https://github.com/betteridiot/seqlogo
Python port of the R Bioconductor `seqLogo` package
https://github.com/betteridiot/seqlogo
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
Python port of the R Bioconductor `seqLogo` package
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/betteridiot/seqlogo
- Owner: betteridiot
- License: bsd-3-clause
- Created: 2018-12-21T22:07:31.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-05T20:39:10.000Z (9 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-10-12T19:28:32.823Z (6 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Size: 91.8 KB
- Stars: 30
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 3
- Open Issues: 5
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-dl4g - seqlogo - Python port of Bioconductor's seqLogo served by WebLogo. (2020) (Software packages / Visualizations)
README
[](https://pypi.org/project/seqlogo/)
[](http://bioconda.github.io/recipes/seqlogo/README.html)
[](https://github.com/betteridiot/seqlogo/blob/master/LICENSE)
# seqlogo
Python port of Bioconductor's [seqLogo](http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/seqLogo.html) served by [WebLogo](http://weblogo.threeplusone.com/)
## Overview
In the field of bioinformatics, a common task is to look for sequence motifs at
different sites along the genome or within a protein sequence. One aspect of this
analysis involves creating a variant of a Position Matrix (PM): Position Frequency Matrix (PFM),
Position Probability Matrix (PPM), and Position Weight Matrix (PWM). The formal format for
a PWM file can be found [here](http://bioinformatics.intec.ugent.be/MotifSuite/pwmformat.php).
---
#### Specification
A PM file can be just a plain text, whitespace delimited matrix, such that the number of columns
matches the number of letters in your desired alphabet and the number of rows is the number of positions
in your sequence. Any comment lines that start with `#` will be skipped.
*Note*: [TRANSFAC matrix](http://meme-suite.org/doc/transfac-format.html) and [MEME Motif](http://meme-suite.org/doc/meme-format.html) formats are not directly supported.
Where  is the probability that at
is the probability that at  position,
position, 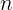 letter is seen.
letter is seen.
This is often generated in a frequentist fashion. If a pipeline
tallies all observed letters at each position, this is called a Position Frequency Matrix (PFM).
The PFM can be converted to a PPM in a straight-forward manner, creating a matrix
that for any given position and letter, the probability of that letter at that position
is reported.
A PWM is the PPM converted into log-likelihood. Pseudocounts can be applied to prevent
probabilities of 0 from turing into -inf in the conversion process. Lastly, each position's
log-likelihood is corrected for some background probability for every given letter in the
selected alphabet.
---
#### Features
* `seqlogo` can use any PM as entry points for analysis (from a file or in array formats)
and, subsequently, plot the sequence logos.
* `seqlogo` was written to support BIOINF 529 :Bioinformatics Concepts and Algorithms
at the University of Michigan in the Department of Computational Medicine & Bioinformatics.
* `seqlogo` attempts to blend the user-friendly api of Bioconductor's [seqLogo](http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/seqLogo.html)
and the rendering power of the [WebLogo](http://weblogo.threeplusone.com/)Python API.
* `seqlogo` supports the following alphabets:
| Alphabet name | Alphabet Letters |
| :--- | :--- |
| **`"DNA"`** | `"ACGT"` |
| `"reduced DNA"` | `"ACGTN-"` |
| `"ambig DNA"` | `"ACGTRYSWKMBDHVN-"` |
| **`"RNA"`** | `"ACGU"` |
| `"reduced RNA"` | `"ACGUN-"` |
| `"ambig RNA"` | `"ACGURYSWKMBDHVN-"` |
| **`"AA"`** | `"ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWY"` |
| `"reduced AA"` | `"ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWYX*-"` |
| `"ambig AA"` | `"ACDEFGHIKLMNOPQRSTUVWYBJZX*-"` |
(**Bolded** alphabet names are the most commonly used)
* `seqlogo` can also render sequence logos in a number of formats:
* `"svg"` (default)
* `"eps"`
* `"pdf"`
* `"jpeg"`
* `"png"`
* All plots can be rendered in 4 different sizes:
* `"small"`: 3.54" wide
* `"medium"`: 5" wide
* `"large"`: 7.25" wide
* `"xlarge"`: 10.25" wide
*Note*: all sizes taken from [this](http://www.sciencemag.org/sites/default/files/Figure_prep_guide.pdf) publication
guide from Science Magazine.
---
#### Recommended settings:
* For best results, implement `seqlogo` within a IPython/Jupyter environment (for inline plotting purposes).
