https://github.com/bcapathshala/professional-backend-setup
This is a professional backend setup for production ready
https://github.com/bcapathshala/professional-backend-setup
Last synced: about 3 hours ago
JSON representation
This is a professional backend setup for production ready
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/bcapathshala/professional-backend-setup
- Owner: BCAPATHSHALA
- Created: 2024-02-14T16:27:50.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-02-14T17:54:40.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-09-05T11:58:27.282Z (5 months ago)
- Size: 53.7 KB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Professional Backend Setup for Production
This guide outlines the steps to set up a professional backend environment for production. Follow these steps to ensure a robust and organized structure for your backend development.
## Screenshot
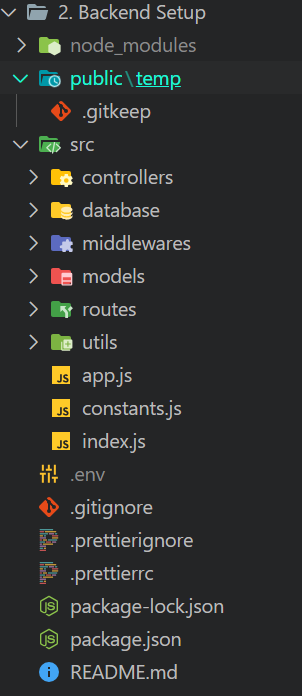
## Step 1: Initialize npm
```bash
npm init
```
## Step 2: Create README.md and Set Up Git Repository
Create a `README.md` file to document your project. Initialize a Git repository, commit your code, and push it to the remote repository.
```bash
# Initialize Git
git init
# Create README.md
touch README.md
# Add and commit files
git add .
git commit -m "Initial commit"
# Create a remote repository and push the code
# Follow the instructions from your chosen hosting service (e.g., GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket)
```
## Step 3: Set Up Public Folder for File Uploads
Create a `public` folder to store files to be served by the server. Ensure files are tracked in version control.
```bash
mkdir public
touch public/temp/.gitkeep
git add public/temp/.gitkeep
git commit -m "Add public folder for file uploads"
```
## Step 4: Create .gitignore
Create a `.gitignore` file to specify files and directories that should be ignored by Git.
```bash
touch .gitignore
# Add entries for files and directories to ignore (e.g., node_modules, .env)
```
## Step 5: Create .env file
Create a `.env` file to store environment variables. Install `dotenv` package to load environment variables from this file.
```bash
touch .env
npm install dotenv
```
## Step 6: Create src Folder for Backend Files
Organize your backend code in a `src` folder. This folder will contain essential files for your backend logic.
```bash
mkdir src
```
## Step 7: Create Essential Files in `src` Folder
```bash
# Create app.js, constant.js, index.js
touch src/app.js src/constant.js src/index.js
```
## Step 8: Setup Nodemon for Automatic Reloading
Install `nodemon` as a development dependency and set up a script in `package.json` for automatic reloading.
```bash
npm install nodemon --save-dev
```
**Update your package.json:**
```json
"scripts": {
"start": "node src/index.js",
"dev": "nodemon src/index.js"
}
```
## Step 9: Setup Prettier for Code Formatting
Install prettier as a development dependency and configure it with a `.prettierrc` file. Also, create a `.prettierignore` file to exclude files from formatting.
```bash
npm install prettier --save-dev
touch .prettierrc .prettierignore
# Configure .prettierrc according to project requirements
```
**Congratulations!** Your professional backend setup is complete. Follow these guidelines to maintain a clean and organized backend codebase.
## Watch video
[Watch Video on How to setup a professional backend project](https://youtu.be/9B4CvtzXRpc?si=eVtBLEfDks8j928d)
Post Created by [Manoj Kumar](https://www.linkedin.com/in/manojoffcialmj/)
Mentor [Hitesh Chaudhary](https://www.linkedin.com/in/hiteshchoudhary/)
