react-devtools#usage-with-react-dom)).
1. In your repo install the React DevTools package as a dev dependency:
```bash
yarn add -D react-devtools
```
2. In a new terminal window run `npx react-devtools` to launch the DevTools standalone app.
3. Add `` to the top of your `` in your React app, e.g. in the [index.html](https://github.com/enuchi/React-Google-Apps-Script/blob/e73e51e56e99903885ef8dd5525986f99038d8bf/src/client/dialog-demo-bootstrap/index.html) file in the sample Bootstrap app.
4. Deploy your app (`yarn run deploy:dev`) and you should see DevTools tool running and displaying your app hierarchy.
5. Don't forget to remove the `` tag before deploying to production.
</details>
<br/>
## ⛏️ Usage <a name = "Usage"></a>
### The included sample app
The included sample app allows inserting/activating/deleting sheets through a simple HTML dialog, built with React. This simple app demonstrates how a React app can interact with the underlying Spreadsheet using Google Apps Script functions.
The included sample app has five menu items that demonstrate how to load pages in various dialogs and sidebars. Sample implementations using different component libraries are included.
- `Sheet Editor` - This is a basic app that opens in a dialog window that demonstrates how to select, create and delete sheets in a Google Sheets documents through server calls. It uses vanilla React with no component library.
- `Sheet Editor (Boostrap)` - The same basic app is included but styled with the Bootstrap library using [`react-bootstrap`](https://react-bootstrap.github.io/). The bootstrap example also contains an example of a page built with typescript (see below).
- `Sheet Editor (MUI)` - A similar example using [`Material UI`](https://mui.com/).
- `Sheet Editor (Tailwind CSS)` - Another example, using [`Tailwind CSS`](https://tailwindcss.com/)
- `About me` - This is just a simple page that demonstrates the use of a sidebar dialog.
Access the dialogs through the new menu item that appears. You may need to refresh the spreadsheet and approve the app's permissions the first time you use it.
Note that if you are choosing to use one framework, for example `Tailwind`, for your project, it is advisable to remove the dependencies for the other component libraries.
<details>
<summary>Here are some steps to take to clean up the repo if you are only using a single library</summary>
1. Uninstall unneeded dependencies (`yarn remove react-bootstrap ...` etc.)
2. Remove the unneeded menu bar items from the server code.
3. Remove the unneeded client code.
4. Update the `clientEntrypoints` in the [vite config file](./vite.config.ts) to only target the relevant apps.
<br/>
</details>
</br>
### Typescript
This project is built mainly with typescript but also supports Javascript, and examples of both are included here, both in server-side and client-side (React) code. The included sample app has a typescript example using the Bootstrap component library.
To use typescript, simply use a typescript extension in either the client code (.ts/.tsx) or the server code (.ts), and your typescript file will compile to the proper format.
For client-side code, see [FormInput.tsx in the Bootstrap demo](./src/client/dialog-demo-bootstrap/components/FormInput.tsx) for an example file. Note that it is okay to have a mix of javascript and typescript, as seen in the Bootstrap demo.
To use typescript in server code, just change the file extension to .ts. The server-side code already utilizes type definitions for Google Apps Script APIs.
A basic typescript configuration is used here that correctly transpiles to code that is compatible with Google Apps Script. However, if you want more control over your setup you can modify the included [tsconfig.json file](./tsconfig.json).
### Adding packages
You can add packages to your client-side React app.
For instance, install `react-transition-group`:
```bash
yarn add react-transition-group
```
Important: Since Google Apps Scripts projects don't let you easily reference external files, this project will bundle an entire app into one HTML file. If you are importing large libraries this can result in a large file. To help reduce the size of these large HTML files, you can try to externalize packages by using a CDN to load packages. For packages that can be loaded through a CDN (usually they will have a UMD build), you can configure the externals and globals details in the [vite config file](./vite.config.ts). You will also need to include a script element in the head of the `index.html` file, loading the library from a CDN, and making sure it supports a UMD build, e.g.
`<script crossorigin src="https://unpkg.com/react-transition-group@4.4.2/dist/react-transition-group.min.js">`.
If set up properly, this will load packages from the CDN in production and will reduce your overall bundle size.
Make sure that you update the script tag with the same version of the package you are installing with yarn, so that you are using the same version in development and production.
### Styles
By default this project supports global CSS stylesheets. Make sure to import your stylesheet in your entrypoint file [index.js](./src/client/dialog-demo/index.js):
```javascript
import './styles.css';
```
Many external component libraries require a css stylesheet in order to work properly. You can import stylesheets in the HTML template, [as shown here with the Bootstrap stylesheet](./src/client/dialog-demo-bootstrap/index.html).
### Modifying scopes
The included app only requires access to Google Spreadsheets and to loading dialog windows. If you make changes to the app's requirements, for instance, if you modify this project to work with Google Forms or Docs, make sure to edit the oauthScopes in the [appscript.json file](./appsscript.json).
See https://developers.google.com/apps-script/manifest for information on the `appsscript.json` structure.
### Calling server-side Google Apps Script functions
This project uses the [gas-client](https://github.com/enuchi/gas-client) package to more easily call server-side functions using promises.
```js
// Google's client-side google.script.run utility requires calling server-side functions like this:
google.script.run
.withSuccessHandler((response) => doSomething(response))
.withFailureHandler((err) => handleError(err))
.addSheet(sheetTitle);
// Using gas-client we can use more familiar promises style like this:
import Server from 'gas-client';
const { serverFunctions } = new Server();
// We now have access to all our server functions, which return promises!
serverFunctions
.addSheet(sheetTitle)
.then((response) => doSomething(response))
.catch((err) => handleError(err));
// Or with async/await:
async () => {
try {
const response = await serverFunctions.addSheet(sheetTitle);
doSomething(response);
} catch (err) {
handleError(err);
}
};
```
In development, `gas-client` will allow you to call server-side functions from your local environment. In production, it will use Google's underlying `google.script.run` utility.
### Autocomplete
This project includes support for autocompletion and complete type definitions for Google Apps Script methods.

All available methods from the Google Apps Script API are shown with full definitions and links to the official documentation, plus information on argument, return type and sample code.
- [@enuchi](https://github.com/enuchi) - Creator and maintainer
See the list of [contributors](https://github.com/enuchi/React-Google-Apps-Script/contributors) who participated in this project.
Part of this project has been adapted from [apps-script-starter](https://github.com/labnol/apps-script-starter), a great starter project for server-side projects ([license here](https://github.com/labnol/apps-script-starter/blob/master/LICENSE)).