* Initially written for Python 3.7, but has shown to work in versions 3.5+ (**Python 2.7 is not supported**)
***
## Setup
### Minimal Requirements:
1. `numpy`
2. `pandas`
3. `weblogo`
**Note**: it is strongly encouraged that `jupyter` is installed as well.
---
#### `conda` environment:
To produce the ideal virtual environment that will run `seqlogo` on a `conda`-based
build, clone the repo or download the environment.yml within the repo. Then run the following
command:
```bash
$ conda env create -f environment.yml
```
---
#### Installation
To install using `pip`: (recommended)
```bash
$ pip install seqlogo
```
To install using `conda`
```bash
$ conda install -c bioconda seqlogo
```
Or install from GitHub directly
```bash
$ pip install git+https://github.com/betteridiot/seqlogo.git#egg=seqlogo
```
***
## Quickstart
### Importing
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seqlogo
```
### Generate some PM data (without frequency data)
For many demonstrations that speak to PWMs, they are often started with PPM data.
Many packages preclude sequence logo generation from this entry point. However,
`seqlogo` can handle it just fine. One point to make though is that if no count
data is provided, `seqlogo` just generates the PFM data by multiplying the
probabilities by 100. This is **only** for `weblogolib` compatability.
```python
# Setting seed for demonstration purposes
>>> np.random.seed(42)
# Making a fake PPM
>>> random_ppm = np.random.dirichlet(np.ones(4), size=6)
>>> ppm = seqlogo.Ppm(random_ppm)
>>> ppm
A C G T
0 0.082197 0.527252 0.230641 0.159911
1 0.070375 0.070363 0.024826 0.834435
2 0.161962 0.216972 0.003665 0.617401
3 0.735638 0.098290 0.082638 0.083434
4 0.179898 0.368931 0.280463 0.170708
5 0.498510 0.079138 0.182004 0.240349
```
### Generate some frequency data and convert to PWM
Sometimes the user has frequency data instead of PWM. To construct a `Pwm` instance
that automatically computes Information Content and PWM values, the user can use
the `seqlogo.pfm2pwm()` function.
```python
# Setting seed for demonstration purposes
>>> np.random.seed(42)
# Making some fake Position Frequency Data (PFM)
>>> pfm = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0, 36, size=(8, 4)))
# Convert to Position Weight Matrix (PWM)
>>> pwm = seqlogo.pfm2pwm(pfm)
>>> pwm
A C G T
0 0.698830 -0.301170 -1.301170 0.213404
1 0.263034 0.552541 -0.584962 -0.584962
2 0.148523 0.754244 0.148523 -3.375039
3 0.182864 -4.209453 0.314109 0.648528
4 -4.000000 0.321928 1.000000 -0.540568
5 -0.222392 -0.029747 0.085730 0.140178
6 0.697437 0.597902 -2.209453 -0.624491
7 0.736966 -0.584962 0.502500 -2.000000
```
### `seqlogo.CompletePm` demo
Here is a quickstart guide on how to leverage the power of `seqlogo.CompletePm`
```python
# Setting seed for demonstration purposes
>>> np.random.seed(42)
# Making a fake PWM
>>> random_ppm = np.random.dirichlet(np.ones(4), size=6)
>>> cpm = seqlogo.CompletePM(ppm = random_ppm)
# Pfm was imputed
>>> print(cpm.pfm)
A C G T
0 8 52 23 15
1 7 7 2 83
2 16 21 0 61
3 73 9 8 8
4 17 36 28 17
5 49 7 18 24
# Shows the how the PPM data was formatted
>>> print(cpm.ppm)
A C G T
0 0.082197 0.527252 0.230641 0.159911
1 0.070375 0.070363 0.024826 0.834435
2 0.161962 0.216972 0.003665 0.617401
3 0.735638 0.098290 0.082638 0.083434
4 0.179898 0.368931 0.280463 0.170708
5 0.498510 0.079138 0.182004 0.240349
# Computing the PWM using default background and pseudocounts
>>> print(cpm.pwm)
A C G T
0 -1.604773 1.076564 -0.116281 -0.644662
1 -1.828788 -1.829031 -3.331983 1.738871
2 -0.626276 -0.204418 -6.091862 1.304279
3 1.557068 -1.346815 -1.597049 -1.583223
4 -0.474749 0.561423 0.165882 -0.550396
5 0.995695 -1.659494 -0.457960 -0.056800
# See the consensus sequence
>>> print(cpm.consensus)
CTTACA
# See the Information Content
>>> print(cpm.ic)
0 0.305806
1 1.110856
2 0.637149
3 0.748989
4 0.074286
5 0.268034
dtype: float64
```
### Plot the sequence logo with information content scaling
```python
# Setting seed for demonstration purposes
>>> np.random.seed(42)
# Making a fake PWM
>>> random_ppm = np.random.dirichlet(np.ones(4), size=6)
