https://github.com/berwin/time-slicing
Break down long tasks into smaller tasks, avoid blocking the main process.
https://github.com/berwin/time-slicing
time-slicing web-performance
Last synced: 11 months ago
JSON representation
Break down long tasks into smaller tasks, avoid blocking the main process.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/berwin/time-slicing
- Owner: berwin
- License: mit
- Created: 2018-12-21T08:18:21.000Z (about 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2019-05-18T09:39:54.000Z (almost 7 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-27T21:48:36.950Z (12 months ago)
- Topics: time-slicing, web-performance
- Language: JavaScript
- Size: 6.84 KB
- Stars: 107
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 4
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-star-libs - berwin / time-slicing
README
# time-slicing
Break down long tasks into smaller tasks, avoid blocking the main process.
## Introduce
Usually synchronous code execution for more than 50 milliseconds is a long task.
Long tasks will block the main thread, causing the page to jam, We have two solutions, Web worker and Time slicing.
We should use web workers as much as possible, but the web worker cannot access the DOM. So we need to split a long task into small tasks and distribute them in the macrotask queue.
For example:
```javascript
setTimeout(_ => {
const start = performance.now()
while (performance.now() - start < 1000) {}
console.log('done!')
}, 5000)
```
The browser will get stuck for one second after the code is executed for five seconds.
We can use the chrome developer tool to capture the performance of the code run.
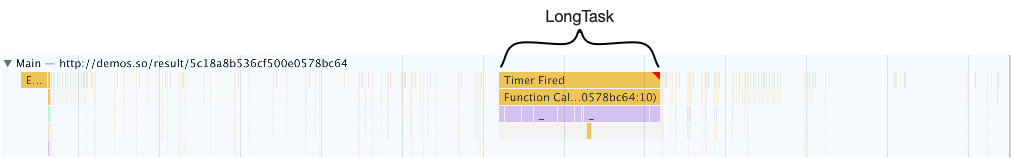
Now, we use time-slicing to cut long tasks, the code is as follows:
```javascript
setTimeout(ts(function* () {
const start = performance.now()
while (performance.now() - start < 1000) {
yield
}
console.log('done!')
}), 5000)
```
In the code, we use the **yield** keyword to split the code and distribute the code in different macrotask queues.
We can use the chrome developer tool to capture the performance of the code run.
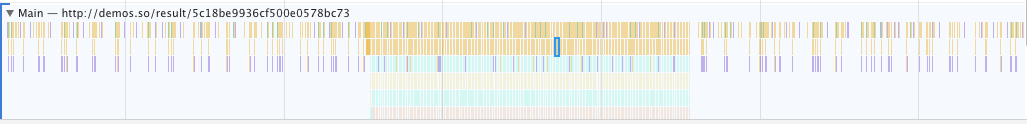
From the figure we can see that the long task is gone, and replaced by a myriad of intensive small tasks.