Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/bensheldon/open311status
Open311 Status monitors and aggregates the status of dozens of Open311 API endpoints, providing benchmarks and comparative insights.
https://github.com/bensheldon/open311status
Last synced: 9 days ago
JSON representation
Open311 Status monitors and aggregates the status of dozens of Open311 API endpoints, providing benchmarks and comparative insights.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/bensheldon/open311status
- Owner: bensheldon
- License: mit
- Created: 2012-05-23T18:52:57.000Z (over 12 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-01-27T17:34:36.000Z (22 days ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-31T07:22:45.946Z (19 days ago)
- Language: Ruby
- Homepage: https://status.open311.org
- Size: 1.53 MB
- Stars: 35
- Watchers: 23
- Forks: 14
- Open Issues: 12
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE.md
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
Open311 Status
==============
**Website**: http://status.open311.org
**Project Backlog**: https://github.com/codeforamerica/open311status/projects/1
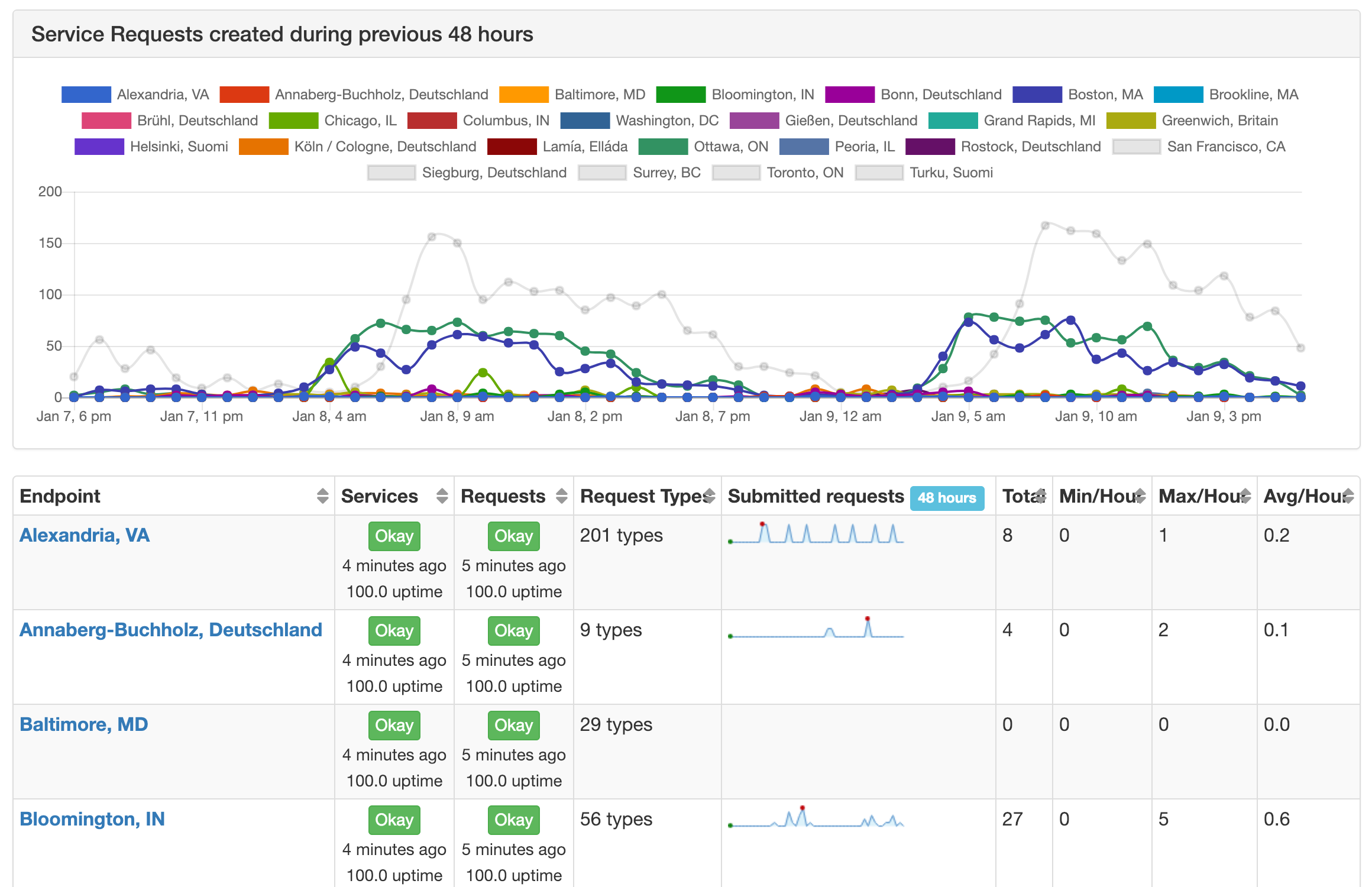
Open311 Status monitors and aggregates the status of dozens of Open311 API endpoints, providing benchmarks and comparative insights into:
- **Upness**: the API is currently available
- **Uptime**: the availability of the API over time
- **Performance**: how quickly the servers respond to API requests
- **Comprehensiveness**: how fully the API is implemented/adopted; e.g. the number of service types that can be submitted through the API
- **Utilization**: how much the 311 service being used; e.g. the number of service requests submitted
## Development
### Adding new API endpoints
To add a new Open311 endpoint, add their API configuration to the [`config/cities.yml`](config/cities.yml) file. This should include:
- `slug`: a unique key for the API endpoint.
- `name`: the human readable name of the city or location.
- `endpoint`: the complete URL of the Open311 api endpoint, ending in a `/`, _without_ `services.xml` or `requests.xml`.
- `jurisdiction` (optional): the `?jurisdiction_id=` parameter, if required.
- `format` (optional): `xml` or `json`; defaults to `xml`/
- `headers` (optional): custom API headers necessary for the API.
Example:
```yml
bruhl:
name: 'Brühl, Deutschland'
endpoint: 'https://www.achtet-auf-bruehl.de/georeport/v2/'
jurisdiction: 'bruehl.de'
```
### Loading real data
By default, running `db:setup` will load cities and generate fake service
requests. To load cities, run `rake cities:load`. And to load service requests,
`rake cities:service_requests`
### Application Dependencies
1. Install Ruby with your ruby version manager of choice, like [rbenv](https://github.com/rbenv/rbenv) or [RVM](https://github.com/codeforamerica/howto/blob/master/Ruby.md)
2. Check the ruby version in `.ruby-version` and ensure you have it installed locally e.g. `rbenv install 2.6.1`
3. Install [bundler](https://bundler.io/) (the latest Heroku-compatible version): `gem install bundler`
4. [Install Postgres](https://github.com/codeforamerica/howto/blob/master/PostgreSQL.md). If setting up Postgres.app, you will also need to add the binary to your path. e.g. Add to your `~/.bashrc`:
`export PATH="$PATH:/Applications/Postgres.app/Contents/Versions/latest/bin"`.
5. [Install PostGIS](https://postgis.net/install/), the Postgres geospatial extension, if it's not included in your distribution. Postgres.app comes with postgis.
### Application Setup
1. Install ruby gem dependencies: `bundle install`
2. Create the databases and load schema and seeds: `bin/rails db:setup`
3. Run the tests: `bin/rspec`
4. Run the server: `bin/rails server`, and visit the web-browser: [`http://localhost:3000`](http://localhost:3000)
#### Migration guide
You may need to run `rake db:gis:setup` to enable PostGIS on your database.