>>> ppm = seqlogo.Ppm(random_ppm)
>>> seqlogo.seqlogo(ppm, ic_scale = False, format = 'svg', size = 'medium')
```
The above code will produce:

### Plot the sequence logo with no information content scaling
```python
# Setting seed for demonstration purposes
>>> np.random.seed(42)
# Making a fake PWM
>>> random_ppm = np.random.dirichlet(np.ones(4), size=6)
>>> ppm = seqlogo.Ppm(random_ppm)
>>> seqlogo.seqlogo(ppm, ic_scale = False, format = 'svg', size = 'medium')
```
The above code will produce:

***
## Documentation
`seqlogo` exposes 5 classes to the user for handling PM data:
1. `seqlogo.Pm`: the base class for all other specialized PM subclasses
2. `seqlogo.Pfm`: The class used for handling PFM data
3. `seqlogo.Ppm`: The class used for handling PPM data
4. `seqlogo.Pwm`: The class used for handling PWM data
5. `seqlogo.CompletePm`: This final class will take any/all of the other PM subclass data
and compute any of the other missing data. That is, if the user only provides a `seqlogo.Pfm`
and passes it to `seqlogo.CompletePm`, it will solve for the PPM, PWM, consensus sequence, and
information content.
Additionally, `seqlogo` also provides 6 methods for converting PM structures:
1. `seqlogo.pfm2ppm`: converts a PFM to a PPM
2. `seqlogo.pfm2pwm`: converts a PFM to a PWM
3. `seqlogo.ppm2pfm`: converts a PPM to a PFM
4. `seqlogo.ppm2pwm`: converts a PPM to a PWM
5. `seqlogo.pwm2pfm`: converts a PWM to a PFM
6. `seqlogo.pwm2ppm`: converts a PWM to a PPM
The signatures for each item above are as follows:
### Classes
```python
seqlogo.CompletePm(pfm = None, ppm = None, pwm = None, background = None, pseudocount = None,
alphabet_type = 'DNA', alphabet = None, default_pm = 'ppm'):
"""
Creates the CompletePm instance. If the user does not define any `pm_filename_or_array`,
it will be initialized to empty. Will generate all other attributes as soon
as a `pm_filename_or_array` is supplied.
Args:
pfm (str or `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame` or Pm): The user supplied
PFM. If it is a filename, the file will be opened
and parsed. If it is an `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame`,
it will just be assigned. (default: None, skips '#' comment lines)
ppm (str or `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame` or Pm): The user supplied
PPM. If it is a filename, the file will be opened
and parsed. If it is an `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame`,
it will just be assigned. (default: None, skips '#' comment lines)
pwm (str or `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame` or Pm): The user supplied
PWM. If it is a filename, the file will be opened
and parsed. If it is an `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame`,
it will just be assigned. (default: None, skips '#' comment lines)
background (constant or Collection): Offsets used to calculate background letter probabilities (defaults: If
using an Nucleic Acid alphabet: 0.25; if using an Aminio Acid alphabet: Robinson-Robinson Frequencies)
pseudocount (constant): Some constant to offset PPM conversion to PWM to prevent -/+ inf. (defaults to 1e-10)
alphabet_type (str): Desired alphabet to use. Order matters (default: 'DNA')
"DNA" := "ACGT"
"reduced DNA" := "ACGTN-"
"ambig DNA" := "ACGTRYSWKMBDHVN-"
"RNA" := "ACGU"
"reduced RNA" := "ACGUN-"
"ambig RNA" := "ACGURYSWKMBDHVN-"
"AA" : = "ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWY"
"reduced AA" := "ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWYX*-"
"ambig AA" := "ACDEFGHIKLMNOPQRSTUVWYBJZX*-"
"custom" := None
(default: 'DNA')
alphabet (str): if 'custom' is selected or a specialize alphabet is desired, this accepts a string (default: None)
default_pm (str): which of the 3 pm's do you want to call '*home*'? (default: 'ppm')
"""
seqlogo.Pm(pm_filename_or_array = None, pm_type = 'ppm', alphabet_type = 'DNA', alphabet = None,
background = None, pseudocount = None):
"""Initializes the Pm
Creates the Pm instance. If the user does not define `pm_filename_or_array`,
it will be initialized to empty. Will generate all other attributes as soon
as a `pm_filename_or_array` is supplied.
Args:
pm_filename_or_array (str or `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame` or Pm): The user supplied
PM. If it is a filename, the file will be opened
and parsed. If it is an `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame`,
it will just be assigned. (default: None, skips '#' comment lines)
alphabet_type (str): Desired alphabet to use. Order matters (default: 'DNA')
"DNA" := "ACGT"
"reduced DNA" := "ACGTN-"
"ambig DNA" := "ACGTRYSWKMBDHVN-"
"RNA" := "ACGU"
"reduced RNA" := "ACGUN-"
"ambig RNA" := "ACGURYSWKMBDHVN-"
"AA" : = "ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWY"
"reduced AA" := "ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWYX*-"
"ambig AA" := "ACDEFGHIKLMNOPQRSTUVWYBJZX*-"
"custom" := None
(default: 'DNA')
alphabet (str): if 'custom' is selected or a specialize alphabet is desired, this accepts a string (default: None)
background (constant or Collection): Offsets used to calculate background letter probabilities (defaults: If
using an Nucleic Acid alphabet: 0.25; if using an Aminio Acid alphabet: Robinson-Robinson Frequencies)
pseudocount (constant): Some constant to offset PPM conversion to PWM to prevent -/+ inf. (default: 1e-10)
"""
seqlogo.Pfm(pfm_filename_or_array = None, pm_type = 'pfm', alphabet_type = 'DNA', alphabet = None,
background = None, pseudocount = None):
"""Initializes the Pfm
Creates the Pfm instance. If the user does not define `pfm_filename_or_array`,
it will be initialized to empty. Will generate all other attributes as soon
as a `pfm_filename_or_array` is supplied.
Args:
pfm_filename_or_array (str or `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame` or Pm): The user supplied
PFM. If it is a filename, the file will be opened
and parsed. If it is an `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame`,
it will just be assigned. (default: None, skips '#' comment lines)
alphabet_type (str): Desired alphabet to use. Order matters (default: 'DNA')
"DNA" := "ACGT"
"reduced DNA" := "ACGTN-"
"ambig DNA" := "ACGTRYSWKMBDHVN-"
"RNA" := "ACGU"
"reduced RNA" := "ACGUN-"
"ambig RNA" := "ACGURYSWKMBDHVN-"
"AA" : = "ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWY"
"reduced AA" := "ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWYX*-"
"ambig AA" := "ACDEFGHIKLMNOPQRSTUVWYBJZX*-"
"custom" := None
(default: 'DNA')
alphabet (str): if 'custom' is selected or a specialize alphabet is desired, this accepts a string (default: None)
background (constant or Collection): Offsets used to calculate background letter probabilities (defaults: If
using an Nucleic Acid alphabet: 0.25; if using an Aminio Acid alphabet: Robinson-Robinson Frequencies)
pseudocount (constant): Some constant to offset PPM conversion to PWM to prevent -/+ inf. (default: 1e-10)
"""
seqlogo.Ppm(ppm_filename_or_array = None, pm_type = 'ppm', alphabet_type = 'DNA', alphabet = None,
background = None, pseudocount = None):
"""Initializes the Ppm
Creates the Ppm instance. If the user does not define `ppm_filename_or_array`,
it will be initialized to empty. Will generate all other attributes as soon
as a `ppm_filename_or_array` is supplied.
Args:
ppm_filename_or_array (str or `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame` or Pm): The user supplied
PPM. If it is a filename, the file will be opened
and parsed. If it is an `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame`,
it will just be assigned. (default: None, skips '#' comment lines)
alphabet_type (str): Desired alphabet to use. Order matters (default: 'DNA')
"DNA" := "ACGT"
"reduced DNA" := "ACGTN-"
"ambig DNA" := "ACGTRYSWKMBDHVN-"
"RNA" := "ACGU"
"reduced RNA" := "ACGUN-"
"ambig RNA" := "ACGURYSWKMBDHVN-"
"AA" : = "ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWY"
"reduced AA" := "ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWYX*-"
"ambig AA" := "ACDEFGHIKLMNOPQRSTUVWYBJZX*-"
"custom" := None
(default: 'DNA')
alphabet (str): if 'custom' is selected or a specialize alphabet is desired, this accepts a string (default: None)
background (constant or Collection): Offsets used to calculate background letter probabilities (defaults: If
using an Nucleic Acid alphabet: 0.25; if using an Aminio Acid alphabet: Robinson-Robinson Frequencies)
pseudocount (constant): Some constant to offset PPM conversion to PWM to prevent -/+ inf. (default: 1e-10)
"""
seqlogo.Pwm(pwm_filename_or_array = None, pm_type = 'pwm', alphabet_type = 'DNA', alphabet = None,
background = None, pseudocount = None):
"""Initializes the Pwm
Creates the Pwm instance. If the user does not define `pwm_filename_or_array`,
it will be initialized to empty. Will generate all other attributes as soon
as a `pwm_filename_or_array` is supplied.
Args:
pwm_filename_or_array (str or `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame` or Pm): The user supplied
PWM. If it is a filename, the file will be opened
and parsed. If it is an `numpy.ndarray` or `pandas.DataFrame`,
it will just be assigned. (default: None, skips '#' comment lines)
alphabet_type (str): Desired alphabet to use. Order matters (default: 'DNA')
"DNA" := "ACGT"
"reduced DNA" := "ACGTN-"
"ambig DNA" := "ACGTRYSWKMBDHVN-"
"RNA" := "ACGU"
"reduced RNA" := "ACGUN-"
"ambig RNA" := "ACGURYSWKMBDHVN-"
"AA" : = "ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWY"
"reduced AA" := "ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWYX*-"
"ambig AA" := "ACDEFGHIKLMNOPQRSTUVWYBJZX*-"
"custom" := None
(default: 'DNA')
alphabet (str): if 'custom' is selected or a specialize alphabet is desired, this accepts a string (default: None)
background (constant or Collection): Offsets used to calculate background letter probabilities (defaults: If
using an Nucleic Acid alphabet: 0.25; if using an Aminio Acid alphabet: Robinson-Robinson Frequencies)
pseudocount (constant): Some constant to offset PPM conversion to PWM to prevent -/+ inf. (default: 1e-10)
"""
```
### Conversion Methods
```python
seqlogo.pfm2ppm(pfm):
"""Converts a Pfm to a ppm array
Args:
pfm (Pfm): a fully initialized Pfm
Returns:
(np.array): converted values
"""
seqlogo.pfm2pwm(pfm, background = None, pseudocount = None):
"""Converts a Pfm to a pwm array
Args:
pfm (Pfm): a fully initialized Pfm
background: accounts for relative weights from background. Must be a constant or same number of columns as Pwm (default: None)
pseudocount (const): The number used to offset log-likelihood conversion from probabilites (default: None -> 1e-10)
Returns:
(np.array): converted values
"""
seqlogo.ppm2pfm(ppm):
"""Converts a Ppm to a pfm array
Args:
ppm (Ppm): a fully initialized Ppm
Returns:
(np.array): converted values
"""
seqlogo.ppm2pwm(ppm, background= None, pseudocount = None):
"""Converts a Ppm to a pwm array
Args:
ppm (Ppm): a fully initialized Ppm
background: accounts for relative weights from background. Must be a constant or same number of columns as Pwm (default: None)
pseudocount (const): The number used to offset log-likelihood conversion from probabilites (default: None -> 1e-10)
Returns:
(np.array): converted values
Raises:
ValueError: if the pseudocount isn't a constant or the same length as sequence
"""
seqlogo.pwm2pfm(pwm, background = None, pseudocount = None):
"""Converts a Pwm to a pfm array
Args:
pwm (Pwm): a fully initialized Pwm
background: accounts for relative weights from background. Must be a constant or same number of columns as Pwm (default: None)
pseudocount (const): The number used to offset log-likelihood conversion from probabilites (default: None -> 1e-10)
Returns:
(np.array): converted values
"""
seqlogo.pwm2ppm(pwm, background = None, pseudocount = None):
"""Converts a Pwm to a ppm array
Args:
pwm (Pwm): a fully initialized Pwm
background: accounts for relative weights from background. Must be a constant or same number of columns as Pwm (default: None)
pseudocount (const): The number used to offset log-likelihood conversion from probabilites (default: None -> 1e-10)
Returns:
(np.array): converted values
Raises:
ValueError: if the pseudocount isn't a constant or the same length as sequence
"""
```
***
## Contributing
Please see our contribution guidelines [here](https://github.com/betteridiot/seqlogo/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md)
***
## Acknowledgments
1. Bembom O (2018). seqlogo: Sequence logos for DNA sequence alignments. R package version 1.48.0.
2. Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE WebLogo: A sequence logo generator,
Genome Research, 14:1188-1190, (2004).